100% found this document useful (24 votes)
14K views3 pagesPathophysiology BPH Case Study
continuation of BPH case study
For anyone's wishing to download my files just look for me in friendster and facebook.. I don't open this account very often.. jst look for satchuna.. thanks..
Uploaded by
yhanneCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (24 votes)
14K views3 pagesPathophysiology BPH Case Study
continuation of BPH case study
For anyone's wishing to download my files just look for me in friendster and facebook.. I don't open this account very often.. jst look for satchuna.. thanks..
Uploaded by
yhanneCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
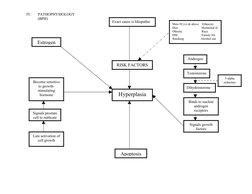
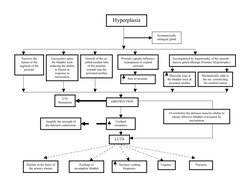
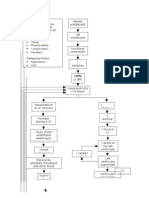
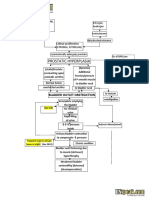
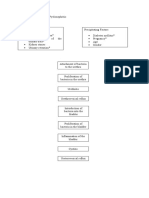
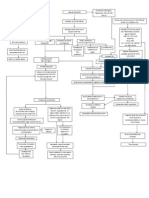
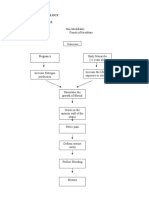
- Pathophysiology of Hyperplasia: Explores risk factors and cellular processes in the pathophysiology of hyperplasia, including hormonal sensitivity and apoptosis.
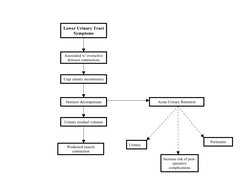
- Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Explains symptomatology related to detrusor muscle function and post-operative complications in lower urinary tract symptoms.