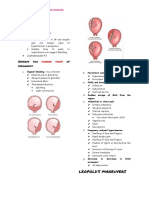
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fundamentals of Nursing
Uploaded by
Maricel DuposCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fundamentals of Nursing
Uploaded by
Maricel DuposCopyright:
Available Formats
INTENSIVE PHASE
HANDOUTS
FUNDAMENTALS OF NURSING
PREPARED BY: BEEJAY WONG
NOVEMBER 2022 Philippine Nursing Licensure Examination
I. NURSING PROCESS
✔ Routine Urinalysis
✔ Culture and Sensitivity
✔ Timed Urine Collection
2. STOOL Specimens
✔ Routine Fecalysis
✔ Culture and Sensitivity
✔ Fat Analysis
1. Assessment ✔ Fecal Occult Blood Test
✔ Collection of data
✔ Organization of data 3. SPUTUM Specimens
✔ Validation of data
✔ Documentation of data ✔ Gross Appearance
✔ Culture and Sensitivity
2. Diagnosis
✔ Actual ✔ Acid Fast Bacillus
✔ Risk
✔ Possible ✔ Cytology
✔ Syndrome
✔ Wellness III. NUTRITION
3. Planning
✔ Short-term goal
✔ Long-term goal
4. Implementation
✔ Independent
✔ Dependent
✔ Interdependent
5. Evaluation
BASAL METABOLIC RATE (BMR)
II. SPECIMEN COLLECTION
Weight (kg)
_________
Height (m)2
❖ NASOGASTRIC TUBE
o Gavage
o Lavage
1. URINE Specimens
TOP RANK REVIEW ACADEMY, INC. Page 1 | 4
o Decompression
o Medications ✔ Insertion:
✔ Removal:
Complications:
1. Hypergycemia
2. Hypoglycemia
3. Infection
✔ Insertion:
✔ Administration:
✔ Removal:
❖ TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION (TPN)
IV. OXYGENATION
✔ Colorless
✔ Odorless
✔ Tasteless
1. Nasal Cannula
2. Simple Face Mask
3. Partial Rebreather Mask
4. Non-Rebreather Mask
5. Venturi
TOP RANK REVIEW ACADEMY, INC. Page 2 | 4
⮚ SUCTIONING
-is the aspiration of secretions through a catheter connected to a suction machine or wall suction outlet.
OROPHARYNGEAL NASOPHARYNGEAL ET/TT
POSITION:
LENGTH:
TIME:
INTERVAL:
⮚ TRACHEOSTOMY
– opening into the trachea through the neck, a tube is
inserted and artificial airway is created.
⮚ INCENTIVE SPIROMETER
-measure the flow of air inhaled through the mouthpiece.
1. Obturator
2. Inner Cannula
3. Outer Cannula
4. Tracheostomy Ties ✔ Improve pulmonary ventilation
✔ Loosen secretions
5. Tracheostomy Cuff ✔ Expand collapsed alveoli
✔ Counteracts the effects of anesthesia
⮚ CHEST DRAINAGE (CTT)
✔ Facilitate gas exchange
- Inserted into pleural cavity to restore negative
pressure (Lung Re-expansion) V. PAIN ASSESSMENT / MANAGEMENT
✔ Pneumothorax Provoked
✔ Hemothorax
✔ Pleural Effusion Quality
Region/Radiation
Severity
Time
PHARMACOLOGIC
1. OPIOIDS
TOP RANK REVIEW ACADEMY, INC. Page 3 | 4
(Acetaminophen, Aspirin)
▪ Full Agonist ( Morphine,
Meperidine, Oxycodone, Fentanyl)
▪ Mixed Agonist – Nalbuphine
3. COANALGESIC
Hydrochloride (Nubain) -have properties that may reduce pain alone or in combination
with other analgesics, relieve other discomforts, potentiate the
effect of pain medications, or reduce the side effects of pain
medications. ( Antidepressants, Anxiolytic, Anticonvulsants,
2. NON-OPIOIDS/NSAIDS
Antispasmodic
I.LEVELS OF PREVENTION
PRIMARY SECONDARY TERTIARY
TARGET: Healthy High-Risk Post-Treatment
GOALS:
TOP RANK REVIEW ACADEMY, INC. Page 4 | 4
You might also like
- CustomizingDocument5 pagesCustomizingEduardo Padilla Lozano100% (1)
- Skills Check List - TheatresDocument6 pagesSkills Check List - TheatresDoyTanNo ratings yet
- Med Surg 2 - 2 Diagnostic Examinations For Gastrointestinal SystemDocument18 pagesMed Surg 2 - 2 Diagnostic Examinations For Gastrointestinal SystemMaxinne RoseñoNo ratings yet
- AMPUTASI BUKAN PILIHAN MANAJEMEN LUKA DIABETES ADALAH SOLUSINYADocument52 pagesAMPUTASI BUKAN PILIHAN MANAJEMEN LUKA DIABETES ADALAH SOLUSINYAasmida sari hasibuanNo ratings yet
