Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
6 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
CharkOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
6 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
6 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
CharkCopyright:
Available Formats
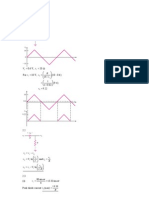
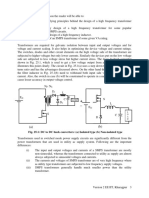
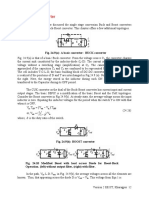
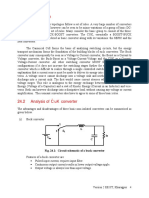
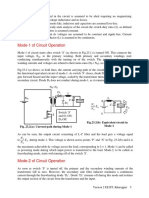
of the three. (In signal electronics the circuit of Fig. 12.
1 (a) is also known as the “maximum
value” circuit). Once the conduction diagram is drawn other waveforms of Fig. 12.1 (c) are
easily obtained from the supply voltage waveforms in conjunction with the conduction table.
The phase current waveforms of Fig. 12.1 (c) deserve special mention. All of them have a
dc component which flows through the ac source. This may cause “dc saturation” in the ac side
transformer. This is one reason for which the converter configuration is not preferred very much
in practice.
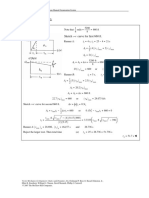
From the waveforms of Fig. 12.1 (c)
3 5π/6
2π ∫π/6
VOAV = 2Vi sin ωt d(ωt)
3 6
= Vi (12.1)
2π
1
⎡ 3 5π/6 ⎤2
VORMS = ⎢ ∫ 2Vi2 sin 2 ωt d(ωt) ⎥
⎣ 2π π/6 ⎦
1
⎡ 3 3 ⎤2
= ⎢1 + ⎥ Vi (12.2)
⎣ 4π ⎦
VORMS
∴ The output voltage form factor = = 1.01 (12.3)
VOAV
VOAV
IO av = ,
R
IO
Ii RMS = I a RMS = I b RMS = I c RMS = (12.4)
3
3 6
VO av IO Vi IO
3
∴ Input power factor = AV
= 2π = (12.5)
3Vi Ii RMS IO 2π
3Vi
3
The harmonics present in vo and ii can be found by Fourier series analysis of the
corresponding waveforms of Fig. 12.1 (c) and is left as an exercise.
Exercise 12.1
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
i) Three phase half wave uncontrolled rectifier uses ________ diodes.
ii) Three phase half wave uncontrolled rectifier requires ________ phase ______ wire
power supply.
Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 6
You might also like
- 01 Three-Phase Diode Rectifiers AsmarDocument65 pages01 Three-Phase Diode Rectifiers AsmarVenkedesh RNo ratings yet
- chp2 2Document7 pageschp2 2karen dejoNo ratings yet
- Multimedia From Wagner To Virtual Reality w2vrDocument89 pagesMultimedia From Wagner To Virtual Reality w2vrErmin AlicNo ratings yet
- PE Lect7.CompressedDocument18 pagesPE Lect7.CompressedWuri Adining BagaskaraNo ratings yet
- L12 Single Phase Uncontrolled RectifierDocument22 pagesL12 Single Phase Uncontrolled Rectifierapi-19951707100% (1)
- 11 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page11 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 1314 01 Solution 1Document17 pages1314 01 Solution 1NG JIAN RONG A20EE0177No ratings yet
- Three-Phase Uncontrolled RectifierDocument13 pagesThree-Phase Uncontrolled RectifierAHMAD ASRI ABD SAMATNo ratings yet
- Exp 3Document7 pagesExp 3Enas QtaifanNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Resistor Networks MSDocument7 pages1.3 Resistor Networks MSInnocent Takunda B ChidamoyoNo ratings yet
- 10.1201 9781315120782-3Document38 pages10.1201 9781315120782-3JAY CHHEDANo ratings yet
- 12 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-12 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- Computer Analysis of Rectifier CircuitsDocument13 pagesComputer Analysis of Rectifier CircuitsSisay FitwiNo ratings yet
- Ac To DC Conversion (Rectifier) : Power Electronics and Drives (Version 3-2003), Dr. Zainal Salam, 2003 1Document41 pagesAc To DC Conversion (Rectifier) : Power Electronics and Drives (Version 3-2003), Dr. Zainal Salam, 2003 1İbrahim KayğanNo ratings yet
- LAB 4: Three-Phase Uncontrolled Rectifier With PSIM Larning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesLAB 4: Three-Phase Uncontrolled Rectifier With PSIM Larning ObjectivesMO 'No ratings yet
- EEE255 Manual Part2Document5 pagesEEE255 Manual Part2Betül MalkoçNo ratings yet
- Ammeter Reading CurrentDocument4 pagesAmmeter Reading CurrentNoorNo ratings yet
