Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Define Business Analysis Approach
Uploaded by
Saurabh Mehta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views2 pagesBAPM Knowledge Area for CBAP
Original Title
KA1 - Business Analysis Planning & Monitoring
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBAPM Knowledge Area for CBAP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views2 pagesDefine Business Analysis Approach
Uploaded by
Saurabh MehtaBAPM Knowledge Area for CBAP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
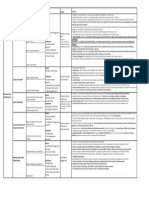
Knowledge Area Task Elements Input & Guidelines Output Key Point
1. Purpose is to define an appropriate method to conduct business analysis activities
Planning Approach 2. Usually Standardized & Formalized in organisations but may be tailored
3. Predictive Approach: minimizing uncertainty and ensuring that the solution is defined before implementation begins in order to maximize
Formality and Level of Detail of Business Analysis Inputs: Needs control and minimize risk.
Deliverables a. Used when the risk of an incorrect implementation is unacceptably high, or when engaging stakeholders presents significant challenges.
Guidelines: Business b. Require formal documentation and representations (Templates etc)
Business Analysis Activities - Business Analysis Analysis c. Tasks are performed in specific phases.
- Breakdown: Deliverables--> Tasks --> Activities Performance Assessment 4. Adaptive approaches: rapid delivery of business value in short iterations in return for acceptance of a higher degree of uncertainty regarding
Approach
- Business Policies - who will perform delivery of the solution
Plan Business Analysis
- Expert Judgement - timing & a. These approaches tend to be preferred when taking an exploratory approach to finding the best solution or for incremental improvement of an
Approach Timing of Business Analysis Work - Methodologies & existing solution.
sequencing,
- Availablility of resources, priority of initiative, Framework b. Informal Documentation: defining requirements and designs through team interaction & feedback on a working solution. Formal documentation is
- deliverable
concurrent activities, regultory deadline/contracts - Stakeholder Engagement - Integrated often produced after the solution is implemented to facilitate knowledge transfer.
Approach Approach c. Tasks are performed iteratively
Complexity & Risk 5. Other Factors: Complexity, regulated Industry, Contractual Obligation, Outsourcing, High staff turnover, SH location
6. Risk & Complexity : No. of Stakeholder more --> Complexity of BA work more.
Other Factor: Size of change, system affected, geographic/cultural considerations, tech. complexities
BA Risk: Experience, domain knowledge, Stakeholder knowledge, time allocated by SH, existing framework, culture
Acceptance
1. Analysis: Purpose is establishing and maintaining effective working relationships with the stakeholders
Inputs: Stakeholder 2. Degree of complexity increases as the number of stakeholders involved the BA activities increases
a. Needs Engagement 3. Analyzing their characteristics and data collected
Perform Stakeholder Analysis Approach 4. Who the SH are? What is their positive/negative influence? Impact of change on SH? Roles of Stakeholders; level of interest in the change
b. Businss Analysis
- List of 5. Company Organization Model & Business Process serve as source of internal Stakeholder.Sponsor identifies SH.
Approach 6. Understand Level of influence of a particular Stakeholder for buy-in/approvals. Develop risk plans if this is less.
Stakeholder
Plan Stakeholder Engagement - characteristics Stakeholder Matrix : Influence v/s Interest;
Define Stakeholder Collaboration Guidelines: - roles & Stakeholder Onion Diagram
- BA Performance Asses. responsibilities 7. Collaboration is different for both internal & external stakeholder
- collaboration & 8. Consider for Collaboration: timing/frequency; location; available tools; delivery method; preferences of SH
- Change Strategy
communication 9. Communication: What needs to be communicated; delivery method (verbal or oral); appropriate audience; time & Frequency of communication;
- Current State Descrp. requirement
Stakeholder Communication Needs geographic location of SH; level of details; level of formality.
1. Purpose is to define how decisions are made about requirements and designs, including reviews, change control, approvals, and prioritization.
2. Defines: the decision makers; process; information required for decision making for requirements & designs
3. Decision Making: SH roles as a decision maker; SME; reviewer of information; approver of decisions; Escalation path
Inputs:
Decision Making 4. Change Control Process:
a. Businss Analysis a. Request change process - steps for proposing change; when to propose changes; who & how can propose changes.