- Clave Roja - Im Myriam Noelia Cruz PoicónDocument29 pagesClave Roja - Im Myriam Noelia Cruz PoicónAle tcNo ratings yet
- PT NotesDocument19 pagesPT NotesVenice Marie CordetaNo ratings yet
- MCN Spontaneous MiscarriageDocument2 pagesMCN Spontaneous MiscarriageBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNo ratings yet
- ED RN skills checklistDocument4 pagesED RN skills checklistJohn Carl Angelo EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Surgery BCA Pancreas Stomach Mar 2020Document5 pagesSurgery BCA Pancreas Stomach Mar 2020Jojo MendozaNo ratings yet
- NGT Nasogastric Tube Key Points: IndicationsDocument7 pagesNGT Nasogastric Tube Key Points: IndicationsHana ChanNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube Insertion: Notes: ComplicationsDocument2 pagesNasogastric Tube Insertion: Notes: ComplicationsAlyssandra LucenoNo ratings yet
- Bandal 3bsna Parotidectomy Pleomorophic AdenomaDocument25 pagesBandal 3bsna Parotidectomy Pleomorophic AdenomasharedNo ratings yet
- Head & Neck TumorsDocument4 pagesHead & Neck TumorsDez RayosNo ratings yet
- PP PPK BedahDocument10 pagesPP PPK Bedahyohanisrassang1979No ratings yet
- Manajemen LukaDocument50 pagesManajemen LukaindraNo ratings yet
- FINALS-PEDIA-ENCODEDDocument62 pagesFINALS-PEDIA-ENCODEDCezanne Danabelle HutallaNo ratings yet
- L1-IM-Colonic Polyps and Polyposis Syndrome (Feb1122)Document9 pagesL1-IM-Colonic Polyps and Polyposis Syndrome (Feb1122)patriciaatan1497No ratings yet
- NGT and OstomyDocument2 pagesNGT and OstomyDarianne B. BasaNo ratings yet
- Defining Characteristic S Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Plan of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale Subjective: Short Term: IndependentDocument1 pageDefining Characteristic S Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Plan of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale Subjective: Short Term: Independentboomer SeargeNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument5 pagesDiarrheamohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- Neonatal IntubationDocument6 pagesNeonatal IntubationAndrea Nur SabrinaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Java Delos Santos Michael JacobDocument2 pagesGrade 12 Java Delos Santos Michael JacobJacob Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- 07.03.44 Neonatal IntubationDocument6 pages07.03.44 Neonatal IntubationAya AshrafNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument3 pagesNCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- Delantar 3bsna Parotidectomy Pleomorophic AdenomaDocument26 pagesDelantar 3bsna Parotidectomy Pleomorophic AdenomasharedNo ratings yet
- Handouts Onco Prof. RojasDocument5 pagesHandouts Onco Prof. RojasChallen CulturaNo ratings yet
- 2 Initial Steps PDFDocument22 pages2 Initial Steps PDFBeatrice Joy TombocNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Disorders RN Review: Nio C. Noveno, RN, MAN Eview of Arts UnctionsDocument24 pagesGastrointestinal Disorders RN Review: Nio C. Noveno, RN, MAN Eview of Arts Unctionsapi-19824701100% (1)
- Top Nursing Skills, Procedures and Normal ValuesDocument25 pagesTop Nursing Skills, Procedures and Normal ValuesericNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing ManagementDocument19 pagesPerioperative Nursing ManagementSarah SeverreNo ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument13 pagesHealth AssessmentImee TolentinoNo ratings yet
- ENT - Salivary Gland Diseases (Almazan)Document4 pagesENT - Salivary Gland Diseases (Almazan)Tj Kevin P-DoctorNo ratings yet
