Professional Documents
Culture Documents
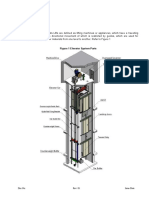
NBC Elevator1 - Termanologies
Uploaded by
kareemulllahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NBC Elevator1 - Termanologies
Uploaded by
kareemulllahCopyright:
Available Formats
ook Supply Bureau Under the License from BIS for LARSEN AND TOUBRO CONSTRUCTION - MANAPAKKAM, CHENNAI
ON 17-03-2017 09:00:59 (123.63.24.35) valid up
7 09:00:59 (123.63.24.35) valid upto31-12-2017
NATIONAL BUILDING CODE OF INDIA
PART 8 BUILDING SERVICES
Section 5 Installation of Lifts, Escalators and Moving Walks:
5A Lifts
1 SCOPE 2.1.4.1 Oil buffer A buffer using oil as a medium
1.1 This Code (Part 8/Subsection 5A) covers the which absorbs and dissipates the kinetic energy of the
requirements for planning, design, installation, descending car or counterweight.
operation, maintenance and inspection of lifts 2.1.4.1.1 Oil buffer stroke The oil displacing
Supplied by Book Supply Bureau Under the License from BIS for LARSEN AND TOUBRO CONSTRUCTION - MANAPAKKAM, CHENNAI ON 17-03-2017
(passenger lifts, goods lifts, hospital lifts, service lifts movement of the buffer plunger or piston, excluding
and dumb waiter) so as to ensure safe movement of the travel of the buffer plunger accelerating device.
people with satisfactory performance.
2.1.4.2 Spring buffer A buffer which stores in a spring
1.2 This Subsection gives information that should be the kinetic energy of the descending car or
exchanged among the architect/engineer, the consulting counterweight.
engineer and the lift manufacturer from the stage of
planning to installation including maintenance. 2.1.4.2.1 Spring buffer load rating The load required
to compress the spring by an amount equal to its stroke.
NOTE The provisions given in this Subsection are primarily
for electric traction lifts; however, most of these provisions are 2.1.4.2.2 Spring buffer stroke The distance, the
also applicable to hydraulic lifts {see good practice [8-5A(1)]}. contact end of the spring can move under a compressive
load until the spring is compressed solid.
2 TERMINOLOGY
2.1.5 Call Indicator A visual and audible device in
For the purpose of this subsection, the following
the car to indicate to the attendant the lift landings from
definitions shall apply.
which calls have been made.
2.1 General Terms Relating to Lifts 2.1.6 Car Bodywork The enclosing bodywork of
2.1.1 Automatic Rescue Device (ARD) A device the lift car which comprises the sides and roof and is
meant to bring a lift stuck between floors due to loss of built upon the car platform.
power, to the nearest landing level in either direction 2.1.7 Car Door Electric Contact An electric device,
and open the doors in order to allow trapped passengers the function of which is to prevent operation of the
to be evacuated. Such a device may use some form of driving machine by the normal operating device of the
internal auxiliary power source for such purpose, lift unless the car door is in the closed position.
complying with all the safety requirements of the lift
during normal run. The speed of travel is usually lower 2.1.8 Car Frame The supporting frame or sling to
than the normal speed. On reaching the level, in case which the platform of the lift car, its safety gear, guide
of manual door lifts, the device shall allow the door to shoes and suspension ropes are attached.
be opened and in case of power operated door lifts the 2.1.9 Car Platform The part of the lift car which
device shall automatically open the door. forms the floor and directly supports the load.
2.1.2 Bottom Car Run-by The distance between the 2.1.10 Clearance
car buffer striker plate and the striking surface of the
car buffer when the car is in level with the bottom 2.1.10.1 Bottom car clearance The clear vertical
terminal landing. distance from the pit floor to the lowest structural or
mechanical part, equipment or device installed beneath
2.1.3 Bottom Counterweight Run-by The distance the car platform, except the guide shoes, rollers, safety
between the counter weight buffer striker plate and the jaw blocks and platform apron or guard located within
striking surface of the counterweight buffer when the 300 mm, measured horizontally from the sides of the
car is in level with the top terminal landing. car platform when the car rests on its fully compressed
2.1.4 Buffer A device designed to stop a descending buffers.
car or counter weight beyond its normal limit of travel 2.1.10.2 Top car clearance The shortest vertical
by storing or by absorbing and dissipating the kinetic distance between the top of the car crosshead, or
energy of the car or counterweight. between the top of the car where no crosshead is
PART 8 BUILDING SERVICES SECTION 5 INSTALLATION OF LIFTS, ESCALATORS AND 5
MOVING WALKS: 5A LIFTS
ook Supply Bureau Under the License from BIS for LARSEN AND TOUBRO CONSTRUCTION - MANAPAKKAM, CHENNAI ON 17-03-2017 09:00:59 (123.63.24.35) valid up
7 09:00:59 (123.63.24.35) valid upto31-12-2017
provided, and the nearest part of the overhead structure 2.1.13 Deflector Sheave An idler pulley used to
or any other obstruction when the car floor is level with change the direction of a rope lead.
the top terminal landing.
2.1.14 Door (Lift Landing Door and Lift Car Door)
2.1.10.3 Top counterweight clearance The shortest
2.1.14.1 Door, centre opening sliding A door which
vertical distance between any part of the counterweight
slides horizontally and consists of two or more panels
structure and the nearest part of the overhead structure
which open from the centre and are usually so
or any other obstruction when the car floor is level with
interconnected that they move simultaneously.
the bottom terminal landing.