Business Analysis
Approach b. Element of CRs - cost & time estimate; Benefits; Risks; Priority; Course of action (multiple alternatives)
Planning & Governance
b. Stakeholder c. priortization of changes, documentation of changes, communication, impact analysis of changes & approval of changes
Monitoring Approach
Engagement Approach 5. Priortization Approach: Timelines, expected value, dependencies, resource constraints, adopted methodologies, and other factors influence how
Plan Business Analysis Change Control Process - Decision makers
requirements and designs are prioritized.
- who is
Governance Approach 6. Consider for Priortization planning : formality & rigour of process; participants; process of priortization; criteria for priortization (cost, risk & value)
Guidelines: responsible to
7. Approval Process: Approval formalizes the agreement between all stakeholders that details are accurate, adequate, and contain sufficient detail to
a. BA performance Asses. priortize and allow for continued progress to be made.
approve changes
Plan Prioritization Approach b. Business Policies a. timing and frequency of approvals are dependent on the size and complexity of the change & risk associated
c. Current State b. When planning the appropriate approval process, business analysts consider the organizational culture and the type of information being approved
d. Legal/Regulatory Info.
Plan for Approval
1. Purpose is to develop an approach for how business analysis information will be stored and accessed
Inputs: 2. Information includes: all the information business analysts elicit, create, compile, and disseminate in the course of performing business analysis.
Organization of Business Analysis Information
a. Business Analysis 3. Organization of Info: info shouldn't b difficult to locate, conflicts with other information, or is needlessly duplicated
Approach a. Relationship among information should be defined properly
Level of Abstraction 4. Abstraction should be different for each stakeholder based on needs of SH, complexity of information, importance of change. High risk
b. Stakeholder Information information is communicated in greater detail
Engagement Approach Management 5. Traceability should be determined to add value without increasing overhead
Plan Business Analysis Plan Tracebility Approach c. Governance Approach Approach 6. Reusing requirements can save an organization time, effort, and cost.
Information Management - how information 7. Candidate for reuse: regulatory req, contractual obligation, quality standard, SLAs, business rules & business processes, product descriptions
Guidelines: stored, accessed, 8. business analysts plan ahead for requirements reuse by identifying how best to structure, store, and access requirements. For this,
Plan for Requirement Reuse requirements must be clearly named, defined, and stored in a repository that is available to other business analysts.
a. BA performance Asses. and utilized.
9. Storage & Access : should be able to indicate status of any stored information and allow modification over time
b. Business Policies
Storage & Access 10. Req. Attributes - Absolute Reference, Author, Complexity, Ownership, Priority, Risk, Source, Stability, Status, Urgency
c. Info Mgmt Tool
d. Legal/Regulatory Info.
Requirements Attributes
1. Purpose is to establish the performance measures, conduct the performance analysis, report on the results of the analysis & identify any necessary
Inputs: Business
Performance Analysis preventive, corrective, or developmental actions. improvements are identified, they become guidelines for the next time a task is executed.
a. Performance Objectives Analysis 2. Reports on business analysis performance can be informal and verbal, or they may include formal documentation
(External) Performance 3. Performance Measures: deliverable due dates, frequency of the changes, review cycles required, task efficiency, qualitative feedback
Identify Business Analysis Assessment Measure b. Business Analysis 4. Possible Measures: Accuracy and Completeness of work, Knowlege of BA, Effectiveness, Org Support, Significance to final solution, meeting
Assessment
Performance Improvements Approach - planned vs actual
Strategic objective, Timeliness
Analyze Results performance 5. Analysis of results may be done at Stakeholder or personnel manager or a Center of Excellence level.
- root cause 6. Recommended actions: Preventive, Corrective, Improvement
Guidelines:
-proposed appr.
Recommend Actions for Improvement Org. Performance Std.
