Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ethiopia - Case Week 3 GSM
Uploaded by
Loan Nguyễn Lê MỹOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ethiopia - Case Week 3 GSM
Uploaded by
Loan Nguyễn Lê MỹCopyright:
Available Formats
(+) (-)
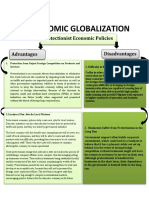
Political environment + industrial Political stability since early 1990s Single-state party and limited
policy under rule of EPRDF, with political freedom requires caution
relatively low country risk for companies doing business with
government and/or accustomed to
Efforts at market liberalization by more open environments
the government of Ethiopia,
including openness to foreign State control of economy remains
investment and privatization of significant, with key sectors off
state-owned businesses limits to foreign investors
Significant investment in public Stated-owned or partly own =>
infrastructure to build foundation unfair competition
for long-term growth
OVERALL: ROLE OF GOV -
Favorable tax and customs regime significant
for businesses that match criteria for
government growth priorities (e.g.,
local manufacturing)
OVERALL: Market
attractiveness degree has been
increased
Ease of doing business Ease of doing business relatively Ease of doing business remains poor
developed by global standards
Construction and property Investor protection, cross-border
registration relatively easier than it trade among areas where
is in other SSA cosuntries performance is relatively poor
Face challenges when
invest in this market
=> affect the way to
entry
Market opportunity Population: more than 90m When compared to global standard:
Ranked 6th For Market OPP GDP per capita remains low, below
most comparison countries
Fast- growing economy; GDP
Possible limits to addressable
PURCHASING market due to income inequality
and low urbanization rate
POWER
Bottom of the
pyramid segment need
Market access Supplier opportunity through lower Fragmented distribution limits
costs and access to potential addressable market and drives up
growing market costs
Wholesale and retail business
reserved for Ethiopian businesses
only
Local knowledge, relationships,
and customs are paramount and
may require reliance on local
partners
Affect to entry mode
Competitive Position Limited competition due to legacy Global brand strength may be
of state-controlled economy, mitigated in environment where
creating opportunities for new foreign influence has been limited
entrants and small upstarts are on level
playing field
Market gap
Protection of intellectual property
may be costly and/or difficult
Difficult to compete
by differentiation
Human resources Low wages can create significant Cross-cultural management may be
cost advantage for labor-intensive difficult for foreign firms, leading to
businesses preference for hiring costly
Ethiopian diaspora
Cut cost. Improve VC
Management
Other Infrastructure challenges for
transport, power,
telecommunications can drive costs
High imported duties: make
offshore products less competitive
on local market
Barriers to WOS or
export (International
business perspective)
You might also like
- Ethiopia Case Week 3 GSMDocument4 pagesEthiopia Case Week 3 GSMduyennguyen.kqmNo ratings yet
- Template For Solving Ethiopia Case Study SOLVEDDocument8 pagesTemplate For Solving Ethiopia Case Study SOLVEDmonk0062006No ratings yet
- Diamond Model Hoffer and BCGDocument6 pagesDiamond Model Hoffer and BCGgeachyNo ratings yet
- IB Questions and AnswersDocument37 pagesIB Questions and AnswersPratik RavjianiNo ratings yet
- Foreign Market EntryDocument5 pagesForeign Market EntryrainanancyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 FdiDocument19 pagesChapter 11 FdiArvilyn ArabellaNo ratings yet
