Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Miñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and Mandible
Uploaded by
Marion Rodelle Miñano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Miñano_[OS 204] PN 2 - Skull and Mandible
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and Mandible
Uploaded by
Marion Rodelle MiñanoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
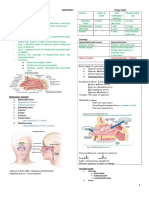
Marion Miñano OS 204 Portfolio Note 2 Skull and Mandible ethmoidal Muscle attachment 7 – Lateral pterygoid
foramina 9 – Medial pterygoid
Skull Supraorbital Nerves and BV will also come out here 11 – Mylohyoid
and Infraorbital 16 - Temporalis
Adult skull foramina Muscles of mastication Medial and lateral pterygoid, Masseter, Temporalis
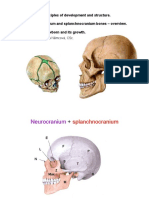
Top – Intramembranous, Bottom - Endochondral Maxillary bone Hollow inside for maxillary sinus; Maxillary hiatus – drainage of Maxilla
Neurocranium Paired – Parietal, Temporal maxillary sinus into nasal cavity Upper jaw; Form anterior nasal spine along inf surface of nasal cavity
Unpaired – Occipital, Ethmoid, Sphenoid Infraorbital Ophthalmic → Ant and pos ethmoidal arteries →Ethmoid bone (palpable); Contains infraorbital margin and inferior orbital surface
Viscerocranium Paired – Nasal, Inferior nasal conchae, Lacrimal, Palatine, ophthalmic Internal carotid A – supplies eyeball thru central retinal A Infraorbital foramen Passage for infraorbital artery and nerve
Zygoma, Maxilla artery Alveolar processes Inferior portions of maxilla; House upper set of
Unpaired – Vomer, Mandible Paranasal sinuses teeth
Foramina Supraorbital, Infraorbital, Mental, Foramen magnum Air-filled chambers; Mucus lining humidify and warm inhaled air; Provides Hard palate Ant - Palatine process of maxilla
Sutures Lambdoid, Coronal, Sagittal resonance; Need a way to drain into nose Pos – Palatine bone
Pterion Meeting of frontal, sphenoid, squamous temporal and parietal Frontal and Maxillary sinus drains into maxillary hiatus (Palpable)
bones Maxillary Maxillary sinus Lateral to nasal cavity in each maxilla
Asterion Meeting of parietal, occipital and temporal bones Ethmoid Right next to eyeballs Zygomatic process Lateral articulation of maxilla w/ zygomatic bone
Neonate skull Sphenoid Most posterior Frontal process Superior articulation of maxilla w/ frontal bone
Many suture still open; Ossifies late in 2nd month; Frontal bone = fusion of 2 frontal Bony septum Formed by perp plate of ethmoid and vomer
bones connected by metopic suture; Mandible + Frontal bones start as 2 halves Vomer – divides posterior part of nasal cavity
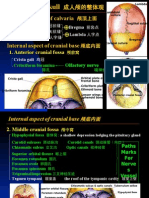
then fuse Landmarks of Cranial Fossa Sella turcica Houses pituitary gland; Easier to go trans-
Fontanelles sphenoidal
Fibrous CT; Allow overlap to lessen transverse and anteroposterior diameters Foramen Passing Structures Medial and lateral Extensions of sphenoid bone
during childbirth; Cover unfused sutures; Allows skull to flex during birth = more Anterior Cranial Fossa pterygoid plates
pliable for passage into birth canal Foramen cecum Emissary vein fr/ superior sagittal sinus Incisive fossa Depression behind incisors
Lateral Overlain by temporalis muscle; Fuse at infancy; Sphenoid Foramina of cribriform Olfactory nerve (CN I ) bundles Incisive foramen Near ant margin of fused palatine processes; Lies
fontanelle fontanelle, Mastoid fontanelle – Closes 18 months after birth plate in hard palate directly behind incisors; Carries
Anterior Largest, becomes bregma; Closes 18 months after birth Middle Cranial Fossa sphenopalatine artery and nasopalatine nerve
fontanelle Optic Canal Optic nerve (CN I); Ophthalmic artery Palatine bone
Posterior Triangular, becomes lambda, Closes 1-2 months after birth Superior Orbital Fissure Oculomotor nerve (CN III); Trochlear nerve (CN IV); Small; Distinct L shape; Form part of hard palate, nasal cavity and orbit
