Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.7 - Theoretical Concepts of Engine Components - EN - REV - 0
Uploaded by
cafubodoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.7 - Theoretical Concepts of Engine Components - EN - REV - 0
Uploaded by
cafubodoCopyright:
Available Formats
WWW.GRUPEL.
EU
THEORETICAL CONCEPTS OF ENGINE
COMPONENTS
MODULE 2.7
DISTRIBUTORS TRAINING
Themes
01 : Special tools
02 : Engine components
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
01 : Special tools
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
01 : Special tools
Each engine needs its specific tools in order to perform the most
demanding jobs.
Examples of Perkins special tools :
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
01 : Special tools
Examples of Iveco FPT tools :
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
02: Engine components
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
02: Engine components
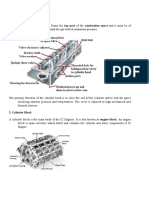
Cylinder
The cylinder consists of three different elements:
Cylinder head, cylinder block and crankcase
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
02: Engine components
Cylinder head
The engine cylinder head may be a single part for all
cylinders or be completely individualized per
cylinder. The cylinder heads are complex
components since they may include the inlet and
outlet channels, the housings of the respective
valves and rockers, cooling chambers and injectors
housing.
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
02: Engine components
Cylinder block
The cylinder block constitutes the housing of the cylinder liners and the base to fix
the cylinder head.
It can be in line shape or in V shape.
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
02: Engine components
Oil sump
The oil sump is where the engine oil is kept.
Also is where the oil pump strainer is going to be to aspirate the oil.
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
02: Engine components
Cylinder liner
Its main functions are to guide the piston in its
movement, to ensure, together with the piston rings
and the piston, the seal of the exhaust gases
contained within the cylinder and to promote the
heat dissipation necessary for the operation of the
engine.
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
03: Engine components
Piston
It’s divided into two parts, crown or head and tab or skirt.
On the side surface are the piston rings housings.
The piston must fulfill the following functions:
to withstand the efforts to which it is subject
to seal, with the piston rings and the cylinder liner,
the volume of the cylinder
promote adequate heat dissipation
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
03: Engine components
Piston rings
The piston rings play a key role in sealing the combustion chamber.
The number of piston rings used depends on the maximum
combustion pressure and engine speed. The higher the
combustion pressure and the slower the rotational speed, the
more are used.
There are two types of piston rings:
Compression rings
Oil scraper rings
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
03: Engine components
Connecting rod
Ensure the connection between the piston
and the crankshaft.
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
03: Engine components
Crankshaft
The crankshaft, together with the connecting rods,
converts the alternating rectilinear movement of
the piston into rotating movement. It consists of
the support and crank trunnions, crank arms and
counterweights.
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
03: Engine components
Camshaft
The camshaft receives movement of the crankshaft
through toothed gears or through toothed wheels
joined by a distribution current. In four-stroke engines,
since the operations only repeat every two engine
revolutions, the rotation speed of this shaft is half the
speed of rotation of the crankshaft.
It has the function to actuate the valves.
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
03: Engine components
Impellers and rockers
They have the function to
transmit the movement between
the camshaft and the valves.
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
03: Engine components
Valves
Usually the intake and exhaust valves have equal dimensions,
however, as they are subject to different temperatures, they
have different materials in their composition.
The purpose of the clearance is to compensate for the
expansion of the valve stem, which occurs when the engine
reaches its normal operating condition.
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
03: Engine components
Injectors
They have the function of atomizing the fuel in the
combustion chamber, pressurized by the injection pump and
set the injection pressure. The nozzles have different number
of atomization holes.
There are several types of injectors, namely the unit injector,
which have the function of compressing and atomizing the
fuel.
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
03: Engine components
Injection pumps
They have the function to compress the fuel to the injectors.
There are rotative and in-line type.
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
03: Engine components
Water pump
Its function is to circulate the coolant through
the engine and the radiator. The water pump
can be coupled to the engine and driven by a
gear or can be actuated by belts.
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
03: Engine components
Oil pump
Its function is to draw the oil from the oil sump and compress it to
a certain pressure for the movable contact elements of the engine,
in order to form a thin layer between elements subjected to wear
The pressure of the oil varies with its temperature, the higher the
temperature, the lower the pressure.