2.1.14.2 Door, mid-bar collapsible A collapsible
2.1.11 Control The system governing starting,
door with vertical bars mounted between the normal
stopping, direction of motion, acceleration, speed and
vertical members.
retardation of moving member.
2.1.14.3 Door, multi-panel A door arrangement
2.1.11.1 Single-speed alternating current control A
whereby more than one panel is used such that the
control for a driving machine induction motor which is
panels are connected together and can slide over one
arranged to run at a single-speed.
another by which means the clear opening can be
2.1.11.2 Two-speed alternating current control A maximized for a given shaft width. Multipanels are used
control for a two-speed driving machine induction in centre opening and two speed sliding doors.
motor which is arranged to run at two different
2.1.14.4 Door, single slide A single panel door which
synchronous speeds either by pole changing of a single
slides horizontally.
motor or by two different armatures.
2.1.14.5 Door, two speed sliding A door which slides
2.1.11.3 Rheostatic control A system of control
horizontally and consists of two or more panels, one of
which is accomplished by varying resistance or
which moves at twice the speed of the other.
reactance or both in the armature or field circuit or both
of the driving machine motor. 2.1.14.6 Door, vertical bi-parting A door which
slides vertically and consists of two panels or sets of
2.1.11.4 Variable voltage motor control (generator field
panels that move away from each other to open and are
control) A system of control which is accomplished
so interconnected that they move simultaneously.
by the use of an individual generator for each lift
wherein the voltage applied to the driving machine 2.1.14.7 Door, vertical lifting A single panel door,
motor is adjusted by varying the strength and direction which slides in the same plane vertically up to open.
of the generator field.
2.1.14.8 Door, swing A swinging type single panel
2.1.11.5 Electronic devices A system of control door which is opened manually and closed by means
which is accomplished by the use of electronic devices of a door closer when released.
for driving the lift motor at variable speed.
2.1.15 Door Closer A device which automatically
2.1.11.6 Alternating current variable voltage (ACVV) closes a manually opened door.
control A system of speed control which is
2.1.16 Door Operator A power-operated device for
accomplished by varying the driving and braking torque
opening and closing doors.
by way of voltage variation of the power supply to the
driving machine induction motor. 2.1.17 Dumb Waiter A lift with a car which moves
in guides in a vertical direction; has a net floor area not
2.1.11.7 Alternating current variable voltage variable
exceeding 1 m2 , total inside height of 1.2 m, whether
frequency (ACVVVF) control A system of speed
or not provided with fixed or removable shelves; has a
control which is accomplished by varying the voltage
capacity not exceeding 250 kg and is exclusively used
and frequency of the power supply to the driving
for carrying materials and shall not carry any person.
machine induction motor.
2.1.18 Electrical and Mechanical Interlock A device
2.1.11.8 Solid-state d.c. variable voltage control A
provided to prevent simultaneous operation of both up
solid-state system of speed control which is
and down relays or power contactors.
accomplished by varying the voltage and direction of
the power supply to the armature of driving machine 2.1.19 Electro-Mechanical Lock A device which
d.c. motor. combines in one unit, electrical contact and a
mechanical lock jointly used for the landing and/or car
2.1.12 Counterweight A weight or series of weights
doors.
to counterbalance the weight of the lift car and part of
the rated load. 2.1.20 Floor Levelling Switch A switch for bringing
6 NATIONAL BUILDING CODE OF INDIA 2016
ook Supply Bureau Under the License from BIS for LARSEN AND TOUBRO CONSTRUCTION - MANAPAKKAM, CHENNAI ON 17-03-2017 09:00:59 (123.63.24.35) valid up
7 09:00:59 (123.63.24.35) valid upto31-12-2017
the car to level at slow speed in case of double speed which either automatically or under the control of the
or variable speed machines. operator, moves the car within the levelling zone
towards the landing only, and automatically stops it at
2.1.21 Floor Selector A mechanism forming a part
the landing.
of the control equipment, in certain automatic lifts,
designed to operate controls which cause the lift car to 2.1.34.2 Levelling device, one way automatic A
stop at the required landings. device which corrects the car level only in case of under
run of the car but will not maintain the level during
2.1.22 Floor Stopping Switch A switch or
loading and unloading.
combination of switches arranged to bring the car to
rest automatically at or near any pre-selected landing. 2.1.34.3 Levelling device, two-way automatic
maintaining A device which corrects the car level
2.1.23 Geared Machine A machine in which the
on both under run and over-run and maintains the level
power is transmitted to the sheave through worm and
worm wheel or spur reduction gearing. during loading and unloading.
Supplied by Book Supply Bureau Under the License from BIS for LARSEN AND TOUBRO CONSTRUCTION - MANAPAKKAM, CHENNAI ON 17-03-2017
2.1.24 Gearless Machine A lift machine in which 2.1.34.4 Levelling device, two way automatic non-
the motive power is transmitted to the driving sheave maintaining A device which corrects the car level
from the motor without intermediate reduction gearing on both under run and over run but will not maintain
and has the brake drum mounted directly on the motor the level during loading and unloading.
shaft. 2.1.35 Levelling Zone The limited distance above
2.1.25 Goods Lift A lift designed primarily for the or below a lift landing within which the levelling device
transport of goods, but which may carry a lift attendant may cause movement of the car towards the landing.
or other personnel necessary for the loading or 2.1.36 Lift An appliance designed to transport
unloading of goods. persons or materials between two or more levels in a
2.1.26 Guide Rails The members used to guide the vertical or substantially vertical direction by means of
movement of a lift car or counterweight in a vertical a guided car. The word elevator is also synonymously
direction. used for lift.
