Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Bonding
Uploaded by
Ananya IyerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Bonding
Uploaded by
Ananya IyerCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Bonding
Define
1.Chemical bond 2. Electrovalent bond 3. Electrovalent compound
4. Electrovalency 5. Covalent bond 6. Covalent compound 7. Covalence 8. Coordinate bond.
2.What is a lone pair of electrons. Draw an electron dot diagram of a hydronium ion (with lone
pair).
3.State why noble gases are unreactive while atoms of elements other than noble gases are
chemically reactive.
4.State the reasons for chemical bonding between two atoms and the methods involved for
achieving the same. State how ‘duplet and octet’ rules are involved for an atom to achieve
stable electronic configuration.
5.State three differences between ‘X’ and ‘X1+’ i.e. an atom and an ion.
6.Explain the terms ‘oxidation’ and reduction’ with reference to an atom or ion.
7.State which of the following are oxidation reactions and which are reduction reactions.
1.Cu → Cu2+ + 2e–
2.Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
3.Sn4+ + 2e–→Sn2+
4.2Cl- → Cl2 + 2e-
5.Fe2+ → Fe3++le–
6.X +2e–→X2-
7.Y-le– → Y1+
8.Z3++le–→Z2+
8.Explain with the help of
(1) An ionic equation
(2) Electron dot structural diagram
(3) Atomic or orbital structural diagram the formation of the following.
(a) Sodium chloride
(b) Calcium oxide
© Magnesium chloride.
(at. Nos. Na = 11, Cl = 17, Ca = 20, O = 8, Mg = 12)
9.Give two differences between the covalent compounds – methane (non-polar) and HCl (polar
10.Explain with the help of –(1) electron dot diagram (2) atomic or orbital structural diagram –
the formation of the following molecules, stating the valency of each element involved.
(a) Hydrogen
(b) Chlorine
© Oxygen
(d) Nitrogen
€ Water
(f) Methane
(g) Carbon tetrachloride
(h) Ammonia
(i) Carbon dioxide
(at. Nos. H = 1, C = 6, N = 7, O = 8, Cl = 17)
11. Molecules of hydrogen and chlorine have single covalent bonds between their atoms while
oxygen has a double covalent and nitrogen a triple covalent bond respectively. Give reason.
12.MgCl2 is soluble in water but insoluble in acetone, while methane is insoluble in water, but
soluble in acetone. Give reason
13.Define Coordinate bond. Explain diagrammatically the lone pair effect of: The nitrogen atom
of the ammonia molecule leading to the formation of ammonium ions (NH4)+
14. Distinguish between electrovalent compound and covalent compound.
15.With reference to a molecule of water, fill in the blanks with the correct word. (at. No. of H =
1, O = 8)
Water is a……… (non-polar/polar) covalent molecule in which the atom of………….
(hydrogen/oxygen) attracts electrons more strongly towards itself. The water molecule shows
the presence of……… (double/one single/two single) covalent bond/s and………. (one/two) lone
pair of electrons present in the………. (hydrogen/oxygen) atom.
You might also like
- IGCSE CHEMISTRY (Katryne)Document7 pagesIGCSE CHEMISTRY (Katryne)PriyantoBudiLaksonoNo ratings yet
- Bonding Student Study GuideDocument15 pagesBonding Student Study GuideJohn Philip NapalNo ratings yet
- Homework Chapter 5 PDFDocument2 pagesHomework Chapter 5 PDFAlif AshrafNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry PP Ch4 Chemical Bonding Molecular StructureDocument6 pages11 Chemistry PP Ch4 Chemical Bonding Molecular StructureJwalant100% (1)
- Lawrance text problemsDocument23 pagesLawrance text problemsvnNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Bonding Help Sheet: 2, (Diamond)Document6 pagesAP Chemistry Bonding Help Sheet: 2, (Diamond)Weiyu TongNo ratings yet
- Chem Ex6answersDocument7 pagesChem Ex6answersVarshLokNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document77 pagesUnit 2sumeyaminNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure: ValencyDocument11 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure: ValencyD SNo ratings yet
- 05 10Document85 pages05 10Sushil KoiralaNo ratings yet
- Homework 4Document7 pagesHomework 4JairoJacobNo ratings yet
- Third Form Chemistry Packet 3Document12 pagesThird Form Chemistry Packet 3Lizbeth ChiNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions March9 For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4Document32 pagesNcert Solutions March9 For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4Sarojini MallickNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding-Wps OfficeDocument16 pagesChemical Bonding-Wps OfficeJoel TitusNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 2 - Part 2Document13 pagesChemistry Module 2 - Part 2Francis RecocoNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY CLASS 9: BALANCING CHEMICAL EQUATIONSDocument8 pagesCHEMISTRY CLASS 9: BALANCING CHEMICAL EQUATIONSMuhammad ObaidullahNo ratings yet