- Ect205 SchemeDocument9 pagesEct205 SchemeExams YcetNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument18 pagesAlternating Current: Multiple Choice QuestionsUrja MoonNo ratings yet
- Notes2 PDFDocument21 pagesNotes2 PDFJameelAhmedNo ratings yet
- QN CollectionDocument96 pagesQN Collectionபொறிஞன்No ratings yet
- Single Phase RectifierDocument11 pagesSingle Phase RectifierYT ZhouNo ratings yet
- Unit4 1 80Document80 pagesUnit4 1 80Mukesh 2004No ratings yet
- AptlDocument5 pagesAptlDesmon SiagianNo ratings yet
- EE3501 01 EE3541 03 Power MeasurementsDocument9 pagesEE3501 01 EE3541 03 Power MeasurementsAvirup BiswasNo ratings yet
- Chap 02Document44 pagesChap 02張亭瑄No ratings yet
- 15 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- Rectifier Half WaveDocument15 pagesRectifier Half WaveFahrizaNo ratings yet
- LAB 12-PE-LabDocument9 pagesLAB 12-PE-LabLovely JuttNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document7 pagesChapter 6William LeiteNo ratings yet
- Assignment Power ElectronicDocument21 pagesAssignment Power ElectronicSeth RathanakNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Answer KeyDocument8 pagesCurrent Electricity - Answer KeyADITYA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document37 pagesUnit 3h2o_kazzike50% (2)
- Applied AerodynamicsDocument23 pagesApplied AerodynamicsAfiorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document21 pagesChapter 2yousifNo ratings yet
- Nee2102 1ec Castro Experiment 3Document9 pagesNee2102 1ec Castro Experiment 3AdrianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Solution D HartDocument32 pagesChapter 3 Solution D HartDavid UribeNo ratings yet
- TransTransmission Matrix (ABCD) Mission Matrix (ABCD) PDFDocument7 pagesTransTransmission Matrix (ABCD) Mission Matrix (ABCD) PDFandywangjsNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 5Document5 pagesTutorial Sheet 5Kanishka MahantyNo ratings yet
- Lab No. 5 Vector MeasurementsDocument14 pagesLab No. 5 Vector Measurementsmihaela0chiorescuNo ratings yet
- Sketch Curve For First 660 FT.: Chapter 11, Solution 72Document2 pagesSketch Curve For First 660 FT.: Chapter 11, Solution 72LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- A Unified Approach For Designing CapacitDocument6 pagesA Unified Approach For Designing CapacitMehmet AKBABANo ratings yet
- 20 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page20 - L-9 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)GagneNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits 1 Mid-Term Exam 1Document5 pagesElectronic Circuits 1 Mid-Term Exam 1정연종No ratings yet
- Book Text2 TransitoriosDocument16 pagesBook Text2 TransitoriosRichard PolNo ratings yet
- Baek 2011Document6 pagesBaek 2011Will TedjoNo ratings yet
- Problem Solutions: For 10 V, 10 0.6 1 9.4 1 0.02 9.22 + +Document18 pagesProblem Solutions: For 10 V, 10 0.6 1 9.4 1 0.02 9.22 + +api-3741518No ratings yet
- Problem Solutions: For 10 V, 10 0.6 1 9.4 1 0.02 9.22 + +Document18 pagesProblem Solutions: For 10 V, 10 0.6 1 9.4 1 0.02 9.22 + +sulayajannyNo ratings yet
- ALTERNATING CURRENTS (Ansset)Document12 pagesALTERNATING CURRENTS (Ansset)vishwanath c kNo ratings yet
- C-Double Line-to-Ground (2L-G) FaultDocument9 pagesC-Double Line-to-Ground (2L-G) FaultEsraa MagdyNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Modeling of Transmission Lines: Figure 4-9Document17 pages4.5 Modeling of Transmission Lines: Figure 4-9shashm024No ratings yet
- Lab ExperimentDocument63 pagesLab Experimentali dhiaNo ratings yet
- JEn Questions Bank EE Power SystemDocument13 pagesJEn Questions Bank EE Power SystemjohnNo ratings yet
- E103 - Mesh Analysis and Nodal AnalysisDocument16 pagesE103 - Mesh Analysis and Nodal AnalysisRick Alviento0% (1)
- Document 1Document4 pagesDocument 1SYAFIQAH ISMAILNo ratings yet
- ECECM2 - BALIDIO ASHLIE JANE - BSECE 3B-MIDTERM ASSIGNMENT 01sep 13, 2023Document1 pageECECM2 - BALIDIO ASHLIE JANE - BSECE 3B-MIDTERM ASSIGNMENT 01sep 13, 2023Ashlie JaneNo ratings yet