2.1.27 Guide Rails Fixing The complete assembly 2.1.37 Lift Car The load carrying unit with its floor
comprising the guide rails bracket and its fastenings. or platform, enclosing bodywork, and car door.
2.1.28 Guide Shoe An attachment to the car frame 2.1.38 Lift Landing That portion of a building or
or counterweight for the purpose of guiding the lift car structure used for discharge of passengers or goods or
or counter weight frame. both into or from a lift car.
2.1.29 Hoisting Beam A beam, mounted immediately 2.1.39 Lift Machine The part of the lift equipment
below the machine room ceiling/machinery space comprising the motor and the control gear therewith,
ceiling, to which lifting tackle can be fixed for raising reduction gear (if any), brake(s) and winding drum or
or lowering parts of the lift machine. sheave, by which the lift car is raised or lowered.
2.1.30 Hospital Lift A lift normally installed in a 2.1.40 Lift Pit The space in the lift well below the
hospital, dispensary or clinic and designed to level of the lowest lift landing served.
accommodate one bed or stretcher along its depth, with 2.1.41 Lift Well The unobstructed space within an
sufficient space around to carry a minimum of three enclosure provided for the vertical movement of the
attendants in addition to the lift operator. lift car(s) and any counterweight(s), including the lift
2.1.31 Landing Call Push A push button fitted at a pit and the space for top clearance.
lift landing, either for calling the lift car, or for actuating 2.1.42 Lift Well Enclosure Any structure which
the call indicator. separates the lift well from its surroundings.
2.1.32 Landing Door The hinged or sliding portion 2.1.43 Operation The method of actuating the control
of a lift well enclosure, controlling access to a lift car of lift machine.
at a lift landing.
2.1.43.1 Automatic operation A method of operation
2.1.33 Landing Zone A space extending from a in which by a momentary activation of a call button the
horizontal plane 400 mm below a landing level to a lift car is set in motion and caused to stop automatically
plane 400 mm above the landing level. at any required lift landing.
2.1.34 Levelling Devices 2.1.43.2 Non-selective collective automatic
2.1.34.1 Levelling device, lift car Any mechanism operation Automatic operation by means of one
PART 8 BUILDING SERVICES SECTION 5 INSTALLATION OF LIFTS, ESCALATORS AND 7
MOVING WALKS: 5A LIFTS
ook Supply Bureau Under the License from BIS for LARSEN AND TOUBRO CONSTRUCTION - MANAPAKKAM, CHENNAI ON 17-03-2017 09:00:59 (123.63.24.35) valid up
7 09:00:59 (123.63.24.35) valid upto31-12-2017
button in the car for each landing level served and one 2.1.43.6 Car switch operation Method of operation
button at each landing, wherein all stops registered by by which the movement of lift car is directly under the
the momentary actuation of landing or car buttons are operation of the attendant by means of a handle.
made irrespective of the number of buttons actuated or
2.1.43.7 Signal operation Same as collective
of the sequence in which the buttons are actuated. With
operation, except that the closing of the door is initiated
this type of operation, the car stops at all landings for
by the attendant.
which buttons have been actuated making the stops in
the order in which the landings are reached after the 2.1.43.8 Double button (continuous pressure)
buttons have been actuated but irrespective of its operation Operation by means of buttons or switches
direction of travel. in the car and at the landings any of which may be used
to control the movement of the car as long as the button
2.1.43.3 Selective collective automatic operation
or switch is manually pressed in the actuating position.
Automatic operation by means of one button in the car
for each landing level served and by up and down buttons 2.1.44 Operating Device A car switch, push button
Supplied by Book Supply Bureau Under the License from BIS for LARSEN AND TOUBRO CONSTRUCTION - MANAPAKKAM, CHENNAI ON 17-03-2017
at the landings, wherein all stops registered by the or other device employed to actuate the control.
momentary actuation of the car made as defined under
2.1.45 Overhead Beams The members, usually of
non-selective collective automatic operation, but wherein
steel, which immediately support the lift equipment at
the stops registered by the momentary actuation of the
the top of the lift well.
landing buttons are made in the order in which the
landings are reached in each direction of travel after the 2.1.46 Over Speed Governor An automatic device
buttons have been actuated. With this type of operation, which brings the lift car and/or counter weight to rest
all up landing calls are answered when the car is by operating the safety gear in the event of the speed in
travelling in the up direction and all down landing calls a descending direction exceeding a predetermined limit.
are answered when the car is travelling in the down
2.1.47 Passenger Lift A lift designed for the transport
direction, except in the case of the uppermost or
of passengers.
lowermost calls which are answered as soon as they are
reached irrespective of the direction of travel of the car. 2.1.48 Position and/or Direction Indicator A device
which indicates on the lift landing or in the lift car or
2.1.43.4 Single automatic operation Automatic
both, the position of the car in the lift well or the
operation by means of one button in the car for each
direction in which the lift car is travelling or both.
landing level served and one button at each landing so
arranged that if any car or landing button has been 2.1.49 Rated Load (Lift) The maximum load for
actuated, the actuation of any other car or landing which the lift car is designed and installed to carry safely
operation button will have no effect on the movement at its rated speed.
of the car until the response to the first button has been
2.1.50 Rated Speed (Lift) The mean of the maximum
completed.
speed attained by the lift car in the upward and
2.1.43.5 Group automatic operation Automatic downward direction with rated load in the lift car.
operation of two or more non-attendant lifts equipped
2.1.51 Retiring Cam A device which prevents the
with power-operated car and landing doors. The
landing doors from being unlocked by the lift car unless
operation of the cars is coordinated by a supervisory
it stops at a landing.