fontanelle Abducens (CN VI); Lacrimal, frontal, nasociliary Horizontal plate Contains greater and lesser palatine foramina – NV
Sutures branches of ophthalmic division of trigeminal nerve ( CN supply of upper teeth; Forms pos portion of hard
Synathroidal (immovable), Formed thru ossification V1); Superior ophthalmic vein palate
Coronal suture Divides frontal and parietal Foramen Rotundum Maxillary division of trigeminal nerve (CN V2) Perpendicular plate Forms part of lateral wall of nasal cavity and
Sagittal suture Divides paired parietal Foramen Ovale Mandibular division of trigeminal nerve (CN V3); choana (posterior nasal aperture)
Lambdoid Divides parietal and temporal Accessory meningeal artery Orbital process Forms part of medial wall of orbit
suture Foramen Spinosum Middle meningeal artery and vein
Bregma Meeting of coronal and sagittal sutures; Bet frontal and parietal Foramen Lacerum Nothing; Internal carotid artery passes over
bones Posterior Cranial Fossa Nasal Complex
Lambda Meeting of lambdoid and sagittal sutures, Bet occipital and Internal Acoustic Facial nerve (CN VII); Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN
parietal Meatus VIII); Labyrinthine artery/ Internal acoustic artery Roof Cribriform plate; Parts of frontal and sphenoid
Ext occipital Bet occiput and subocciput; Landmark at posterior occipital Jugular Foramen Glossopharyngeal nerve(CN IX); Vagus nerve (CN X); bones
protuberance bone, Sometimes form islets Accessory nerve (CN XI); Sigmoid sinus; Posterior Floor Palatine processes of maxilla; Horiz plates of
Cranial cavity meningeal artery palatine bones
Internal surface, 3 large depressions from bowl-shaped floor Hypoglossal Canal Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) Lateral walls Ethmoid bone; Maxillae; Inferior nasal conchae;
Anterior cranial Shallowest; Occ by inferior and anterior parts of frontal lobes Foramen Magnum Medulla oblongata; Vertebral arteries; Meningeal Perpend plates of palatine and lacrimal bones
fossa Ant – frontal bone branches of vertebral arteries; Spinal roots of accessory Frontal bone
Greater part – Orbital parts of frontal bone nerves (CN XI) Connected to nasal complex thru opening of cribriform plate and ethmoid
Mid – Ethmoid sinus; Ethmoid sinus separated to orbit by lamina papyracae
Pos – Body and lesser wings of sphenoid Nasal bone
Middle cranial Butterfly shape; Border bet mid and pos cranial fossa Jaw and Roof of Mouth Paired bones; Medial edge of each maxilla articulates w/ lateral edge of bone;
fossa Central – Sella turcica, Sphenoid Articulates w/ frontal bone (nasion); Commonly fractured
Lateral – Greater wings of sphenoid, Squamous parts of Mandible Lacrimal bone
temporal bones (lat), Petrous parts of temporal bones (pos) Entire lower jaw; Supports inferior teeth; Provides attachment for muscles of Small paired from medial wall of each orbit
Posterior Largest and deepest; Lodges cerebellum, pons and medulla mastication Lacrimal groove Inferior opening for nasolacrimal duct (drains tears
cranial fossa oblongata Horizontal body Contains mental foramen w/c transmits mental into nasal cavity)
Mostly – Occipital bone nerve (CN V) for chin Lacrimal fossa Houses lacrimal sac (drains tears into nasal cavity)
Ant and cent – Dorsum sellae of sphenoid Rami Ascending vertical posterior; Medial contains not lacrimal gland
AL – Petrous and mastoid parts of temporal bones mandibular foramen – transmits inf alveolar nerve Lacrimal gland Secrete tears; Travels posteromedially → Lacrimal
Orbit and BV for teeth sac → Nasolacrimal duct → Inferior nasal concha
Roof – Orbital part of frontal bone and Lesser wing of sphenoid Alveolar process Ridge that contains teeth Vomer
Floor – Orbital surface of maxilla, Maxillary process of zygoma and orbital process
Angle of mandible Intersection of rami and body Thin, flat forms part of posteroinferior part of nasal septum; Laterally –
of palatine bone