- EE21L Experiment 4Document11 pagesEE21L Experiment 4asnajhjas asashladaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 14 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page14 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 11 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page11 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- Depth Anything: Unleashing The Power of Large-Scale Unlabeled DataDocument18 pagesDepth Anything: Unleashing The Power of Large-Scale Unlabeled Dataroyalatlas.stashNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information Systems: ITEC 1010 Information and OrganizationsDocument77 pagesIntroduction To Information Systems: ITEC 1010 Information and Organizationsmanojmis2010No ratings yet
- CV Bookkeeper Resume ExampleDocument2 pagesCV Bookkeeper Resume ExampleCos_sensNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter - ArraysDocument26 pagesNCERT Solutions Class 12 Computer Science Chapter - ArraysinfinilifeNo ratings yet
- ML-C and C Micro PDFDocument94 pagesML-C and C Micro PDFvulcanescuNo ratings yet
- Pico Bricks Ebook 15Document234 pagesPico Bricks Ebook 15PifNo ratings yet
- Service Advisory - Corrosive Sulfur in Power Bushings: Product Group Insulation & ComponentsDocument2 pagesService Advisory - Corrosive Sulfur in Power Bushings: Product Group Insulation & ComponentsCarlos CastellonNo ratings yet
- Kids Scooters CatalogDocument46 pagesKids Scooters CatalogwalterquispeochoaNo ratings yet
- Installation Profiles Xmlweb1Document44 pagesInstallation Profiles Xmlweb1ben_tosNo ratings yet
- 308.8355.3.4-7 DEUTZ-FAHR Product Range 2021 EN 1Document80 pages308.8355.3.4-7 DEUTZ-FAHR Product Range 2021 EN 1gilanoNo ratings yet
- 5.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN RoutingDocument5 pages5.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN RoutingMuhammad AfNanzNo ratings yet
- Stream Control Transmission Protocol SCTPDocument46 pagesStream Control Transmission Protocol SCTPAnonymous g6KREjNo ratings yet
- MATERIAL HANDLING TIRES - Cauchos de MontacargasDocument33 pagesMATERIAL HANDLING TIRES - Cauchos de MontacargasDavid AlfonzoNo ratings yet
- PC1 - Portal Essentials PDFDocument100 pagesPC1 - Portal Essentials PDFAnonymous GGuA0vbGhGNo ratings yet
- Innovative Conceptual Design - Theory and Application of Parameter AnalysisDocument247 pagesInnovative Conceptual Design - Theory and Application of Parameter AnalysissakthivelNo ratings yet
- RadikalismeDocument18 pagesRadikalismeindah listiowatiNo ratings yet
- RCG Instrumentation CablesDocument38 pagesRCG Instrumentation CablesNo BiiNo ratings yet
- VFP Questions - Test 1Document1 pageVFP Questions - Test 1Rahul JoshiNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1350630719314220 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S1350630719314220 MainDikehiNo ratings yet
- Cwa14050 03 2000 NovDocument73 pagesCwa14050 03 2000 Nov김종희No ratings yet
- FormA Project Title and Synopsis For PSMDocument2 pagesFormA Project Title and Synopsis For PSMelleyashahariNo ratings yet
- Visual Notification Assistant Datasheet enDocument2 pagesVisual Notification Assistant Datasheet enArthur Alves OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Experience:: Naveen Kumar VemulapalliDocument2 pagesExperience:: Naveen Kumar VemulapalliiamabigstoneNo ratings yet
- Micro DNC 2 User Manual EnglishDocument30 pagesMicro DNC 2 User Manual Englishmtpvina.hdnNo ratings yet
- Metlogix - Oprogramowanie M3 - 2012 ENDocument5 pagesMetlogix - Oprogramowanie M3 - 2012 END.T.No ratings yet
- FullBulletinReport 5555 29112019 125642Document11 pagesFullBulletinReport 5555 29112019 125642Chief Minister's Helicopter Flight, SindhNo ratings yet
- Functional Manual: Kelvin HughesDocument55 pagesFunctional Manual: Kelvin HughesMohamed ElhossenyNo ratings yet
- Scifest - 2021 - 22Document8 pagesScifest - 2021 - 22Sanjog RathodNo ratings yet
- Eaton DX-RT 06-10 kVA User ManualDocument56 pagesEaton DX-RT 06-10 kVA User ManualTiago PereiraNo ratings yet