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
03: Engine components
Thermostatic Valves: Their function is to
regulate the engine’s coolant temperature.
Thermostatic valves consist of a housing which
contains a wax therein, which expands with the
temperature rise of the engine coolant and allows
the valve to open.
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
03: Engine components
Turbocharger
The turbocharger is driven by the exhaust of the
engine through a turbine, which transmits its
movement to a compressor that allows the suction
and compression of the air. In practice the
turbocharger allows the increase of the engine
displacement without increasing the size of the
engine, giving a higher power for a reduced size.
MODULE 2.7. | Theoretical concepts of engine components|
Thank you
You might also like
- Honda Breeze Industrial Report: Session 2017-2021Document30 pagesHonda Breeze Industrial Report: Session 2017-2021Atta AttaullahNo ratings yet
- It Abhinav Main 22Document11 pagesIt Abhinav Main 22Abhinav GhoshNo ratings yet
- Lab Name: Demonstration and Study The Different Parts of Car Section ModelDocument17 pagesLab Name: Demonstration and Study The Different Parts of Car Section ModelHussain Ahmad DhillonNo ratings yet
- 3 Lab Manual ICE 3171923 Odd 2021Document24 pages3 Lab Manual ICE 3171923 Odd 2021Akhilesh NavikNo ratings yet
- Audi 2.0 Ltr. 4-Cylinder TDI Engine EA288evo Series: Self-Study Programme 671Document40 pagesAudi 2.0 Ltr. 4-Cylinder TDI Engine EA288evo Series: Self-Study Programme 671asd100% (6)
- Lab Session 3Document14 pagesLab Session 3Shahid FarooqNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument44 pagesInternal Combustion EnginesPoseidonNo ratings yet
- Vehicle EngineDocument31 pagesVehicle EnginenoahNo ratings yet
- Fuelihng of IC EngineDocument124 pagesFuelihng of IC EngineTalha MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- IC Engine - Lecture 1Document55 pagesIC Engine - Lecture 1darshan008No ratings yet
- Assignment in EorDocument3 pagesAssignment in Eorkerbzb15No ratings yet
- ICE Lecture NotesDocument12 pagesICE Lecture NotesRajueswar100% (1)
- 01 Engine System LG956LDocument100 pages01 Engine System LG956LGeorge Jhonson100% (11)
- Labreport 2Document5 pagesLabreport 2Ezaz ul haqNo ratings yet
- Fahel Bodi ReportDocument20 pagesFahel Bodi ReportFahel Bin NoorNo ratings yet
- Ch2Document34 pagesCh2papipapiiNo ratings yet
- LG936 Training Material: Chapter 3 Engine Structure PrincipleDocument51 pagesLG936 Training Material: Chapter 3 Engine Structure Principlemliugong100% (2)
- Industrial Plants AssignementDocument11 pagesIndustrial Plants Assignementjoseph james makafuNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Diesel Engine, System of Injection, Fuel ChargingDocument5 pagesKeywords: Diesel Engine, System of Injection, Fuel ChargingNikola PetrovicNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument41 pagesLab Reportharoon100% (1)
- Principles of An Internal Combustion Engine - Rev.2Document37 pagesPrinciples of An Internal Combustion Engine - Rev.2Nitish GunessNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine Repair and Maintenance 03Document20 pagesDiesel Engine Repair and Maintenance 03Mas Dwi LestariNo ratings yet
- 4 Strock (1) M - MergedDocument13 pages4 Strock (1) M - MergedDilshadNo ratings yet
- Fuel Is Any Material That Can Be Made ToDocument13 pagesFuel Is Any Material That Can Be Made TojhanelleNo ratings yet
- 2 Report-Arab-ContractorsDocument24 pages2 Report-Arab-ContractorsHunter studyNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITIESDocument14 pagesACTIVITIESlamsonmarkninoeNo ratings yet
