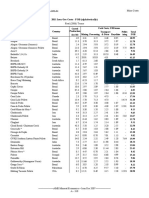
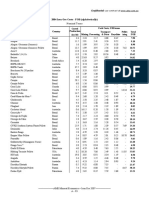
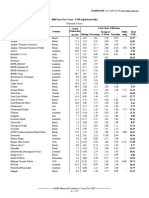
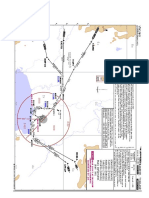
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Identification Phase Study
Uploaded by
ricardov2009Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Identification Phase Study
Uploaded by
ricardov2009Copyright:
Available Formats
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
Issue No. Version 2.1 Issued March 2007
Copyright © BHP Billiton 2007
All rights reserved.
This publication is copyright. No part of this publication may be used or reproduced in any manner without prior permission in writing from
BHP Billiton.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 2 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
TABLE OF CONTENTS
DEFINITION ....................................................................................................................................................................4
PURPOSE STATEMENT ................................................................................................................................................4
PROJECT STANDARD...................................................................................................................................................4
RELATED DOCUMENTS................................................................................................................................................4
1. GENERAL................................................................................................................................................. 5
1.1 STUDY SCOPE .................................................................................................................................................5
1.2 STUDY ORGANISATION APPROACH .............................................................................................................5
1.3 STUDY REPORT ...............................................................................................................................................5
2. STRATEGY............................................................................................................................................... 7
3. MARKET ANALYSIS................................................................................................................................ 8
4. RISK MANAGEMENT............................................................................................................................... 9
5. MINERALS SPECIFIC ............................................................................................................................ 10
5.1 GEOLOGY AND MINERAL RESOURCES......................................................................................................10
5.2 MINING ............................................................................................................................................................13
5.3 METALLURGICAL PROCESSING ..................................................................................................................16
5.4 INFRASTRUCTURE ........................................................................................................................................18
5.5 ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT....................................................................................................................18
5A. PETROLEUM SPECIFIC........................................................................................................................ 20
5A1. RESOURCES AND RESERVES ......................................................................................................................20
5A2. ENGINEERING AND CONSTRUCTION ..........................................................................................................21
6. HUMAN RESOURCES ........................................................................................................................... 22
7. PROJECT EXECUTION ......................................................................................................................... 23
8. OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................................. 24
9. INFORMATION MANAGEMENT............................................................................................................ 25
10. HEALTH, SAFETY, ENVIRONMENT AND COMMUNITY ................................................................. 26
11. EXTERNAL RELATIONS ................................................................................................................... 28
12. CAPITAL COST ESTIMATE............................................................................................................... 29
13. OPERATING COST ESTIMATE......................................................................................................... 31
14. OWNERSHIP, LEGAL AND CONTRACTUAL................................................................................... 33
15. INVESTMENT EVALUATION............................................................................................................. 34
16. PROJECT STATUS AND REVIEWS.................................................................................................. 37
17. WORK PLAN ...................................................................................................................................... 38
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 3 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
DEFINITION
The primary objective of an Identification (or Concept) PhaseStudy is to demonstrate that an investment opportunity is
sufficiently attractive to justify the expense of more detailed study. The Identification Phase study should establish
strategic fit and likely attractiveness of the business case. It identifies possible alternatives to be evaluated during the
next phase, Selection (or Pre-Feasibility), should the investment opportunity warrant further investigation.
PURPOSE STATEMENT
The purpose of this manual is to ensure that all Identification Phase Studies for which a recommendation is made to
proceed to Selection Phase Study:
• Are carried out in accordance with BHP Billiton’s minimum requirements for the definition and execution of Capital
Investments as defined in the Investment Policy;
• Prepared with a consistent approach based on agreed evaluation techniques.
• Provide economic justification to proceed to Selection Phase;
• Provide high-level risk analysis showing that no intolerable high residual risks have been identified;
• Describe alternatives to be evaluated in the Selection Phase;
• Provide a detailed scope of work, schedule, resourcing plan and cost estimate for the Selection Phase.
For the purpose of this standard, it is assumed that the investment opportunity has been screened to determine
alignment with the BHP Billiton/CSG strategy and that the opportunity will be refined to establish whether the opportunity
is worth further investigation: as illustrated in the table in Section 4.2 of the Investment Policy.
PROJECT STANDARD
In this BHP Billiton project standard, the term project covers any type of Capital Investment — either growth capital or
sustaining capital.
Due to the very diverse nature of BHP Billiton’s business and the varying size of projects, this standard is intended to
represent the minimum requirements applicable to the management, preparation and completion of a Identification
Phase Study, irrespective of the size, nature, complexity or location of a particular project. It is expected that only
Identification Phase studies leading to formal recommendation to proceed to Selection Phase will meet this standard.
Unsuccessful Identification Phase studies may be reported (for archive) to any standard acceptable to CSG
management.
Each project demands different approaches and abilities to respond to issues as they arise. While this project standard
ensures that the primary purpose of achieving minimum project management standards is not compromised, it does not
diminish the need for the project owner and project personnel to meet project challenges in a flexible/adaptive manner.
Every cost-effective improvement should be considered in an effort to improve the value of the project and/or reduce the
risks associated with the project. If any of the requirements set out here cannot be satisfied, or do not apply to the
project being considered, the reasons and justifications thereof must be clearly stated.
An Identification Phase Study should be executed using the guidelines set out in this standard.
RELATED DOCUMENTS
• Investment Policy.
• Standard for a Selection Phase Study.
• Standard for a Definition Phase Study.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 4 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
1. GENERAL
1.1 STUDY SCOPE
Before proceeding with the Identification Phase Study, the Project Leader/Director should define the scope of the Study.
The Study should be structured to identify:
• The potential of the new or expanded business opportunity;
• The general features of the opportunity including potential cases to be studied in the next phase (the Selection
Phase study);
• The key business drivers for the opportunity, major risks and any potential intolerable high residual risks;
• The order of magnitude of cost estimates for the alternatives being assessed for the opportunity;
• Technical issues needing further investigation, such as geological drilling or test work required;
• Significant risk issues requiring further detailed assessment such as concerning HSEC, regulatory environment,
political stability etc.
• The costs and time to undertake both the Identification Phase Study and any further development work to enable a
Selection Phase Study to be completed;
• The resources and services required for undertaking further work on the opportunity.
1.2 STUDY ORGANISATION APPROACH
Prior to the actual commencement of the Identification Phase Study, the Project Leader/Director should:
• Establish the Terms of Reference for the Study and the deliverables for the Study;
• Establish an owner’s team to direct and manage the Study, ensuring that the appropriate skills are brought to bear;
• Establish the contracting methodology, selection criteria and scope of work for external consultants and contractors
to be used in the Study
• Assign the scope to the owner’s lead personnel, consultants, contractors or external groups;
• Establish mechanisms to control, monitor and report progress of the Study; and
• Agree the format, frequency and circulation of a progress report of the Study with the CSG sponsor.
1.3 STUDY REPORT
A Identification Phase Study report shall be prepared that presents the findings of the Study and reports on the
requirements highlighted in this standard.
The elements given in this standard are provided as a checklist. It is not expected that detailed analysis will be available
for all elements and sub-elements. However, the level of documentation provided for each item should reflect the level
of risk assessed for that item, with potentially high risk/high impact issues being covered in greater depth than less
critical ones. The report should provide assurance that all items have been considered by a qualified and knowledgeable
person, that the most significant risk issues have been identified and that the scope of work and budget for the Selection
Phase Study has been adequately defined to address that item. This will usually be covered by a single paragraph in the
report, except for high risk issues.
The report should include an Executive Summary that addresses the following;
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 5 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
NO. ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
1.3.1 Overview Provide an overview of the project, highlighting the objective, main economic
benefits, the key business risks and the way forward.
1.3.2 Recommendations Recommend or not recommend that the identified opportunity warrants further
funding to investigate the economic benefits of its development. The
recommendation should demonstrate the viability of the preferred alternative
business opportunity and the potential risk for reward in pursuing the
opportunity further.
The recommendations may present a case for further alternatives to be
considered at Identification Phase Study level, or a full recommendation for
advancing the examination to Selection Phase Study status. The
recommendation should present the alternatives to be considered for
geological, mining or petroleum extraction, metallurgical and marketing in the
Selection Phase Study.
1.3.3 Project Description Include a statement of the scope of the opportunity, with any exclusion
and Scope specifically nominated.
Also include a description of the primary features of the opportunity and where
appropriate, a description of location, history, ownership, topography and
climate.
1.3.4 Scope of Study Include a statement as to the scope of the studies performed to date, any
exclusion or major assumptions made.
1.3.5 Key Indicators and Present the Key Indicators for the opportunity.
Benchmarking Include order of magnitude benchmarking of unit capital cost, unit operating
cost, Execution Phase and the ramp-up schedule. Explain any major
differences between the opportunity and the benchmarks, if data are available
to support the basis of such an analysis.
1.3.6 Significant risk issues Address significant issues and risks as highlighted in Appendix 2 of the
Investment Policy with the focus on assessing the probabilities of converting
the proposed project into a viable investment, following commitment.
1.3.7 Remaining Study Estimate of the resources, costs and time to progress through the next phases
Phase Costs & up to authorisation (i.e. a scope of work, schedule & estimate for the Selection
Schedule and Definition Phases)
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 6 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
2. STRATEGY
The Identification Phase Study should include an analysis of the business opportunity alternatives and a statement as to
whether (or not) the proposed project is relevant to and/or compliant with the BHP Billiton Strategic Plan and the
Customer Sector Strategic Plan.
Only the potential economic benefits of the project to BHP Billiton need be presented in conjunction with the Business
Strategy Statement.
The Study report should provide an outline of the following issues.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
2.1 Industry Attractiveness • Key supply and demand drivers.
• Revenue growth factors.