operation system including automatic dispatching
means whereby selected cars at designated dispatching 2.1.52 Roping Multiple A system of roping where,
points automatically close their doors and proceed on in order to obtain a multiplying factor from the machine
their trips in a regulated manner. to the car, multiple falls of rope are run around sheave
on the car or counterweight or both. It includes roping
Typically, it includes one button in each car for each
arrangement of 2 to 1, 3 to 1, etc.
floor served and up and down buttons at each landing
(single buttons at terminal landings). The stops set up 2.1.53 Safety Gear A mechanical device attached to
by the momentary actuation of the car buttons are made the lift car or counterweight or both, designed to stop
automatically in succession as a car reaches the and to hold the car or counterweight to the guides in
corresponding landings irrespective of its direction of the event of free fall, or, if governor operated, of over-
travel or the sequence in which the buttons are actuated. speed in the descending direction. Any anticipated
The stops set up by the momentary actuation of the impact force shall be added in the general drawing or
landing buttons may be accomplished by any lift in the layout drawing.
group, and are made automatically by the first available
2.1.54 Service Lift A passenger cum goods lift meant
car that approaches the landing in the corresponding
to carry goods along with people.
direction.
8 NATIONAL BUILDING CODE OF INDIA 2016
ook Supply Bureau Under the License from BIS for LARSEN AND TOUBRO CONSTRUCTION - MANAPAKKAM, CHENNAI ON 17-03-2017 09:00:59 (123.63.24.35) valid up
7 09:00:59 (123.63.24.35) valid upto31-12-2017
NOTE Typically in an office building this may be required 2.2.2 Acceleration Rate of change of z-axis velocity,
to carry food or stationeries, in a residential building to carry
attributed to lift motion control.
luggage or accommodate a stretcher and in a hotel to be used
for food trolleys or baggage. There is a need in such lifts, to 2.2.3 Axis of Measurement Orthogonal reference
take care of the dimensions of the car and the door clear axes for the measurements as follows:
opening in line with the type of goods that may have to be
carried based on mutual discussion between the supplier and a) X-axis Axis perpendicular to the plane of
the customer. Also, such lifts shall have buffer railings in the car front door (that is back to front),
the car at suitable height to prevent damage to the car panels
when the goods are transported. Typically such lifts, if b) Y-axis Axis perpendicular to X and Z (that
provided with an automatic door, may use some means to is side to side), and
detect trolleys and stretcher movement in advance to protect
the doors against damage. The car floor load calculations c) Z-axis Axis perpendicular to the car floor
and car area of such a lift is as in the case of a passenger lift (that is vertical).
except that these are not meant to carry heavy concentrated
loads. 2.2.4 Equivalent Sound Pressure Level (LAeq)
Average A-weighted sound pressure level, using
2.1.55 Sheave A rope wheel, the rim of which is
frequency weighting A and time weighing fast,
grooved to receive the suspension ropes but to which
the ropes are not rigidly attached and by means of which determined within defined boundaries.
power is transmitted from the lift machine to the 2.2.5 Jerk Rate of change of z-axis acceleration,
suspension ropes. attributed to lift motion control. It is expressed in metre
per second cube (m/s3).
2.1.56 Slack Rope Switch Switch provided to open
the control circuit in case of slackening of rope(s). NOTE The passenger perception of vertical ride quality
during jerk is represented by the assessment of vertical vibration
2.1.57 Suspension Ropes The ropes by which the during non-constant acceleration.
car and counter weight are suspended. 2.2.6 Lift Ride Quality Sound levels in the car, and
2.1.58 Terminal Slow-Down Switch A switch when vibration of the car floor, relevant to passenger
actuated shall compulsorily cut off the high speed and perception, associated with lift motion.
switch on the circuitry to run the lift in levelling speed 2.2.7 Peak to Peak Vibration Levels Sum of the
before reaching on terminal landings. magnitudes of two peaks of opposite sign separated by
2.1.59 Terminal Stopping Switch Normal Switch a single zero crossing.
for cutting off all the energizing current in case of 2.2.8 Sound A-weighted sound pressure level
car travelling beyond the top or bottom terminal measured in decibels (dB).
landing or a switch that cuts off the energizing current
so as to bring the car to a stop at the top or bottom 2.2.9 Sound Pressure Level (Lp,A) Ten times the
terminal landing level in the respective direction of logarithm to the base 10 of the ratio of the square of
travel. the sound pressure measured (pA) to the square of the
reference sound pressure (p0).
2.1.60 Terminal Stopping Device Final A device
Lp,A = 10 log (pA2/p02) dBA
which automatically causes the power to be removed
NOTE The reference sound pressure level (p0) is 20 µPa
from an electric lift driving machine motor and brake,
(2 × 105 Pa). The measured sound pressure, pA, is in Pascals,
independent of the functioning of the normal terminal using frequency weighting A.
stopping device, the operating device or any emergency
terminal stopping device, after the car has passed a 2.2.10 V95 Value of velocity within defined
terminal landing. boundaries or limits, in which 95 percent of observed
values fall. This value is used statistically to estimate
2.1.61 Total Headroom The vertical distance from typical levels.
the level of the top lift landing to the bottom of the
machine room slab. 2.2.11 Velocity Rate of change of z-axis
displacement, attributed to lift motion control.
