Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Another Sample
Uploaded by
Luthar James JimenezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Another Sample
Uploaded by
Luthar James JimenezCopyright:
Available Formats
STM 007: General Biology 1
Module #21 Student Activity Sheet
Name: Class number: _
Section: _ Schedule: Date:
Lesson Title: The Major Events in Photosynthesis including its Materials:
Light-Dependent and the Light-Independent Reactions SAS
References:
Learning Targets: www.khanacademy.org
At the end of this module, I should be able to: www.passmyexams.co.uk
1. Discuss the concept of light-dependent and light-independent
reactions
2. Compare the differences between light-dependent and light-
independent reactions
A. LESSON PREVIEW/REVIEW
Introduction
Study the following picture. Label the parts of the photosynthesis process and explain based from your
prior knowledge about it.
B. MAIN LESSON
Content and Skill-Building
Read and analyze the following notes carefully. Once you encounter terms you think are important, do
not forget to ENCIRCLE them and HIGHLIGHT their descriptions
What is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis – is the process by which green plants
and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods from
carbon dioxide and water. Photosynthesis in plants generally
involves the green pigment chlorophyll and generates oxygen as a
byproduct.
The energy that makes almost all life on earth possible
ultimately comes from the sun. In the process of photosynthesis,
plants capture the energy in sunlight and convert it into chemical
bonds in glucose. The plants and the organisms that eat plants use the energy from glucose to form ATP, the
This document is the property of PHINMA EDUCATION 1
STM 007: General Biology 1
Module #21 Student Activity Sheet
Name: Class number: _
Section: _ Schedule: Date:
energy from the breakdown of ATP fuels the chemical reactions of life.
I would like you to imagine what happens to the sweetest mango that you ever tasted. Do you have an
idea how it came to be so sweet? Yes, the sugar in the mango fruit is a product of photosynthetic process. The
leaves in the branches of mango tree absorb the light energy from the sun, and convert it to chemical energy in
the form of chemical bonds in glucose, the simplest sugar. Millions of leaves are catching light energy to make
simplest sugar which were stored in the tree trunks, roots and branches. When the fruiting season comes,
flowers come and this sugar will be stored in the fruits, as long as it is sunny every day, the fruits are sweeter
but in areas where sun is not shining so hot, fruits are not that sweet. Why apples and pear are not so sweet?
Yes, it’s because these fruits were not grown in the tropics where equator is found and the temperature is hot
and warm most of the time.
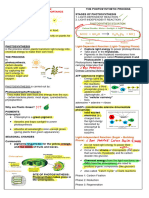
Major events in Photosynthesis are the following:
1. Sunlight and carbon dioxide are absorbed by the plant cells found in the leaves,
2. Chloroplasts in plant cells contain chemical compounds Chlorophyll, that traps sun’s heat to start the
photosynthesis. Chlorophyll absorbs green wavelengths from the sun, making plants look green.
Conversion of light energy to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH)
3. Photosynthesis strips hydrogen from water molecule leaving only oxygen. Hydrogen atoms are
mixed together with carbon dioxide to make a sugar that the plant can use as food. Excess sugar is
stored as starch (food) in the roots or fruits.
4. The oxygen which left from the transformation is released back into the air through the stomata of
the leaves. The sugar created by photosynthesis is sent to the rest of the plant for food.
What is the light reaction of photosynthesis?
Light reactions need light to produce organic energy molecules (ATP and NADPH). They are initiated
by colored pigments, mainly green colored chlorophylls.
What is the dark reaction of photosynthesis?
Dark reactions make use of these organic energy molecules (ATP and NADPH). This reaction cycle is
also called Calvin Benison Cycle, and it occurs in the stroma.
What is the main purpose of the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis?
The overall function of light-dependent reactions, the first stage of photosynthesis, is to convert solar
energy into chemical energy in the form of NADPH and ATP, which are used in light-
independent reactions and fuel the assembly of sugar molecules. These two chemical energies are so
important in the light-independent reaction in photosynthesis.
What are the functions of ATP and NADPH?