Mental protuberance Point of chin triangular (farming plow)
Lat – Zygomatic process of frontal bone, Orbital process of palatine bone
Condylar process Terminates at the head of mandible for TMJ Articulations of Vomer Midline – maxilla and palatine bones
Med – Frontal bone, Frontal process of maxilla, Lacrimal bone, Ethmoid bone
Coronoid process Insertion of temporalis muscle Horiz pos projection – sphenoid bone
Pos – Sphenoid bone
Temporalis – fanlike at side of head; Elevate jaw Vert plate – perpend plate of ethmoid bone
Supraorbital Transmits supraorbital BV and nerve; Sometimes foramen
and close mouth Vomer + perpend plate = bony nasal septum
notch
Mylohyoid line Attachment of mylohyoid (floor of mouth) Ethmoid bone
Anterior and Bet frontal and ethmoid bone; Transmits Ant and Pos BV and
Mental spines Attachment for tongue muscles (geniohyoid, Most int hidden bone; Bet nasal (ant), sphenoid (pos) and parts of frontal (lat)
posterior nerves coming from Ophthalmic A
genioglossus)
Functions of Ethmoid Forms anteromedial floor of cranium; Roof of nasal Zygomaxillaryfronto inward; Contrecoup fracture – no fracture at point of
cavity; Part of nasal septum and medial orbital wall; suture impact but occurs on opposite side of cranium
Ethmoidal air cells Pterygo Bridge bet posterior maxilla (palatine Bone Flaps Craniotomy - section of neurocranium (bone flap) is
Crista galli Most superior; Median ridge of bone projects sup maxillar process) and pterygoid plates elevated or removed; Adult pericranium has poor bone
into ant cranial fossa fr/ lamina perpendicularis y (sphenoid bone); Posteriormost part of forming properties = little regeneration after bone loss;
Cribriform plate Roof of ethmoid bone; Pair of perforated plates on maxilla → pterygoid pits → sphenoid Successful when bone is reflected w/ overlying muscle
each side of crista galli bones and skin, retaining blood supply; Craniectomy – bone
Ethmoid sinus Lateral part of nasal cavity and medial to orbit flap not replaced
Middle nasal concha Lateral side of nose and forms lateral walls of nasal Development of Calvaria and some parts of cranial base - IM ossification;
cavity Horizontal Buttresses Cranium Most parts of cranial base – EC ossification; Neonate –
Superior nasal concha Smaller projection of bone Transmits impact fr/ midface region to back of skull Smooth calvaria, Prominent frontal and parietal
Paranasal sinuses Divide into frontal, ethmoid and maxillary sinus Type Level Suture eminences, Disproportionally large cranium; Adult – face
Inferior concha Midface Buttresses is 1/3 of cranium
Inferolateral wall of nasal cavity; Covered with mucosa; Well vascularized; Superior Superior Orbital part of frontal bone; Cribriform plate of Age Changes in Rapid growth of face = eruption of deciduous teeth; Vert
Longest and broadest of all conchae orbital ethmoid Face growth of upper face – dento-alveolar development of
rim alveolar bone; Enlargement of frontal and facial regions
Middle Inferior Orbital processes of maxilla, infraorbital, linked w/ paranasal sinuses
Passageways within facial bones Horizontal orbital maxillary; Temporal process of zygoma; Obliteration of Internal surface – 30-40 years; External surface – After 10
rim Zygomatic process of temporal bone Cranial Sutures years; Bregma → Sagittal → Coronal → Lambdoid
Passage Location Structures Inferior Maxillary Maxillary teeth; Hard palate Age Changes in Cranial bones thinner and lighter with age; Diploe filled w/
alveolar Cranium gray gelatinous material; Bone marrow lost blood cells
Greater and Palatine bone Palatine vessels; Greater and lesser palatine
process and fat = gelatinous appearance
lesser palatine nerve (CN V2)
foramina Mandibular Buttresses Craniosynostosis Premature closure of suture; 1 per 2000 births; Abnormal
Superior Lower Mandible (for both) and Cranial development → Exaggerated forces on dura mater; More
Incisive Pos to incisors Nasopalatine nerve (CN V2)