- Engine Component 1Document6 pagesEngine Component 1anuradhaNo ratings yet
- Final Engine ProjectDocument38 pagesFinal Engine Projectvinayharish02002No ratings yet
- AURTTE008Document7 pagesAURTTE008yash KhatodeNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Engine Parts Design: G.T.U. B.E. (Mech) Sem-Viii 2011-12Document61 pagesReciprocating Engine Parts Design: G.T.U. B.E. (Mech) Sem-Viii 2011-12Divyraj JadejaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering-2 PracticalDocument35 pagesThermal Engineering-2 PracticalAlok Anand100% (1)
- CH 2 Engine ComponentDocument23 pagesCH 2 Engine Componenteyukaleb4No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 CrankshaftDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 2 CrankshaftAUNG0% (1)
- Week 3 JDVP ModuleDocument17 pagesWeek 3 JDVP ModuleMarcel Baring ImperialNo ratings yet
- What Are The Main Parts of An Automobile Engine?: 1. Cylinder BlockDocument13 pagesWhat Are The Main Parts of An Automobile Engine?: 1. Cylinder BlockMr. Jerome Nithin GladsonNo ratings yet
- Final Engine Report.Document28 pagesFinal Engine Report.Chethu ChethuNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1.1 Background InformationDocument32 pagesChapter One 1.1 Background InformationChidinma Glory Ejike100% (1)
- Mar Power Week 1Document15 pagesMar Power Week 1DarkxeiDNo ratings yet
- Reverse Engineering of A Rotary Injection Fuel Pump Project ReportDocument38 pagesReverse Engineering of A Rotary Injection Fuel Pump Project ReportZuber AbbunaverNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 ME LABORATORYDocument7 pagesActivity 6 ME LABORATORYAlan Jade de LeonNo ratings yet
- EngineDocument41 pagesEngineGurmeet Mehma100% (5)
- To Study The Stationary and Moving Automobile Parts PDFDocument16 pagesTo Study The Stationary and Moving Automobile Parts PDFTAHIR QAMAR100% (2)
- Central RailwayDocument14 pagesCentral RailwayLazy ManNo ratings yet
- Atb 203-Automotive Petrol Engines: M.Hema Kumar, M.Tech., Assistant Professor, Dept of Automobile EngineeringDocument65 pagesAtb 203-Automotive Petrol Engines: M.Hema Kumar, M.Tech., Assistant Professor, Dept of Automobile EngineeringMathankumar RNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 PDFDocument11 pagesExercise 5 PDFErica AbelardoNo ratings yet
- Assignment #1Document4 pagesAssignment #1Usman Ali Usman AliNo ratings yet
- IC Engines Power Transmission: Module ContentDocument8 pagesIC Engines Power Transmission: Module ContentVinayaka GpNo ratings yet
- Mte 3 Report 4Document8 pagesMte 3 Report 4Zeke KazamiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Lab ReportDocument60 pagesThermodynamics Lab ReportMuhammad Nouman RashidNo ratings yet
- Construction Details PDFDocument58 pagesConstruction Details PDFP.Prem Kumar AP - I - MechanicalNo ratings yet
- Abhay Mini InternshipDocument23 pagesAbhay Mini InternshipAbhay Raaj YadavNo ratings yet
- Course: Ic Engine LabDocument8 pagesCourse: Ic Engine LabUsman Ali Usman AliNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Deactivation System - An IntroductionDocument20 pagesCylinder Deactivation System - An IntroductionGiridharan VNo ratings yet
- Cams Day 2Document86 pagesCams Day 2u2003067No ratings yet
- Module 3 PDFDocument27 pagesModule 3 PDFkaushal shivaprakashNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power StationDocument30 pagesDiesel Power StationGerald EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Mbeya Institute of Science and Technology: Power Plants Lecture No 6 Diesel Engine Power PlantsDocument68 pagesMbeya Institute of Science and Technology: Power Plants Lecture No 6 Diesel Engine Power PlantsNyandaMadili MalashiNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Seminar AssociateDocument20 pagesAcknowledgement: Seminar Associateabbas abbuNo ratings yet