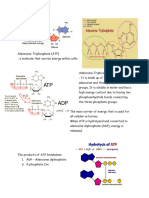
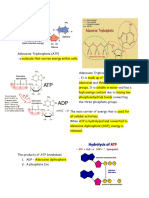
ATP or Adenosine Triphosphate, as we know is the carrier of energy for the cells to do its functions by
detaching its phosphate molecule and it becomes ADP. ADP is like a discharged battery and has no energy so
it will go back to mitochondria of the cell to recharge and be an ATP again, without ATP, cells will not be able
to do its cellular functions.
ATPs are used as the main energy source for
metabolic functions. They are consumed by energy-requiring
(endothermic) processes and produced by energy-releasing
(exothermic) processes in the cell.
Use for the synthesis of organic molecules
Power up the muscle contractions
Used in active transport of large molecules in the plasma
membrane
NADPH on the other hand is Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP+ is
a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as lipid and nucleic acid synthesis, which require NADPH as a
reducing agent. NADPH is the reduced form of NADP+. NADP+ differs from NAD+ in the presence of an
additional phosphate group on the 2' position of the ribose ring that carries the adenine moiety. In
This document is the property of PHINMA EDUCATION 2
STM 007: General Biology 1
Module #21 Student Activity Sheet
Name: Class number: _
Section: _ Schedule: Date:
photosynthetic organisms, NADPH is produced by ferredoxin-NADP + reductase in the last step of the electron
chain of the light reactions of photosynthesis. NADPH is the form of energy that is produced during Calvin
Cycle, it is the product of CO 2 fixation during Calvin Cycle which is the second phase of photosynthesis. The
first phase is light dependent reaction. It is essentially a form of chemical energy that is produced by light-
dependent reaction.
Functions of NADPH
NADPH is used as reducing power for the biosynthetic reactions in the light-independent reactions to
assimilate carbon dioxide.
It is used to help turn the carbon dioxide into glucose.
It is also needed in the reduction of nitrate into ammonia for plant assimilation in nitrogen cycle
How ATP and NADPH were created?
Look at the picture below, inside the plant cell are chloroplast containing chlorophyll where sunlight was
trapped and absorbed and mixed with water, water was split into oxygen and hydrogen ions, oxygen was
released as end product and ATP and NADPH were created, these two have so much energy needed for the
light independent reactions in photosynthesis.
Below is a picture of both light-dependent reactions in photosynthesis and light-independent reactions
in photosynthesis happening inside the chloroplasts of a plant cell. In first phase, the chlorophyll inside the
chloroplast trapped and absorbed energy from the sun
and mixed it with water, hydrogen molecules were split
leaving oxygen and release as end product, and the
ATP and NADPG were created. This happens inside the
thylakoids. On the second phase, ATP and NADPH
were mixed with carbon dioxide and 3 carbon sugar and
other molecules were created every cycle, while ADP
and NADP were recycled back to thylakoids again for
recharging or recycling. This is a continuous cycle.
The light-independent reactions, or dark
reactions, of photosynthesis are chemical reactions that
convert carbon dioxide and other compounds into
glucose. These reactions occur in the stroma, the fluid-
filled area of a chloroplast outside of the thylakoid
membranes. ATP and NADPH were mixed with carbon
dioxide to make sugar or starch. It is also called the
Calvin Cycle shown below, let’s analyze the picture,
how sugar is made here?
ATP and NADPH produced from the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis are now mixed with carbon
dioxide in the light-independent reactions in photosynthesis producing sugar. Look at the picture and the
formula on top, can you see where sugar is? Yes, the C6H12O6 is the glucose, this the formula for sugar.
For every cycle, 3 carbon sugar is created and stored. Cycles are faster if the sun is shining too hot. The used-
up ATP becomes ADP and the NADPH becomes NADP, these are then recharged or recycled back to the
light-dependent reactions to become ATP and NADPH again, and the cycle continues as long as there is
continuous supply of sunlight.
This cycle is repeating itself fast or slow depending upon the presence of sunlight, without sunlight, plants
will not be able to make their own food.
