Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Terran Beown Biology Four Fungi Types
Terran Beown Biology Four Fungi Types
Uploaded by
TB - 12LR 691349 Central Peel SSOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Terran Beown Biology Four Fungi Types
Terran Beown Biology Four Fungi Types
Uploaded by
TB - 12LR 691349 Central Peel SSCopyright:
Available Formats
What are they?
zygospore fungi- mould- small balck dots- look similar to break when its expired- indudes bread
mould, and other saprotrophs, a few parasites of protists and small invertebrate animals
Club fungi- these are all short lived reproductive structures called fruiting bodies or basidiocarps
sac fungi- powdery mildew on leaves that turn into truffles to the morels and truffles used in
gourmet meals
imperfect fungi- greenish colour found on mouldy fruit, cyclosporine obtained from a fungus that
lives in soil called
What do they do?
zygospore fungi- Infect and decompose things like bread. Protects the contents from drying and
other hazards
Club fungi- the mycelium begins growing, expanding outward like spokes of a wheel to produce
the basidiocarps at the ends.
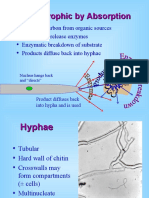
sac fungi- break down hard to digest materials in wood and bone
imperfect fungi- used after transplant operations to suppress the patient's immune system,
helping avoid rejection of the transplant organ
Fun facts
zygospore fungi- the zygospore remains dormant until conditions for growth are favourable
again
Club fungi- commonly called smuts and rusts you can see the serious damage they cause to
cereal crops such as corn, wheat and rye.
sac fungi- this group also includes single cell yeast
imperfect fungi- appear to not have a sexual phase of reproduction as other fungi do
How they reproduce
zygospore fungi- zygospores are diploid structures that develop after two haploid hyphae of
opposite types called mating strands. Reproduce asexually,
Club fungi- the complete reproductive cycle of a club fungus involves a complex sequence of
events
sac fungi- reproduce asexually
imperfect fungi- reproduce asexually
Where they can be found
zygospore fungi- bread, food
Club fungi-lawn, forests, tree trunks
sac fungi- mostly used in meals, dispersed through the wind, water and animals
imperfect fungi- found growing on mouldy fruit
You might also like
- Mushroom Cultivation PDFDocument34 pagesMushroom Cultivation PDFkasthuri kasthuriNo ratings yet
- GEN BIO II - MidtermsDocument14 pagesGEN BIO II - MidtermsVenniecine LopezNo ratings yet
- FUNGI Grade 3Document65 pagesFUNGI Grade 3Astika RahayuNo ratings yet
- 3.2. Keanekaragaman Makhluk Hidup (Fungi)Document42 pages3.2. Keanekaragaman Makhluk Hidup (Fungi)Bagus Dwi PermanaNo ratings yet
- Deuteromycota EnglishDocument6 pagesDeuteromycota EnglishMuhammad Nur50% (2)
- BIO 102 by DR Keshinro OMDocument32 pagesBIO 102 by DR Keshinro OMfaborodeharyomideNo ratings yet
- Fungi (Definition Paragraph-Classification)Document6 pagesFungi (Definition Paragraph-Classification)jefriNo ratings yet
- IPDocument19 pagesIPAnuj Abner Samuel BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Biology Kingdom FungiDocument26 pagesBiology Kingdom FungiFrance SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Classification of FungiDocument5 pagesClassification of FungiSoumit PaulNo ratings yet
- DeutromycetesDocument10 pagesDeutromyceteshendra_s_backNo ratings yet
- How Do Fungi Eat?Document4 pagesHow Do Fungi Eat?Zeke CoronacionNo ratings yet
- Fungi Spring 2011Document23 pagesFungi Spring 2011Kenzie SmithNo ratings yet
- Fungi 2Document11 pagesFungi 2Nur QistinaNo ratings yet
- 1.5 FungiDocument57 pages1.5 FungiaixyaehNo ratings yet
- What Are FungiDocument2 pagesWhat Are FungiErika FraynaNo ratings yet
- Early Blight of Potato: Pathogen Alternaria SolaniDocument7 pagesEarly Blight of Potato: Pathogen Alternaria SolaniHamid AfridiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Notes On MoldsDocument13 pagesLecture 2 Notes On MoldsRyan Carlo CondeNo ratings yet
- YeastDocument17 pagesYeastvyoma agarwalNo ratings yet
- Module On FungiDocument10 pagesModule On FungiIsha GishNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument6 pagesFungiJocelyn SarcaogaNo ratings yet
- Cell DiversityDocument28 pagesCell DiversityMarielle MatunogNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument2 pagesAsexual ReproductionReshma MohabeirNo ratings yet