2.1.62 Travel The vertical distance between the
bottommost and topmost lift landings served by the lift. 2.2.12 Vibration Variation with time of the
magnitude of acceleration, when the magnitude is
2.2 Terms Relating to Performance Requirements alternately greater and smaller than a reference level.
for Lifts It is expressed in m/s2.
2.2.1 A95 Values of acceleration or vibration within 2.3 Terms Relating to Planning and Design of Lifts
defined boundaries or limits, in which 95 percent of
observed values fall. This value is used statistically to 2.3.1 Door Closing Time (tc) Time period measured
estimate typical levels. from the instant that car doors start to close until the
doors are locked.
PART 8 BUILDING SERVICES SECTION 5 INSTALLATION OF LIFTS, ESCALATORS AND 9
MOVING WALKS: 5A LIFTS
ook Supply Bureau Under the License from BIS for LARSEN AND TOUBRO CONSTRUCTION - MANAPAKKAM, CHENNAI ON 17-03-2017 09:00:59 (123.63.24.35) valid up
7 09:00:59 (123.63.24.35) valid upto31-12-2017
2.3.2 Door Opening Time (to) Time period measured NOTE The value of (a d ) shall be obtained by the lift
manufacturer from the building engineer/structural engineer.
from the instant that car doors start to open until they
are open 800 mm. 2.4.2 Normal Operation Operation mode in which
2.3.3 Door-to-Door Time (T) Time period measured the lift performs when not in seismic mode or in seismic
from the instant that car doors start to close to the instant stand-by mode.
that the car doors are open 800 mm at the next adjacent 2.4.3 Retaining Device Mechanical device securely
floor. fixed to a structural member of the lift car,
2.3.4 Handling Capacity (HC) The number of counterweight frame designed to retain the lift car and
passengers that a lift system can theoretically transport counterweight within its guide rails during seismic
during the up-peak traffic condition with car occupancy activity.
of 80 percent of the actual capacity expressed as a 2.4.4 Seismic Mode Special mode in which the lift
percent of the total building population. operates after detection of seismic trigger level.
Supplied by Book Supply Bureau Under the License from BIS for LARSEN AND TOUBRO CONSTRUCTION - MANAPAKKAM, CHENNAI ON 17-03-2017
2.3.5 Interval (INT) Time period between successive 2.4.5 Seismic Stand-By Mode Special mode in which
car arrivals at the main terminal floor with cars loaded the lift operates after detection of primary earthquake
to any value. wave without the activation of the seismic detection
2.3.6 Nominal Travel Time (NTT) The nominal travel system.
time is defined as the time it would take to run a distance 2.4.6 Seismic Trigger Level Seismic acceleration
of the total travel at the rated speed of the lift without which is used to activate a seismic detection system.
taking into account the acceleration and deceleration
of the car or the intermediate stops of real runs. 2.4.7 Snag Point The point of interference between
flexible elements (for example, ropes, chains, travelling
2.3.7 Passenger Arrival Rate Percentage of a cable, etc) and fixed elements (for example, by guide
buildings population arriving within a 5 min period. rail brackets, guide rail clip bolts, fishplates, vanes,
2.3.8 Passenger Average Transfer Time (tp) Average and similar devices).
period of time required for a single passenger to enter 2.5 Terms Related to Maintenance of Lifts
or leave the lift car.
2.5.1 Competent Maintenance Person Designated
2.3.9 Passenger Average Waiting Time (AWT) person, suitably trained, qualified by knowledge and
Average period of time from the instant a passenger practical experience, provided with necessary
registers a landing call or joins a queue, until the instructions and supported within their maintenance
responding lift begins to open its doors at the boarding organization to enable the required maintenance
floor. AWT is not the same as INT. operations to be safely carried out.
2.3.10 Round Trip Time (RTT) The average time 2.5.2 Installation Completely installed passenger
taken by a single lift to make a trip from the main lift or good passenger lift or accessible goods only lift
terminal back to the main terminal, starting from the or service lift.
time the car doors open at the main terminal until the
car doors re-open at the main terminal after serving all 2.5.3 Installer Natural or legal person who takes
demand along the way. responsibility for the design, manufacture, installation
and placing on the market of lifts.
2.3.11 Single Floor Flight Time (tf1) Period of time
measured from the instant that the car doors are locked 2.5.4 Maintenance Organization Company or part
until the lift is level at the next adjacent floor. of company where competent maintenance person(s)
carry out maintenance operation on behalf of the owner
2.3.12 Single Floor Transit Time (tv) Period of time of the installation.
required to transit two adjacent floors at rated speed.
2.3.13 Sky Lobby A sky lobby is the main floor 3 GENERAL
for local groups in the upper part of a very tall 3.1 Conformity with Lifts Act and Rules
building.
3.1.1 The installation shall generally be carried out in
2.4 Terms Relating to Seismic Operation of Lifts conformity with Lift Acts and Rules, wherever they are
in force.