This document is the property of PHINMA EDUCATION 3
STM 007: General Biology 1
Module #21 Student Activity Sheet
Name: Class number: _
Section: _ Schedule: Date:
Skill-building Activities
Let’s practice! After completing each exercise, you may refer to the Key to Corrections for feedback.
Try to complete each exercise before checking your work. Write your score on your paper.
Exercise 1: Based from what you have learned in your teacher’s discussion, fill in the Frayer Model
below about your understanding of the concept of the major events in photosynthesis.
Definition: Characteristics:
Examples:
Non-examples:
Definition: Characteristics:
Examples:
Non-examples:
Exercise 2: Use the words from the word bank to fill in the chart and see how the light-dependent
reactions and the Calvin cycle differ in their different specific events.
O2 CO2 H2O thylakoid membrane
stroma NADPH sugars (glucose) Requires light
ATP Doesn’t require light
LIGHT-INDEPENDENT REACTIONS
LIGHT-DEPENDENT REACTIONS
(CALVIN CYCLE)
LOCATION
This document is the property of PHINMA EDUCATION 4
STM 007: General Biology 1
Module #21 Student Activity Sheet
Name: Class number: _
Section: _ Schedule: Date:
REACTANTS
PRODUCTS
LIGHT
Exercise 3: Write T if the statement is true and F if the statement is false.
T 1. Photosynthesis always happens in the presence of sunlight.
T 2. Oxygen is a waste product of photosynthesis.
F 3. Chloroplast traps the sunlight and convert it into ATP.
F 4. The animals are also part of the photosynthetic process because they give off oxygen.
T 5. All plants have green coloring because of chlorophylls.
Check for Understanding
You have almost finished answering your module today. To check further your understanding in this
lesson, kindly answer the following activity below. After completing, you may refer to the Key to
Corrections for feedback. Try to complete this activity before checking your work. Write your score on
your paper.
Circle T if the statement is TRUE. Circle F if the statement is FALSE and use the blank provided to
correct the underlined word/phrase.
1.) T F Increasing light intensity decreases the rate of photosynthesis.
Increases
2.) T F Carbon dioxide molecules enter the light-dependent reactions from the
atmosphere.
Light-Independent reactions
3.) T F Photosynthesis uses energy from ATP and high energy electrons from NADPH
produced in the light-dependent reactions to make glucose in the Calvin cycle.
Light-Independent
4.) T F The light-dependent reaction produces ATP, NADPH, and carbon dioxide.
Oxygen
Use the letters in the diagram at the left to identify the parts of the
chloroplast.
B stroma
C thylakoid
A granum
This document is the property of PHINMA EDUCATION 5
STM 007: General Biology 1
Module #21 Student Activity Sheet
Name: Class number: _
Section: _ Schedule: Date:
C. LESSON WRAP-UP
Summary / Frequently Asked Questions
1) How are pigments related to photosynthesis?
Pigments absorb light used in photosynthesis.
In photosynthesis, the sun’s energy is converted to chemical energy by photosynthetic organisms.
However, the various wavelengths in sunlight are not all used equally in photosynthesis. Instead,
photosynthetic organisms contain light-absorbing molecules called pigments that absorb only specific
wavelengths of visible light, while reflecting others.
The set of wavelengths absorbed by a pigment is its absorption spectrum. In the diagram below, you
can see the absorption spectra of three key pigments in photosynthesis: chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and β-
carotene. The set of wavelengths that a pigment doesn't absorb are reflected, and the reflected light is
what we see as color. For instance, plants appear green to us because they contain many chlorophyll a
and b molecules, which reflect green light.
Each photosynthetic pigment has a set of wavelengths that it absorbs, called an absorption spectrum.
Absorption spectra can be depicted by wavelength (nm) on the x-axis and the degree of light absorption on
the y-axis. The absorption spectrum of chlorophylls includes wavelengths of blue and orange-red light, as
is indicated by their peaks around 450-475 nm and around 650-675 nm. As a note, chlorophyll a absorbs
slightly different wavelengths than chlorophyll b. Chlorophylls do not absorb wavelengths of green and
yellow, which is indicated by a very low degree of light absorption from about 500 to 600 nm. The
absorption spectrum of β-carotene (a carotenoid pigment) includes violet and blue-green light, as is
indicated by its peaks at around 450 and 475 nm.