Mandibular teeth Malformations common in males than females; Scaphocephaly –
foramen in hard palate
Inferior sagittal; Plagiocephaly – coronal/lambdoid on one side
of maxilla
Mandibular only; Oxycephaly or Turricephaly – coronal (more
Infraorbital Inferior to orbit Infraorbital artery; Infraorbital nerve (CN V2)
common in females; No effect on brain development
foramen in maxilla
Lacrimal Lacrimal bone Nasolacrimal duct
groove Clinical Correlates (add from Moore)
Mandibular Med surface Inferior alveolar blood vessels; Inferior alveolar
foramen of ramus of nerve (CN V3) Head Injuries Disturbance in the level of consciousness – most
mandible common symptom; Almost 10% of all deaths in US –
Mental Inf to 2nd Mental blood vessels; Mental nerve (CN V3) caused by injury (1/2 involve brain); Occur mostly in
foramen premolar on young persons 15-24 years; Commonly caused by motor
AL surface of accidents
mandible Headaches and May indicate serious intracranial problem; Neuralgias –
Facial Pain severe throbbing and stabbing pain along course of nerve
caused by demyelinating lesion
Other bones of skull Injury to Superciliary arches – sharp bony ridges; May lacerate
Superciliary skin and cause bleeding; Bruising of skin surrounding
Zygomatic Bone Arches orbit → fluid and blood accumulation in CT → upper
Forms part of orbit and cheeks; Prom zyg arch is formed by articulation w/ eyelid around eye (black eye)
temporal bone; Processes form tripod structure; Many sutures (synarthrodial) Malar Flush Redness of skin covering zygomatic process = rise in
found at end of processes temp in fevers (TB, lupus)
Frontal process Articulates w/ frontal bone (via frontozygomatic Fractures of Maxillae and Associated Bones
suture) Le Fort I Horizontal fractures of Maxillae → Maxillary process→
Maxillary process Articulates w/ maxillary bone Fracture Nasal septum → Pterygoid plates of sphenoid
Temporal process Articulates w/ temporal bone Le Fort II PL parts of maxillary sinuses →Infraorbital foramina,
Temporal Bone Fracture lacrimals or ethmoids → Nose bridge; Entire central part
Facial (CN VII) and Vestibulocochlear (CN VIII) nerve pass thru int acoustic of face separated fr/ cranium
meatus; Susceptible to motor accidents Le Fort III Horizontal fractures thru sup orbital fissures, and ethmoid
Sphenoid Bone Fracture and nasal bones → Greater wings of sphenoid and
Under skull; Articulates with ethmoid, palatine and ethmoid at front; Pterygoid frontozygomatic structures
plates are extensions for muscle attachment Fractures of Usually 2 fractures (1 on each side); On coronoid
Occipital Bone Mandible process – uncommon and single; On neck of manible –
transverse and TMJ dislocated; On angle of mandible –
oblique and involve bony socket/alveolus of 3rd molar
Buttresses of the face – transmit impact; prevent collapse of two structures tooth; On body of mandible – pass thru socket of canine
tooth
Bilateral Vertical Buttresses Resorption of Caused by teeth extraction; Tooth begins to fill in w/ bone
Type Location Suture Alveolar Bone and alveolar process begins to resorb; In some, mental
foramina disappear – expose mental nerves to injury;
Nasom Most medial; Bridge bet ant hard palate Nasal bone to frontal
Loss of all teeth → decrease in vert facial dimension and
axillary and frontal bone; Midface to frontal area; Nasofrontal
mandibular prognathism
bone suture
Fractures of Hard blows in thin areas produce depressed fractures;
Zygom Lateral part of midface; Fr/ 2nd molar Nasal bone to frontal Linear calvarial fractures – fracture lines often radiate
Calvaria
aticom (inf) to side of orbital (lat) to frontal area;
away in 2 or more directions; Comminuted fractures –
axillary bone (sup); Bridge bet lateral maxilla, Zygomaticomaxillary
bone broken into several pieces, if thick, may bend
zygomatic process and frontal bone suture;
You might also like
- Cranial Nerves Functional ComponentsDocument7 pagesCranial Nerves Functional ComponentsCoy EnNo ratings yet