• Industry structures.
• Diversity of suppliers and customers.
• Industry cost curve.
• Forecast project position.
• Price assumption.
• Historical and forecast margins.
2.2 Strategic Rationale • Value adding sources, historically and forecast.
• Project’s ability to exploit these opportunities.
• BHP Billiton’s capacity to achieve Value Improvement
2.3 Strategic Fit • Strategy fit with BHP Billiton’s framework and the customer sector
strategic plan.
• Review of project to business strategy.
2.4 Strategic Alternatives • Strategic alternatives including exit / no go option.
• Basis of potential project being best option.
• Potential of staged development.
• Ownership and control.
2.5 Scenario Analysis • Scenario development process used so far.
• Considerations of BHP Billiton’s global scenario.
• Potential scenarios and impact on alternatives.
2.6 Exit Strategy • Basis of exit strategy.
• Defined triggers or milestones for exit decision.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 7 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
3. MARKET ANALYSIS
The Identification Phase Study should address the proposed basis of marketing the products to be produced. Industry
norms for the product revenue and costs to market should be reported.
The Study report should address the following aspects and include a statement on how the requirements have been met
for each element. General and current marketing studies available within the CSG for the relevant commodity will
normally be adequate for this purpose, except in the case of a commodity not already produced by BHPB or for a
proposed product that is outside currently accepted quality specifications.
NO. ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
3.1 Product Specification Specify the standard to be achieved for products. This may be a targeted
quality or demonstrated by test work.
3.2 and Demand and Supply Briefly state the world demand and supply forecasts, utilising externally
3.3 Forecasts produced existing data or reports. Outline the key drivers for consumption.
3.4 Marketing Strategy If a new product specification is proposed, identify entry and competitive
strategies.
Provide estimate of volumes and market share, and potential for growth, based
on competition and demand / supply forecasts.
3.5 Pricing Strategy Present any potential pricing strategies different from the norm.
3.6 Customers Identify potential customers, along with any available benchmarks of price or
competitors position in the market.
3.7 Marketing Contacts Not required to be reported.
and Contracts
3.8 Revenue Forecasts Provide a forecast of the Gross and Net Revenues from sales, based on
industry information on Demand and Supply Forecasts.
Attempt to include estimated range of outcomes and sensitivities of revenues
to changes in market scenarios.
3.9 Marketing Resources Include commentary only, if a new product or specification is proposed to BHP
and Organisation Billiton.
3.10 Product Shipping, Report the likely product shipping, storage and distribution system.
Storage and Outline the cycle times from the project to customer.
Distribution
Outline the stockpile sizes required.
3.11 Competitor Analysis Name the competitors.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 8 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
4. RISK MANAGEMENT
Risk Management activities should be consistent with the BHP Billiton Enterprise-wide Risk Management (EWRM)
Policy, Standards and Guidelines. This section specifies the overarching requirements necessary to provide an
integrated and holistic view of the key risk issues: the sources and extent of uncertainty in the investment opportunity.
This view should comprise a complete profile that includes all sources of risk, including those assessed in detail as
required by other sections of this Standard.
The activities should be directed at:
• Provide an outline assessment of the most significant risk issues associated with the investment opportunity.
Particularly those arising from the market and strategy analyses.
• Define, in the Identification Phase Study, any special control actions that may be required to manage residual risk to
a tolerable level.
• Plan and prepare for risk management activity that will be required in the Selection Phase Study.
• Assess the practicability of managing the risks associated with the project if it progresses to Execution and then into
Operation.
The Study report should address the following sub-elements and include a statement on how the specific requirements
have been met for each sub-element.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
4.1 Risk Issues Conduct a facilitated outline risk assessment workshop as per EWRM Standard No. 2. It
is preferable that the facilitator is independent of the project team.
The risk register should follow the format given in EWRM Guideline 1.2. It should specify
for each risk issue:
• The major causes/drivers
• The potential impacts (upside and downside)
• The controls already in place within BHP Billiton (e.g. company policies and
standards)
• A broad description of any further control actions anticipated.
Note:
Refer to EWRM Guideline 2.4 for guidance on the application of EWRM Standard No. 2 to
investment risk management.
4.2 Risk control strategies Provide an outline Risk Register as in EWRM Guideline 1.1 that contains, for each risk
issue, the causes, impacts, existing control and required actions. Risk issues should be
rated per EWRM Standard No. 1 showing Residual Risk Rating, Risk Control
Effectiveness and Gross Exposure. The risk registers should document those controls
already in place that are to be relied upon.
Note:
The Cura risk management information system is the BHP Billiton endorsed means to
hold, analyse and report risk management information.
4.3 Risk Management Provide an outline Risk Control Action Plan for those additional controls required to
Plans manage residual risk to a tolerable level. Risk Control Actions should be justified through
cost benefit analysis per EWRM Standard No. 5.
Provide a Risk Management Plan for the Selection Phase showing the risk management
work required. The Plan should identify the risk management resources needed and
particularly the skills and tools required in undertaking of the work.
For further information on requirements refer to the Risk Assurance and Assessment website.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 9 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
MINERALS SPECIFIC
5. MINERALS SPECIFIC
5.1 GEOLOGY AND MINERAL RESOURCES
All aspects material to the geology and resource evaluation should be investigated and reported. The investigation and
report should include, but not be limited to the items and issues mentioned within these standards. Work must be
performed by or under the direction of competent geologist and/or resource practitioner or consultants based on data
and information derived from the investigation. A detailed knowledge of the resource is not expected, however the study
should highlight all significant gaps in the understanding of the resource and state clearly the work plan required to
acquire that understanding during later study phases. It is expected that a resource model, primarily consisting of
inferred or higher classification material, will be available to form the basis for a Selection (Pre-Feasibitliy) Phase Study.
Projects not yet developed to inferred resource status should usually be considered exploration stage projects.
The BHP Billiton Ore Reserves Policy sets out the Mineral Resource and Ore Reserve reporting requirements according
to the “Australasian Code for Reporting of Mineral Resources and Ore Reserves” (the JORC Code).
Any discussion of the issues must clearly distinguish which data and information is attained through direct observation,
inference, or assumption.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
5.1.1 Conventions Document the conventions used for the project and clearly define:
• The units used for the project;
• Key terms and nomenclature used; and
• The Project Coordinate System and its relationship to World Coordinates.
5.1.2 Tenure State whether:
• The right to explore has been obtained;
• A clear process to obtain secure tenure and licence has been identified
and understood; and
• A clear mechanism (purchase, lease, option or compensation agreement)
to obtain access to the necessary surface rights for the mine, process
plant, tailings disposal and infrastructure is in place.
5.1.3 Regional Geology Provide a summary of the regional geology, the stratigraphic, structural and
tectonic setting for the ore body that forms the basis of this Study.
5.1.4 Exploration History Detail the exploration history, work completed by whom, when and the
techniques used. This should include a description of the various
interpretations made over time.
5.1.5 Data Acquisition Provide a description of the methods used to acquire data for a preliminary
evaluation of the deposit, including an assessment of the representivity,
accuracy and precision of the data acquired. Identify the source and collection
method of data and describe quality control and assurance procedures used.
Note:
The distribution of data will be such to allow for a preliminary interpretation of
the geological framework for the ore body. Lithologies, alteration, structure,
ore-types and metallurgical characteristics are to be assumed or estimated
from available samples. The continuity of the mineralization is assumed.
Geological and Topographic Mapping: Outline a description of the
geological and topographic mapping undertaken.
Drilling and Other Sampling Methods: Describe the sample methods:
including surface, grab or channel sampling if undertaken.
Drill data acquisition description should include:
• Drilling methods and a comparison of methods used;
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 10 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
MINERALS SPECIFIC
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
5.1.5 Data Acquisition • Drilling locations;
(continued)
• Sampling and analytical methodologies;
• In-situ density sampling and test work (wet and dry density, moisture
content, porosity etc.); and
• Residual sample storage.
Data Management: Include a description of the data management:
• Survey control, hole position and set-up angle;
• Down hole position and survey method;
• Data organisation, storage and security; and audit trail.
Logging: Reference the drill logging system used:
• Geological (including lithological, structural, mineralogical etc.);
• Hydrogeological;
• Geophysical; and
• Geotechnical.
Geochemical Analysis: Include the validation of the geochemical analysis,
description and summary results.
5.1.6 Deposit Geology Provide a description of the local geology that hosts the ore body. Indicate
preferred and possible alternate and likely ranges of interpretations.
The description should cover:
• Lithology including host and wall rock lithologies;
• Structure;
• Mineralization; and
• Alteration.
Illustrate the geology data and interpretations using summary cross sections,
longitudinal sections and plans where possible.
Note:
The deposit geology, mineralogy and continuity of the mineralization must be
understood on a general and global scale.
5.1.7 Resource Estimation Provide a description and justification of the methods and techniques used to
estimate the in-situ resource. Indicate ranges of possible outcomes.
Any resource models developed should estimate the global resource covering
the key ore body parameters and characteristics (inferred where necessary)
suitable for a conceptual life of mine planning. Alternate models and
interpretations should be assessed to indicate ranges of possible outcomes.
Geological Interpretation and Exploratory Data Analysis: Include data
analysis by geological and modelling domains (where possible) with
justification of domains chosen and discussion of the links to the geology.
Analysis may consist of:
• Univariate classical statistical analysis;
• Bi-variate and multi-variate classical statistics; and
• Geostatistics.
Block Modelling: If undertaken, include the following:
• Choice of block size, orientation and origin;
• Domains, grades and densities; and
• Model validation.
Resource Classification: Include a description and justification of the criteria
used.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 11 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
MINERALS SPECIFIC
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
5.1.7 Resource Estimation Mineral Resource Estimation Results: Include the following resource
(cont’d) estimation results:
• Cut-off determination, including presentation of tonnes and grade versus
cut-off illustrations;
• Range of possible outcomes for Tonnes and Grade, based on the current
knowledge of the deposit and alternative geological interpretations.
