Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Purpose of Drainge
Uploaded by
Nwachukwu Umeh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageWaste water contains harmful substances and must be safely drained and treated before discharge. Legal regulations require contaminated waste water not enter waterways and connect to sewage systems if available. Drainage systems must collect and drain waste, resist approved waste, prevent user contact, and rapidly drain waste. Certain substances that could damage systems or not be treated, like gases, toxics, and fats, must be retained and drained separately.
Original Description:
Original Title
purpose of drainge
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWaste water contains harmful substances and must be safely drained and treated before discharge. Legal regulations require contaminated waste water not enter waterways and connect to sewage systems if available. Drainage systems must collect and drain waste, resist approved waste, prevent user contact, and rapidly drain waste. Certain substances that could damage systems or not be treated, like gases, toxics, and fats, must be retained and drained separately.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pagePurpose of Drainge
Uploaded by
Nwachukwu UmehWaste water contains harmful substances and must be safely drained and treated before discharge. Legal regulations require contaminated waste water not enter waterways and connect to sewage systems if available. Drainage systems must collect and drain waste, resist approved waste, prevent user contact, and rapidly drain waste. Certain substances that could damage systems or not be treated, like gases, toxics, and fats, must be retained and drained separately.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
5 The purpose of drainage 5.
1 The safe drainage of waste water
5 The purpose of drainage
5.1 The safe drainage of waste water
Waste water contains substances that can be harmful to people and the environment. For example,
infectious diseases can be transmitted by human excretions from toilet facilities. For this reason, waste water
must be safely drained in a hygienic and ecological manner and treated before it is discharged into lakes or
rivers.
5.2 Legal principles and requirements
The requirement to drain waste water safely, hygienically and ecologically has been adopted by the legal
regulations of many countries. Even though the legal regulations may differ in terms of their details, they
share the same principles for safe waste water drainage:
• contaminated waste water must not be discharged or allowed to seep into waterways.
• if there is a public sewage system, waste water must be discharged into the public sewage system.
The following drainage system requirements arise from the legal principles:
• suitable for collecting and draining waste water
• resistant to approved types of waste water
• prevents contact between the user of the drainage system and the waste water
• fast and direct draining of the waste water into the sewage system
5.3 Prohibited substances for drainage systems
In order to comply with the legal principles and requirements, substances which cause the drainage system
to malfunction or which cannot be removed from the waste water through conventional treatment processes
must not be discharged into drainage systems. Such substances must be retained at the source and drained
or disposed of appropriately. These include:
• gases and vapours
• toxic, flammable, explosive and radioactive substances
• malodorous substances
• discharges from cesspits, manure pits and feed silos
• substances that can cause the sewage system to malfunction such as sand, scree, debris, ash, slag
• viscous and muddy substances such as bitumen, limescale, cement slurry
• oils, lubricants, gasoline, benzene, petroleum ether, kerosene, solvents, halogenated hydrocarbons, etc.
• acids and alkalis in harmful concentrations
• waste water above 60 °C which, after mixing, raises the temperature of the waste water in the sewage
system to over 40 °C.
The use of rubbish and kitchen waste grinders is not recommended in drainage systems and can even be
prohibited by country-specific regulations. Substances and liquids from these types of grinders can lead to
increased deposits and subsequently block the drainage system.
14 5037289099 ©
int.en 21169-19/358
You might also like
- 1968 Plymouth Service ManualDocument960 pages1968 Plymouth Service ManualСергей Филиппов100% (1)
- Clinical Data Management, IInd EditionDocument18 pagesClinical Data Management, IInd EditionThomas Eipe100% (1)
- Unit 2Document95 pagesUnit 2rangaNo ratings yet
- Sludge Treatment SYstem-1Document21 pagesSludge Treatment SYstem-1SanaNo ratings yet
- Building Materials Lab ManualDocument21 pagesBuilding Materials Lab Manualapi-348488925100% (3)