Most photosynthetic organisms have a variety of different pigments, so they can absorb energy from a
wide range of wavelengths. The two groups of pigments that are important in plants include chlorophylls
and carotenoids.
2) How does temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis?
The higher the temperature then typically the greater the rate of photosynthesis, photosynthesis is a
chemical reaction and the rate of most chemical reactions increases with temperature. However, for
photosynthesis at temperatures above 40°C the rate slows down. This is because the enzymes involved in
the chemical reactions of photosynthesis are temperature sensitive and destroyed at higher temperatures.
To better understand the effects of temperature on photosynthesis it is important to know the effect of
temperature on the enzymes involved in photosynthesis. Enzymes are affected a great deal by
temperature. If the temperature is too cold the enzymes move around too slowly to meet the substrate and
for a reaction to occur. As the temperature increases though, so does the rate of reaction. This is because
heat energy causes more collisions between the enzyme and the substrate. However, as you will
remember all enzymes are proteins and at too high temperatures the proteins break down. The active site
of the enzyme becomes distorted and so the substrate no longer fits and hence the reaction does not
occur. We say that the enzyme has been denatured.
Greenhouses are used to capitalize on the effects of higher temperatures increasing the rate of
photosynthesis. Plants from regions of warmer climates can successfully grow in colder regions by using
greenhouses.
The rate of photosynthesis does not increase with higher temperatures for all plants. Plants which grow
in colder climates have an optimum rate of photosynthesis at low temperatures. Therefore, different types
of plants have optimum temperatures for photosynthesis.
Thinking about Learning
This document is the property of PHINMA EDUCATION 6
STM 007: General Biology 1
Module #21 Student Activity Sheet
Name: Class number: _
Section: _ Schedule: Date:
You have reached already the end of the lesson today! Congratulations and thank you for doing every
task provided for you from the different activities.
Did you have challenges learning the concepts in this module? If yes, what are they?
If none, which parts of the module helped you learn the concepts?
Some question/s I want to ask my teacher about this module is/are:
Answer Key
Answers to Skill-Building Exercises:
Exercise 1
Definition: Characteristics:
first major set of processes in photosynthesis, in -are initiated by colored pigments, mainly
which light energy is initially converted into green colored chlorophylls
chemical energy as ATP and NADPH
Examples: Non-examples:
-absorption of light energy through the chlorophyll; -light-independent reactions/Calvin Cycle
mixed with water and results to Oxygen
Definition: Characteristics:
dark reactions of photosynthesis are - make use of organic energy molecules (ATP and
chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and NADPH). This reaction cycle is also called Calvin
other compounds into glucose Cycle, and it occurs in the stroma.
Examples: Non-examples:
-carbon dioxide mixed with ATP and NADPH to light-dependent reactions
make sugar
Exercise 2
LIGHT-INDEPENDENT REACTIONS
LIGHT-DEPENDENT REACTIONS (CALVIN CYCLE)
LOCATION thylakoid membrane of chloroplast stroma of chloroplast
REACTANTS light, water CO2
PRODUCTS ATP; NADPH; Oxygen sugar
LIGHT Requires light Doesn’t require light
Exercise 3
1.T 2. T 3.F 4. F 5.T
Answers to Check for Understanding:
1. F 3. F B Stroma
2. F 4. F C thylakoid
A granum
This document is the property of PHINMA EDUCATION 7
You might also like
- Biology Reviewer 2nd QuarterDocument3 pagesBiology Reviewer 2nd Quarter젶레이100% (4)
- AQA AS Physics A Chapter 3 Textbook AnswersDocument4 pagesAQA AS Physics A Chapter 3 Textbook Answerscathylister33% (3)
- Habitable Zone SimulationDocument3 pagesHabitable Zone Simulationncl121420% (1)