• Comparison of the current resource estimates with previous estimates and
comment on the differences and the reason for those differences; and
• Mineral Resource tabulation, by classification and domain.
Note:
Tonnage and grade of the deposit to be estimated by a Competent Person and
should be at least known at the Inferred classification (as per JORC code).
5.1.8 Metallurgical and Data presented and discussion should include:
Environmental • Documenting of the metallurgical and environmental samples taken;
Characterisation
• Ore and Gangue mineralogy;
• Chemistry of minerals present; and
• Chemistry of the ore and waste rock types, including net acid generating
(NAG) capacity.
Note:
Typically this would be supported by initial field observations.
5.1.9 Hydrogeology Deposit Hydrology: Provide a preliminary description of the ground water
regime likely to be encountered within the deposit. This discussion should
identify likely risks by identifying potential outcomes and the likelihood of each
occurrence.
Project Water Supply: If the project requires a water supply that could be
provided from underground water sources, then a description of the proposed
options and the test work needed to define these options is required.
5.1.10 Geotechnical Provide a general description of the known or likely geotechnical domains, the
Appraisal rock mass character and the potential impact on mine planning and
operations. Identify potential risks and ranges of possible outcomes and
translate them into likely impacts on mining.
5.1.11 Risk Management Provide a discussion of the most significant technical risks associated with the
study and if possible, the method of mitigation to be adopted following this
Study. In particular discuss the potential outcomes and the impacts of the
range of outcomes for key outputs such as tonnes and grade, and items such
as continuity, ore body geometry, boundaries, and contacts etc.
5.1.12 Forward Work Provide a description and cost estimate of the geological, drilling and resource
Program work to be undertaken during the Selection Phase of the project.
Comment on whether such work is to improve the confidence in and/or to add
to the existing resource.
5.1.13 Mineral Resource Produce the project Mineral Resource statement and state whether compliant
Statement with the JORC code.
A Mineral Resource estimate derived from outside sources may not be JORC
compliant, and as such cannot be signed off by a BHP Billiton Competent
Person. However, as a result of this phase, a work program must be put in
place to bring the Mineral Resource to JORC compliance status.
Note:
This must be a stand-alone statement that can be lifted out of the Study for
public reporting purposes in accordance with BHP Billiton’s Ore Reserve
Policy and must be signed by the Competent Person.
For further information on requirements refer to the Mine Planning Network website.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 12 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
MINERALS SPECIFIC
5.2 MINING
The Study should investigate and report on the most likely mining scenario based on the existing body of knowledge,
which supports the contention that the opportunity presented by the project may be viable. Generally, the depth of
Study required does not extend beyond rule of thumb or industry standard assumptions, first pass assessments, or
application of proven methods to a similar deposit.
The professional judgment of a competent mining engineer or consultant, based on cursory or minimal information, will
be sufficient in many areas.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
5.2.1 General Mine Planning Conventions: Document the conventions used for the mining Study including
Criteria full description of the survey co-ordinate system used and its relationship to the
Universal Coordinate System.
Define key terms and nomenclature used.
Site Description: Present a summary description, including but not limited to:
• Local and regional conditions, including climatic, surface and seismic;
• Tenure conditions, including ownership, mineral titles, water rights,
operating licenses and surface access rights;
• Site access plus existing and proposed local and regional infrastructure;
• General site location map
Resource Description: Summarise key issues, including:
• Particular aspects of the geological model on which the mine plan places
high reliance (e.g. ore types, high grade zones etc.)
• Material characteristics and their variability that may affect major decisions
about mining or processing methods.
Geotechnical Parameters: Summarise preliminary key geotechnical
assumptions based on the available information, including:
• Geotechnical data by material class or rock type, including where
appropriate in-situ stress regimes;
• Geotechnical recommendations for mine design, incorporating ground
support requirements, equipment selection, and equipment performance.
Hydrogeological Considerations: Summarise key issues, including:
• Surface and groundwater regimes;
• Any historical data such as water analysis, water table level and
fluctuation, porosity, permeability, etc.;
• Possible water control practices.
Gas Regimes: Summarise, where applicable, the available information and
data to establish the nature of in-situ gas regimes (to extent possible) and the
likely impacts on mining.
Ventilation: Summarise, where applicable, the regulatory requirements and
the proposed ventilation system required (including a preliminary design
schematic).
Environment and Cultural Considerations: Summarise the key issues and
considerations that impact on, or influence the mine plan and mine design.
Process and Market Considerations: Summarise the key issues that impact
on, or influence the mine plan and mine design, including:
• Market assessment of factors such as demand, supply and price.
• Recovery or yield of the mineral commodity;
• Mineral processing parameters.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 13 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
MINERALS SPECIFIC
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
5.2.1 General Mine Planning Economic Criteria: Summarise the key issues and considerations that impact
Criteria (continued) on or influence the mine plan and mine design, including:
• Revenue Drivers: price, recovery, treatment terms, etc.
• Cost Drivers: mining cost assumptions, overheads, sustaining capital, etc.
5.2.2 Mine Design General Approach: Provide a description of the preliminary or conceptual
mine design, including an assessment of the accuracy and precision of the
data acquired and risks associated with the mine design.
The report as a minimum, should include a listing, description and explanation
of the mine design parameters applied to the project, including the following
main headings:
Mineable Resource Model: Provide a description of the mineable resource
model as developed from the geological resource model and other sources,
including:
• Development of the mineable resource model using factors such as cut off
grade, ore dilution, ore recovery, assumed SMU, grade control data,
mineral processing response, etc.;
• Mineable Resource tabulation with relevant discussion as to the
confidence level of the estimate.
Note:
A good guideline is that the overall limits of the deposit are known and that an
overall resource tonnage and grade can be inferred from the available data.
Mine Production Rate: Provide a description of the range of mine production
rates suggested to be applied to the project.
Mining Method: Provide descriptions of the potential mining methods to be
applied based on:
• Available site information and regional or deposit type knowledge;
• Methods previously applied to the ore deposit;
• Existing mine operations of similar magnitude and nature elsewhere.
Ore/Waste Determination: Provide a description of the proposed criteria for
ore / waste determination that would be used in planning and design for the
proposed mining operations as presumed from similar operations or from
historical data.
Mining Limits: Provide a description of the methodology applied to estimate
the final mining limits from the mineable resource model, based on
• The physical and economic parameters;
• Mineable resource model used and the confidence therein;
• Method by which the results were verified or validated;
Illustrate schematically the final limits in maps and sections.
Overall Mine Layout: Include a schematic description to a level of detail
consistent with the level of understanding of the project.
Information and discussion presented, where applicable should include but not
be limited to, the following:
• A summary of design criteria applied and key assumptions;
• Tabulation of ore reserves (if available) or mineable resource and
resources (including waste) by classification, rock type, etc. within the
design;
• Sections and plans produced to show proposed positioning of mine
excavations, waste dumps, ore stockpiles, ore processing plant and the
mine infrastructure
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 14 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
MINERALS SPECIFIC
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
5.2.2 Mine Design Ore Reserves Statement: It is not generally expected that a JORC compliant
(continued) statement can be made at the Identification Phase stage. However, if a
statement is made it must be JORC compliant. Note that the Ore Reserve
cannot be published at this stage, refer to the BHPB Ore Reserves Policy
5.2.3 Mine Operations Production Sequence and Schedule: Provide a preliminary mining sequence
and schedule.
• Ore production and feed to process;
• Ore and waste excavation;
• Waste disposal movements;
Mine Equipment Requirements: Provide a listing and description of the size
and type of mine equipment assumed, including a Capital and operating cost
estimate.
Overburden and Waste Disposal: Provide a general description of the
waste/overburden material disposal sites and methods, including:
• Waste disposal site selection and design criteria;
• Environmental and cultural considerations to disposal sites;
• Condemnation activities and results;
• Mining activities for waste disposal.
Operations Summary: Provide a summary of the schedules developed for the
mining operations and present summarised annual statistics to include:
• Manning levels for all mining activity related personnel;
• Infrastructure required to support the mining operations;
Operations Management: Provide a cursory description of the mine
operations proposed for the project, including:
• Mine equipment operation and maintenance;
• A schedule of mine operation activities.
5.2.4 Cost Estimates Present summary tabulations to illustrate:
• Mine capital expenditure;
• Mine operating costs.
Note:
Sufficient data would have been collected to provide global estimates based on
scaled or industry history for the size and type of operations contemplated.
Reference to in house data on operations of similar magnitude
and scope will be adequate.
5.2.6 Risk Management Provide a discussion of the most significant technical risks associated with the
mining aspects of the project and if possible, the method of control to be
adopted following this Study.
In particular there must be a discussion of the potential value outcomes and
likely impacts to mining from items such as reserves, production risk, mining
method, schedules, operating costs and capital expenditure.
5.2.7 Future Work Program Provide a Work Plan with costing and implementation program for a Selection
Phase Study on the opportunity of the proposed project. Highlight key
technical data to be acquired during the Selection Phase in order to
confidently establish the preferred development option.
For further information on requirements refer to the Mine Planning Network website.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 15 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
MINERALS SPECIFIC
5.3 METALLURGICAL PROCESSING
The Study should investigate and report on the most likely processing option that supports the contention that the
opportunity presented by the project may be viable and identify all options to be considered in the next phase. The level
of input required for this study would only be of a conceptual and/or preliminary basis. The Study report should address
the following.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
5.3.1 Conventions Document the conventions used for the project and clearly define:
• Measurement units – the SI system is the standard, with conversions
quoted if other units are employed;
• Key terms, symbols and abbreviations.
Note:
The use of the word “ore” is deemed to apply to both mined ore and to plant
feedstocks in the case of downstream processing (e.g. smelters and refineries.