- Treatment of Water: 4 Process Will Be Used To Treat Waste Water in Steel IndustryDocument19 pagesTreatment of Water: 4 Process Will Be Used To Treat Waste Water in Steel IndustryReshab SahooNo ratings yet
- State MachineDocument8 pagesState MachineUriel Cruz MedelNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 4-WASTEWATER - 1.pptx Filename - UTF-8''CHAPTER 4-WASTEWATER 1Document117 pagesCHAPTER - 4-WASTEWATER - 1.pptx Filename - UTF-8''CHAPTER 4-WASTEWATER 1Muhammad Fazlan Aliff100% (1)
- Fluid and Electrolyte Therapy, Calculation of Fluids and Its AdministrationDocument11 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Therapy, Calculation of Fluids and Its AdministrationAnusha Verghese100% (2)
- Water Treatment System-Iit NoteDocument14 pagesWater Treatment System-Iit NoteBhaswar MajumderNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : KG Given To HelperDocument4 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : KG Given To HelperCatherine AbabonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4A Characteristics and Systems Characteristics and SystemsDocument31 pagesChapter 4A Characteristics and Systems Characteristics and SystemsnazatussimazNo ratings yet
- Filters and Filtration HydraulicsDocument18 pagesFilters and Filtration HydraulicsRej Idio OcampoNo ratings yet
- Science 10 q3 Week 4 Lessons 8-11Document33 pagesScience 10 q3 Week 4 Lessons 8-11JennyFloresNicolas100% (2)
- Sewage and Effluent Spillages Management AwarenessDocument10 pagesSewage and Effluent Spillages Management AwarenessjonathanelaineNo ratings yet
- Stream Filters For Industrial UseDocument8 pagesStream Filters For Industrial UseVasudev Water SolutionNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment: PDF Generated At: Fri, 03 Jun 2011 10:58:38 UTCDocument181 pagesWastewater Treatment: PDF Generated At: Fri, 03 Jun 2011 10:58:38 UTCJo Wiart100% (4)
- Clean Water Act - 1 Hour PresentationDocument36 pagesClean Water Act - 1 Hour PresentationPatrick GoNo ratings yet
- Sludge TreatmentDocument9 pagesSludge Treatmentrollrams100% (1)
- 3.1.WasteWater Treatment Procedure - FLOCDocument4 pages3.1.WasteWater Treatment Procedure - FLOChaseeb100% (1)
- Internal Cleaning of Piping System PDFDocument6 pagesInternal Cleaning of Piping System PDFNight WatchNo ratings yet
- Natural and Built Environment PDFDocument16 pagesNatural and Built Environment PDFBrylle De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document92 pagesUnit 4Deepak Narayan PaithankarNo ratings yet
- 3 Sewage WW & Flow Diagram Lec3 4 5Document123 pages3 Sewage WW & Flow Diagram Lec3 4 5Aslam LaghariNo ratings yet
- Module 1 MIWDocument55 pagesModule 1 MIWDivyashree BMNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document92 pagesUnit 4Deepak Narayan PaithankarNo ratings yet
- Systems of Sewage DisposalDocument21 pagesSystems of Sewage DisposalathirarejizachariahNo ratings yet
- Hose Assembly Cleanliness PDFDocument7 pagesHose Assembly Cleanliness PDFGokulNo ratings yet
- Treatment Processes: ScreensDocument5 pagesTreatment Processes: ScreensSajil KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Shaheen Hyd2Document41 pagesShaheen Hyd2Shaheen Al YafayNo ratings yet
- Sludge Dewatering Technologies PDFDocument9 pagesSludge Dewatering Technologies PDFTahaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Sewage Collection and CinveyanceDocument33 pagesTopic 5 Sewage Collection and CinveyanceMark NalNo ratings yet
- Liquid Waste Management IiDocument66 pagesLiquid Waste Management Iirodgers omondiNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution ManagementDocument18 pagesWater Pollution ManagementAhsan NawazNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Wastewater: Environmental Engineering Unit-IDocument124 pagesCharacteristics of Wastewater: Environmental Engineering Unit-IDragos NojeaNo ratings yet
- EE-II - Unit I - Planning of Sewerage System-Lecture NotesDocument74 pagesEE-II - Unit I - Planning of Sewerage System-Lecture NotesNaveen Kumar soniNo ratings yet
- Why Treat Brine Waste Prior To DisposalDocument2 pagesWhy Treat Brine Waste Prior To DisposalStellaNo ratings yet
- Filtering Samples Online AnalyzersDocument5 pagesFiltering Samples Online AnalyzersMenwer AttarakihNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Sanitary SystemDocument36 pagesGroup 3 - Sanitary SystemAyesa AgravanteNo ratings yet
- The Arsenic Rule: Water Treatment Plant Residuals: Issues in Management and DisposalDocument56 pagesThe Arsenic Rule: Water Treatment Plant Residuals: Issues in Management and DisposalIgnacioNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment and Supply Presentation Group 1 WeekendDocument37 pagesWater Treatment and Supply Presentation Group 1 WeekendetrimageoffreyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document12 pagesLecture 1Hamza RahimNo ratings yet
- Philippine Clean Water ACT OF 2004Document36 pagesPhilippine Clean Water ACT OF 2004Stephanie CanibanNo ratings yet
- How To Flush Gearboxes and Bearing Housings: Noria CorporationDocument6 pagesHow To Flush Gearboxes and Bearing Housings: Noria CorporationiagoramonNo ratings yet
- EE2 Notes PDFDocument93 pagesEE2 Notes PDFPrasad ShelarNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities Module 2 Lesson 5Document4 pagesBuilding Utilities Module 2 Lesson 5Bryan ManlapigNo ratings yet
- Secondary Wastewater TreatmentDocument18 pagesSecondary Wastewater TreatmentSumaiya Rashid100% (1)
- Sewage and SanitationDocument27 pagesSewage and SanitationVaibhav KhatingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document128 pagesLecture 11Bilal NisarNo ratings yet
- Sewerage System Enviornmental EngineeringDocument32 pagesSewerage System Enviornmental EngineeringShivam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Sewerage SystemDocument57 pagesChapter 3 Sewerage SystemYahye AbdukadirNo ratings yet
- Env1 Units4Document13 pagesEnv1 Units4YADVENDRA SINGH TIWARINo ratings yet
- Project Report 2019SATYWANDocument43 pagesProject Report 2019SATYWANYOGENDRANo ratings yet
- Sewer AppurtanenceDocument72 pagesSewer Appurtanencekarthika100% (1)
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument7 pagesWaste Water TreatmentMuhammad SyafiqNo ratings yet
- DE Report Sem 6Document30 pagesDE Report Sem 6Parth PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument31 pagesChapter 1 Introductionshiksha gauliNo ratings yet
- URA-2002-2021-General Guidelines For Waste Water DisposalDocument22 pagesURA-2002-2021-General Guidelines For Waste Water DisposalprashantshirkeNo ratings yet
- Module - 2 - ContinuedDocument19 pagesModule - 2 - ContinuedRohieth Raj SNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Cleaning Flushing and Passivation of Chilled Water PipingDocument14 pagesMethod Statement For Cleaning Flushing and Passivation of Chilled Water PipingTawrez KhatibNo ratings yet
- 15CE405 Sanitary Engineering and Design-Unit 1 - Part 2Document21 pages15CE405 Sanitary Engineering and Design-Unit 1 - Part 2gfgfghNo ratings yet
- Session 07 Sewage Treatment (2021-22) PDFDocument42 pagesSession 07 Sewage Treatment (2021-22) PDFLeslie LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9 (PPT WaterDocument17 pagesChapter - 9 (PPT Waterhabib panaNo ratings yet
- Et P Installation Write UpDocument11 pagesEt P Installation Write Upshivangi saxenaNo ratings yet
- SeweargeDocument32 pagesSeweargeSameer TalwarNo ratings yet
- Advantages:: The Discharge of Untreated or Partially Treated Wastewater Into The Environment Results in TheDocument5 pagesAdvantages:: The Discharge of Untreated or Partially Treated Wastewater Into The Environment Results in ThePrashant ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Plant Design: Pollution ControlDocument37 pagesChemical Engineering Plant Design: Pollution ControlMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Mo Mbimmai International in Bim Management 2Document29 pagesMo Mbimmai International in Bim Management 2Nwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Geberit Solvent Fields of ApplicationDocument3 pagesGeberit Solvent Fields of ApplicationNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- System With Geberit HDPE Sovent and Geberit SuperTubeDocument2 pagesSystem With Geberit HDPE Sovent and Geberit SuperTubeNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Expansion Socket DesignDocument12 pagesExpansion Socket DesignNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- COMMISSIONINGDocument2 pagesCOMMISSIONINGNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- PlanningDocument3 pagesPlanningNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Mixed Installation of GeberitDocument3 pagesMixed Installation of GeberitNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Waste Water PrefabricationDocument5 pagesWaste Water PrefabricationNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Top 15 Plumber Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesTop 15 Plumber Interview QuestionsNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Laying The Branch Discharge Pipe in The Ceiling, Single StackDocument2 pagesLaying The Branch Discharge Pipe in The Ceiling, Single StackNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Sewage System ExplainedDocument1 pageSewage System ExplainedNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Types of Waste WaterDocument1 pageTypes of Waste WaterNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Direction Change in Vertical Pipe SectionsDocument2 pagesDirection Change in Vertical Pipe SectionsNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Systems For Preventing BackpressureDocument2 pagesSystems For Preventing BackpressureNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Outlets 45L 60LDocument1 pageOutlets 45L 60LNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Building DrainageDocument1 pageBuilding DrainageNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- 1.1 System Overview 1.2 FunctionDocument8 pages1.1 System Overview 1.2 FunctionNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
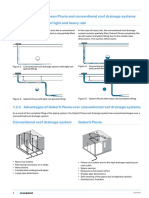
- 1.2.2 Difference Between Pluvia and Conventional Roof Drainage Systems Behaviour in The Case of Light and Heavy RainDocument1 page1.2.2 Difference Between Pluvia and Conventional Roof Drainage Systems Behaviour in The Case of Light and Heavy RainNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- GW04 20 04 02 1.200ml Automatic Soap DispenserDocument2 pagesGW04 20 04 02 1.200ml Automatic Soap DispenserNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Touchless Soap Dispenser Knud Holscher: CollectionDocument1 pageTouchless Soap Dispenser Knud Holscher: CollectionNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Pluvia Roof OutletsDocument1 pagePluvia Roof OutletsNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Liquid Soap Dispensers: Surface AutomaticDocument2 pagesLiquid Soap Dispensers: Surface AutomaticNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- WICHTECH (E) Gerard Wichtech Sales Brochure 2015 ( - GenuineGerard) PDFDocument28 pagesWICHTECH (E) Gerard Wichtech Sales Brochure 2015 ( - GenuineGerard) PDFNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Setting Up and Running A School Library: Peace Corps Information Collection and Exchange Publication No. ED204Document146 pagesSetting Up and Running A School Library: Peace Corps Information Collection and Exchange Publication No. ED204Nwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Gerard Hotel Collection BrochureDocument4 pagesGerard Hotel Collection BrochureNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Wichflow Smarthome CatalogDocument22 pagesWichflow Smarthome CatalogNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- (P) Electric Waterheaters - WICHTECHDocument5 pages(P) Electric Waterheaters - WICHTECHNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- (E) FlowPlumb Wichtech Sales BrochureDocument17 pages(E) FlowPlumb Wichtech Sales BrochureNwachukwu UmehNo ratings yet
- Respondent MemorialDocument22 pagesRespondent MemorialRajat KaushikNo ratings yet
- 7 - Modified Slenderness Ratio For Built-Up MembersDocument13 pages7 - Modified Slenderness Ratio For Built-Up Membersخوێندن لە ئەوروپاNo ratings yet
- Ug Cogtr Tran 10.2Document413 pagesUg Cogtr Tran 10.2Ashwin SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Permanent Magnet DC MotorDocument7 pagesPermanent Magnet DC MotorJesse Jones Seraspe100% (1)
- 4 Curriculum StructureDocument19 pages4 Curriculum StructurealiyazahirNo ratings yet
- MessageDocument5 pagesMessageธีรพิชญ์ ศรีสมวงศ์No ratings yet
- AIC Plans - All Key Characters and Responsibility Apr. 23Document26 pagesAIC Plans - All Key Characters and Responsibility Apr. 23Tiran AsawrusNo ratings yet
- Full CCNP Service Provider Routing LabDocument14 pagesFull CCNP Service Provider Routing LabMksNo ratings yet
- ZXCTN Seamless MPLS (BGP LU) Principles and Applications - R1.1Document24 pagesZXCTN Seamless MPLS (BGP LU) Principles and Applications - R1.1kyi lwinNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xi Chapter 01 Sets Practice Paper 01Document3 pagesMaths Class Xi Chapter 01 Sets Practice Paper 01Ayush Abhinandan RathNo ratings yet
- Kohat - WikipediaDocument15 pagesKohat - Wikipediazarbaz khan Afridi khanNo ratings yet
- Fuel Filtration Systems: Products and Custom SolutionsDocument28 pagesFuel Filtration Systems: Products and Custom Solutionsphilip connieNo ratings yet
- The Negative Impact of Cigarette Smoking: Mapeh (Health) 8-Quarter 4Document60 pagesThe Negative Impact of Cigarette Smoking: Mapeh (Health) 8-Quarter 4JOHN FRITS GERARD MOMBAYNo ratings yet
- 11 Chapter 3Document72 pages11 Chapter 3Swati SagvekarNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report in The 1st HRPTA Meeting 2023-2024Document2 pagesNarrative Report in The 1st HRPTA Meeting 2023-2024Mervin BauyaNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Indowebster.com) - RemoteControl Connections PDFDocument18 pages(WWW - Indowebster.com) - RemoteControl Connections PDFmas-jirunNo ratings yet
- CholinesteraseDocument2 pagesCholinesteraseGeorge-Alexandru MarinescuNo ratings yet
- Change Pointer in The Material Master in SAP ECCDocument1 pageChange Pointer in The Material Master in SAP ECCTaufik KadarusmanNo ratings yet
- Arlorio 05 Phenolic Antioxidantsin Cacao Hulls PhysiologyDocument6 pagesArlorio 05 Phenolic Antioxidantsin Cacao Hulls Physiologydjguevara1No ratings yet
- Bullying THESISDocument19 pagesBullying THESISlenard CasimNo ratings yet
- English 1-2-1Document7 pagesEnglish 1-2-1Arlene Suan Paña SevensixfourzeroNo ratings yet
- Accounts Receivable and Inventory ManagementDocument2 pagesAccounts Receivable and Inventory ManagementEden EspirituNo ratings yet