Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Water To Check Vessel intrigety-CE
Water To Check Vessel intrigety-CE
Uploaded by
manish3180 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Water to check vessel intrigety-CE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesWater To Check Vessel intrigety-CE
Water To Check Vessel intrigety-CE
Uploaded by
manish318Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
(@Ee Pant insites
a
Water testing is
more complex
than air testing
Use Water to Check Vessel Integrity
Hydrostatic testing offers advantages but requires care
PRESSURE TESTING is a vital step in equipment
maintenance and modification, When everything
goes wel, we have confidence in equipment integ-
rity, However, a filed pressure tes creates salery
concerns, We must design our equipment, develop
«esting procedures and implemenc saecy steps that
assume failure can occur. Afterall if we knew
equipment would pass every time — there wasn’ any
possibility of failure — we wouldn't have to pressure
rescarall,
“The most important decision in pressure testing is
what to select asthe test fluid. Most vessels are tested
‘with either air or water Sometimes ather gases (6g.
nitrogen) of liquids are used but these cases are rare
Airand water have overwhelming benefits in being
cheap, readily available and safe to handle
“The major safer issue in selecting berween air and
waters what happens if che vessel fils. Pneumatic
energy release is much greater than hydrostatic energy
release because air expands much more than water
when pressure containment fil
Even so, some plants use ar for pressure testing
Water contaminates specific processes. Ifyou put
‘water in a sensitive process and can’t get tou again,
water may not be a choice.
‘Water testing is more complex than air esting.
‘You must configure the equipment and piping 0
allow for correctly filling, holding and draining che
wate. In spite ofthe added complexity, I prefer the
safer approach of using water whenever possible
ere are some of my guidelines and design criteria
for using water for pressure testing, Many of these
points are especially important in dealing with tll
vessels, such asthe 130+ call istillaion column
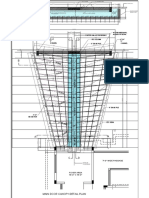
depicted in Figure 1. There, che water height adds 56
psi of static pressure on the bottom
* Confirm chat water deivery pressure is sufficient
to get o the rop ofthe vessel or equipment lop.
+ Have the capability to vent from all enclosed
spaces and loops in the process when filling,
+ Ensure the system is designed
for Full vacuum or has means of
Figure Ta
ail3e00
flu poser
avoiding pulling to low a pres-
sure when draining the water,
+ Allow for hydrostatic head
along the height of the vessel in
seating design maximum allow-
able working pressure (MAWP)
and test pressures
wenng
* Check thatthe foundations can beat the load
when cesting. Depending upon location, this
may include verification that the water-filled load.
is acceptable even during an earthquake. You
usually don’t need to consider waterAilled load
at maximum wind speed. You have plenty of
‘warning of coming hurricanes and would’ be
pressure testing during them,
+ Filland deain che system ata controlled rate, Be
= ©
——
-
- aa ac
Hess @
aware chat internal restitions inside the equip-
‘ment may sec maximum fill or dean rates, For
instance, bubble-cap or valve trays inside towers
may limie draining rates.
+ Assess water quality agains che vessel’ material
‘of construction, The prime example of what 0
watch for is chloride contene of the water if you
are dealing wich stainless steel equipment of
piping.
+ Make sure thae connected piping systems chat
aren isolated during pressure testing can deal
with the test pressue,
+ Thoroughly go over cesting procedures in suit
able management of change, process safety man-
agement, and hazard and operability reviews.
+ Keep personnel away from areas where pressure
testing is taking place,
“The rower in Figure 1 poses five potential erouble
spots fora hydrostatic pressure test: two sections oF
valve crays, rwo sections with incernal partitions crea
PLANT INSITES OO)
ing potential dead spots, as well as che extra 56 psi of
static pressure on the bottom.
Restricting fill and drain rates to appropriate
values will prevent damage to che valve trays. The
dead spots requite ether internal venting or external
venting through nozzles to prevent the relatively weak
internals from bearing excessive load (wen fling) or
hhaving a partial vacuum pulled (when draining). les
crucial to account forthe static head from the vessel
height in secing MAW and test pressures. The vessel
was successfully pressure tested with all incernals in
place by aking all factors ino account and allowing
for them,
Water is safe, reliable medium for pressure test-
ing, However, ike al other plant work, such esting
takes planning and though to correctly design che
equipment and piping. @
BY ANDREW SLOLEY, contributing editor
ASloley@purman net
‘quatty counts..choose O:
tho nedusty has Wened
ion contol solutions. The Rangor QC"
ISaunivorsal contol valve ILofiors varsailiy,
daplapiity anc ease of martenarce in almost
Sy appoaton. Tre Rangar dasigned!
fer usein steam, cnemcal gas anc
ryogene laud applesions
Broad productlines provide
solutors for vrualy any projec
Superior quality precuct
surpassed only by the service anc
supper.