5.3.2 Ore Characteristics Detail the method and results of the initial ore and waste Metallurgical
Characterisation work (including any assumptions), which should address the
following:
• Ore and waste mineralogy, mineral species, grain size and texture;
• Mineral chemistry and relevant physical properties (e.g. SG distribution), in
particular, minor deleterious elements or minerals, that typically present
commercial, environmental or technical issues in processing and
marketing;
• Details of any evidence that indicates ore variability and the presence of
significantly metallurgically different ore types.
Detail how any metallurgical samples were obtained and what considerations
(and assumptions) were made to ensure that test work was carried out on
samples that are representative of future processing plant feed or blends.
5.3.3 Laboratory Test Work Detail any basic metallurgical test work conducted to identify potential
processing options as follows:
• Identification of the samples tested and the scale of the test work
conducted;
• Metallurgical test method adopted for each unit operation;
• Test work results obtained;
• Interpretation of these test results including the derivation of metallurgical
processing options from the results;
• Degree of metallurgical behaviour variability indicated.
5.3.4 Process Selection and Detail potential mineral or metallurgical processing options identified, that are
Basis likely to capture the maximum value of the ore body at an acceptable level of
risk, from:
• Laboratory ore characterisation data and laboratory test work; and
• Any historical metallurgical test programs that have been carried out on the
ore body, including who completed the work, when it was completed, the
metallurgical techniques used and the interpretation of results. Where
appropriate, any differences should be highlighted and discussed: or
• Details of metallurgically similar ore bodies that have been identified that
could be used as a benchmark for ore characterisation, process route
selection and processing risks.
Provide the details of all selected processing flow sheets and indicate:
• All potential block flow diagrams considered and/or the most likely flow-
sheet to be adopted and the reasons for its selection;
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 16 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
MINERALS SPECIFIC
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
5.3.4 Process Selection and • Any alternative processing options to be considered in the Selection
Basis (cont’d) Phase;
• Possible product specifications indicated by the test work results;
• Preliminary Process design criteria.
Address any key technology issues relating to the processing of the ore and
the handling and storage of plant residues including:
• Potential source, costs and terms for technology needed to be acquired;
• Whether the technology has been used before, where used and the
success or otherwise of its use;
• Whether patented or proprietary;
• Extent of further test work required to validate its use on this project;
• Areas where, if the technology were developed, BHP Billiton would achieve
significant competitive advantage. Estimate the potential benefits to allow
focussed research and development activities to be proposed.
5.3.5 Facility Description Include, as a minimum for selected alternative evaluated, the following:
• Conceptual block process diagram;
• Preliminary mass, energy and water balances;
• Possible plant, infrastructure and disposal sites for plant residues, and
location footprint plan.
• Product quality specifications;
• Annual ore and product capabilities;
• Predicted plant availability;
• Preliminary consumption rates for major operating and maintenance
consumables and utilities;
• Product handling and transportation strategy (pipeline / rail / shipping).
• Ramp-up rate from commissioning to full production.
• Capital and Operating Costs
5.3.6 Future Work Program Provide a description of the metallurgical investigations and test programs
proposed for all alternatives identified to be undertaken during the Selection
Phase and include:
• Direction of the future investigation, including the objectives and reasons;
• Scope of the investigative work; and
• Costs and schedule.
5.3.7 Risk Management Provide a preliminary risk assessment of those processing routes considered
for selection to identify specific risks such as:
• Technical risks associated with the processing route selected and
alternatives considered;
• Key process performance parameters including those which are the
processing economic drivers;
• The likely range of outcomes for the key drivers and the methods used to
estimate these ranges;
• Process scale up if likely to present significant process risk or whether the
scale up behaviour is well known and proven.
Where significant processing risks are identified, provide a clear control
strategy that would include pilot testing of the process at an appropriate
demonstration plant scale in the Selection (Pre-Feasibility) or Definition
Phase.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 17 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
MINERALS SPECIFIC
For further information on requirements refer to the Processing Network website.
5.4 INFRASTRUCTURE
For the purpose of this standard, infrastructure is defined as all facilities of a non-production nature required to support
and sustain the operation and typically includes items tabled below.
Major aspects of both on and off-site infrastructure should be outlined in the Identification Phase Study to identify the
proposed development of infrastructure needed to support the project. On-site infrastructure comprises facilities of a
non-production nature, which are proposed to be located on lands controlled or owned by BHP Billiton. Off-site
infrastructure comprises facilities of a supporting services nature, proposed to be located away from the lease on lands
controlled by BHP Billiton or leased from others. The Identification Phase Study should identify which items of
infrastructure are located on or off site.
The extent to which existing infrastructure may be available to support a project, should be stated in the Identification
Phase Study. Identification Phase studies should identify options and optimisation cases and develop basic evaluations
to justify further review at the next stage.
The battery limits between on-site infrastructure and mining and processing facilities must be clearly stated. Similarly
the battery limits between off-site infrastructure to be developed and existing infrastructure needs to be stated.
The Identification Phase Study should address these issues.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
5.4.1 Infrastructural Define the requirements for the following, in accordance the statements above:
Requirements Utilities: Power, fuel, water and other utilities – compressed air, steam etc.
Disposal and Drainage: Sewage, waste disposal, tailings and stormwater
drainage.
Buildings and Facilities: Administration and service buildings,
accommodation, warehouses and community related facilities – housing,
schools, clinics, etc.
Transport Infrastructure: Roads, rail, port and airstrips.
Communications: Landlines, satellite - including IT/IS interfaces.
Temporary Facilities: Temporary facilities required during construction –
power, water, accommodation, catering, lay-down areas, waste disposal etc.
Other: Security, fire protection, health facilities etc.
5.4.2 Location Study Identify potential locations proposed for the infrastructure.
Note:
Ground-level geotechnical survey (by surface observation and local pits), and
topographical investigations via existing data should be completed, to provide
a reasonable level of support for the viability of the locations selected.
5.4.3 Engineering Design Include significant parameters and factors influencing the engineering design
Basis and basis of the Study:
Deliverables • Site conditions – general data;
• Environmental – potential limitations.
5.5 ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT
For the purposes of indicating the potential capital cost of the project, it is necessary for the engineering thereof to be
developed to the extent that the owner can define the scope of work of the project, in order to;
• Establish an order of magnitude estimate of the capital cost for the alternatives identified for the Identification Phase
study.
• Provide an indication of the project schedule
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 18 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
MINERALS SPECIFIC
As engineering development (including a preliminary site selection) is critical to defining the right business opportunity, it
is a key component for the early phase of Front End Loading.
The minimum requirements for a Identification Phase Study are as follows:
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
5.5.1 Basis of Design Preliminary Design Basis document covering:
• Site conditions – topographical, seismological, climatic data
• Environmental – potential issues and limitations.
• Logistical Limitations.
• Criteria for operability, reliability and maintainability.
5.5.2 Location Study Potential locations for the production facilities, infrastructure and waste
disposal sites.
Note:
Topographical & geotechnical information via existing data should be
presented, to provide a reasonable level of support for the viability of the
locations selected.
5.5.3 Technology Selection Outline any new and/or competing technologies (in particular prototypes) being
considered.
5.5.4 Engineering For all production facilities and infrastructural requirements, provide the
Deliverables following (where applicable) on a preliminary basis:
• Key items of mechanical equipment
• High level Electrical Single Line Diagrams
• Plant Layout Drawing
5.5.5 Forward Work Provide a description and cost estimate of the engineering work to be
Program undertaken during the Selection Phase of the project.
Consideration should be given to:
• The engineering tools to be used (i.e. computer aided engineering 2D, 3D
etc.)
• The principles of Front End Loading; and
• The use of value improvements practices.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 19 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
PETROLEUM SPECIFIC
5A. PETROLEUM SPECIFIC
5A1. RESOURCES AND RESERVES
The Identification Phase Study is focused on determining the potential value of the resources and beginning to formulate
a subsurface development plan. It is also important to identify key unknowns and potential sub-surface risks associated
with reserves and resource estimates.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
5A1.1 Security of Title Review the work completed at the strategic screening phase to ensure no
material change in the assumptions and conclusions, namely:
• Key features of the title, licence or contract
• Net working and net revenue interests
• Key milestones and dates
• Operator, title or production continuity
5A1.2 Geological Setting • Outline the geological setting of the “play”.
• Explain the extent and geometry of the plant and source and potential
hydrocarbon migration pathways.
• Discuss potential for additional exploration activity on the play fairway
and the impact this may have on future development options.
5A1.3 Structural Framework • Define the key features of the structure, outlining uncertainties and risks
that could impact on the project.
• Discuss how the planned appraisal, geoscience and engineering will
address these risks.
5A1.4 Recoverable Volumes • Describe the well results to date.
• Describe the reservoirs intersected and the fluid contacts encountered or
interpreted.
• Describe the probabilistic range of contingent resources that the
development is expected to recover.
• Provide a range of production profiles.
5A1.5 Sub-Surface • Describe the key uncertainties and risks associated with the sub-surface
Development Plan development plan.
• Outline alternative sub-surface development plans that were considered
and why they were not selected.
• Discuss how the planned appraisal, geoscience and engineering work
programs will address the key resource uncertainties and risks and allow
definitive choice of a single development plan.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 20 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
PETROLEUM SPECIFIC
5A2. ENGINEERING AND CONSTRUCTION
The Identification Phase Study is focused on outlining engineering concepts based on the current resource and reserves
estimates. This phase should also identify key technical risks/uncertainties and any threshold issues that need to be
addressed.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
5A2.1 Option Definition Include coarse identification of concepts to provide an indication of the
potential value of the project and to assist in the identification of any key
threshold issues.
5A2.2 Engineering Definition Include:
• An outline field development plan;
• Preparation in order of magnitude: CAPEX, OPEX and schedule
estimates;
• Rough comparison with equivalent projects.