You might also like
- International Institute of Business Analysis Standard RequirementsFrom EverandInternational Institute of Business Analysis Standard RequirementsNo ratings yet
- KA2 - Elicitation & CollaborationDocument1 pageKA2 - Elicitation & CollaborationSaurabh MehtaNo ratings yet
- 02 BA Training - Enterprise AnalysisDocument43 pages02 BA Training - Enterprise AnalysisDhruvi RavalNo ratings yet
- BABOK Requirements Elicitation and CollaborationDocument16 pagesBABOK Requirements Elicitation and CollaborationwilliamNo ratings yet
- Blessing Ali Resume 4-3Document2 pagesBlessing Ali Resume 4-3roddyarch4No ratings yet
- White Blue Modern Business Analyst Resume PDFDocument1 pageWhite Blue Modern Business Analyst Resume PDFWesleeNo ratings yet
- BA 12 Months PDFDocument3 pagesBA 12 Months PDFSahil PatelNo ratings yet
- Business Analyst ResumeDocument2 pagesBusiness Analyst ResumeWaleed AbbasiNo ratings yet
- ProductNote Certificate in Business AnalyticsDocument5 pagesProductNote Certificate in Business AnalyticsJayakrishnaraj AJDNo ratings yet
- BABOK 2 Big PictureDocument1 pageBABOK 2 Big PictureMrobbo1984No ratings yet
- Adewale Bello: 6031 Pineland DR, Dallas, TX 75231 Email: Cell: (682) 334-2888 Summary of QualificationsDocument3 pagesAdewale Bello: 6031 Pineland DR, Dallas, TX 75231 Email: Cell: (682) 334-2888 Summary of Qualificationszakir itrecruitNo ratings yet
- Managing The Portfolio of Applications: BusinessDocument24 pagesManaging The Portfolio of Applications: BusinessJennyferNo ratings yet
- Requirements (Specif Ied & Modelled) : 7.4 Define Requirements A RchitectureDocument1 pageRequirements (Specif Ied & Modelled) : 7.4 Define Requirements A RchitectureMacNo ratings yet
- Nikhil Kumaar's 15+ Years Experience in Business TransformationDocument1 pageNikhil Kumaar's 15+ Years Experience in Business TransformationNikhil_gherwarNo ratings yet
- KA5 - Req Analysis & Design DefDocument2 pagesKA5 - Req Analysis & Design DefSaurabh MehtaNo ratings yet
- JD028 I95dev BusinessAnalystDocument2 pagesJD028 I95dev BusinessAnalystbhargavrd20No ratings yet
- Best Practices For Business AnalystDocument29 pagesBest Practices For Business AnalystSatish GuptaNo ratings yet
- BENCHMARKING AND QUALITY TOOLSDocument47 pagesBENCHMARKING AND QUALITY TOOLSFarshan SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Six Knowledge Areas - SynopsisDocument16 pagesSix Knowledge Areas - SynopsisUpendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Plan Stakeholder EngagementDocument4 pages3.2 Plan Stakeholder EngagementSushmita RoyNo ratings yet
- De Guzman Data Mapping TemplateDocument17 pagesDe Guzman Data Mapping TemplateVivien De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Applying UML and PatternsDocument39 pagesApplying UML and PatternsAbinavNo ratings yet
- Project Scope ManagementDocument48 pagesProject Scope ManagementRutu BarveNo ratings yet
- Coursework SpecificationDocument7 pagesCoursework SpecificationTaiyab HaiderNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis and AutomtionDocument3 pagesData Analysis and AutomtionAshwin GirishNo ratings yet
- Q1 What Is The of BA in Team Size and PRDocument3 pagesQ1 What Is The of BA in Team Size and PRNikhil KulkarniNo ratings yet
- UML Models: Jennifer Campbell CSC340 - Winter 2007Document7 pagesUML Models: Jennifer Campbell CSC340 - Winter 2007Peter L. MontezNo ratings yet
- Plan BA ApproachDocument7 pagesPlan BA ApproachskumaritesNo ratings yet
- BA Training Course ContentDocument4 pagesBA Training Course ContentMS ShabilNo ratings yet
- Business Analyst Cheat SheetDocument1 pageBusiness Analyst Cheat SheetWasim KhanNo ratings yet
- BA Course Screen Shot 1Document14 pagesBA Course Screen Shot 1Rahul VemuriNo ratings yet
- How To Tailor Your Resume/CV For A Dream Job: Angelo Biviano and Hassan AminiDocument25 pagesHow To Tailor Your Resume/CV For A Dream Job: Angelo Biviano and Hassan AminiBryan StoneNo ratings yet