- Table FourDocument7 pagesTable FourLawrence AckahNo ratings yet
- WNHS Neo BowelWashoutDocument2 pagesWNHS Neo BowelWashoutNazila HanaNo ratings yet
- Biopsy: Mahendraraj, M.T 110020599Document39 pagesBiopsy: Mahendraraj, M.T 110020599karinarakhmaNo ratings yet
- Maternal Child Health Nursing Physical Assessment and Labor DiscomfortsDocument18 pagesMaternal Child Health Nursing Physical Assessment and Labor DiscomfortsVanessa Mae Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Git Problems: Oral and Esophageal DisordersDocument18 pagesNursing Management of Git Problems: Oral and Esophageal Disorderslcpot_se7en7505100% (2)
- NCM 116a (Caronongan)Document6 pagesNCM 116a (Caronongan)2225334No ratings yet
- APPENDICITISDocument18 pagesAPPENDICITISdytaNo ratings yet
- Rle 107 MTDocument15 pagesRle 107 MTKrizia Claire Marie RedondoNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Diagnostic ProceduresDocument8 pagesModule 6 - Diagnostic ProceduresrishellemaepilonesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- Continence Problem at HomeDocument71 pagesContinence Problem at HomeZayar HmunNo ratings yet
- Xavier University Case Study: Surgical Ward Rotation RequirementsDocument38 pagesXavier University Case Study: Surgical Ward Rotation RequirementsBrandy Jaffar100% (1)
- Kinethics 1&2 - Pharma 3Document6 pagesKinethics 1&2 - Pharma 3Bulda, Princess Kaye R.No ratings yet
- KKKKDocument22 pagesKKKKMARY CLAIRE SUMILHIGNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Term 2Document13 pagesRespiratory Term 2Abegail QuintoNo ratings yet
- Git Procedures 1232011019427452 2Document15 pagesGit Procedures 1232011019427452 2api-19824701No ratings yet
- Assessment... : 1. Bedside Swallowing Examination 2. Instrumental AssessmentDocument10 pagesAssessment... : 1. Bedside Swallowing Examination 2. Instrumental Assessmentbaidurisolehah3955No ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY CONDITIONS Lecture AidDocument4 pagesRESPIRATORY CONDITIONS Lecture AidStephanie Pearl AldaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ParacentesisDocument5 pagesAbdominal ParacentesisBinal Joshi75% (4)
- Enteral Tube Care & MaintenanceDocument35 pagesEnteral Tube Care & MaintenanceAbu JamalNo ratings yet
- TARLAC STATE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AWARDED LEVEL III PHASE I STATUSDocument2 pagesTARLAC STATE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AWARDED LEVEL III PHASE I STATUSMina SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Respi Infectious Course OutlineDocument5 pagesRespi Infectious Course OutlineDhan Marco HamacNo ratings yet
- Wound AssessmentDocument64 pagesWound AssessmentKeown MukhtarNo ratings yet
- LRPD InglesDocument5 pagesLRPD InglesYuleika Zulema Pachas MachaNo ratings yet
- Exfoliative CytologyDocument9 pagesExfoliative Cytologymiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- Pulmonology May 28Document76 pagesPulmonology May 28Brielle ShoppNo ratings yet
- Rle RequirementsDocument8 pagesRle RequirementsUzziel Galinea TolosaNo ratings yet
- A New Approach To The Deposition of Elemental Boron and Boron-Based Coatings by Pulsed Magnetron Sputtering of Loosely Packed Boron Powder TargetsDocument6 pagesA New Approach To The Deposition of Elemental Boron and Boron-Based Coatings by Pulsed Magnetron Sputtering of Loosely Packed Boron Powder TargetsyouamareNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument2 pagesTable of ContentsPewter VulturelynxNo ratings yet