5A2.3 New Technologies Include:
• Review and update as necessary, information with respect to the
enabling technologies and gaps, including required forward Work Plan.
• Outline any competing technologies and explain the choice of the
selected technology.
• Develop BHPP/industry action plan to address gaps.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 21 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
6. HUMAN RESOURCES
Based on the outline of the potential Operations Management Plan (see Section 8), a brief review of human resources
must be conducted to report on the following issues according to the standard stated:
• An assessment of the skills required and available to execute and operate the planned facilities;
• The sources of human resources available;
• The potential human resource impacts if the potential project was to be developed.
The issues which should be addressed include:
• Most significant HR risk issues;
• Organisation model to be potentially adopted;
• Cultural fit;
• Recruitment and training strategy;
• Employee relations strategy;
• Performance management and compensation strategy;
• Statutory obligations and requirement pertaining to the employment of local and expatriate staff.
• Cultural issues applicable to the project.
At the Identification Phase, the extent of definition and evaluation of these issues need only to be outlined, with an
emphasis on identifying most significant risk issues.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 22 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
7. PROJECT EXECUTION
At the Identification Phase, the owner’s team should develop an outline of the potential approach to Project Execution
that forms the proposed basis for implementing the project. This outline should address the following.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
7.1 Scope State the physical scope of the project along with any major assumptions.
7.2 Work Breakdown Not applicable to a Identification Phase study.
Structure (WBS)
7.3 Execution Broadly outline the proposed approach to execution and delivery of the
Methodology following phases.
7.4 Project Organisation Broadly address the Project Organisation for the following phases through
to authorisation
7.5 Project Health, Safety, Identify key or special health, safety, environment and security issues that
Environment and will require management through all phases of the project.
Security
7.6 Planning and Prepare a schedule showing the major activities during subsequent studies
Scheduling and phases, execution and start-up of the project. .
7.7 Engineering Explain the approach to engineering delivery, including the requirements for
specialist input, the application of new technologies, the use of computer
aided engineering, reviews (constructability, operability, and maintainability)
and the engineering resources required for the following phases.
7.8 Procurement and Identify key items of equipment with long lead times or critical technology
Contracts issues including potential manufacturers and suppliers.
7.9 Construction Outline the broad approach in principle to construction, industrial relations,
labour resourcing, logistics and specific construction issues.
7.10 Pre-commissioning Outline the broad approach to pre-commissioning and commissioning
and Commissioning including any important requirements due to new technology or a particular
site or location, shutdowns, tie-ins etc.
For further information on requirements refer to the Project Management website.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 23 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
8. OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
The Identification Phase Study should include a general appraisal and commentary of the possible methods of
establishing (or increasing) BHP Billiton’s capability to establish, commission, start-up and operate the proposed facility
and associated infrastructure.
The Identification Phase Study report should address the following issues with supportable statements meeting the
following standards.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
8.1 Organisation Include the broad structure of the Operations group needed to support the
development and operation of the potential project and a statement to this
effect.
8.2 Resources and Present an assessment of the resourcing and sourcing of the proposed
Sources of Personnel operating workforce.
8.3 Operating Cycles No assessment is required.
8.4 Conditions of No assessment is required.
Employment
8.5 Accommodation Briefly investigate the basis of accommodation and state the results and any
assumptions made.
8.6 Operations Report on the operability of the proposed facilities and the plant options
considered, taking into account lessons learnt.
8.7 Maintenance Report on the maintainability of proposed facilities by means of
benchmarking and/or experienced judgement.
8.8 Transport & Logistics Include an assessment of logistic transport requirements to support the
potential project.
8.9 Administration No assessment is required.
8.10 Other Operational No assessment is required, unless addressed elsewhere in this standard,
Issues i.e. marketing, HSE, information management.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 24 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
9. INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
This standard requires the development of an Information Management Plan that includes a brief commentary on the
issues outlined in this document. The Information Management Plan will be refined throughout the project development
phases and should support the Project Execution Plan.
The Information Management Plan should address two areas:
• Development of the Information Management and Technology requirements of the project team during project
execution;
• Development of the Information Management and Technology requirements in support of the Asset Management
Plan that will encompass the requirements during operations.
Minimum requirements of the plan should reflect sufficient investigatory work to support the defined level of accuracy for
the Identification Phase Study.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
9.1 Knowledge Outline the plans for the capture and sharing of data, information and the body
Management of knowledge developed during the project.
Outline the plans for ownership of project intellectual property, software
licences and hardware.
9.2 Information Systems Information Systems Planning: Assess IT Service Delivery Partner’s country
presence and depth/quality of local IT market. Estimate number of users and
indicate core systems likely to be required for the project.
Electronic Business: Identify opportunities for electronic trading with
customers and suppliers in the supply chain.
Information Systems Architecture: Check threats and opportunities to BHP
Billiton’s standard use of computing, data/voice communications equipment
and applications. Conduct preliminary IS strategy in support of the Operating
Strategies.
Project Technical Support: Outline the general approach to implementing
and supporting, during the Selection Phase and Definition Phase stages:
• Data backup and security;
• Remote communications and transfer of electronic data;
• Project management and control systems;
• Document management;
• Office systems and equipment;
• Access / interface with 3rd party system involved in the development of
project data/deliverables (capital estimate, etc.);
• Training of project team.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 25 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
10. HEALTH, SAFETY, ENVIRONMENT AND
COMMUNITY
The Study report should address the following sub-elements and include a statement on how specific requirements have
been met for each sub-element.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
10.1 Health, Safety, Conduct and report on a preliminary, qualitative Health, Safety, Environment
Environment and and Community (HSEC) risk assessment in accordance with the BHP Billiton
Community Risk HSEC Risk Management Guideline to:
Assessment
• Identify hazards and aspects, and assess and compare the risks
associated with the various project options;
• Identify any potential intolerable high residual risks that are unlikely to be
controlled or mitigated to a reasonably practicable level, (include Statutory
Requirements and Country Risk);
• Seek professional appraisal to determine whether environmental and
social issues appear resolvable;
• Identify any potential unfavourable public responses to the project (by
consulting local people where possible);
• Identify in-principle solutions to the most significant risk issues;
• Nominate the risk-based preferred project options;
• Identify issues that could substantially influence cost estimates; and
• Identify baseline environmental and social surveys likely to be required for
a full Environmental and Social Impact Assessment and develop a
completion plan aligned with the Project Schedule.
Develop a plan for H & S Risk Assessment and Environmental and Social
Impact Assessment studies that is aligned with the Project Schedule and will
be required going forward.
10.2 Statutory Identify the HSEC statutory requirements and commitments to stakeholders
Requirements and associated with the project and prepare a Statutory Requirements and
Environmental & Approvals Register and a Stakeholder Commitments Register. In particular:
Social Impact
• Outline applicable project permitting processes and likely time
Assessment (E&SIA)
requirements;
• Highlight any requirements (e.g. permits, environmental licences, land
ownership issues) that could present a risk to the progress of the project
and provide an indicative timeframe for meeting these requirements.
Potential mitigation measures should also be considered and documented;
and
• Identify and document the scope and requirements of the Project E&SIA.
Include reference to significant baseline studies and investigations required
and link them to the Project Schedule.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 26 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
10.2 Statutory Social impact aspects should include preliminary coverage of significant
Requirements and threats and opportunities and give a brief appraisal of the influence of potential
E&SIA (cont’d) stakeholders on the proposed project, particularly the local community. Include
discussion of the following aspects:
• Socio-economic considerations;
• Relocation requirements;
• Local service Industries;
• Community services;
• Off-site housing and accommodation;
• Workforce availability; and
• Recruitment.
10.3 HSEC Management Develop an outline HSEC management and monitoring plan based on the BHP
and Monitoring Plan Billiton Charter and HSEC Policy and Standards, including:
• The management of HSEC risks;
• Strategies for the management of Environmental and Community aspects,
e.g. national and international standards and codes, stakeholder
identification, social issues;
• Control of Environmental emissions, including potential harmful emissions
and hazardous materials and wastes
• Requirements for resource and biodiversity conservation;
• Stakeholder rights, values, opportunities and capacity for involvement; and
• The HSEC Management System development.
Identify if the project options will be significant energy or fossil fuel consumers
(Greenhouse Gas emissions >100,000tpa CO2 equivalent) and complete a
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Assessment.
Note:
The level of detail covered should be such that the Selection Phase can
incorporate these philosophies.
10.4 Closure Plan Identify and summarise any significant decommissioning, closure and
rehabilitation issues. Consider post mining land-use options.
For further information on requirements refer to the HSEC website.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 27 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
11. EXTERNAL RELATIONS
The Study report should address the following sub-elements and include a statement on how specific requirements have
been met for each sub-element.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
11.1 Stakeholders The major stakeholders who may have or could in the future have an
interest must be identified and their potential relationships described.
11.2 External Relations External Relations matters that could impact on the project options should
Program be evaluated and documented, including:
• National, Provincial and Local Government - a general appraisal of the
likely views of the government to developing the potential project,
including legislative/regulatory frameworks;
• Non Government Organisations – an assessment of the likely views of
NGOs to the development of the potential project; and
• International Trade Considerations - significant issues that could
impact on the project.
Report only aspects of external relations programs that are special or
unique.
Describe the External Relations and Communications Strategy that will be
used in the next stage.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 28 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
12. CAPITAL COST ESTIMATE
This section sets out the minimum standards applicable to preparing a Capital Cost Estimate for the Identification
Phase.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
12.1 Accuracy of Estimate Develop capital cost estimates for Project Identification Phase Studies to
be targeted within an accuracy of + 30% to ± 35%. On completion of the
Study the accuracy of the estimate shall be assessed.
12.2 Basis of Estimate Basis: Include a description of the estimating basis used and in particular
any deviations from the Cost Estimating guideline. The estimate must be
referenced to the scope of work.
