Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIO
Uploaded by
Joycey T0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesBIO
Uploaded by
Joycey TCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
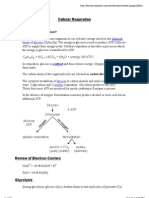
1. Describe the formula of glucose.
�6 �12 �6 - Glucose has the formula of 6 carbon atoms, 12
hydrogen atoms and 6 oxygen. Glucose is a monosaccharide
containing an aldehyde group (-CHO).
2. Describe the structure of ATP.
One adenine, one ribose sugar and three phosphate groups. (The
structure of ATP includes the adenine - a nitrogenous base,
phosphate groups, ribos sugar.)
3. Write the formula for respiratory quotient.
������ �� ��2 ��� ��� ���� ����
RQ =
������ �� �2 �� ��� ���� ����
4. What are the respiratory quotients of carbohydrate, lipid, protein?
a. Carbohydrates = 1.0
b. Lipids = 0.7
c. Proteins = 0.9
5. Describe how many ATP being produced in aerobic respiration.
38 ATP
6. Describe Glycolysis, Krebs cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation.
a. Glycolysis
→ The splitting of glucose, with phosphorylation, to form 2
pyruvates, 2 reduced NAD (NADH), and 2 ATP as a net gain from a
glucose molecule, in the cytoplasm. (the breakdown of glucose to
produce pyruvate)
b. Krebs cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
→ A series of enzyme controlled reactions in the matrix of the
mitochondria; Citrate, 6C, is formed from acetyl CoA + oxaloacetate,
4C (step 1). Citrate is then decarboxylated to yield ��2 and
dehydrogenated to release hydrogen ions, these will reduce NAD
and FAD, producing 2 ATP (step 2).
c. Oxidative Phosphorylation
→ The process by which ATP synthesis is coupled to the
movement of electrons through the mitochondrial ETC and
associated consumption of oxygen, in the inner membrane if
mitochondrion.
7. Differentiate aerobic respiration with anaerobic respiration in
terms of efficiency.
Aerobic respiration is more efficient than anaerobic respiration
since it produces more ATP (38:2).
8. Describe the process occur in the matrix of mitochondria.
The link reaction and the Krebs cycle
9. Differentiate Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, Oxidative phosphorylation in
terms of ATP produce.
a. Glycolysis = 4 ATP (net gain 2 ATP)
b. Krebs cycle = 2 ATP
c. Oxidative Phosphorylation = 28 ATP
10. Where anaerobic respiration takes place?
In the cytoplasm
11. What is ATP and describe its function?
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) works as an universal energy
currency to captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown
of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes.
12. ATP synthase means what…
The enzyme that catalyses the phosphorylation of ADP to form
ATP (the enzyme that breaks ATP).
13. Differentiate Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, Oxidative phosphorylation in
terms of location where their processes occur.
a. Glycolysis = cytoplasm
b. Krebs cycle = matrix of mitochondrion
c. Oxidative Phosphorylation = inner membrane of a mitochondrion
14. Describe the energy released when one phosphate bond breaks
from ATP.
ATP + �2 � → ADP
↓
30.5 KJ Mol → Pi
15. Describe ATP in terms of structure
One adenine, one ribose sugar and three phosphate groups.
16. Describe the functions of Aerenchyma in rice.
To diffuse gases to the other parts of the plant, ensuring the cells
in the roots have air present, so that they can respire aerobically
(plant tissue containing air spaces / forms air channels in the leaves ,
stem and roots).
17. How important oxygen is in aerobic respiration?
Because it’s the final electron acceptor of the ETC, which maintain
hydrogen Ion concentration gradient. (without oxygen, humans &
animals can’t respire aerobically; it assists the movement of
electrons, resulting the production of ATP; it the combines with the
electrons and hydrogen ions to form water.
18. Differentiate Aerobic with anaerobic respiration.
a. Aerobic respiration :
∙ Requires oxygen
∙ Occurs in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of the cell
∙ Produces 38 ATP
b. Anaerobic respiration :
∙ Doesn’t require oxygen
∙ Occurs in the cytoplasm only
∙ Produces only 2 ATP
19. How cyanide affects ATP shortage?
It blocks the electron transported in the electron transport chain.
20. Calculate the RQ of oleic acid (olive oil).
C18H34O2 + 25.5 O2 → 18CO2 + 17H2O + energy.