2.4.1 Design Acceleration (ad) The horizontal
acceleration to be used for calculation of forces 3.1.2 It is the responsibility of the owner of the
(moments acting on lift systems and arising from premises where the lift will be installed, to obtain
seismic events). necessary permission from the Authority before and
10 NATIONAL BUILDING CODE OF INDIA 2016
You might also like
- Introduction to Fly-By-Wire Flight Control SystemsFrom EverandIntroduction to Fly-By-Wire Flight Control SystemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 737 Performance Reference Handbook - EASA EditionFrom Everand737 Performance Reference Handbook - EASA EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- 4748 Evsjv 'K M Ru, Awzwi, de Æqvwi 11, 2021: Lifts, Escalators and Moving Walks 4.1 GeneralDocument57 pages4748 Evsjv 'K M Ru, Awzwi, de Æqvwi 11, 2021: Lifts, Escalators and Moving Walks 4.1 GeneralFerdous WahidNo ratings yet
- Myanmar Lift and Escalator CodeDocument93 pagesMyanmar Lift and Escalator CodeRamkumar KumaresanNo ratings yet
- Flasher Protective Bar Photobarrie R Audible Signal: Basic Diagram of Automated Guided VehicleDocument20 pagesFlasher Protective Bar Photobarrie R Audible Signal: Basic Diagram of Automated Guided Vehiclepiludariarajvant2521100% (1)
- Additional Requirements For Bus Construction: Automotive Industry StandardDocument59 pagesAdditional Requirements For Bus Construction: Automotive Industry StandardVishwas VaidyaNo ratings yet
- 3wheel 2ET2500Document12 pages3wheel 2ET2500Raymundo MartinezNo ratings yet
- Retenedor de Camion RVR32Document4 pagesRetenedor de Camion RVR32Juan Carlos Camacho PuelloNo ratings yet
- Report - Automated Guided VehicleDocument21 pagesReport - Automated Guided VehicleSatish HSNo ratings yet
- Guide shuttle rack system operatorsDocument27 pagesGuide shuttle rack system operatorsHasnain KanchwalaNo ratings yet
- R305PDocument2 pagesR305PCoreconNo ratings yet
- Dieci TRUCK MIXERS - 22Document5 pagesDieci TRUCK MIXERS - 22Dan PatchNo ratings yet
- Aerial Ropeways For Transportation of Passengers - Continuous Movement Monocable With Automatic Grips - Code of Practice For Design and ConstructionDocument12 pagesAerial Ropeways For Transportation of Passengers - Continuous Movement Monocable With Automatic Grips - Code of Practice For Design and ConstructionAbinashBeheraNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica Erp025-030vcDocument8 pagesFicha Tecnica Erp025-030vcRAUL HERRERANo ratings yet
- Aerial Rescue Ladder Eng 332537 PDFDocument12 pagesAerial Rescue Ladder Eng 332537 PDFRobertYinglingNo ratings yet
- 2100-In040 - En-P HANDLING INSTRUCTIONSDocument12 pages2100-In040 - En-P HANDLING INSTRUCTIONSJosue Emmanuel Rodriguez SanchezNo ratings yet
- UN Regulations 12Document30 pagesUN Regulations 12Christopher-toby Clarenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Towing Winch Emergency Release Systems-Cu Aplicare Din 2020Document4 pagesTowing Winch Emergency Release Systems-Cu Aplicare Din 2020tonyNo ratings yet
- Gov BD BNBC 2012 08 04Document42 pagesGov BD BNBC 2012 08 04Sara MillerNo ratings yet
- A-Frame Assembly OperationDocument10 pagesA-Frame Assembly OperationRashad MuradovNo ratings yet
- IS17386_2020Document16 pagesIS17386_2020vishnu nayakNo ratings yet
- JSA07510E-AA V300 Villa Elevator Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument24 pagesJSA07510E-AA V300 Villa Elevator Operation and Maintenance ManualMahmoud RobNo ratings yet
- Engine Room Crane and Safety FeaturesDocument11 pagesEngine Room Crane and Safety Featuresmister_no34No ratings yet
- Elevator Test Method Rev. 1 (Dood)Document12 pagesElevator Test Method Rev. 1 (Dood)ThomasNo ratings yet
- Ais 0988Document54 pagesAis 09889822776848No ratings yet
- Mobile Lab RegulationDocument9 pagesMobile Lab RegulationMuhammad ZohaibNo ratings yet
- RCAR - Bumper - Test - Procedure - 2 - 2 - 2020Document33 pagesRCAR - Bumper - Test - Procedure - 2 - 2 - 2020hekiNo ratings yet
- Euro Ncap Far Side Test and Assessment Protocol v24Document38 pagesEuro Ncap Far Side Test and Assessment Protocol v24loyioso1No ratings yet
- Vehicle Lift Method of Statement Rev. 1Document9 pagesVehicle Lift Method of Statement Rev. 1ThomasNo ratings yet
- AIS-099 & Amd 1 To 3Document112 pagesAIS-099 & Amd 1 To 3김동은No ratings yet
- Reg 52Document68 pagesReg 52Dragana VojnovicNo ratings yet
- National Building Code of India (2005) - Installation of Escalators & ElevatorsDocument39 pagesNational Building Code of India (2005) - Installation of Escalators & Elevatorsz3cyber70% (20)
- Apm Terminals Hopper Manual: Port of CallaoDocument34 pagesApm Terminals Hopper Manual: Port of CallaoSaray Fernández SaavedraNo ratings yet
- EconoTon II IIR 999938 0200Document54 pagesEconoTon II IIR 999938 0200Julio LopezNo ratings yet
- Sop 001 KCMCDocument7 pagesSop 001 KCMCAsaad ChughtaiNo ratings yet
- AFT 031 Bus Specs Oct 2019 002 201020131812Document35 pagesAFT 031 Bus Specs Oct 2019 002 201020131812Engineers rockNo ratings yet
- 介绍dw1000无钥匙汽车系统Document16 pages介绍dw1000无钥匙汽车系统Jay LeeNo ratings yet