Definition of Costs: Sufficiently define operating costs to allow an
accurately defined financial evaluation to be undertaken.
Base Date and Exchange Rates: The estimate to be expressed in the
functional currency of the project. State the base date of the capital cost
estimate and the exchange rate conversion factors used.
Estimate Strategy: The basis of the estimate should state the strategy
followed and should demonstrate a methodology that is appropriate in
support of the stated accuracy of the Study. Any element prepared by
third parties should be in accordance with this strategy.
12.3 Work Breakdown Prepare a preliminary estimate breakdown structure to at least a facility
Structure level.
12.4 Structure of Estimate Structure capital cost items according to the estimate breakdown
structure.
12.5 Presentation of the Present capital costs as:
Estimate
• Direct and Indirect Costs;
• Owners Costs including Pre-production, Commissioning; and
• Provisions including Foreign Exchange, Escalation and Contingency.
12.6 Owners Costs Specifically identify owners and pre-production costs; these need only be
factorised values.
12.7 Escalation and Foreign Highlight any escalation provisions and show them separately: the basis
Exchange of calculation should be shown.
Foreign exchange components of the costs need not be identified, unless
the information is readily available and deemed as reasonably
representative.
12.8 Working and Sustaining Respectively identify working and sustaining capital as percentages of
Capital annual revenue and of capital cost.
12.9 Contingency Include a contingency allowance in accordance with the Cost Estimating
guideline. Clearly state the methodology for calculating or arriving at the
allowance.
12.10 Cash Flow Forecasting Include an assessment on an annual basis for the development i.e.
Selection Phase Study and Definition Phase Study, and the execution of
the project.
12.11 Sources of Data Identify sources of cost data i.e.:
• Previous Identification Phase Studies for similar projects;
• Benchmarked estimate data;
• EPC/EPCM contractors, Equipment vendors and Bulk material
suppliers;
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 29 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
For further information on requirements refer to Toolkit PT157D (Cost Estimating) Appendix 1 and the Project
Management website.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 30 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
13. OPERATING COST ESTIMATE
This section sets out the minimum standard for an Operating Cost Estimate for the Identification Phase.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
13.1 Accuracy of Estimate Develop operating cost estimates with a targeted accuracy of ± 30 percent to
± 35 percent.
13.2 Basis of estimate Basis: Include a description of the basis of estimate, and in particular any
deviation from the Cost Estimate guideline.
Base Date and Exchange Rates: State the base date of the operating cost
estimate. This should be the same base date as stated for the Capital Cost
estimate. The estimate will be expressed in the functional currency of the
project. The exchange rate conversions used should be stated.
Definition of Costs: Provide a definition of costs between capital and
operating costs, sufficient to allow a preliminary financial evaluation to be
undertaken.
13.3 Structure of Estimate Present Operating Costs in the form per the following:
Fixed Operating Costs
(i) Labour Costs: Present a broad assessment of staffing requirements
and of the unit labour costs based on the operating philosophy of the
facilities.
(ii) Fixed overheads: Factorise fixed overheads from similar projects.
Variable Operating Costs
(i) Chemicals, Reagents and Fuel: Base significant chemical, reagent
and fuel quantities and costs on likely rates derived from test work or
industry norms.
(ii) Operating Consumables: Base rates of consumption for operating
consumables on factorised costs.
(iii) Product Transport and Insurance: Derive the rates for transportation
and insurance costs associated with the transportation of product from
factorised costs. Derive quantities of product to be transported and
insured from estimates and unit costs applied.
(iv) Maintenance, Consumables and Spares: Factorise Maintenance,
Consumables and Spares costs from similar projects where possible.
Note:
The operating cost estimate should include only a contingency provision for
undefined areas and a commentary and reasoning for the provision.
13.4 Contingency Any contingency included in the operating cost estimate should be justified and
Allowance shown separately.
13.5 Presentation of the • Ensure fixed operating costs are outputs that can input directly into the
Estimate Financial Model.
• Express the Variable Operating Costs in costs per tonne of ore milled in a
format to be agreed that shows units per tonne of ore milled and unit rates
used. The output will be used input directly into the Financial Model.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 31 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
13.6 Start-up Costs Ensure the Capital Cost estimate includes owner’s costs and pre-production
costs up to the date of introduction of ore for commissioning purposes.
Note:
Thereafter, annual operating costs shall take effect, including all special start-
up costs. These need not be assessed in detail for Identification Phase
Studies, but should be factorised from capital and operating cost relationships.
The basis of derivation should be reported.
13.7 Escalation Do not make allowance for escalation within the operating cost estimate, as
this will be included in the Financial Analysis. Identify any input costs likely to
be subject to unusual escalation rates that exceed the inflation assumptions
ensure that these are included in the nominal outcomes included in the
Investment Evaluation Model.
13.8 Sources of Data Identify sources of cost data i.e.:
• Current operating data;
• OEM data provided;
• Benchmarked data.
For further information on requirements refer to Toolkit PT157D (Cost Estimating) Appendix 1and the Project
Management website.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 32 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
14. OWNERSHIP, LEGAL AND CONTRACTUAL
The minimum requirements for a Identification Phase Study related to the issues of Ownership, Legal and Contractual
issues include the following.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
14.1 OWNERSHIP Ore Deposit: Define ownership of the ore body and make reference to the
sources of information.
Lands: Define ownership of land needed for the project and any rights and
prior uses.
14.2 LEGAL Sovereign: Include an opinion of a qualified person in respect of sovereign
risk issues.
14.3 CONTRACTUAL There is no requirement to detail or to demonstrate potential contractual
issues in the Identification Phase Study.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 33 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
15. INVESTMENT EVALUATION
The Investment Evaluation section of the Study Report should address the following issues and include a statement,
with reference to appropriate evidence, on how the specific requirements have been met for each sub-element. All
investment evaluation work must be completed in accordance with BHP Billiton's Investment Evaluation Standards (IES)
and should follow the guidance provided in the Investment Evaluation Practices (IEP).Terms used in this section are
described in the Glossary section of the IES and the Financial Metrics Glossary.
The minimum requirements applicable to the Financial Analysis for a Identification Phase Study are as follows.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
15.1 Valuation Methodology Confirm full compliance with the IES or describe any areas of non-
compliance and the reasons for such non-compliance. Discuss the
materiality of any non-compliance and any potential impact on the
investment decision to proceed to the next phase.
15.2 Investment Evaluation Describe the investment evaluation practices employed for this investment
Practices opportunity. If the modelling is not aligned with the IEP then describe any
differences, the reasons, and any plans to align the model with the IEP.
Describe any peer reviews or audits carried out as part of the investment
evaluation work, their findings and any outstanding issues and any plans to
address in subsequent phases.
15.3 Valuation Summary Present a summary of the outcomes of the investment evaluation work for
Results the recommended alternative only.
Describe the unique characteristics and the physical and/or transactional
scope of the proposed investment, and any significant residual risk, other
issues or constraints associated with the investment opportunity.
Include the following outputs: (at least to BHP Billiton in-country value level)
• Deterministic Case Summary
• Deterministic Valuation Matrix
• Deterministic Tornado Plot
Key Metrics: For the recommended alternative provide a summary of the
following:
• The absolute expenditure profile (i.e. the total expenditure for the
Optimised With Alternative) including both growth and sustaining capital
• The incremental expenditure profile (i.e. the difference between the total
expenditure for the Optimised With and Optimised Without Alternative)
including both growth and sustaining capital
• The initial investment (or project) expenditure profile (refer Section 2.3
of the Investment Policy for guidance).
Note:
Show expenditure profiles annually for first 5 years and then annual average
thereafter, in nominal, BHP Billiton share terms.
Cash Flow streams: For the recommended alternative, discuss the profile
of the NPV and the profile of the 4 streams of real Unleveraged Free Cash
Flow (Revenue, Capex, Opex, Taxes and Royalties) in accordance with the
IEP. Present in both absolute terms (i.e. for the Optimised With Alternative)
and in incremental terms (i.e. for the Optimised With minus Without
Alternatives).
Use graphs of the NPV, four cash streams, and of the components of each
of the four cash streams plus any other important parameters to explain the
fundamental source of economic value for this investment opportunity.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 34 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
15.4 Strategic Choices and Describe the strategic choices that BHP Billiton faces and the alternative
Investment that are to be evaluated in the next phase for full value capture of the
Alternatives investment opportunity.
Compare and contrast the differences between the alternatives and
demonstrate how, based on an understanding of value and risk, the
recommended alternative for the Identification Phase Study was chosen.
Use Deterministic Cases, Tornado Plots, NPV range and NPV Probability
distribution to compare alternatives and distinguish the recommended
alternative.
Describe how the Optimised Without and Optimised With Alternatives have
been chosen to demonstrate the NPV of the opportunity.
15.5 Optionality, Identify and discuss the key opportunities to enhance value through the
Incremental existence of any options (e.g. future expansion, future development phases,
Investments & future curtailment or abandonment phases, etc) embedded or assumed in
Potential Upside the investment. Detail their costs and value using matched incremental
investment and NPV waterfall diagrams to explain. Highlight any future
information and/or decision points these options depend upon.
Discuss any other potential upside that exists with this investment
opportunity that may "unlock" future value if conditions change and describe
the circumstances for such upside to become reality.
15.6 Key Assumptions Describe the Key Assumptions (refer BE&E Key Assumptions secure
intranet site) that were used as part of the valuation work including but not
limited to:
• Discount Rate (real) including the source and use of any Country Risk
Premium
• Product Price (Real) - including any premiums or discounts from BHP
Billiton protocols
• Exchange Rates (Real)
• Inflation Rates
• Any other macro-economic assumptions
Describe any differences in the assumptions used for each Alternative and,
if applicable, describe the methodology used to model these differences.
15.7 Key Project Variables Describe how the key project variables (e.g. production rate, Capex, Opex,
etc) were identified and selected for inclusion in the investment evaluation.