������ �� ��2 ��� ��� ���� ���� 18
RQ = = = 0.70588 ≈ 0.706
������ �� �2 �� ��� ���� ���� 25.5
21. NADH stand for…
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Hydrogen
You might also like
- Bio RevisionDocument4 pagesBio RevisionJoycey TNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Si Worksheet 10Document5 pagesAnswer Key Si Worksheet 10Jersey BarquillaNo ratings yet
- How Cells Harvest EnergyDocument8 pagesHow Cells Harvest EnergyDJ ISAACS25% (4)
- Respiration in Hingher PlantsDocument6 pagesRespiration in Hingher PlantsTrillionare HackNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Points To RememberDocument6 pagesChapter 14 Points To RememberSaksham YadavNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle Produce ATPDocument7 pagesGlycolysis and Krebs Cycle Produce ATPkayannaNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument15 pagesRespiration in Plantsyahake5036No ratings yet
- Topic 8 Cell Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesTopic 8 Cell Respiration and PhotosynthesisCedric Williams100% (1)
- Respiration in PlantsDocument29 pagesRespiration in PlantsJahanzeb SafdarNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration PogilDocument7 pagesCellular Respiration PogilEmmaNo ratings yet
- Energy and Respiration Part 2Document28 pagesEnergy and Respiration Part 2Eva SugarNo ratings yet
- CBTA FOCUS AREA REVISION QUESTIONS ON RESPIRATIONDocument3 pagesCBTA FOCUS AREA REVISION QUESTIONS ON RESPIRATIONMolly KuttyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis & Respiration: By: James Grant & Aimee IrvinDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis & Respiration: By: James Grant & Aimee IrvindunklinjNo ratings yet
- Resp and Photo Study GuideDocument3 pagesResp and Photo Study GuidenikvNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationBio Sciences75% (4)
- Cellular Respiration STUDY GUIDEDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration STUDY GUIDEJee MascardoNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument52 pagesCellular RespirationCici SintamayaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration in Micro-OrganismDocument13 pagesAerobic Respiration in Micro-OrganismIshwarya LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument28 pagesCellular RespirationPrecy Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- AP Bio CHAPTHER 9 Guided ReadingDocument7 pagesAP Bio CHAPTHER 9 Guided ReadingSadmoodNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and Its Pathways: Arvin G. Concha Mst-BioDocument17 pagesMitochondria and Its Pathways: Arvin G. Concha Mst-Biocassidy conchaNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Ms. K. Smith Bhs-Biology 6 FormDocument47 pagesRespiration: Ms. K. Smith Bhs-Biology 6 FormJanae CampbellNo ratings yet
- 2023 2024 b3502 Lecture 15 Carbohydrate+Metabolism+Cont Shuttle+Systems+and+Krebs+Cycle Their+SignificanceDocument14 pages2023 2024 b3502 Lecture 15 Carbohydrate+Metabolism+Cont Shuttle+Systems+and+Krebs+Cycle Their+Significancepitsolerato60No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds GlucoseDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds Glucosemegamega11No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument5 pagesCellular RespirationCaptain MarvelNo ratings yet
- BIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Document39 pagesBIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Shariq KhanNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 RespirationDocument11 pagesTopic 5 RespirationPriya Kumar100% (1)
- Kami Export - ALEXA CADENA - 13 Cellular Respiration-SDocument6 pagesKami Export - ALEXA CADENA - 13 Cellular Respiration-SALEXA CADENANo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument38 pagesCellular RespirationZinedine HornachozNo ratings yet
- A2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationDocument20 pagesA2 Biology Notes Cellular RespirationArnel100% (1)
- Chapter 9: Cellular RespirationDocument36 pagesChapter 9: Cellular RespirationMary GarciaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Unit 5: Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene TechnologyDocument138 pagesUnit 5: Unit 5: Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene TechnologyMovie FlexNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: ATP Production from GlucoseDocument16 pagesCellular Respiration: ATP Production from GlucoseBhillee Agas ValdezNo ratings yet
- Bio Tutorial 7Document4 pagesBio Tutorial 7Viyasinei KumaramoneyNo ratings yet
- Cell RespiDocument30 pagesCell Respi11009911No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration WorksheetDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration WorksheetKlit MejanNo ratings yet
- Science of Living SystemsDocument52 pagesScience of Living Systemshimanshu_agraNo ratings yet
- How cells harvest energy from foodDocument19 pagesHow cells harvest energy from foodskywalkerNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Review KEY GuideDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration Review KEY GuideerikabeltranNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants class 11 Notes Biology summaryDocument5 pagesRespiration in Plants class 11 Notes Biology summaryMANDAL VIKRAMNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: ATP Generation Through Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle & Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration: ATP Generation Through Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle & Oxidative PhosphorylationJuan ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Pyruvate, Krebs, ElectransDocument7 pagesPyruvate, Krebs, Electransfionadaguman2002No ratings yet