- European Commission: The Traineeships OfficeDocument3 pagesEuropean Commission: The Traineeships Officenasrine hachimNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Half LifeDocument5 pagesRadioactive Half LifeVietNo ratings yet
- BIG-IP Access Policy Manager CustomizationDocument118 pagesBIG-IP Access Policy Manager CustomizationDhananjai SinghNo ratings yet
- Helmut Lethen - Cool Conduct - The Culture of Distance in Weimar Germany (Weimar and Now - German Cultural Criticism) - University of California Press (2001) PDFDocument265 pagesHelmut Lethen - Cool Conduct - The Culture of Distance in Weimar Germany (Weimar and Now - German Cultural Criticism) - University of California Press (2001) PDFJaco CMNo ratings yet
- BS 0812-114 - 1989Document12 pagesBS 0812-114 - 1989عمر عمرNo ratings yet
- TR 101 - Issue 2Document101 pagesTR 101 - Issue 2ergismiloNo ratings yet
- Slogan Goes Here: Local Store Importing CompanyDocument1 pageSlogan Goes Here: Local Store Importing Company5gt6kdfdqhNo ratings yet
- ECF/SSF : 08 : 11: Rotex Double Rack and Pinion Actuator SeriesDocument20 pagesECF/SSF : 08 : 11: Rotex Double Rack and Pinion Actuator SeriesProcess Controls & ServicesNo ratings yet
- Valplast: Flexible, Esthetic Partial DenturesDocument4 pagesValplast: Flexible, Esthetic Partial Denturesአነኬ ቹህቺዶሃሠኪቺጆቺNo ratings yet
- Southwest Globe Times - Sep 8, 2011Document16 pagesSouthwest Globe Times - Sep 8, 2011swglobetimesNo ratings yet
- Philippine School Action Plan for Scouting ProgramDocument1 pagePhilippine School Action Plan for Scouting ProgramLaira Joy Salvador - ViernesNo ratings yet
- Math207 Portfolio1 2Document5 pagesMath207 Portfolio1 2api-297797024No ratings yet
- Literature Review On OscilloscopeDocument5 pagesLiterature Review On Oscilloscopedhjiiorif100% (1)
- Dead Reckoning and Estimated PositionsDocument20 pagesDead Reckoning and Estimated Positionscarteani100% (1)
- Hotel Training ReportDocument14 pagesHotel Training ReportButchick Concepcion Malasa100% (1)
- Touch-Tone Recognition: EE301 Final Project April 26, 2010 MHP 101Document20 pagesTouch-Tone Recognition: EE301 Final Project April 26, 2010 MHP 101Sheelaj BabuNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten Quarter 4 Standards For Lesson PlansDocument2 pagesKindergarten Quarter 4 Standards For Lesson PlansLydiaDietschNo ratings yet
- Op Art PresentationDocument17 pagesOp Art PresentationSilvija PećanacNo ratings yet
- Personal SWOT AnalysisDocument8 pagesPersonal SWOT AnalysisNamNo ratings yet
- Lauren Tarshis - (I Survived 05) - I Survived The San Francisco Earthquake, 1906Document66 pagesLauren Tarshis - (I Survived 05) - I Survived The San Francisco Earthquake, 1906Olga de Ramos100% (1)
- Congress Vienna QuestionsDocument5 pagesCongress Vienna QuestionsElliott CookNo ratings yet
- Test 5 Trig Functions 21Document4 pagesTest 5 Trig Functions 21Isabelle Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Logistic Growth Rate Functions Blumberg1968Document3 pagesLogistic Growth Rate Functions Blumberg1968Jonnathan RamirezNo ratings yet
- Who Are The Pleiadian Emissaries of LightDocument3 pagesWho Are The Pleiadian Emissaries of LightMichelle88% (8)
- Gaudapadacharya - The Founder of The Tradition of Advaita VedantaDocument4 pagesGaudapadacharya - The Founder of The Tradition of Advaita VedantasukubhNo ratings yet
- 14-01 Lista de Laptops - DistribuidoresDocument29 pages14-01 Lista de Laptops - DistribuidoresInkil Orellana TorresNo ratings yet
- Rhythm MP - The Music Page - Theory Made Easy For Little Children Level 1Document9 pagesRhythm MP - The Music Page - Theory Made Easy For Little Children Level 1AmilacicNo ratings yet