- The Skull - Anatomy BonesDocument100 pagesThe Skull - Anatomy BonesFatima Kh SalahNo ratings yet
- 01 Head and Neck JMDocument16 pages01 Head and Neck JMJowi SalNo ratings yet
- FM 5130Document66 pagesFM 5130Aswini Kr KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy NotesDocument8 pagesNeuroanatomy NotesJustine May Gervacio100% (1)
- Cranial Bones and Meninges RevisionDocument20 pagesCranial Bones and Meninges Revisionbannanastew7975No ratings yet
- Identify The Boundaries of The Infratemporal FossaDocument7 pagesIdentify The Boundaries of The Infratemporal FossaHARSHDESAI56929640No ratings yet
- Mind Map On The History of Science, Technology and SocietyDocument1 pageMind Map On The History of Science, Technology and SocietyJohn Michael Vincent CarreonNo ratings yet
- 1 - The SkullDocument68 pages1 - The Skullaboody omerNo ratings yet
- ACL GRC Risk Manager - Usage Guide V1.1Document28 pagesACL GRC Risk Manager - Usage Guide V1.1Rohit ShettyNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and MandibleDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and MandibleMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Head FactoidsDocument17 pagesHead FactoidsENo ratings yet
- SkullDocument26 pagesSkulldr.b1100100% (2)
- ENT Prelims TransDocument45 pagesENT Prelims TransRaven CocjinNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Origin Course Exit Site Function I. OlfactoryDocument5 pagesNuclear Origin Course Exit Site Function I. OlfactorybobNo ratings yet
- Bones - ChecklistDocument3 pagesBones - ChecklistHarvey DomingoNo ratings yet
- Understanding the anatomy of the middle earDocument3 pagesUnderstanding the anatomy of the middle earMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Infratemporalfossa PpsDocument7 pagesInfratemporalfossa PpsНемосјановић ЋудмилаNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1. Head 2. Neck 3. Upper Limb 4. Lower Limb 5. Thorax 6. Back 7. Abdomen 8. PelvisDocument4 pagesAnatomy 1. Head 2. Neck 3. Upper Limb 4. Lower Limb 5. Thorax 6. Back 7. Abdomen 8. Pelvisjdavies231No ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 4 - Parotid GlandDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 4 - Parotid GlandMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Infra Temporal FossaDocument7 pagesInfra Temporal FossaНемосјановић ЋудмилаNo ratings yet
- 4bi 1le Active RecallDocument4 pages4bi 1le Active RecallAlexandryaHaleNo ratings yet
- Activity-Sheet 6-MC Bio4-ArcigaDocument5 pagesActivity-Sheet 6-MC Bio4-ArcigaArciga, Sheena Mae BienNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Organ of Hearing and BalanceDocument1 pageAnatomy of The Organ of Hearing and BalanceJose Raphael Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves and Their BranchesDocument3 pagesCranial Nerves and Their BranchesAeileeNo ratings yet
- Open AnatomyDocument50 pagesOpen AnatomyalukiasuNo ratings yet
- Board Review Blood SupplyDocument6 pagesBoard Review Blood Supplynewguy927No ratings yet
- The MandibleDocument115 pagesThe MandiblenavjotsinghjassalNo ratings yet
- Posterior Cranial Fossa-Decamber2009Document47 pagesPosterior Cranial Fossa-Decamber2009mmaam_11No ratings yet
- Norma BasalisDocument21 pagesNorma BasalisIndirackshi SundararajanNo ratings yet
- 5 - Maxillary Artery & Pterygoid Veinous PlexusDocument2 pages5 - Maxillary Artery & Pterygoid Veinous PlexusHorn DudeNo ratings yet
- #PLEMARCH2019 Anatomy (Type Text) : - o o o - o o oDocument3 pages#PLEMARCH2019 Anatomy (Type Text) : - o o o - o o oAnn Ross VidalNo ratings yet
- Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma SurgeryDocument18 pagesJuvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma Surgeryarief ardaNo ratings yet
- 1.12 ANATOMY - The Ears Surface Anatomy and Landmarks, External, Middle and Inner Portions, Blood Vessels and NervesDocument5 pages1.12 ANATOMY - The Ears Surface Anatomy and Landmarks, External, Middle and Inner Portions, Blood Vessels and NervesPaolo NaguitNo ratings yet