- Creating Sri Lankan Multinationals PWC GlobalDocument6 pagesCreating Sri Lankan Multinationals PWC GlobalIsharaGamageNo ratings yet
- Competition, Competitiveness, and Growth in Sub-Saharan AfricaDocument18 pagesCompetition, Competitiveness, and Growth in Sub-Saharan AfricaUndral ONo ratings yet
- Global TradeDocument7 pagesGlobal TradeAyan GhoshNo ratings yet
- International BusinessDocument100 pagesInternational BusinessKiran Virani100% (1)
- Task 3 SolutionDocument12 pagesTask 3 SolutionAiza AyazNo ratings yet
- Foreign Market Entry ModesDocument4 pagesForeign Market Entry ModesChirag SuraniNo ratings yet
- The Ways in Which Firms Can Enter Into International MarketDocument4 pagesThe Ways in Which Firms Can Enter Into International Marketsuji490No ratings yet
- International BusinessDocument88 pagesInternational BusinessKiran ViraniNo ratings yet
- International Finance: The Impacts of Cross Border Mergers and AcquisitionsDocument14 pagesInternational Finance: The Impacts of Cross Border Mergers and AcquisitionsFier DaouzNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of FDI in Multi-Brand RetailDocument14 pagesPros and Cons of FDI in Multi-Brand RetailSushant MishraNo ratings yet
- The OLI Paradigm June 13Document15 pagesThe OLI Paradigm June 13ChandanNo ratings yet
- Pestle Analysis Example Tcm18 27108Document2 pagesPestle Analysis Example Tcm18 27108Kaviya Kavi100% (1)
- Finals ECONDEVDocument28 pagesFinals ECONDEVNicolette EspinedaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7.1 Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)Document16 pagesLesson 7.1 Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)Thy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Trabajo: Derecho Empresarial y LaboralDocument11 pagesTrabajo: Derecho Empresarial y LaboralPool SandovalNo ratings yet
- Trade Measures and Int'l OrganizationsDocument18 pagesTrade Measures and Int'l OrganizationsCedrick Babalcon AunzoNo ratings yet
- Multinational Enterprise (MNE) - A BusinessDocument2 pagesMultinational Enterprise (MNE) - A BusinessJasmine CarpioNo ratings yet
- Foreign Investment Flows & BarriersDocument16 pagesForeign Investment Flows & Barriersbabita_27No ratings yet
- Globalisation and International Business Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesGlobalisation and International Business Cheat Sheet: by ViaNISCHAL MATHNo ratings yet
- KDQTDocument9 pagesKDQTHân MinhNo ratings yet
- Low Cost Country Sourcing Navigating Uncharted Opportunities Abroad 1Document13 pagesLow Cost Country Sourcing Navigating Uncharted Opportunities Abroad 1Dasun LakshithNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Bergerac Systems - Challenge of Backward IntegrationDocument4 pagesGroup 7 Bergerac Systems - Challenge of Backward Integrationkiller dramaNo ratings yet
- Consulting Experience Project: Jio MartDocument7 pagesConsulting Experience Project: Jio Martdiksha dagaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - International BusinessDocument29 pagesGroup 4 - International Businessangelo austriaNo ratings yet
- Nataliemoore - Globalisation and International BusinessDocument2 pagesNataliemoore - Globalisation and International BusinessTejal Dhulla - ShahNo ratings yet
- Functional AreasDocument2 pagesFunctional AreasZayra AndayaNo ratings yet
- Article FrontierMyanmar Seizing FDI Opportunities 2017Document2 pagesArticle FrontierMyanmar Seizing FDI Opportunities 2017chdahm66No ratings yet
- Ronnel M. Durias Bsentrep-4b (Strategic Management)Document19 pagesRonnel M. Durias Bsentrep-4b (Strategic Management)Mercy A. AudenciaNo ratings yet