15.8 Competitive Position Describe how the investment opportunity ranks on an industry comparison.
Use appropriate industry cost curves and charts to quantify and explain the
ranking.
Describe how the investment will impact the competitive position of BHPB
for this commodity. Explain any limitations of this analysis.
15.9 Taxation Describe the in-country taxation environment and regime associated with
the investment opportunity e.g. Tax depreciation rates, as well as issues
associated with repatriating funds to the ultimate BHP Billiton corporate
parent entity e.g. Withholding taxes.
Report on any special taxation issues for the investment opportunity e.g.
Special tax rates or legal and structuring alternatives.
Note:
Contact Group Tax for assistance in completing this analysis.
15.10 Forward Work Plan Describe the following for the next phase of the investment evaluation work:
• Resources expected to be applied
• The major activities and tasks for completion with particular attention to
any areas of non-compliance with the IES
• The timetable and any key milestones for completion.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 35 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
15.11 Deliverables (for The deliverables expected for this element (Investment Evaluation) as part
reference only) of the study phase must include:
• The investment approval request
• A completed section of the overall Study Report with text and graphics
addressing the above sub-elements (Section 15 in total)
• Any presentation materials that support the Study Report
• The related investment evaluation models in electronic file format which
support the Study Report
Note:
List the full name and location of these files.
For further information on requirements refer to the Business Evaluation & Economics website.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 36 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
16. PROJECT STATUS AND REVIEWS
During the Identification Phase Study, a progress report should be prepared which as a minimum should report on the
following:
• Progress made to date;
• Cost and effort expended;
• Key concerns;
• Any changes to scope, schedule and budget.
On completion of the Identification Phase Study, the owner’s team should report on the following.
NO. SUB-ELEMENT MINIMUM REQUIREMENT
16.1 Status And Quality Of Describe:
Studies • The achieved progress and extent of evaluation achieved compared to the
expected level at end of the Definition Phase Study;
• Significant issues or areas that have not achieved progress or a level of
adequate definition, compared to minimum standards for other elements;
• The processes and status of preparation, checking and authorisation of
major outputs from the Identification Phase Study.
16.2 Cost and Effort Levels Include a statement of the costs and effort levels expended up to the date of
to Date the report based on:
• Field investigations;
• Test work;
• External services;
• Internal services.
Note:
The statement should show the costs and effort levels by general categories
so the extent of investigations and Study activities by discipline, i.e. geology,
metallurgy etc. can be assessed.
16.3 Peer Review Reference any Peer Reviews undertaken and whether or not the outcomes of
these reviews have been incorporated. The report need not summarise or
present the Peer Review findings themselves.
Note:
Peer Reviews may include comments on the processes of preparation,
checking and authorisation used by parties participating in the Identification
Phase Study.
16.4 Contributions to Date Include a statement of contributions made by BHP Billiton personnel and all
external organisations in particular their role and the nature of their respective
contribution.
16.5 Tollgates Include references to the standards adopted or any variations previously
agreed to from those standards, to establish the criteria for Identification Phase
Tollgate assessment.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 37 of 38 Version 2.1
BHP Billiton Standard for an Identification Phase Study
17. WORK PLAN
The owner’s team should prepare a Work Plan for the next phase namely the Selection Phase. In drawing up the work
plan, the processes detailed in the Investment Policy and the requirements highlighted in Section 1.1 and 1.2 of the
Selection Phase standard should be addressed.
The Work Plan should, as a minimum, present the following:
• Objectives of the Selection Phase Study;
• A scope statement which would include
- A preliminary description of the base case and alternatives to be evaluated,
- A process to be used to develop the definitive range of alternatives to be studied,
- Key technical or commercial issues for further investigation highlighting any potential project ‘intolerable high
residual risks’ or threshold issues that must be addressed, and
- Any additional drilling, sampling and/or testwork to be undertaken;
• The deliverables to be developed to constitute the Selection Phase Study;
• The minimum standards to be achieved during the Selection Phase Study and if not the BHP Billiton Standard for a
Selection Phase Study, why they have to be varied;
• Key Performance Indicators to be achieved during the Selection Phase and required to support the project to
proceed with the Definition Phase Study;
• The execution approach, and who and what organisations (including likely consultants and specialists) will be
responsible to perform the Selection Phase Study work including the contracting strategy for engaging such
organisations;
• The organisational structure and key resources nominated to lead the Selection Phase and functional areas,
including roles and responsibility to be assigned and a schedule for the mobilisation of key personnel;
• A schedule for the Selection Phase Study to an “activity” or “task” level of detail, including key study activities and
milestones. The schedule should include allow sufficient time for the completion of the study documentation, the
review of the Selection Phase study by the IPR team, and the preparations of all documentation/submissions for
approval;
• A detailed estimate of the cost to complete the Selection Phase Study including appropriate provisions for
undefined work;
• Procedures and systems to be employed;
• Communication and co-ordination processes;
• Reporting requirements;
• Interfaces and involvement of external organisations;
In the event that the report recommends further work before a decision is made to proceed to the Selection Phase, a
Work Plan should be prepared based on the above.
Commercial-in-Confidence Page 38 of 38 Version 2.1
You might also like
- GLD Capitulo 11 3 y 11 4 Ultima Version 24 04 15 12 00 HDocument74 pagesGLD Capitulo 11 3 y 11 4 Ultima Version 24 04 15 12 00 HAlvaro Torres Bozzo100% (1)
- Cost Estimation HandbookDocument160 pagesCost Estimation HandbookKay KaiNo ratings yet
- Project Controls Coding StructureDocument7 pagesProject Controls Coding Structurejehd21350No ratings yet
- JU-001-04-0222-0000-00-1C-0001 - WBS Mina JustaDocument15 pagesJU-001-04-0222-0000-00-1C-0001 - WBS Mina JustaAzul BlueNo ratings yet
- CC2 in-SOL-160 Business and Solution Requirements - GCR10443 Freight Auto-Netting v1.0Document16 pagesCC2 in-SOL-160 Business and Solution Requirements - GCR10443 Freight Auto-Netting v1.0Ramki PNo ratings yet
- NI 43-101 Technical Report on Quebrada Blanca Phase 2 Feasibility Study 2016Document222 pagesNI 43-101 Technical Report on Quebrada Blanca Phase 2 Feasibility Study 2016tjuang garces martinezNo ratings yet
- GLD.031 Major Capital Projects (Minerals)Document35 pagesGLD.031 Major Capital Projects (Minerals)rebolledojf100% (3)
- AMEC FS Guidelines 042806Document354 pagesAMEC FS Guidelines 042806Panji Aji Wibowo100% (1)
- Risk Based Cost Estimating PDFDocument286 pagesRisk Based Cost Estimating PDFI Kailash RaoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Open Pit Design and Sequencing Mine2 4DDocument177 pagesAdvanced Open Pit Design and Sequencing Mine2 4DAnonymous dFe07lhCQ2No ratings yet
- In-SOL-160 Business and Solution Requirements Budgeting and Forecasting Functional Integration V 1 0Document58 pagesIn-SOL-160 Business and Solution Requirements Budgeting and Forecasting Functional Integration V 1 0Ramki PNo ratings yet
- p6 Eppm User PDFDocument475 pagesp6 Eppm User PDFAnonymous YaIkNE7AUNo ratings yet
- CII 166 - 4 CII Best Practices (Resumo)Document92 pagesCII 166 - 4 CII Best Practices (Resumo)pedroNo ratings yet
- FEL Aplication in Mining Capital ProjectsDocument36 pagesFEL Aplication in Mining Capital ProjectsWilliam CurieNo ratings yet
- Canariaco PFSDocument513 pagesCanariaco PFSleckter85No ratings yet
- Project Code OF Accounts - AS Appli ED I N THE MI NI NG AND MI Neral Processi NG I Ndustri ES TO Faci LI Tate Benchmarki NGDocument22 pagesProject Code OF Accounts - AS Appli ED I N THE MI NI NG AND MI Neral Processi NG I Ndustri ES TO Faci LI Tate Benchmarki NGjppreciadom100% (1)
- Project Control For Engineering CII P6 - 1 PDFDocument35 pagesProject Control For Engineering CII P6 - 1 PDFRyanNo ratings yet
- Corani 43-101 Dec 2011Document291 pagesCorani 43-101 Dec 2011Kevin MárquezNo ratings yet
- AWP The Silver BulletDocument32 pagesAWP The Silver BulletQiuniuNo ratings yet
- AA - Monograph 12Document12 pagesAA - Monograph 12Jessica Kovacic100% (1)
- 314 2-Ac15Document115 pages314 2-Ac15Romner CordovaNo ratings yet