- CBAP NotesDocument3 pagesCBAP NotesAnubha JainNo ratings yet
- Why Did You Apply For This PositionDocument4 pagesWhy Did You Apply For This PositionTaufiq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Requirements-Process (Compatibility Mode)Document30 pagesRequirements-Process (Compatibility Mode)nmhuong90No ratings yet
- BAPlanningAndMonitoring BusinessAnalysisDocument5 pagesBAPlanningAndMonitoring BusinessAnalysisHitesh N RNo ratings yet
- Business AnalysisDocument1 pageBusiness AnalysisAung MinNo ratings yet
- LIFE INS BA EXPERIENCED TRANSFORMATION PROGRAMSDocument1 pageLIFE INS BA EXPERIENCED TRANSFORMATION PROGRAMSBunnyNo ratings yet
- BABOK® Guide 2.0 - What's in It For You?Document3 pagesBABOK® Guide 2.0 - What's in It For You?Yvan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Business Analyst Workshop GuideDocument6 pagesBusiness Analyst Workshop GuideMC SaravananNo ratings yet
- 02 Fundamentals of Business AnalysisDocument21 pages02 Fundamentals of Business AnalysisNInaAntalkNo ratings yet
- BABOK - Summary of Requirements Analysis and DocumentationDocument15 pagesBABOK - Summary of Requirements Analysis and DocumentationmeristarNo ratings yet
- BABOKDocument44 pagesBABOKAlexey Savchuk100% (2)
- BA SummaryDocument7 pagesBA SummarySagar DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Business Requirements Presentation To : Project NameDocument14 pagesBusiness Requirements Presentation To : Project NameChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Fashioninc Hompage Design BRDDocument8 pagesFashioninc Hompage Design BRDVikram hostNo ratings yet
- Business Analyst Online TrainingDocument2 pagesBusiness Analyst Online TrainingTanishsadan ANo ratings yet
- C3 - Plan Business Analysis ApproachDocument5 pagesC3 - Plan Business Analysis ApproachTuyếtNguyễnThịÁnhNo ratings yet
- CBAPBusinessAnalystGlossary PDFDocument16 pagesCBAPBusinessAnalystGlossary PDFismed iqbalNo ratings yet
- Business Analyst Change Management in North NJ Resume Lana GropenDocument3 pagesBusiness Analyst Change Management in North NJ Resume Lana GropenLanaGropenNo ratings yet
- Babok 3.0 Tasks & Their Inputs and OutputsDocument6 pagesBabok 3.0 Tasks & Their Inputs and OutputsSangeetha Bhat100% (2)
- Certified Business Analyst Foundation Level Syllabus: International Business Analysis Qualifications BoardDocument104 pagesCertified Business Analyst Foundation Level Syllabus: International Business Analysis Qualifications BoardRishabh JhawarNo ratings yet
- Requirements Definition TemplateDocument8 pagesRequirements Definition TemplateJay PatelNo ratings yet
- WP How To Use The Dgi Data Governance FrameworkDocument17 pagesWP How To Use The Dgi Data Governance Frameworkvala2012100% (1)
- Business Analysis Professional - Apex Global - DemoDocument33 pagesBusiness Analysis Professional - Apex Global - DemoApex GlobalNo ratings yet
- (WEEK 2) Process Identification 1Document36 pages(WEEK 2) Process Identification 1AVICENA NAUFALDONo ratings yet
- Introduction to Business Analysis Techniques and Knowledge AreasDocument12 pagesIntroduction to Business Analysis Techniques and Knowledge AreasShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Reduce Customer Wait Times Business RequirementsDocument17 pagesReduce Customer Wait Times Business RequirementsAsfdsaFdsafdsaNo ratings yet
- Applicant(s) Declaration (PTS) - Step 2Document1 pageApplicant(s) Declaration (PTS) - Step 2Saurabh MehtaNo ratings yet
- KA4 - Strategy AnalysisDocument2 pagesKA4 - Strategy AnalysisSaurabh MehtaNo ratings yet
- KA5 - Req Analysis & Design DefDocument2 pagesKA5 - Req Analysis & Design DefSaurabh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Analyze Solution Performance and ValueDocument2 pagesAnalyze Solution Performance and ValueSaurabh MehtaNo ratings yet
- KA3 - Req Life CycleDocument2 pagesKA3 - Req Life CycleSaurabh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Practical Data Science With PythonDocument922 pagesPractical Data Science With PythonSaurabh Mehta100% (20)