- Azubz 04Document70 pagesAzubz 04Anonymous N8IdLrsHn9No ratings yet
- General Anatomy - 9Document2 pagesGeneral Anatomy - 9ayaaqassimalmodafarNo ratings yet
- General Discription of MusclesDocument25 pagesGeneral Discription of Musclesapi-19641337No ratings yet
- 7 Pterygopalatine Fossa and OrbitsDocument18 pages7 Pterygopalatine Fossa and OrbitsAmbg GhalyNo ratings yet
- Special Senses: The Ear, Audition & EquilibriumDocument28 pagesSpecial Senses: The Ear, Audition & EquilibriumLucky NguyenNo ratings yet
- Norma Basalis Externa - 240306 - 175247Document18 pagesNorma Basalis Externa - 240306 - 175247Hager AbouzaidNo ratings yet
- Skull, Cranial Cavity and Venous SinusesDocument30 pagesSkull, Cranial Cavity and Venous SinusesZobayer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy: Lesson 3: The Structure of Mastication: The Jaws and DentitionDocument11 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy: Lesson 3: The Structure of Mastication: The Jaws and DentitionMarian AlecsNo ratings yet
- Kraniofacijalne Duplje: Fossa Cranii AnteriorDocument8 pagesKraniofacijalne Duplje: Fossa Cranii AnteriorFanserbiaNo ratings yet
- 7mm Frog Embryo - EMBLabDocument3 pages7mm Frog Embryo - EMBLabIvy Cruz100% (1)
- Medial MaxillectomyDocument12 pagesMedial MaxillectomyYayan AkhyarNo ratings yet
- Superior Aspect of Calvaria: Suture Suture SutureDocument11 pagesSuperior Aspect of Calvaria: Suture Suture Sutureapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Cranium & Facial Bones Anatomy Lab 1Document27 pagesCranium & Facial Bones Anatomy Lab 1trollingNo ratings yet
- EAR Anatomy, Physiology, Embryology & Congenital AnomalyDocument6 pagesEAR Anatomy, Physiology, Embryology & Congenital AnomalyThakoon TtsNo ratings yet
- Total Maxillectomy and Orbital ExenterationDocument18 pagesTotal Maxillectomy and Orbital ExenterationMaliha TahirNo ratings yet
- GRDA Intro Head&NeckDocument18 pagesGRDA Intro Head&NeckKingNo ratings yet
- Medial MaxillectomyDocument12 pagesMedial MaxillectomyasiyazaidiaNo ratings yet
- Maxillary ArteryDocument11 pagesMaxillary ArterySridevi KNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy (Dr. ElNashar)Document19 pagesSurgical Anatomy (Dr. ElNashar)shehla khanNo ratings yet
- Medial MaxillectomyDocument12 pagesMedial MaxillectomyJamesNo ratings yet
- 4mm Frog EmbryoDocument3 pages4mm Frog EmbryoIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- The MeningesDocument23 pagesThe Meningesanjhulz0% (1)
- Temporal Fossa & Infratemporal Fossa and Muscles of Mastication (2)Document22 pagesTemporal Fossa & Infratemporal Fossa and Muscles of Mastication (2)pposs9220No ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Lab Guide to 12 Cranial NervesDocument3 pagesNeuroanatomy Lab Guide to 12 Cranial NervesmekonekoNo ratings yet
- Shanz - Ent 1.07 NoseDocument4 pagesShanz - Ent 1.07 NosePetrina XuNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Cranium (Tulang) Pembagian Tulang Cranium Neurocranium Calvarium Basis Cranii Splancho-Cranium Foramen/Fissura IsiDocument4 pagesAnatomi Cranium (Tulang) Pembagian Tulang Cranium Neurocranium Calvarium Basis Cranii Splancho-Cranium Foramen/Fissura IsiSyahril Gilang RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Head and NeckDocument208 pagesHead and NeckStephanie ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract AnatomyDocument36 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract AnatomyNatalie HuiNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and LarynxDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and LarynxMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 4 - Parotid GlandDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 4 - Parotid GlandMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Understanding the anatomy of the middle earDocument3 pagesUnderstanding the anatomy of the middle earMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 4 - Parotid GlandDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 4 - Parotid GlandMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and LarynxDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and LarynxMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- LogDocument119 pagesLogcild MonintjaNo ratings yet
