100% found this document useful (1 vote)
532 views23 pagesPython Tools for Data Scientists
This section provides tools for collecting data from various sources in Python. It summarizes several packages:
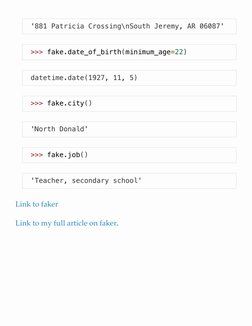
1) Faker - Generates fake test data like names, addresses, and dates in one line of code.
2) Random User Generator API - Generates random user profiles in one line of code for testing.
3) OpenML - Accesses datasets from the OpenML repository in one line of code using sklearn.
4) Various other packages are mentioned for scraping websites, extracting time series data, analyzing search trends, scraping social media, and accessing statistics APIs.
Uploaded by
MaheshBirajdarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
532 views23 pagesPython Tools for Data Scientists
This section provides tools for collecting data from various sources in Python. It summarizes several packages:
1) Faker - Generates fake test data like names, addresses, and dates in one line of code.
2) Random User Generator API - Generates random user profiles in one line of code for testing.
3) OpenML - Accesses datasets from the OpenML repository in one line of code using sklearn.
4) Various other packages are mentioned for scraping websites, extracting time series data, analyzing search trends, scraping social media, and accessing statistics APIs.
Uploaded by
MaheshBirajdarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction: Overview of Python tools and tricks for data scientists, focusing on acquiring datasets.
- faker: Create Fake Data: Guide on using the Faker library to generate fake data for testing purposes.
- Random User: Generate Random User Data: Explanation on how to use Random User API to create fake user data efficiently.
- fetch_openml: Get OpenML's Dataset: Utilizing OpenML datasets in Python using a single line of code through the sklearn library.
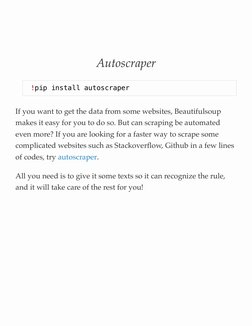
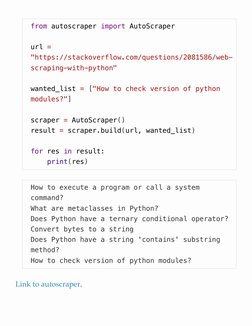
- Autoscraper: Introduction to Autoscraper for extracting data from websites efficiently.
- pandas-reader: Extract Data: Details on extracting series data into Pandas DataFrames from various internet sources.
- pytrends: Get the Trend of a Keyword: Explains how to track keyword trends on Google Search over time using pytrends.
- snscrape: Instructions for scraping data from social media services in Python.
- Datacommons: Methods to fetch statistics about locations using Datacommons in a single line of code.
- Get Google News Using Python: Guide on using GoogleNews Python library to fetch news articles over specific time intervals.