- BMT Basic Maintenance Tasks For KONE Monospace With KCE TechnologyDocument24 pagesBMT Basic Maintenance Tasks For KONE Monospace With KCE TechnologyMohammad Younus BaigNo ratings yet
- Electronic Stability Control Systems: Automotive Industry StandardsDocument20 pagesElectronic Stability Control Systems: Automotive Industry StandardsZvezdan DjurdjevicNo ratings yet
- Filt Comfort and Convenience FeaturesDocument2 pagesFilt Comfort and Convenience FeaturesBuddhika DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - General Requirements: Part - Iv Lifts PagesDocument56 pagesChapter 1 - General Requirements: Part - Iv Lifts PagesNidas SameeraNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Heavy Industries: Electric Counterbalance TrucksDocument12 pagesHyundai Heavy Industries: Electric Counterbalance TrucksDragan PilipovićNo ratings yet
- Service-Worthiness Tests and Analyses For New Freight Cars Adopted 1987, Revised Purpose and ScopeDocument19 pagesService-Worthiness Tests and Analyses For New Freight Cars Adopted 1987, Revised Purpose and Scopeoliveira1305No ratings yet
- Regenerate 200 and 400Document5 pagesRegenerate 200 and 400Luisa BlancoNo ratings yet
- Specifications of Advance Life Support AmbulanceDocument32 pagesSpecifications of Advance Life Support AmbulanceAbiramiNo ratings yet
- UR MXX 2017Document5 pagesUR MXX 2017SRARNo ratings yet
- Lift Schedule of Tender SpecificationDocument33 pagesLift Schedule of Tender Specificationchia yeewahNo ratings yet
- Is.13944.1994 Window RetensionDocument13 pagesIs.13944.1994 Window Retensionrpagarwal2No ratings yet
- RCAR Bumper Test Procedure For AutomobilesDocument32 pagesRCAR Bumper Test Procedure For Automobilestrev3rNo ratings yet
- Codes For Lifts and EscalatorsDocument19 pagesCodes For Lifts and EscalatorsMing Hong100% (1)
- Vertical Transportation: Commercial, Hotel, Hospital, Etc)Document5 pagesVertical Transportation: Commercial, Hotel, Hospital, Etc)fdarchitectNo ratings yet
- AC 665-1010 - en (Safety Instructions)Document54 pagesAC 665-1010 - en (Safety Instructions)Arslan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Reconditioned R305 Small Assembly With Lift: Features Benefits AGV OptionsDocument2 pagesReconditioned R305 Small Assembly With Lift: Features Benefits AGV OptionsCoreconNo ratings yet
- Inspector's Guide: Gen2 Machine Room-Less Elevator System - The Next Generation of ElevatorsDocument16 pagesInspector's Guide: Gen2 Machine Room-Less Elevator System - The Next Generation of Elevatorsbugse100% (2)
- JCB Telehandlers Spec 4024d5Document28 pagesJCB Telehandlers Spec 4024d5jakalae5263No ratings yet
- Ece-R 152Document26 pagesEce-R 152EzgiNo ratings yet
- Bendix Service Data SD-23-7541 Air Disc BrakeDocument28 pagesBendix Service Data SD-23-7541 Air Disc BrakeW Morales0% (1)
- GRSG 96 04eDocument57 pagesGRSG 96 04eMuhammad BarilNo ratings yet
- Is-14225 1995 OcbDocument15 pagesIs-14225 1995 Ocb김동은No ratings yet
- Standard Lift SpecificationDocument13 pagesStandard Lift SpecificationAhmedNo ratings yet
- S&e S5 Module 3 StudentDocument61 pagesS&e S5 Module 3 StudentkareemulllahNo ratings yet
- ORGANISATIONDocument1 pageORGANISATIONkareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Preventing Youth Violence: An Overview of The Evidence (2015)Document100 pagesPreventing Youth Violence: An Overview of The Evidence (2015)Children's InstituteNo ratings yet
- List of Government Mental Hostptal Updated1Document9 pagesList of Government Mental Hostptal Updated1kareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Session - 5Document10 pagesSession - 5kareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Program Distribution 5TH Sem 28 09 2021Document1 pageProgram Distribution 5TH Sem 28 09 2021kareemulllahNo ratings yet
- QP 2022 BS Services7a and CDocument2 pagesQP 2022 BS Services7a and CkareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Archimedes principle design ideas for flood managementDocument3 pagesArchimedes principle design ideas for flood managementkareemulllahNo ratings yet
- AD-8 Design Brief 28.04.2023Document4 pagesAD-8 Design Brief 28.04.2023kareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Memorial Plan: Way T O AbcDocument1 pageMemorial Plan: Way T O AbckareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Hms URBAN DESIGN - 2Document28 pagesHms URBAN DESIGN - 2dinesh royalNo ratings yet
- Efficient Land Use StrategiesDocument2 pagesEfficient Land Use StrategieskareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Notes 54-3Document25 pagesNotes 54-3kareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Hms URBAN DESIGN - 3Document11 pagesHms URBAN DESIGN - 3dinesh royalNo ratings yet
- Plan of IdDocument1 pagePlan of IdkareemulllahNo ratings yet
- VII SEM B.ARCH. (CBCS - 2018 SCHEME) - AD VII SyllabusDocument2 pagesVII SEM B.ARCH. (CBCS - 2018 SCHEME) - AD VII SyllabuskareemulllahNo ratings yet
- STRUCTURES PPT 6th SEMDocument8 pagesSTRUCTURES PPT 6th SEMkareemulllahNo ratings yet
- SQCB Importent QuestionsDocument3 pagesSQCB Importent QuestionskareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Toowoomba Map 20Document1 pageToowoomba Map 20kareemulllahNo ratings yet