- SWST PresentationDocument21 pagesSWST PresentationRodora PerezNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science GR 7 q1 Week 1 Subtask 1Document17 pagesEnvironmental Science GR 7 q1 Week 1 Subtask 1Majin BuuNo ratings yet
- Student Module 1 Genbio1Document5 pagesStudent Module 1 Genbio1Lezel LaracasNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument41 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respirationjhenjhentot24No ratings yet
- Gen Biology 1 q2 Wk1Document33 pagesGen Biology 1 q2 Wk1kai lifurnitureNo ratings yet
- NatSci2 Chapter 5Document32 pagesNatSci2 Chapter 5kayNo ratings yet
- Bio 12 AModule 7Document7 pagesBio 12 AModule 7Ivan RamirezNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science SHS 16.2 PhotosynthesisDocument15 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 16.2 PhotosynthesisPamela MalihanNo ratings yet
- Q2 Reviewer in General BiologyDocument7 pagesQ2 Reviewer in General BiologyariannealzagaNo ratings yet
- M2 - General Bio 1 - Q2Document10 pagesM2 - General Bio 1 - Q2Remilyn GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 101 Module 5Document5 pagesGen Bio 101 Module 5Kyne GasesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (Stem)Document10 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (Stem)Theworld Magic100% (1)
- Earth and Life Science SHS 16.2 PhotosynthesisDocument15 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 16.2 PhotosynthesisWinsear VardeNo ratings yet
- Biology 9 Unit 7 - PhotosynthesisDocument28 pagesBiology 9 Unit 7 - PhotosynthesisLo ViNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Mod 9-11Document7 pagesGen Bio Mod 9-11Arabella BrionesNo ratings yet
- M2 - General Bio 1 - Q2Document12 pagesM2 - General Bio 1 - Q2Remilyn GonzalesNo ratings yet
- BCH 223 Assignment 1 2021Document6 pagesBCH 223 Assignment 1 2021Nosibusiso KhaliphaNo ratings yet
- Atp Adp CycleDocument20 pagesAtp Adp CycleBierzo JomarNo ratings yet
- Biology - Module 5Document11 pagesBiology - Module 5ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument82 pagesEnergy TransformationAlodia PastorizoNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4 Part 1 Last Minute Revision ReallyacademicsDocument67 pagesBiology Unit 4 Part 1 Last Minute Revision ReallyacademicsWill AndyNo ratings yet
- Cellular Energy Resp PhotoDocument85 pagesCellular Energy Resp Photomuhra khaeld salim al abo aldariiNo ratings yet
- Botany Lab Activity 7Document5 pagesBotany Lab Activity 7PaulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PhotosynthesisDocument41 pagesChapter 2 PhotosynthesisTshering ChodenNo ratings yet
- Unveiling The Light Reaction Event in PhotosynthesisDocument18 pagesUnveiling The Light Reaction Event in Photosynthesiszbplayer8No ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 5 Energy Flow, Ecosystems and The Environment - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-Level PDFDocument9 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 5 Energy Flow, Ecosystems and The Environment - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-Level PDFsammam mahdi samiNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio1 2ND Q.module 1Document9 pagesGen Bio1 2ND Q.module 1Lara FloresNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesGroup 4 - Photosynthesisditucalan.ha2003No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 123Document4 pagesPhotosynthesis 123Alyssa L.J. Dela Cruz (Aly)No ratings yet
- 15 Quarter 1 Module 15-light-INDEPENDENT-reactionsDocument19 pages15 Quarter 1 Module 15-light-INDEPENDENT-reactionsMah Jane Divina0% (1)
- Summary Notes Topic 5 Energy Flow Ecosystems and The Environment Edexcel (IAL) Biology A LevelDocument9 pagesSummary Notes Topic 5 Energy Flow Ecosystems and The Environment Edexcel (IAL) Biology A LevelLulwa KhaskiehNo ratings yet
- Bio Phto and CellularDocument4 pagesBio Phto and Cellulargbs040479No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PhotosynthesisDocument60 pagesChapter 5 Photosynthesisvijaypanwar_2000No ratings yet