- TRAINING MATERIAL OPTIONS TRADINGDocument31 pagesTRAINING MATERIAL OPTIONS TRADINGSaurabh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Your Guide for Options Trading in a NutshellDocument12 pagesYour Guide for Options Trading in a NutshellSaurabh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Quality ImplementationDocument454 pagesOracle Quality ImplementationZubair KhanNo ratings yet
- Physical Asset Management HandbookDocument441 pagesPhysical Asset Management HandbookFachransjah AliunirNo ratings yet
- Plantweb Optics Data Lake: Transform Data Into Intelligent Business DecisionsDocument7 pagesPlantweb Optics Data Lake: Transform Data Into Intelligent Business DecisionskEWQ 865kNo ratings yet
- Effects of Standard Costing On The Profitability of Manufacturing CompaniesDocument17 pagesEffects of Standard Costing On The Profitability of Manufacturing CompaniesjobademuNo ratings yet
- Koppers 1996Document14 pagesKoppers 1996Gabriel De PaulaNo ratings yet
- TAIL Project NewsletterDocument9 pagesTAIL Project NewsletterAbdul R. MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Title Defense Format (Updated) - 022313Document13 pagesTitle Defense Format (Updated) - 022313Mary Lyn RaseNo ratings yet
- The Visual Semiotics of Tarot Images A SDocument22 pagesThe Visual Semiotics of Tarot Images A SOlga VereliNo ratings yet
- Semester Plan Grade 12 (Action Pack)Document10 pagesSemester Plan Grade 12 (Action Pack)Sara KhatabNo ratings yet
- Historian ConceptsDocument46 pagesHistorian ConceptsDinh VuNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument10 pagesProposalanon_218391549No ratings yet
- NCM 102 M5&6 StudentDocument4 pagesNCM 102 M5&6 StudentkasjdkasNo ratings yet
- CHN Defense (NCP)Document1 pageCHN Defense (NCP)Kyla Mae JumaritoNo ratings yet
- Freshmind The Subtle of AdventureDocument8 pagesFreshmind The Subtle of AdventureBrighty ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Information Ethics in The Twenty First CenturyDocument10 pagesInformation Ethics in The Twenty First Centurysanna097No ratings yet
- Brochure (15)Document36 pagesBrochure (15)PRASANT KUMARNo ratings yet
- Barquilla Patrice R. MIL MODULE 1Document5 pagesBarquilla Patrice R. MIL MODULE 1Johnrick RabaraNo ratings yet
- d64974gc10 Odi 11g Integration and Administration Ag 160425204507Document311 pagesd64974gc10 Odi 11g Integration and Administration Ag 160425204507Prudvi Kumar MukkaNo ratings yet
- The Venus Connection - Sanat KumaraDocument11 pagesThe Venus Connection - Sanat KumaraGoddessLight50% (4)
- Definition Of: Management Information Systems (MIS)Document15 pagesDefinition Of: Management Information Systems (MIS)Mega_ImranNo ratings yet
- 09 Electrotechnics: (Working Title)Document52 pages09 Electrotechnics: (Working Title)Geoffrey AlleyneNo ratings yet
- Block-1 MCO-6 Unit-3 PDFDocument32 pagesBlock-1 MCO-6 Unit-3 PDFMuskan SharmaNo ratings yet
- The NCMB Data Privacy ManualDocument19 pagesThe NCMB Data Privacy ManualDOLE Region 6No ratings yet
- Why McDonalds Is Successful in IndiaDocument40 pagesWhy McDonalds Is Successful in Indiaashbay100% (1)
- Nature and Elements of Communication LessonDocument82 pagesNature and Elements of Communication LessonMarissa Urnos100% (6)
- SHS TVL Media Information LirteracyDocument11 pagesSHS TVL Media Information LirteracyJerrylyn ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics TheoriesDocument1 pageNursing Informatics Theoriesallfonso100% (1)
- Japan Test ReportDocument35 pagesJapan Test ReportAlexandra PeltierNo ratings yet
- Protocol Specification For Interfacing To Data Communication NetworksDocument159 pagesProtocol Specification For Interfacing To Data Communication NetworksmadhuhanuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1--Professional Communication in a Digital, Social, Mobile World E 2Document31 pagesChapter 1--Professional Communication in a Digital, Social, Mobile World E 2abuazzoumNo ratings yet