- Engine Performance Study GuideDocument34 pagesEngine Performance Study GuideJean R. Desir100% (1)
- Naval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyFrom EverandNaval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyNo ratings yet
- October Revision Final (darsenglizy.com موقع درس انجليزي)Document17 pagesOctober Revision Final (darsenglizy.com موقع درس انجليزي)cafubodoNo ratings yet
- Catalogue 4830 DDocument2 pagesCatalogue 4830 DcafubodoNo ratings yet
- كونكت بلس - 2 ابتدائي - ترم 1 - مذكرة 2Document86 pagesكونكت بلس - 2 ابتدائي - ترم 1 - مذكرة 2cafubodoNo ratings yet
- Time Swtiches CatalogDocument15 pagesTime Swtiches CatalogcafubodoNo ratings yet
- مذكرة ديسكفر للصف الثاني الابتدائي الترم الاولDocument62 pagesمذكرة ديسكفر للصف الثاني الابتدائي الترم الاولcafubodoNo ratings yet
- ماث - 5 ابتدائي - ترم 1 - مذكرة 2 - ذاكروليDocument72 pagesماث - 5 ابتدائي - ترم 1 - مذكرة 2 - ذاكروليcafubodoNo ratings yet
- Automatic Fuel Tank Monitoring Tracking Theft DeteDocument4 pagesAutomatic Fuel Tank Monitoring Tracking Theft DetecafubodoNo ratings yet
- MTU Gendrive Spec 2000G 05 3D W2ADocument4 pagesMTU Gendrive Spec 2000G 05 3D W2AcafubodoNo ratings yet
- AtyS D M LeafletDocument2 pagesAtyS D M LeafletcafubodoNo ratings yet
- G16 IntelysisDocument190 pagesG16 IntelysiscafubodoNo ratings yet
- Day Tanks - Model DT CutsheetDocument3 pagesDay Tanks - Model DT CutsheetcafubodoNo ratings yet
- 2.3 - Controllers Part 2 - EN - REV - 0Document38 pages2.3 - Controllers Part 2 - EN - REV - 0cafubodoNo ratings yet
- JY Series: 1 POLE - 3, 5A Medium Load ControlDocument8 pagesJY Series: 1 POLE - 3, 5A Medium Load ControlcafubodoNo ratings yet
- Rimula r4x 15w40 MsdsDocument20 pagesRimula r4x 15w40 MsdscafubodoNo ratings yet
- WP5B2368 3Document1 pageWP5B2368 3cafubodoNo ratings yet
- كلمة حقDocument136 pagesكلمة حقcafubodoNo ratings yet
- Is209 12a Esshutterfan SDDocument3 pagesIs209 12a Esshutterfan SDcafubodoNo ratings yet
- TLL130 Installation InstructionsDocument2 pagesTLL130 Installation InstructionscafubodoNo ratings yet
- Dse334 PC Software Manual enDocument36 pagesDse334 PC Software Manual encafubodo100% (2)
- 2.2 - Controllers Part 1 - en - REV - 0Document21 pages2.2 - Controllers Part 1 - en - REV - 0cafubodoNo ratings yet
- 2.5 - Theoretical Concepts of Consumables Replacement - EN - REV - 0Document26 pages2.5 - Theoretical Concepts of Consumables Replacement - EN - REV - 0cafubodoNo ratings yet
- Mutual Standby With Dse 7310 & Dse333Document3 pagesMutual Standby With Dse 7310 & Dse333cafubodoNo ratings yet
- Tails GuideDocument33 pagesTails GuidecafubodoNo ratings yet
- 2.6 - Theoretical Concepts of Alternator Inspection and Maintenance - EN - REV - 0Document47 pages2.6 - Theoretical Concepts of Alternator Inspection and Maintenance - EN - REV - 0cafubodoNo ratings yet
- Eac 171-1Document20 pagesEac 171-1cafubodoNo ratings yet
- Parts Breakdown: Technical ServiceDocument3 pagesParts Breakdown: Technical ServicecafubodoNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics: 16V2000G65E G3Document5 pagesGeneral Characteristics: 16V2000G65E G3cafubodoNo ratings yet
- Model Exam 1: Question 1 1)Document35 pagesModel Exam 1: Question 1 1)cafubodoNo ratings yet
- Rosenberg Image enDocument20 pagesRosenberg Image encafubodoNo ratings yet
- Ecar 171 Issued Oct 2020Document35 pagesEcar 171 Issued Oct 2020cafubodoNo ratings yet
- Main Girders: CrossDocument3 pagesMain Girders: Crossmn4webNo ratings yet
