0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views7 pagesParallelogram Law of Vectors
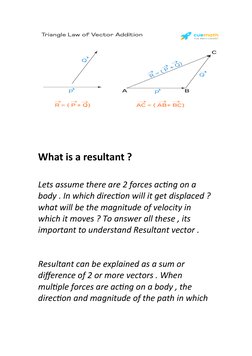
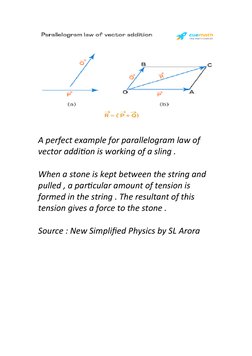
The document discusses vectors and their properties. It defines vectors, unit vectors, position vectors, displacement vectors, and how to calculate the magnitude of a vector. It also explains the triangle law of vector addition and parallelogram law of vector addition. The parallelogram law states that if two vectors are represented by the sides of a parallelogram, their resultant is represented by the diagonal of the parallelogram.
Uploaded by
deezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views7 pagesParallelogram Law of Vectors
The document discusses vectors and their properties. It defines vectors, unit vectors, position vectors, displacement vectors, and how to calculate the magnitude of a vector. It also explains the triangle law of vector addition and parallelogram law of vector addition. The parallelogram law states that if two vectors are represented by the sides of a parallelogram, their resultant is represented by the diagonal of the parallelogram.
Uploaded by
deezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd