Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12.4.practical Activity
Uploaded by
ALPHONCE ODHIAMBO0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesOriginal Title
12.4.PRACTICAL ACTIVITY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pages12.4.practical Activity
Uploaded by
ALPHONCE ODHIAMBOCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
PRACTICAL ACTIVITIES
[REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS & ANIMALS]
Examining the stages of mitosis
About 2 mm of a root tip of onion bulb is cut off and placed on a microscope slide.
A stain e.g. aceto-orcein is added and the root tip macerated using a scapel.
A cover slip is added and observations made.
Different stages of mitosis can be observed.
Examining the stages of meiosis
An unopened bud of Tradescantia is obtained
The anther is removed and placed on a microscope slide.
A few drops of hydrochloric acid and acetic-orcein stain are added.
A cover slip is placed on the anther.
Pressing the cover slip gives a thin squash, which is observed under the microscope.
Different stages of meiosis are observed.
To observe the structure of Rhizopus
Rhizopus grow on moist bread left under suitable temperature
A piece of moist bread is placed on a petri-dish or enclosed in a plastic bag and observe
daily for four days.
Under a low power microscope the sporangia and stolons can be observed.
To examine spores on sori of ferns
Obtain the fern plant.
Detach a frond from the plant and observe the under-side using a hand lens to see the
raised brown patches - the sori.
Open up the sorus to observe the sporangia.
Powered by: Www.Atikaschool.Org
To examine spores on sori of ferns
Obtain the fern plant.
Detach a frond from the plant and observe the under-side using a hand lens to see the
raised brown patches - the sori.
Open up the sorus to observe the sporangia.
Examine insect and wind pollinated flowers
Obtain insect pollinated flowers e.g. crotalaria, hibiscus/Ipomea, Solanum, incunum.
Note the scent, colour and nectar guides.
A description of the calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium is made.
Obtain a wmd pollinated flower e.g.,' maize, star-grass, sugar-cane, Kikuyu grass.
Observe the glumes, spikes and spikelet.
Examine a single floret, and identify the androecium and gynoecium.
Classifying fruits
Obtain different fruits - oranges, mangoes, maize, castor oil, bean pod, black jack .
Observe the fruits, classify them into succulent, dry-dehiscent or indehiscent.
Dissection of Fruits
Obtain an orange and a mango fruit.
Make a transverse section.
Observe the cut surface and draw and label the parts.
Note that the fruit is differentiated into epicarp, mesocarp and endocarp.
Obtain a pod of a legume.
Open up the pod and observe the exposed surface.
Draw and label the parts.
Note that the fruit wall is not differentiated.
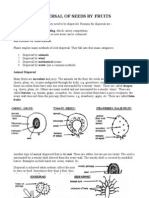
Dispersal of fruits and seeds
Obtain animal dispersal fruits, like oranges, tomatoes, black jack, sodom apple.
Identify the way by which each is adapted to dispersal by animals.
Obtain wind dispersed fruit/seed e.g. Nandi flame, Jacaranda Sonchus, cotton seed,
Tecoma.
Sourced From: http://www.atikaschool.or g/kcse-biology-notes
You might also like
- Ii Puc Lab ManualDocument73 pagesIi Puc Lab ManualFrag GamingNo ratings yet
- Botany Act12Document4 pagesBotany Act12Krianne Chris DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Plants Pollen2Document15 pagesPlants Pollen2api-294162496No ratings yet
- Class 9 Bio PracticalsDocument23 pagesClass 9 Bio PracticalsRaj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Fruit and Seed Dissection LABDocument3 pagesFruit and Seed Dissection LABCatherine JacksonNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Bio Exp 6Document14 pagesLab Report Bio Exp 6SyamirConan50% (2)
- Plantbreedingpractical PDFDocument25 pagesPlantbreedingpractical PDFAyehu ChekolNo ratings yet
- INVESTIGATORY Project - Dispersal of Seeds 1 (Final)Document27 pagesINVESTIGATORY Project - Dispersal of Seeds 1 (Final)Uma100% (3)
- Plant Male and Female GametophyteDocument1 pagePlant Male and Female GametophyteQwerty UiopNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 Angiosperm Plant BodyDocument13 pagesActivity 7 Angiosperm Plant BodyHerlyn SabulaanNo ratings yet
- SHORT NOTES Chapter 1Document4 pagesSHORT NOTES Chapter 1barikbiswaranjan240No ratings yet
- Fruits and Seeds ImradDocument8 pagesFruits and Seeds ImradJoses CalindasNo ratings yet
- Collecting InsectsDocument11 pagesCollecting InsectsAlma AlmaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument8 pagesReproduction in PlantsRenuNo ratings yet
- Daryl GuinayenDocument9 pagesDaryl GuinayenEmmanuel GallidoNo ratings yet
- Viticulture ManualDocument66 pagesViticulture Manualpanaglaw100% (2)
- Biology Investigatory Project: TOPIC: Study of Pollination in Sunflower and LegumeDocument15 pagesBiology Investigatory Project: TOPIC: Study of Pollination in Sunflower and Legumecharusrirajkumar27No ratings yet
- Seeds and Seeds Class 5 Notes CBSE EVS Chapter 5 (PDF)Document6 pagesSeeds and Seeds Class 5 Notes CBSE EVS Chapter 5 (PDF)krishna GNo ratings yet
- Dispersal of Seeds by FruitsDocument6 pagesDispersal of Seeds by FruitsAnil PantNo ratings yet
- Natsci002 End Term A.Y. 2019 - 2020 Ma. Victoria V. Manzan, RN, MN Florence Joy F. Octaviano, RN, ManDocument6 pagesNatsci002 End Term A.Y. 2019 - 2020 Ma. Victoria V. Manzan, RN, MN Florence Joy F. Octaviano, RN, ManJanice Gentile AlisonNo ratings yet
- Natsci002 End Term A.Y. 2019 - 2020 Ma. Victoria V. Manzan, RN, MN Florence Joy F. Octaviano, RN, ManDocument6 pagesNatsci002 End Term A.Y. 2019 - 2020 Ma. Victoria V. Manzan, RN, MN Florence Joy F. Octaviano, RN, ManJanice Gentile AlisonNo ratings yet
- Lab Report BiologyDocument8 pagesLab Report BiologyFatin NabilahNo ratings yet
- Asexual Propagation by Miming Momaming PDFDocument6 pagesAsexual Propagation by Miming Momaming PDFLebron DoggiNo ratings yet
- Methods of Plant Propagation: Sexually and Asexually Propagating PlantsDocument30 pagesMethods of Plant Propagation: Sexually and Asexually Propagating PlantsCarrylle Janne NovalNo ratings yet
- Plant Dissection LabDocument9 pagesPlant Dissection Labmischa.noelleNo ratings yet
- Experiment To Observe Temporary Mount of A Leaf Peel To Show StomataDocument3 pagesExperiment To Observe Temporary Mount of A Leaf Peel To Show StomataEliseo Pamandanan0% (1)
- Dispersal of Seeds-1Document10 pagesDispersal of Seeds-1samuelsimte024No ratings yet
- Plant Pathology Fst3Document19 pagesPlant Pathology Fst3Alishba SherazNo ratings yet
- Seed Report OutlineDocument2 pagesSeed Report OutlineAshlee JornadalNo ratings yet
- Organoleptic Evaluation of The Different Parts of Plant (Flower, Fruits, and Seeds)Document13 pagesOrganoleptic Evaluation of The Different Parts of Plant (Flower, Fruits, and Seeds)Joanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerNo ratings yet
- Vegetative PropogationDocument4 pagesVegetative PropogationkzrdurNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project: Podar International SchoolDocument11 pagesBiology Investigatory Project: Podar International SchoolJayshree nemadeNo ratings yet
- Growing Plants Without SeedsDocument9 pagesGrowing Plants Without Seedschristian capunongNo ratings yet
- Im Toolbox Invertebrates Collecting Micro Land Snails in Terrestrial and Freshwater HabitatsDocument5 pagesIm Toolbox Invertebrates Collecting Micro Land Snails in Terrestrial and Freshwater HabitatsVladut BratfaleanNo ratings yet
- Dispersal of Seed by Various Agencies: Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument12 pagesDispersal of Seed by Various Agencies: Biology Investigatory Projectalan Chacko100% (5)
- Chapter 3 STD 10Document19 pagesChapter 3 STD 10SHRESTH FFNo ratings yet
- Wa0016.Document7 pagesWa0016.HamzaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Various PlantsDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of Various PlantsSakshi TewariNo ratings yet
- BryophytesDocument5 pagesBryophytesGilbert DullerNo ratings yet
- 1.reproduction in Plant PDFDocument54 pages1.reproduction in Plant PDFAnkit JyaniNo ratings yet
- Garden Seed Handbook Part 31Document5 pagesGarden Seed Handbook Part 31gezarolNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 - SSES - Science - Q2 - Wk5 - GLAKDocument20 pagesGrade 6 - SSES - Science - Q2 - Wk5 - GLAKMelanie TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Butterfly BlitzDocument8 pagesButterfly Blitzapi-515711176No ratings yet
- Objectives 1,2Document5 pagesObjectives 1,2Gaurav RajNo ratings yet
- Botany Lec 1Document48 pagesBotany Lec 1Ordinary GuitaristNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mushroom Cultivation: Presented by Shipra PariharDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Mushroom Cultivation: Presented by Shipra PariharSimran KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Bio 3Document4 pagesBio 3sumitverma78929.svNo ratings yet
- Biology - Lab Report 7 and 8Document6 pagesBiology - Lab Report 7 and 8Unnati NihalaniNo ratings yet
- Growing Cherry Tree Plants From SeedDocument26 pagesGrowing Cherry Tree Plants From Seednschober3No ratings yet
- BIO Notesanual - TeacherDocument38 pagesBIO Notesanual - TeacherredegeneratedNo ratings yet
- Xii Biology Practical 2022-23 5 January 23Document35 pagesXii Biology Practical 2022-23 5 January 23Swarup PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Aim 2Document2 pagesAim 2Dhruv PaulNo ratings yet
- Vanilla BookDocument34 pagesVanilla Bookpvdas100% (2)
- Bio Practical Notes XiiDocument10 pagesBio Practical Notes XiimrinalinimalavigaNo ratings yet
- Term I Practical Notes 2021-2022Document36 pagesTerm I Practical Notes 2021-2022ABHISEKNo ratings yet
- Bio2206 BIO TECH (Sample Collection)Document36 pagesBio2206 BIO TECH (Sample Collection)Ibrahim MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument7 pagesReproduction in PlantsrupeshNo ratings yet
- Sexual Propagation in Plants: Most Higher Plants Start Their Life As Vegetative Prop UnitDocument41 pagesSexual Propagation in Plants: Most Higher Plants Start Their Life As Vegetative Prop UnitDoni DarimastNo ratings yet
- Xi Biology PracticalDocument79 pagesXi Biology PracticalBinod ThapaNo ratings yet
- 14.1.1.introduction To Measurement of GrowthDocument11 pages14.1.1.introduction To Measurement of GrowthALPHONCE ODHIAMBONo ratings yet
- 12.4.role of A PlacentaDocument3 pages12.4.role of A PlacentaALPHONCE ODHIAMBONo ratings yet
- 11.3.energy Flow in An EcosystemDocument10 pages11.3.energy Flow in An EcosystemALPHONCE ODHIAMBONo ratings yet
- 11.5.ecology Practical ActivitiesDocument3 pages11.5.ecology Practical ActivitiesALPHONCE ODHIAMBONo ratings yet
- Tending OperationsDocument26 pagesTending Operationstacamp da100% (2)
- 9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument10 pages9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersMohammad Shahidullah ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Seeds of Woody Plants in The United StatesDocument916 pagesSeeds of Woody Plants in The United StatesГеоргийАкулининNo ratings yet
- Aisole Victor ReportDocument69 pagesAisole Victor ReportOlabiwonnu Temitope100% (1)
- Tissue CultureDocument29 pagesTissue CultureWiardah Kholijah MatondangNo ratings yet
- Target: Pre-Medical-2023/neet/nurture/phase-I/internal Test-02/19.05.2021Document4 pagesTarget: Pre-Medical-2023/neet/nurture/phase-I/internal Test-02/19.05.2021Ananya BalajiNo ratings yet
- Plant Identification and Sources of LiteratureDocument8 pagesPlant Identification and Sources of LiteraturevincentotienoNo ratings yet
- Lec19 PDFDocument11 pagesLec19 PDFsyakiraNo ratings yet
- QC ChecklistDocument2 pagesQC ChecklistTonny FebryanNo ratings yet
- Indoor PlantsDocument16 pagesIndoor PlantsBae ThorNo ratings yet
- FlowersDocument12 pagesFlowersAMITANSHUNo ratings yet
- Plant PropagationDocument36 pagesPlant PropagationDeepa ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 11th Bio Botany Book Back 1 Mark Questions and Answers Mr. P. Nanthish Kumar EM-1Document7 pages11th Bio Botany Book Back 1 Mark Questions and Answers Mr. P. Nanthish Kumar EM-1r shivajiNo ratings yet
- One Liner Question Bank For General AgricultureDocument212 pagesOne Liner Question Bank For General AgricultureRuchismita PandaNo ratings yet
- 1.the Living WorldDocument16 pages1.the Living WorldMainak ChandaNo ratings yet
- Pollinator PreferencesDocument4 pagesPollinator Preferencesapi-510366840No ratings yet
- User Guide To Collection 6 MODIS Land Cover (MCD12Q1 and MCD12C1) ProductDocument18 pagesUser Guide To Collection 6 MODIS Land Cover (MCD12Q1 and MCD12C1) ProductjlomeNo ratings yet
- PT Q2 Grade 5Document9 pagesPT Q2 Grade 5Janice Sumaylo BaluranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29 (+28) : Resource Acquisition, Nutrition and Transport in Vascular PlantsDocument34 pagesChapter 29 (+28) : Resource Acquisition, Nutrition and Transport in Vascular PlantsYashika YashikaNo ratings yet
- Trophic LevelsDocument4 pagesTrophic LevelsBaileyNo ratings yet
- A Higher-Level Phylogenetic Classification of TheDocument40 pagesA Higher-Level Phylogenetic Classification of Thealejandra sanchezNo ratings yet
- Timber Technology Grade 8 - Crossword Labs (Lefgal Answers)Document1 pageTimber Technology Grade 8 - Crossword Labs (Lefgal Answers)Richard LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Mel Bartholomew - All New Square Foot GardeningDocument276 pagesMel Bartholomew - All New Square Foot GardeningLili David100% (11)
- SOALAN PT3 2016 S55C2 S9 Jirim Adalah Bahan Yang Mempunyai Jisim Dan Memenuhi RuangDocument4 pagesSOALAN PT3 2016 S55C2 S9 Jirim Adalah Bahan Yang Mempunyai Jisim Dan Memenuhi RuangAs MozacNo ratings yet
- Jasmine Breeding PDFDocument5 pagesJasmine Breeding PDFUmais nabiNo ratings yet
- Transplanting of SeedlingsDocument20 pagesTransplanting of SeedlingsMarycon NacitoNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument24 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectAhalya Bai SahooNo ratings yet
- PlPath233 III DISEASES OF FIELD CROPS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT PDFDocument108 pagesPlPath233 III DISEASES OF FIELD CROPS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT PDFPravin KhaireNo ratings yet
- ગ્રીનહાઉસમાં ઉગાડાતા શાકભાજી અને ફૂલ પાકોમાં રોગ નિયંત્રણDocument79 pagesગ્રીનહાઉસમાં ઉગાડાતા શાકભાજી અને ફૂલ પાકોમાં રોગ નિયંત્રણchirag sabhayaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Agr 232Document1 pageCase Study Agr 232Najwan AfiqNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (109)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (595)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineFrom EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (216)