- Project Code of Accounts: AACE International Recommended Practice No. 20R-98Document14 pagesProject Code of Accounts: AACE International Recommended Practice No. 20R-98Mohamed HassanNo ratings yet
- Atdp Es 000098 - Estimate ClassesDocument10 pagesAtdp Es 000098 - Estimate Classesjonodo89No ratings yet
- Construction Industry InstituteDocument62 pagesConstruction Industry InstituteYoseph BirruNo ratings yet
- Delivering smarter mining feasibility studiesDocument4 pagesDelivering smarter mining feasibility studiesEmmanuel CaguimbalNo ratings yet
- Barrick 2017 Operations and Technical Update 2Document219 pagesBarrick 2017 Operations and Technical Update 2Rudy Dwi PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Simulation Techniques in Oyu Tolgoi Underground Development SchedulingDocument9 pagesSimulation Techniques in Oyu Tolgoi Underground Development SchedulingNIEVES MORALES SUBIABRENo ratings yet
- User Manual - Maintainer Maintenance ExecutionDocument143 pagesUser Manual - Maintainer Maintenance Executionrsanjuan100% (1)
- Anglo Project Way RD 01 - WBS Structure Guideline PDFDocument16 pagesAnglo Project Way RD 01 - WBS Structure Guideline PDFJoséCalderónNo ratings yet
- ICME-UNEP Tailings Management Case StudiesDocument66 pagesICME-UNEP Tailings Management Case Studiesabozman123No ratings yet
- Idaho Cobalt ProjectDocument218 pagesIdaho Cobalt ProjectCatalina LunaNo ratings yet
- Asanko Phase 2 PFS NI 43 101Document603 pagesAsanko Phase 2 PFS NI 43 101Gonzalo Muñoz MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Construction Project Administration: Dr. Abubakar SharafatDocument100 pagesConstruction Project Administration: Dr. Abubakar Sharafatmalik awansNo ratings yet
- FS - K.HILL BATTERY-GRADE MANGANESE PROJECT - K-Hill-FS-11142022Document482 pagesFS - K.HILL BATTERY-GRADE MANGANESE PROJECT - K-Hill-FS-11142022girl2wise100% (1)
- Ausimm Guide To Authors 2011Document21 pagesAusimm Guide To Authors 2011Brian HutchinsonNo ratings yet
- Barrick Safety and Health Management System PDFDocument40 pagesBarrick Safety and Health Management System PDFsaira tahirNo ratings yet
- T14 - Project Turnover Standard 2022Document61 pagesT14 - Project Turnover Standard 2022Mohamed AtefNo ratings yet
- Construction Project EngineeringDocument136 pagesConstruction Project EngineeringIoana Crisu100% (3)
- Documents - MX Pdricii PDFDocument40 pagesDocuments - MX Pdricii PDFRomner CordovaNo ratings yet
- C Cs 10 007 Watermains Rev 1Document15 pagesC Cs 10 007 Watermains Rev 1Johnny vargas suclupeNo ratings yet
- Capital Cost Mining PDFDocument263 pagesCapital Cost Mining PDFsue1001No ratings yet
- Economics of Mine Planning and Equipment SelectionDocument9 pagesEconomics of Mine Planning and Equipment SelectionFrancisca MiguelNo ratings yet
- 2014 PEA Report PDFDocument384 pages2014 PEA Report PDFreginaNo ratings yet
- PDRIDocument102 pagesPDRISergio Alan Martinez100% (1)
- Cost EstimationDocument76 pagesCost EstimationsoxalNo ratings yet
- Cerro Del Gallo Pre Feasibility Report FINAL 31jan2020 WebDocument351 pagesCerro Del Gallo Pre Feasibility Report FINAL 31jan2020 WebRicardoe RodriguezNo ratings yet
- XXX Capital Projects Procedures ManualDocument210 pagesXXX Capital Projects Procedures Manualzhangj5No ratings yet
- 6 Dry Tailings Facility DesignDocument159 pages6 Dry Tailings Facility DesignElPepeNo ratings yet
- Introduction to CII Best PracticesDocument162 pagesIntroduction to CII Best PracticesDavid SueldoNo ratings yet
- Bankable Feasibility Study (BFS) For Mining ProjectDocument22 pagesBankable Feasibility Study (BFS) For Mining ProjectSalli Marindha100% (2)
- Oyu Tolgoi Oct 2014Document547 pagesOyu Tolgoi Oct 2014Carlos A. Espinoza MNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Estimation of Gripper TBMDocument22 pagesAnalysis and Estimation of Gripper TBMRey Engel Rosas CarbajalNo ratings yet
- Capestone Technical Report PDFDocument193 pagesCapestone Technical Report PDFLevent ErgunNo ratings yet
- Cost Contingency Analysis and EvaluationDocument6 pagesCost Contingency Analysis and EvaluationOla M. SamaraNo ratings yet
- Project Control For Construction CII P6 - 5 PDFDocument52 pagesProject Control For Construction CII P6 - 5 PDFRyanNo ratings yet
- PEpC 1Document44 pagesPEpC 1Claudio Makarovsky100% (1)
- Conceptual Mining Study StandardDocument31 pagesConceptual Mining Study StandardJonB64100% (1)
- The Basel Ii "Use Test" - a Retail Credit Approach: Developing and Implementing Effective Retail Credit Risk Strategies Using Basel IiFrom EverandThe Basel Ii "Use Test" - a Retail Credit Approach: Developing and Implementing Effective Retail Credit Risk Strategies Using Basel IiNo ratings yet
- Process Improvement for Effective Budgeting and Financial ReportingFrom EverandProcess Improvement for Effective Budgeting and Financial ReportingNo ratings yet
- StockpileDocument9 pagesStockpilericardov2009No ratings yet
- Slag Formation SinteringDocument10 pagesSlag Formation Sinteringricardov2009No ratings yet
- 2010 Prod CostsDocument31 pages2010 Prod Costsricardov2009No ratings yet
- Mine Costs Table for Iron Ore OperationsDocument31 pagesMine Costs Table for Iron Ore Operationsricardov2009No ratings yet
- 2009 Prod CostsDocument31 pages2009 Prod Costsricardov2009No ratings yet
- 2008 Prod CostsDocument31 pages2008 Prod Costsricardov2009No ratings yet
- 2004 Prod CostsDocument31 pages2004 Prod Costsricardov2009No ratings yet
- 2006 Prod CostsDocument31 pages2006 Prod Costsricardov2009No ratings yet
- 2005 Prod CostsDocument31 pages2005 Prod Costsricardov2009No ratings yet
- 2001 Prod CostsDocument29 pages2001 Prod Costsricardov2009No ratings yet
- 2002 Prod CostsDocument31 pages2002 Prod Costsricardov2009No ratings yet
- Different Project Topics of BSNLDocument3 pagesDifferent Project Topics of BSNLAbhijit Tripathy0% (1)
- Statics: Vector Mechanics For EngineersDocument32 pagesStatics: Vector Mechanics For EngineersArdaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 STEM 12 2P SIP FINALDocument17 pagesGroup 1 STEM 12 2P SIP FINALFhing FhingNo ratings yet
- Hoist by TechnologyDocument6 pagesHoist by TechnologyAnonymous ntE0hG2TPNo ratings yet
- Relative Density and Load Capacity of SandsDocument14 pagesRelative Density and Load Capacity of SandsgatotNo ratings yet
- I PU Assignment 2023-24 For WorkshopDocument12 pagesI PU Assignment 2023-24 For Workshopfaruff111100% (1)
- 2 Phantom Forces Gui Scripts in OneDocument11 pages2 Phantom Forces Gui Scripts in OneAthallah Rafif JNo ratings yet
- PI734DDocument8 pagesPI734Deng_hopaNo ratings yet
- Life Saving Appliance: Personal Life-Saving Appliances Lifeboats & Rescue Boats LiferaftsDocument18 pagesLife Saving Appliance: Personal Life-Saving Appliances Lifeboats & Rescue Boats Liferaftsdafa dzaky100% (1)
- Remote Sensing Mineral Exploration LithiumDocument16 pagesRemote Sensing Mineral Exploration LithiumGerald Darshan MogiNo ratings yet
- Home Automation Chapter 1Document7 pagesHome Automation Chapter 1Nishant Sawant100% (1)
- Build a Homebrew Pre-Amplified MicrophoneDocument3 pagesBuild a Homebrew Pre-Amplified MicrophoneMacario Imbudo BukatotNo ratings yet
- Taoism and The KabbalahDocument26 pagesTaoism and The KabbalahJim Weaver100% (2)
- Vdocuments - MX - Control Systems by Nagrath Gopal Solution Manual PDFDocument128 pagesVdocuments - MX - Control Systems by Nagrath Gopal Solution Manual PDFPriyadarshini SahooNo ratings yet
- DSBV87ALP Two-Stage Differential Pressure Control Valve SpecsDocument2 pagesDSBV87ALP Two-Stage Differential Pressure Control Valve SpecsadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Ael Igniter CordsDocument1 pageAel Igniter CordsAlexander OpazoNo ratings yet
- CS401 Mcqs For Final TermDocument20 pagesCS401 Mcqs For Final Termsara.arshad.ch4No ratings yet
- II PUC PHYSICS - Previously Appeared Questions and Answers For 2021 Exam by MANJUNATH BDocument52 pagesII PUC PHYSICS - Previously Appeared Questions and Answers For 2021 Exam by MANJUNATH BVishal Ramesh100% (1)
- Model146C DynamicGasCal 156file - 18125Document150 pagesModel146C DynamicGasCal 156file - 18125api-26966403100% (1)
- CP 108: Home Assignment Topics-2021Document2 pagesCP 108: Home Assignment Topics-2021Biswajit PaulNo ratings yet
- Diagnoza Wstępna Klasa IDocument3 pagesDiagnoza Wstępna Klasa IMagda StręciwilkNo ratings yet
- Small Cells 2013 BrochuresDocument22 pagesSmall Cells 2013 BrochuresChungwa ChanjiNo ratings yet
- Nominal Pipe Size, Nominal Diameter & Outside Diameter For PipesDocument1 pageNominal Pipe Size, Nominal Diameter & Outside Diameter For PipesmdnorNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon ReactionsDocument2 pagesHydrocarbon ReactionsJessa Libo-onNo ratings yet
- VTBS 20-3DDocument1 pageVTBS 20-3Dwong keen faivNo ratings yet
- Phylum Chordata TransesDocument2 pagesPhylum Chordata TransesMaribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- The Mini Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (Mini-PCNL) and Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) in Pediatric PatientsDocument4 pagesThe Mini Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (Mini-PCNL) and Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) in Pediatric PatientsMarius DanilaNo ratings yet
- Study Journal Lesson 23-32 - LisondraDocument3 pagesStudy Journal Lesson 23-32 - Lisondrasenior highNo ratings yet
- CCTmanual 56Document226 pagesCCTmanual 56Jim Barrón GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Rift Vally BC N RegularDocument308 pagesRift Vally BC N RegularCabdisacid yasinNo ratings yet