- Interesting Facts (Compiled by Andrés Cordero 2023)Document127 pagesInteresting Facts (Compiled by Andrés Cordero 2023)AndresCorderoNo ratings yet
- Dyna 2000 LiteDocument2 pagesDyna 2000 LiteRNKNo ratings yet
- 03 - 42 STCP-Ahm AssetDocument46 pages03 - 42 STCP-Ahm AssetARP MEILNo ratings yet
- PiXL Knowledge Test ANSWERS - AQA B1 CORE Science - Legacy (2016 and 2017)Document12 pagesPiXL Knowledge Test ANSWERS - AQA B1 CORE Science - Legacy (2016 and 2017)Mrs S BakerNo ratings yet
- Eagle Test ReportDocument25 pagesEagle Test ReportMuhammad FahadNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Head FixDocument8 pagesCatalogo Head FixANDREA RAMOSNo ratings yet
- Timber, PVCu and aluminium window and door hardware systemsDocument24 pagesTimber, PVCu and aluminium window and door hardware systemsOmul Fara NumeNo ratings yet
- Polygenic InheritanceDocument13 pagesPolygenic InheritanceSandeep Kumar RaghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- Edmonson - Pageantry Overture - AnalysisDocument3 pagesEdmonson - Pageantry Overture - Analysisapi-426112870No ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument70 pagesSample QuestionsBushra MaryamNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Urban RegenerationsDocument23 pagesPresentation of Urban RegenerationsRafiuddin RoslanNo ratings yet
- How Do I Prepare For Public Administration For IAS by Myself Without Any Coaching? Which Books Should I Follow?Document3 pagesHow Do I Prepare For Public Administration For IAS by Myself Without Any Coaching? Which Books Should I Follow?saiviswanath0990100% (1)
- 20ME901 Automobile Engineering Unit 3Document74 pages20ME901 Automobile Engineering Unit 36044 sriramNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behaviour Group Assignment-2Document4 pagesOrganizational Behaviour Group Assignment-2Prateek KurupNo ratings yet
- mcs2019 All PDFDocument204 pagesmcs2019 All PDFRheydel BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Indonesia Banks Bank Mandiri Trading Buy on Strong 9M21 EarningsDocument8 pagesIndonesia Banks Bank Mandiri Trading Buy on Strong 9M21 EarningsdkdehackerNo ratings yet
- X RayDocument16 pagesX RayMedical Physics2124No ratings yet
- Agilent Cool On-Column Operation ManualDocument42 pagesAgilent Cool On-Column Operation Manualdmcevoy1965No ratings yet
- Final - WPS PQR 86Document4 pagesFinal - WPS PQR 86Parag WadekarNo ratings yet
- BarclaysDocument5 pagesBarclaysMehul KelkarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Threats Differentiated Reading Comprehension Ver 1Document20 pagesEnvironmental Threats Differentiated Reading Comprehension Ver 1Camila DiasNo ratings yet
- GD&T WIZ Tutor Covers The Vast Breadth of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Without Compromising On The Depth. The Topics Covered AreDocument1 pageGD&T WIZ Tutor Covers The Vast Breadth of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Without Compromising On The Depth. The Topics Covered AreVinay ManjuNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1 Application FormDocument13 pagesAppendix 1 Application FormSharifahrodiah SemaunNo ratings yet
- AIOUDocument2 pagesAIOUHoorabwaseemNo ratings yet
- Ahu, Chiller, Fcu Technical Bid TabulationDocument15 pagesAhu, Chiller, Fcu Technical Bid TabulationJohn Henry AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Best Home Oxygen Concentrators-Lowest Prices & Fast Shipping (Oxygen Machines) - 2021 - YuwellDocument1 pageBest Home Oxygen Concentrators-Lowest Prices & Fast Shipping (Oxygen Machines) - 2021 - YuwellPelayanan ResusitasiNo ratings yet