- ALE Review MycologyDocument44 pagesALE Review MycologyJayson BasiagNo ratings yet
- 1 - Mycology-Chapter-OneDocument70 pages1 - Mycology-Chapter-OneMimo HemadNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Fungi NotesDocument4 pagesKingdom Fungi NotesAmi GNo ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument52 pagesFUNGIkeira raishaNo ratings yet
- SMB3103Document147 pagesSMB3103xasantalan3No ratings yet
- Different Forms of Common Mushroom Production From AgroDocument16 pagesDifferent Forms of Common Mushroom Production From AgroAkshitaNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of MushroomDocument17 pagesLife Cycle of MushroomAayush ShNo ratings yet
- Kingdomfungi 170304171711Document34 pagesKingdomfungi 170304171711trisha abadNo ratings yet
- Chap 5-Bio320 (Fungi)Document49 pagesChap 5-Bio320 (Fungi)Radius JuliusNo ratings yet
- Fungi Kingdom - Short Discussion and QuizDocument23 pagesFungi Kingdom - Short Discussion and Quizlovely joy banaybanayNo ratings yet
- 3..morphology Importance of FungiDocument21 pages3..morphology Importance of Fungichansadavid52No ratings yet
- FungiDocument4 pagesFungiMayda RiveraNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 MicroorganismDocument30 pagesTopic 3 MicroorganismFaith VooNo ratings yet
- The Fungi Kingdom: By: Ghazi, Maria, Svetlana and BenDocument10 pagesThe Fungi Kingdom: By: Ghazi, Maria, Svetlana and BenAdam AlonNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Eumycota - The True Fungi2Document33 pagesKingdom Eumycota - The True Fungi2Mauricio LarrainNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviwerDocument3 pagesBio Reviweranmbeltran31No ratings yet
- FungiDocument38 pagesFungiRamayono RayNo ratings yet
- Zygospore: Phylum: ZygomycotaDocument16 pagesZygospore: Phylum: ZygomycotaDavid NindiNo ratings yet
- 6.KINGDOM FUNGI and PLANTAEDocument36 pages6.KINGDOM FUNGI and PLANTAEChrisel BantuganNo ratings yet
- Kingdom FungiDocument31 pagesKingdom Fungiraul sinatoNo ratings yet
- ParawordDocument4 pagesParawordCHRISTIAN HOWARD SAGUBAYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 STD 10Document19 pagesChapter 3 STD 10SHRESTH FFNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Rust and SmutDocument3 pagesDifference Between Rust and SmutKhadijaNo ratings yet
- General Structure and Classification of Fungus: Sakshi SinghDocument12 pagesGeneral Structure and Classification of Fungus: Sakshi SinghShiksha singh Shiksha singhNo ratings yet
- Evelyn Hone College Lecture 5 2022 Fungi KingdomDocument30 pagesEvelyn Hone College Lecture 5 2022 Fungi KingdomJoyce KapembwaNo ratings yet
- Sporulation of Fungus Project Biology (Cbse 12)Document24 pagesSporulation of Fungus Project Biology (Cbse 12)Nandita Banerjee89% (19)
- BSECSCI 14 (Fungi) Patinga, Christine Mae V.Document4 pagesBSECSCI 14 (Fungi) Patinga, Christine Mae V.Christian PatingaNo ratings yet
- Keanekaragaman Tumbuhan Berkayu Dan BerbijiDocument69 pagesKeanekaragaman Tumbuhan Berkayu Dan BerbijiSandy HarbianNo ratings yet
- Yeasts 2023Document82 pagesYeasts 2023am6443559No ratings yet
- Molds YeastDocument8 pagesMolds YeastAnandNo ratings yet
- Basic Mycology: Russell G. Panem, RMT School of Medical Technology Chinese General Hospital CollegesDocument47 pagesBasic Mycology: Russell G. Panem, RMT School of Medical Technology Chinese General Hospital CollegesJaellah MatawaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Algae, Fungi, Protozoa, HelminthsDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Algae, Fungi, Protozoa, HelminthsRudraksh PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Pink Lined Illustration Communication Training Talking PresentationDocument14 pagesPink Lined Illustration Communication Training Talking PresentationJimmy Q MadroneroNo ratings yet
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Reproduction in Plants - RBSE GuideDocument3 pagesRBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Reproduction in Plants - RBSE GuideAlpine AcademiaNo ratings yet
- Growing Wild MushroomsDocument50 pagesGrowing Wild Mushroomsviki90% (10)
- Mushroom Spotter's Deck: A Field Guide to Fungi & Their Age-Old WisdomFrom EverandMushroom Spotter's Deck: A Field Guide to Fungi & Their Age-Old WisdomNo ratings yet