- Structure and Bonding Properties ExplainedDocument14 pagesStructure and Bonding Properties ExplainedAnonymous nb6QWzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 11e FinalDocument26 pagesChapter 10 11e Finalmaniz442No ratings yet
- CH1O3 Questions PDFDocument52 pagesCH1O3 Questions PDFPrince T MashandaNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument53 pagesIonic and Covalent BondingdomaincontrollerNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Worksheet on Covalent and Dative BondsDocument1 pageChemical Bonding Worksheet on Covalent and Dative BondsPedro PendowskiNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument25 pagesChemical BondingShashank BgNo ratings yet
- F321 Bonding and StructureDocument10 pagesF321 Bonding and StructureDoc_Croc100% (1)
- CH 3 - Lewis Sturcture 7th Ed PDFDocument90 pagesCH 3 - Lewis Sturcture 7th Ed PDFNora AounNo ratings yet
- Bonding Assignment AnswersDocument8 pagesBonding Assignment AnswersvkeylinNo ratings yet
- 8.5 Drawing Lewis Structures PDFDocument11 pages8.5 Drawing Lewis Structures PDFHarshal BandkarNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 _Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure_.Document25 pagesNCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 _Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure_.h85195709No ratings yet
- Chemical Bond class-11 NOTESDocument35 pagesChemical Bond class-11 NOTESsibaranjandash2007No ratings yet
- Physical Science Chap. 8 (II)Document6 pagesPhysical Science Chap. 8 (II)Chaitali SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument8 pagesChemical BondingJoe AppiahNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 31Document31 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 31vishnu kumar patelNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 04: Structure of Molecules (Topic Wise Questions)Document18 pagesChapter # 04: Structure of Molecules (Topic Wise Questions)husain aliNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry I - Tutorial 5Document6 pagesGeneral Chemistry I - Tutorial 5Duc Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- JR Chemistry - Chapter Wise Important Questions - Part 1Document21 pagesJR Chemistry - Chapter Wise Important Questions - Part 1githa80% (352)
- Covalent Bonding Lesson 1Document3 pagesCovalent Bonding Lesson 1GILVERTNo ratings yet
- ch4 13Document26 pagesch4 13Jamunadevi RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions Weeks 1-10 PDFDocument22 pagesTutorial Questions Weeks 1-10 PDFCharlotteNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument23 pagesBondingAkniet RysbekovaNo ratings yet
- 4 Chemical BondingDocument63 pages4 Chemical BondingArvin LiangdyNo ratings yet
- Chemical-Bond NoteDocument9 pagesChemical-Bond NoteDixit GautamNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Concise Chemistry Chemical Bonding SolutionsDocument30 pagesClass 10 Concise Chemistry Chemical Bonding SolutionsPIYUSH DikshitNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Covalent Bonds 2012 VersionDocument9 pagesUnit 8 Covalent Bonds 2012 VersionLê Đình TrungNo ratings yet
- CompleteDocument17 pagesCompleteTelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 NotesDocument13 pagesChapter 8 NotesmrbookoNo ratings yet
- Ionic, Covalent and Coordinate Bonding TypesDocument27 pagesIonic, Covalent and Coordinate Bonding TypesSachin Kumar50% (2)
- Chapter 4.1-Lewis StructureDocument4 pagesChapter 4.1-Lewis StructureSupia NazmaNo ratings yet
- As Ws 10.3 (1) Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesAs Ws 10.3 (1) Chemical Bondinglee_wei_deNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 ChemicalbondingDocument23 pagesChapter2 ChemicalbondingAbbyNo ratings yet
- 4 Chemical Bonding - After Review - 8!10!2019Document24 pages4 Chemical Bonding - After Review - 8!10!2019AFAQ HYDNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8-9Document13 pagesChapter 8-9api-201479236No ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry BondingDocument18 pagesIb Chemistry BondingAaron Bonner100% (1)
- Group 2 Physical ScienceDocument10 pagesGroup 2 Physical ScienceJay Em Kristel MengulloNo ratings yet
- Myp 10 Chemistry 2012 13 Bonding Worksheet Name ClassDocument1 pageMyp 10 Chemistry 2012 13 Bonding Worksheet Name ClassOğuzhan ÖzcanNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bond NotesDocument10 pagesCovalent Bond Notesapi-197752333No ratings yet
- "Covalent Bonding": Pre-AP Chemistry Charles Page High School Stephen L. CottonDocument105 pages"Covalent Bonding": Pre-AP Chemistry Charles Page High School Stephen L. CottoninayahviNo ratings yet
- CT 1 - QP - Icse - X - GSTDocument2 pagesCT 1 - QP - Icse - X - GSTAnanya IyerNo ratings yet
- CT 2 - QP - ICSE - X - BankingDocument1 pageCT 2 - QP - ICSE - X - BankingAnanya IyerNo ratings yet