- Biology Accel Syllabus 2011-2012Document3 pagesBiology Accel Syllabus 2011-2012Mike DeleonNo ratings yet
- DOC-20161226-WA0009 DiagramaDocument61 pagesDOC-20161226-WA0009 DiagramaPedroNo ratings yet
- C.Abdul Hakeem College of Engineering and Technology, Melvisharam Department of Aeronautical Engineering Academic Year 2020-2021 (ODD)Document1 pageC.Abdul Hakeem College of Engineering and Technology, Melvisharam Department of Aeronautical Engineering Academic Year 2020-2021 (ODD)shabeerNo ratings yet
- Impact of Retrofitting Existing Combined Heat and Power Plant With Polygeneration of Biomethane PDFDocument16 pagesImpact of Retrofitting Existing Combined Heat and Power Plant With Polygeneration of Biomethane PDFAwais Salman0% (1)
- Emw 2007 FP 02093Document390 pagesEmw 2007 FP 02093boj87No ratings yet
- Logic NotesDocument19 pagesLogic NotesCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Process Costing Exercises Series 1Document23 pagesProcess Costing Exercises Series 1sarahbeeNo ratings yet
- Sat Vocabulary Lesson and Practice Lesson 5Document3 pagesSat Vocabulary Lesson and Practice Lesson 5api-430952728No ratings yet
- Runyankore-Rukiga Dictionary Launch: President Yoweri Museveni's SpeechDocument28 pagesRunyankore-Rukiga Dictionary Launch: President Yoweri Museveni's SpeechThe New Vision50% (2)
- Astm C892 - 00Document5 pagesAstm C892 - 00reneeNo ratings yet
- Recipes From The Perfect Scoop by David LebovitzDocument10 pagesRecipes From The Perfect Scoop by David LebovitzThe Recipe Club100% (7)
- Purpose in LifeDocument1 pagePurpose in Lifeaashish95100% (1)
- Ad149 Manual RDocument69 pagesAd149 Manual RCharityNo ratings yet
- CBSE DetailsDocument6 pagesCBSE DetailsNARESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Muscular SystemDocument29 pagesChapter 7 - Muscular SystemlNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Mat435Document2 pagesAssignment 2 Mat435Arsene LupinNo ratings yet
- SAT Practice TestDocument77 pagesSAT Practice TestfhfsfplNo ratings yet
- 12/1/2014 Powder MetallurgyDocument29 pages12/1/2014 Powder Metallurgysofyan sam0% (2)
- Straight LineDocument15 pagesStraight LineAyanNo ratings yet
- Why Are Solids Are Floating On My Secondary Clarifier - Biological Waste TreatmDocument6 pagesWhy Are Solids Are Floating On My Secondary Clarifier - Biological Waste TreatmIsaac FernándezNo ratings yet
- Esteem 1999 2000 1.3L 1.6LDocument45 pagesEsteem 1999 2000 1.3L 1.6LArnold Hernández CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Digging Deeper: Can Hot Air Provide Sustainable Source of Electricity?Document2 pagesDigging Deeper: Can Hot Air Provide Sustainable Source of Electricity?Рустам ХаджаевNo ratings yet
- Inferring The Speaker's Tone, ModeDocument31 pagesInferring The Speaker's Tone, Modeblessilda.delaramaNo ratings yet
- A Year On A FarmDocument368 pagesA Year On A FarmvehapkolaNo ratings yet
- DISPOSABLE GLOVES CATALOG 2023npDocument4 pagesDISPOSABLE GLOVES CATALOG 2023npTeodylee CruzNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis and Design of Pressure Hulls - The State of The Art and Future TrendsDocument118 pagesStructural Analysis and Design of Pressure Hulls - The State of The Art and Future TrendsRISHABH JAMBHULKARNo ratings yet
- Determinants - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02) - Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024Document3 pagesDeterminants - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02) - Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024Apurv ChitranshNo ratings yet
- DR PDFDocument252 pagesDR PDFa_ouchar0% (1)
- The Light Fantastic by Sarah CombsDocument34 pagesThe Light Fantastic by Sarah CombsCandlewick PressNo ratings yet