- LAMOTH Annual Report FINALDocument22 pagesLAMOTH Annual Report FINALkareemulllahNo ratings yet
- SunEarthTools SunPath 1634835017178Document3 pagesSunEarthTools SunPath 1634835017178kareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Mod5Document126 pagesContemporary Mod5kareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Chinese Students' Reflections on Hiroshima Peace Memorial MuseumDocument26 pagesChinese Students' Reflections on Hiroshima Peace Memorial MuseumkareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Tange - Hiroshima Peace Memorial MuseumDocument6 pagesTange - Hiroshima Peace Memorial MuseumkareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Centralized AC System in 40 CharactersDocument11 pagesCentralized AC System in 40 CharacterskareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Transportation Systems in Buildings - Notes-1Document6 pagesMechanical Transportation Systems in Buildings - Notes-1kareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Japanese Pastel Streets Newsletter - by SlidesgoDocument27 pagesJapanese Pastel Streets Newsletter - by SlidesgokareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems - Notes-2Document5 pagesAir Conditioning Systems - Notes-2kareemulllahNo ratings yet
- NBC Elevator1 - Selection of LiftsDocument1 pageNBC Elevator1 - Selection of LiftskareemulllahNo ratings yet
- Violence ADocument236 pagesViolence AEndry AbidinNo ratings yet
- Boiler Tube LeakageDocument20 pagesBoiler Tube LeakageSayan AichNo ratings yet
- Forms6i 10GDocument42 pagesForms6i 10GRolando OcañaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Nursing Process and Administration-PharmaDocument13 pagesModule 4 - Nursing Process and Administration-PharmaKelsey MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Clash of Clans Hack Activation CodeDocument2 pagesClash of Clans Hack Activation Codegrumpysadness7626No ratings yet
- 8959C4F253F33BB139F788350D0E6D0035455AB9A56BFAC9F3070E66F25AC10EDocument20 pages8959C4F253F33BB139F788350D0E6D0035455AB9A56BFAC9F3070E66F25AC10Edroping cowsNo ratings yet
- Resolution No. 100 - Ease of Doing BusinessDocument2 pagesResolution No. 100 - Ease of Doing BusinessTeamBamAquinoNo ratings yet
- Easergy PS100 48VDC Power SupplyDocument2 pagesEasergy PS100 48VDC Power SupplyRichard SyNo ratings yet
- Solvents and Their Nomenclauture PDFDocument10 pagesSolvents and Their Nomenclauture PDFAashish GauravNo ratings yet
- Australia vs. France ReportDocument5 pagesAustralia vs. France ReportammeNo ratings yet
- 20171121hulten JBS 6-3 PDFDocument13 pages20171121hulten JBS 6-3 PDFJe RomeNo ratings yet
- Crafted Furniture Business PlanDocument30 pagesCrafted Furniture Business PlanSufianNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes: Quarter 1 - Module 3Document9 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes: Quarter 1 - Module 3John Vincent Salmasan100% (5)
- Dynamic Arc Recognition and TerminationDocument12 pagesDynamic Arc Recognition and TerminationArun BabuNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Test4prep AI-900 v2020-09-07 by Abdullah 25qDocument19 pagesMicrosoft Test4prep AI-900 v2020-09-07 by Abdullah 25qANIMESH301No ratings yet
- Newspaper Layout DummyDocument1 pageNewspaper Layout Dummy1w2e3r4t5y100% (9)
- Nfpa Codes PDFDocument12 pagesNfpa Codes PDFphe zenNo ratings yet
- A Quick Guide To The FMD Pro PDFDocument24 pagesA Quick Guide To The FMD Pro PDFstouraNo ratings yet
- Manual For The Implementation of International Development Cooperation Projects of SloveniaDocument7 pagesManual For The Implementation of International Development Cooperation Projects of SloveniarefikrosicNo ratings yet
- 11608-Driving Women Fiction and PDFDocument240 pages11608-Driving Women Fiction and PDFAleksi KnuutilaNo ratings yet
- Licence Acoknowledgement SlipDocument1 pageLicence Acoknowledgement SlipBicky ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Kick Control: BY: Naga Ramesh D. Assistant Professor Petroleum Engineering Dept. KlefDocument13 pagesKick Control: BY: Naga Ramesh D. Assistant Professor Petroleum Engineering Dept. Klefavula43No ratings yet
- Citroen C4 Picasso/Grand Picasso BilmetropolenDocument5 pagesCitroen C4 Picasso/Grand Picasso BilmetropolenAlberto Miglino100% (1)
- Media Palnning ProcessDocument3 pagesMedia Palnning ProcessSrinivas KumarNo ratings yet
- Hidden Secrets of The Alpha CourseDocument344 pagesHidden Secrets of The Alpha CourseC&R Media75% (4)
- EIA For Maize & Wheat Milling Plant DEI PDFDocument110 pagesEIA For Maize & Wheat Milling Plant DEI PDFSasira Fionah100% (2)
- Hotel Reservation System: Hotel OAK-RAY, KandyDocument22 pagesHotel Reservation System: Hotel OAK-RAY, KandysaminaNo ratings yet
- Nitric Acid - Nitrous Acid - Nitrogen Oxides - Ullman's EncyclopediaDocument49 pagesNitric Acid - Nitrous Acid - Nitrogen Oxides - Ullman's Encyclopediapoly6icsNo ratings yet
- GLOBAL AMITY INSURANCE QUOTE FOR HONDA CITYDocument1 pageGLOBAL AMITY INSURANCE QUOTE FOR HONDA CITYoniNo ratings yet
- Business Plan ForbesDocument4 pagesBusiness Plan ForbesMoiz AhmedNo ratings yet