- CT 3 - QP - IC - X - Linear InequationsDocument1 pageCT 3 - QP - IC - X - Linear InequationsAnanya IyerNo ratings yet
- Merchant of Venice COMPILED Each Line AnswersDocument224 pagesMerchant of Venice COMPILED Each Line AnswersAnanya IyerNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Study For In-Plane Cyclic Behavior of Low Aspect-Ratio Steel-Concrete Composite WallsDocument11 pagesAn Experimental Study For In-Plane Cyclic Behavior of Low Aspect-Ratio Steel-Concrete Composite Wallsci_balaNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science 7Th Edition Bill W Tillery full chapterDocument51 pagesIntegrated Science 7Th Edition Bill W Tillery full chapterwilliam.berry830100% (5)
- Animated ghumster characterDocument61 pagesAnimated ghumster characterramana VemsNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics Mcqs and Fill in The Blanks 2023Document8 pagesModern Physics Mcqs and Fill in The Blanks 2023LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Heriot-Watt University - Dubai Campus Pelton Wheel LabDocument8 pagesHeriot-Watt University - Dubai Campus Pelton Wheel LabAbelBayartNo ratings yet
- Coagulation and Flocculation-5 A6eff65eDocument83 pagesCoagulation and Flocculation-5 A6eff65eredy puthNo ratings yet
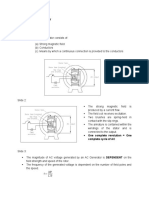
- Ac Generator TheoryDocument3 pagesAc Generator TheoryKrizelle ManaloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 The Manufacturing Process 2020Document48 pagesLecture 2 The Manufacturing Process 2020Noam ShemlaNo ratings yet
- Dual High Broadband AntennaDocument2 pagesDual High Broadband AntennaРоманКочневNo ratings yet
- Zoomlion TC7030B Tower Crane Technical SpecsDocument13 pagesZoomlion TC7030B Tower Crane Technical SpecsfiarNo ratings yet
- Siemens Arcadis Varic C ArmDocument2 pagesSiemens Arcadis Varic C ArmFady Sobhy AzizNo ratings yet
- Estimating Flyrock Distance in Bench Blasting Through Blast Induced Pressure Measurements in RockDocument8 pagesEstimating Flyrock Distance in Bench Blasting Through Blast Induced Pressure Measurements in RockM Arif Satrio AgungNo ratings yet
- Physics STPM Past Year Questions With Answer 2006 PDFDocument18 pagesPhysics STPM Past Year Questions With Answer 2006 PDFxiaokiaNo ratings yet
- A Conceptual Study of Finger-Type Slug Catcher For Heavy-Oil FieldsDocument8 pagesA Conceptual Study of Finger-Type Slug Catcher For Heavy-Oil FieldsfanziskusNo ratings yet
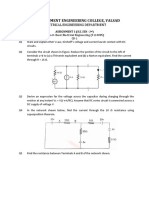
- BEE Assignment Even 2020Document5 pagesBEE Assignment Even 2020Aditya PatelNo ratings yet
- 0002unit 2 NotesDocument22 pages0002unit 2 Noteskishan kumarNo ratings yet
- Obsolete Product(s) - Obsolete Product(s) : Quad Smart Power Solid State Relay For Complete H-Bridge ConfigurationsDocument33 pagesObsolete Product(s) - Obsolete Product(s) : Quad Smart Power Solid State Relay For Complete H-Bridge Configurationsmarino246No ratings yet
- Combined Effect of Damage and Plastic Anisotropy On The Ductility Limit of Thin Metal SheetsDocument8 pagesCombined Effect of Damage and Plastic Anisotropy On The Ductility Limit of Thin Metal SheetsKrunal MoreyNo ratings yet
- Unit Shut Down ProcedureDocument41 pagesUnit Shut Down Procedurernumesh1100% (2)
- BC546B, BC547A, B, C, BC548B, C Amplifier Transistors: NPN SiliconDocument6 pagesBC546B, BC547A, B, C, BC548B, C Amplifier Transistors: NPN SiliconNadia Ayelen GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Buildings 11 00543Document25 pagesBuildings 11 00543Gigi AguasNo ratings yet
- Research of The Inverse Time Characteristic Curve For The Electronic Thermal RelayDocument4 pagesResearch of The Inverse Time Characteristic Curve For The Electronic Thermal RelayGeorge MateiNo ratings yet
- 3900 Chair ManualDocument44 pages3900 Chair ManualAyham DarwichNo ratings yet
- Powder Properties Test Method Alm Pa 650: Nylon 12 Laser Sintering MaterialDocument1 pagePowder Properties Test Method Alm Pa 650: Nylon 12 Laser Sintering MaterialLuiskar MedinaNo ratings yet
- Sencore LC103 Operation and Application ManualDocument65 pagesSencore LC103 Operation and Application ManualXenawise0% (1)
- Volume 2 Highways Structures: Design (Substructures and Special Structures), Materials Section 2 Special StructuresDocument86 pagesVolume 2 Highways Structures: Design (Substructures and Special Structures), Materials Section 2 Special Structuresgeorge santiagoNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Revision Sheet (Part A) - Physics - Standard 10Document3 pagesCurrent Electricity - Revision Sheet (Part A) - Physics - Standard 10mNo ratings yet
- Legendre's Linear EquationsDocument3 pagesLegendre's Linear Equationscoder.sanjNo ratings yet
- Acid-base titration of aspirinDocument4 pagesAcid-base titration of aspirinZari Sofia Leviste100% (1)
- CPP-Solution of Triangle SMC NEWDocument2 pagesCPP-Solution of Triangle SMC NEWtechnical yogeshNo ratings yet