Sategcally bested Sonice
CContora with factory tains
spociists,
Dont watt any longer to parner wh
the industnys leader n process conta
Ca us today st 785-472 4461 for ermediate
‘CONTROL VALVES + REGULATORS.
WESTERN STATES & COMI-CONDOR
s to offer 150 years of
Relies
WESTERN STATES MACHINE
Hamilton, OH, USA
> Vertical Filtering Centrifuges
Solid Bow! Decanting Centrifuges
Available Desian Features:
Stainless Steel / Hasteloy
> oGMP Designs
#4 Polish / Elecropolished
> Clean-in-Place
> Integrated Controls with PLC
> XP Electnes
> Star-Up/ Training / Service
ets kee UN
t dor
DIDIER Reo eel
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 30608794701Document3 pages30608794701manish318No ratings yet
- M-056 - Data SheetR1Document1 pageM-056 - Data SheetR1manish318No ratings yet
- Taxi FairDocument1 pageTaxi Fairmanish318No ratings yet
- A Guide To Storage Tank Repair Based On API 653 StandardDocument7 pagesA Guide To Storage Tank Repair Based On API 653 Standardmanish318No ratings yet
- Design of Storage Tanks For Internal PressureDocument7 pagesDesign of Storage Tanks For Internal Pressuremanish318No ratings yet
- Missing Number WorksheetDocument3 pagesMissing Number Worksheetmanish318No ratings yet
- Rec 2Document1 pageRec 2manish318No ratings yet
- AnchorDocument4 pagesAnchormanish318No ratings yet
- Preliminaries Alpha PREPBOOK 2023 2024 1681735869Document14 pagesPreliminaries Alpha PREPBOOK 2023 2024 1681735869manish318No ratings yet
- AnchorageDocument5 pagesAnchoragemanish318No ratings yet
- WindDocument5 pagesWindmanish318No ratings yet
- Heating Coil Design CalculationDocument3 pagesHeating Coil Design Calculationmanish318No ratings yet
- BillsDocument1 pageBillsmanish318No ratings yet
- Print of Xi - An Hyatt RegencyDocument1 pagePrint of Xi - An Hyatt Regencymanish318No ratings yet
- Main Door Canopy Section-DDocument1 pageMain Door Canopy Section-Dmanish318No ratings yet
- Int PressDocument8 pagesInt Pressmanish318No ratings yet
- Nozzle Load Calculation - U-FA 201Document32 pagesNozzle Load Calculation - U-FA 201manish318No ratings yet
- Nozzle NeckDocument1 pageNozzle Neckmanish318No ratings yet
- WeightDocument3 pagesWeightmanish318No ratings yet
- Seismic AnalysisDocument6 pagesSeismic Analysismanish318No ratings yet
- Foundation LoadingsDocument1 pageFoundation Loadingsmanish318No ratings yet
- EngDocument13 pagesEngmanish318No ratings yet
- Main Door Canopy PlanDocument1 pageMain Door Canopy Planmanish318No ratings yet
- Main Door Canopy Section-CDocument1 pageMain Door Canopy Section-Cmanish318No ratings yet
- Eng 2015Document103 pagesEng 2015manish318No ratings yet
- Main Door Canopy ElevationDocument1 pageMain Door Canopy Elevationmanish318No ratings yet
- A Glimpse of Our Life TodayDocument3 pagesA Glimpse of Our Life Todaymanish318No ratings yet
- DA073-01 Mid #50-#75 - ProtocolDocument27 pagesDA073-01 Mid #50-#75 - Protocolmanish318No ratings yet
- Crude Oil Stroage Tanks SpecsDocument48 pagesCrude Oil Stroage Tanks Specsmanish318No ratings yet
- WoodTech Aquadur PU For InteriorDocument2 pagesWoodTech Aquadur PU For Interiormanish318No ratings yet