- Rodamas Case - Syndicate 6Document32 pagesRodamas Case - Syndicate 6Damar HutomoNo ratings yet
- CSD Innovation Industry Trends GA Presentation ACSDADocument17 pagesCSD Innovation Industry Trends GA Presentation ACSDAFredy ForeroNo ratings yet
- GCWORLDDocument5 pagesGCWORLDBRYLLE JOE SOLIVANo ratings yet
- PESTEL ANALYSIS - Answer Book 1Document3 pagesPESTEL ANALYSIS - Answer Book 1RAJ PATELNo ratings yet
- Industry Parameters IT ServicesDocument10 pagesIndustry Parameters IT ServicesSudikcha KoiralaNo ratings yet
- 1timeairlines Case Analysis: 1. Incorporation and HistoryDocument12 pages1timeairlines Case Analysis: 1. Incorporation and HistoryDejene DeribaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document52 pagesChapter 14Pia SurilNo ratings yet
- PPTXDocument9 pagesPPTXRahulNo ratings yet
- Caie A2 Business 9609 Theory v1Document41 pagesCaie A2 Business 9609 Theory v1Tapiwa RusikeNo ratings yet
- CASE 5 Final ReportDocument6 pagesCASE 5 Final Reportmaruf chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Benefits and Costs of FDIDocument4 pagesBenefits and Costs of FDImarriette joy abadNo ratings yet
- Poters ForcesDocument11 pagesPoters ForcesRaja MohsinNo ratings yet
- More Exam Preparation - Paper 2 Structured Questions: Section ADocument10 pagesMore Exam Preparation - Paper 2 Structured Questions: Section AAejaz MohamedNo ratings yet
- Samenvatting IBDocument26 pagesSamenvatting IBA.L.E.K. Wit, deNo ratings yet
- SM - AniketDocument1 pageSM - AniketNimit ParikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. External Economies of Scale & The International Location of ProductionDocument7 pagesChapter 7. External Economies of Scale & The International Location of ProductionSarahfahriNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Competing in International MarketsDocument59 pagesStrategies For Competing in International MarketsMI chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document1 pageChapter 9Ngọc LinhNo ratings yet
- MSME PRIMER From Local To Global Borderless Business For MSMEsDocument19 pagesMSME PRIMER From Local To Global Borderless Business For MSMEschristopher_musniNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On External Analysis of Indian Telecommunication IndustryDocument13 pagesA Presentation On External Analysis of Indian Telecommunication IndustrySiddharth DasNo ratings yet
- The Superincumbent'S Dilemma: 2019 Value Creators ReportDocument6 pagesThe Superincumbent'S Dilemma: 2019 Value Creators ReportTrip KrantNo ratings yet
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocument15 pagesForeign Direct InvestmentThu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Trade and Competitiveness Global PracticeFrom EverandTrade and Competitiveness Global PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Final Exam - Ibc04.k45Document2 pagesFinal Exam - Ibc04.k45Loan Nguyễn Lê MỹNo ratings yet
- Management Science Syllabus K45 - 2020Document4 pagesManagement Science Syllabus K45 - 2020Loan Nguyễn Lê MỹNo ratings yet
- EIMDocument10 pagesEIMLoan Nguyễn Lê MỹNo ratings yet
- Costco Global ExpansionDocument15 pagesCostco Global ExpansionLoan Nguyễn Lê MỹNo ratings yet
- Service Blueprinting and Discrete Simulation in HoDocument10 pagesService Blueprinting and Discrete Simulation in HoLoan Nguyễn Lê MỹNo ratings yet
- TutorDocument1 pageTutorLoan Nguyễn Lê MỹNo ratings yet
- English HL P1 Nov 2019Document12 pagesEnglish HL P1 Nov 2019Khathutshelo KharivheNo ratings yet
- Imc Case - Group 3Document5 pagesImc Case - Group 3Shubham Jakhmola100% (3)