- C6H12O6 + 6O2 - 6CO2 + 6H2O +ATP: RespirationDocument2 pagesC6H12O6 + 6O2 - 6CO2 + 6H2O +ATP: RespirationHarleen BalNo ratings yet
- Biological OxidationDocument14 pagesBiological OxidationSHRIKANTNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 4 CARBOHYDRATE-GLYCOLYSISDocument20 pagesLECTURE 4 CARBOHYDRATE-GLYCOLYSISBiology BảoNo ratings yet
- ADPATPand Cellular RespirationDocument43 pagesADPATPand Cellular RespirationJessa CabusaoNo ratings yet
- PARAS, Mark Heinrich B. - Homework 6 - Lecture Biochemistry CHEM 40 BSN 1EDocument2 pagesPARAS, Mark Heinrich B. - Homework 6 - Lecture Biochemistry CHEM 40 BSN 1EMark Heinrich B. ParasNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration AP POGILDocument7 pagesCellular Respiration AP POGILPhil NanceNo ratings yet
- Energy and Respiration A2 NotesDocument15 pagesEnergy and Respiration A2 NotesMoe Chelsea100% (4)
- RESPIRATION: THE BREAKDOWN OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS FOR ENERGYDocument4 pagesRESPIRATION: THE BREAKDOWN OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS FOR ENERGYAlfiya ShereefNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme KatabolismeDocument3 pagesMetabolisme KatabolismeGiska AliyaNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument38 pagesCellular RespirationItsYaBoiRZ YTNo ratings yet
- 12 RespirationDocument3 pages12 RespirationSan Siddz100% (1)
- RespirationDocument11 pagesRespirationthushyanthNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 6Document35 pagesBIOL223-Lab 6chicken friesNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria: By-Akshita Nautiyal Kashyap Panchal Yogesh VishwakarmaDocument23 pagesMitochondria: By-Akshita Nautiyal Kashyap Panchal Yogesh VishwakarmasekharurlaNo ratings yet
- 13 Cellular Respiration-KEYDocument8 pages13 Cellular Respiration-KEYfkjnf100% (1)
- Apnea of Prematurity: UnderstandingDocument2 pagesApnea of Prematurity: UnderstandingEmil JaniakNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document7 pagesActivity 3Naditha Putri HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Dyspnea On Exertion - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument7 pagesDyspnea On Exertion - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfyohanNo ratings yet
- Static, Dynamic and Specific ComplianceDocument7 pagesStatic, Dynamic and Specific ComplianceSajal SahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Respiratory SystemDocument20 pagesChapter 8 - Respiratory Systemmnurnazri10No ratings yet
- Measuring Lung CapacityDocument6 pagesMeasuring Lung CapacitydrockriotNo ratings yet
- Control of Mechanical VentilationDocument6 pagesControl of Mechanical VentilationMichael LevitNo ratings yet
- Dr Mohammed Jamsheed's Guide to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDSDocument53 pagesDr Mohammed Jamsheed's Guide to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDSavicennax100% (1)
- Protections of the Upper Airway Shield the Lower AirwayDocument3 pagesProtections of the Upper Airway Shield the Lower AirwayPaul JacksonNo ratings yet
- Oxygen InhalationDocument47 pagesOxygen InhalationKomalNo ratings yet
- Effect of Pursed Lips Breathing For Oxygen Saturation and Peak Expiratory Flow Rate: Systematic ReviewDocument5 pagesEffect of Pursed Lips Breathing For Oxygen Saturation and Peak Expiratory Flow Rate: Systematic ReviewRudi HariyonoNo ratings yet
- Abbreviations in PhysiotherapyDocument53 pagesAbbreviations in PhysiotherapyPhysiotherapist AliNo ratings yet
- 3.2. KARBOHIDRAT II GlikolisisDocument27 pages3.2. KARBOHIDRAT II GlikolisisRikka TakaradaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceSandeepNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesPhysiology of Respiratory SystemAngelica Joan SorianoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 8 Respiratory System PDFDocument58 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 8 Respiratory System PDFJobelleNerpiolAbaoNo ratings yet
- Case Study CopdDocument7 pagesCase Study CopdIrveen Joy RamirezNo ratings yet
- Here are the labeled parts of the respiratory system:nosenasal cavity pharynxlungsmouthlarynxtracheaDocument27 pagesHere are the labeled parts of the respiratory system:nosenasal cavity pharynxlungsmouthlarynxtracheaExequiel RamientosNo ratings yet
- Assessing Thorax LungsDocument20 pagesAssessing Thorax Lungskyla boncacasNo ratings yet
- TracheostomyDocument11 pagesTracheostomyBryan DorosanNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument40 pagesElectron Transport ChainUtkarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PhysiologyDocument33 pagesRespiratory PhysiologybhagathbabuNo ratings yet
- Ujian 1Document10 pagesUjian 1Tajul Azhar BaharudinNo ratings yet
- ICD Reference CodesDocument2 pagesICD Reference CodesRavi Pal100% (1)
- SCHOOL COPY Gen Bio 1 - Q2Module 5Document23 pagesSCHOOL COPY Gen Bio 1 - Q2Module 5PLS help me get 1k subsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Shortness of BreathDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Shortness of Breathkarl de guzmanNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY OrganDocument24 pagesRESPIRATORY OrganAnuvabNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Science 8Document340 pagesCambridge Science 8Matthew MetcalfeNo ratings yet
- Add A Heading 1Document3 pagesAdd A Heading 1api-524260600No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology and Classification of Respiratory Failure. Tejpreet Singh Lamba. 2016Document9 pagesPathophysiology and Classification of Respiratory Failure. Tejpreet Singh Lamba. 2016Danitza VeraNo ratings yet