- Consortium of National Law Universities: Provisional 3rd List - CLAT 2020 - PGDocument3 pagesConsortium of National Law Universities: Provisional 3rd List - CLAT 2020 - PGSom Dutt VyasNo ratings yet
- Is Electronic Writing or Document and Data Messages Legally Recognized? Discuss The Parameters/framework of The LawDocument6 pagesIs Electronic Writing or Document and Data Messages Legally Recognized? Discuss The Parameters/framework of The LawChess NutsNo ratings yet
- Financial Performance Report General Tyres and Rubber Company-FinalDocument29 pagesFinancial Performance Report General Tyres and Rubber Company-FinalKabeer QureshiNo ratings yet
- The Music Tree Activities Book Part 1 Music Tree Summy PDF Book by Frances ClarkDocument3 pagesThe Music Tree Activities Book Part 1 Music Tree Summy PDF Book by Frances ClarkRenata Lemes0% (2)
- Contract of Lease (711) - AguilarDocument7 pagesContract of Lease (711) - AguilarCoy Resurreccion Camarse100% (2)
- Assignment 2 Malaysian StudiesDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 Malaysian StudiesPenny PunNo ratings yet
- Manhole DetailDocument1 pageManhole DetailchrisNo ratings yet
- SRL CompressorsDocument20 pagesSRL Compressorssthe03No ratings yet
- Describe The Forms of Agency CompensationDocument2 pagesDescribe The Forms of Agency CompensationFizza HassanNo ratings yet
- Kolehiyo NG Lungsod NG Lipa: College of Teacher EducationDocument3 pagesKolehiyo NG Lungsod NG Lipa: College of Teacher EducationPrincess LopezNo ratings yet
- CebuanoDocument1 pageCebuanoanon_58478535150% (2)
- Do You Agree or Disagree With The Following StatementDocument2 pagesDo You Agree or Disagree With The Following StatementVũ Ngọc Minh ThuNo ratings yet
- Best Interior Architects in Kolkata PDF DownloadDocument1 pageBest Interior Architects in Kolkata PDF DownloadArsh KrishNo ratings yet
- AITAS 8th Doctor SourcebookDocument192 pagesAITAS 8th Doctor SourcebookClaudio Caceres100% (13)
- Diva Arbitrage Fund PresentationDocument65 pagesDiva Arbitrage Fund Presentationchuff6675No ratings yet
- Kipor Diesel Generator KDE23SS3 CatalogueDocument32 pagesKipor Diesel Generator KDE23SS3 CatalogueAbbasNo ratings yet
- DH 0507Document12 pagesDH 0507The Delphos HeraldNo ratings yet
- Qafqaz UniversityDocument3 pagesQafqaz UniversityQafqazlife QUNo ratings yet
- DE1734859 Central Maharashtra Feb'18Document39 pagesDE1734859 Central Maharashtra Feb'18Adesh NaharNo ratings yet
- Dragon Ball AbrigedDocument8 pagesDragon Ball AbrigedAlexander SusmanNo ratings yet
- Filehost - CIA - Mind Control Techniques - (Ebook 197602 .TXT) (TEC@NZ)Document52 pagesFilehost - CIA - Mind Control Techniques - (Ebook 197602 .TXT) (TEC@NZ)razvan_9100% (1)
- National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005Document17 pagesNational Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005praharshithaNo ratings yet
- Lifeline® Specialty: Fire Resistant QFCI Cable: Fire Resistant, Flame Retardant Halogen-Free Loose Tube - QFCI/O/RM-JMDocument2 pagesLifeline® Specialty: Fire Resistant QFCI Cable: Fire Resistant, Flame Retardant Halogen-Free Loose Tube - QFCI/O/RM-JMkevinwz1989No ratings yet
- Foucault, M.-Experience-Book (Trombadori Interview)Document11 pagesFoucault, M.-Experience-Book (Trombadori Interview)YashinNo ratings yet
- LEWANDOWSKI-olso 8.11.2015 OfficialDocument24 pagesLEWANDOWSKI-olso 8.11.2015 Officialmorpheus23No ratings yet
- MOM-II Lec 9 Unsymmetrical BendingDocument27 pagesMOM-II Lec 9 Unsymmetrical BendingNashit AhmedNo ratings yet
- лк CUDA - 1 PDCnDocument31 pagesлк CUDA - 1 PDCnОлеся БарковськаNo ratings yet
- Simple Past and Past Continuous Notes and ExercisesDocument5 pagesSimple Past and Past Continuous Notes and ExercisesConstantina KouverianosNo ratings yet