- Topic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument70 pagesTopic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeJai CataluñaNo ratings yet
- Revision List - HL Topic 8: 8.1 MetabolismgDocument3 pagesRevision List - HL Topic 8: 8.1 MetabolismgFULYA YALDIZNo ratings yet
- What I Know: Quarter 2 - Module 1 Energy TransformationDocument8 pagesWhat I Know: Quarter 2 - Module 1 Energy TransformationLyka Mae BenitoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis NotesDocument12 pagesPhotosynthesis NotesSulthan Ramiz100% (1)
- Quarter 2 Module 1 General Biology 1 SCDocument31 pagesQuarter 2 Module 1 General Biology 1 SCAldrin James DafunNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument5 pagesEnergy TransformationmunozayshiaNo ratings yet
- GeneralBiology1-EnergyinLivingSystems - Q2 - Week-1 3Document11 pagesGeneralBiology1-EnergyinLivingSystems - Q2 - Week-1 3richellefayereynosoNo ratings yet
- Chemical ProcessesDocument4 pagesChemical ProcessesKeano GelmoNo ratings yet
- LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION - Discussrion Ni MaamDocument3 pagesLIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION - Discussrion Ni MaamAiejeoff JordanNo ratings yet
- 2 8 PhotosynthesisDocument27 pages2 8 Photosynthesisıamnıkolaı 4No ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEM Light Dependent ReationDocument1 pageECOSYSTEM Light Dependent Reationmelissa.romanNo ratings yet
- The Energy in Living SystemsDocument20 pagesThe Energy in Living SystemsAngel Mae Masa FloresNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Study Guide Photosynthesis Equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O - C6H12O6 + 6O2Document4 pagesPhotosynthesis: Study Guide Photosynthesis Equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O - C6H12O6 + 6O2vscolegit shoppeNo ratings yet
- Significant Events of The Calvin CycleDocument4 pagesSignificant Events of The Calvin CycleBernadette PasionNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument14 pagesBioenergeticsmunozayshiaNo ratings yet
- GB - 1st Quarter - wk8 - PDFDocument12 pagesGB - 1st Quarter - wk8 - PDFHeaven LeighNo ratings yet
- Science: Mahay Integrated Secondary SchoolDocument8 pagesScience: Mahay Integrated Secondary Schoollavenia acdalNo ratings yet
- WHLP Gen Bio 1 2nd QuarterDocument5 pagesWHLP Gen Bio 1 2nd QuarterSir JoshNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem A4Document6 pagesEcosystem A4Tristan SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 2 SummaryDocument43 pagesBiology Unit 2 SummaryYuh moddaNo ratings yet
- Light ReactionDocument17 pagesLight Reactionmshtalam.edNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Exploration Guide - Cell Metabolism #3Document6 pagesAP Biology Exploration Guide - Cell Metabolism #3Gunnar OlsonNo ratings yet
- Ch. 4Document22 pagesCh. 4EmilyNo ratings yet
- Ch. 8 Photosynthesis F17Document70 pagesCh. 8 Photosynthesis F17bae loonaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Unit TwoDocument158 pagesBiology Notes Unit TwoBlohsh KeenenNo ratings yet
- ZumdahlDocument17 pagesZumdahlmohammedraafat1977No ratings yet
- Second Quarterly Examination in General Biology 1 SY 2022-2023Document10 pagesSecond Quarterly Examination in General Biology 1 SY 2022-2023Ruby Uriarte100% (1)
- Solar & Lunar Eclipses 2000-2100Document9 pagesSolar & Lunar Eclipses 2000-2100SANo ratings yet
- Newton's Second LawDocument4 pagesNewton's Second LawMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Description of Indian CoalfieldDocument25 pagesDescription of Indian CoalfieldAjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Combustion: Luminous Gas Flame Flame Front Luminous Non-LuminousDocument18 pagesCombustion: Luminous Gas Flame Flame Front Luminous Non-LuminousMd. Ahsanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Standard Spreadsheet For Batch ColumnDocument14 pagesStandard Spreadsheet For Batch ColumnBagadi AvinashNo ratings yet
- Rab 5 KW PAK PURDocument3 pagesRab 5 KW PAK PURilhamNo ratings yet
- WeCommunities - BrochureDocument6 pagesWeCommunities - BrochurejayanthfunucationNo ratings yet
- Genepax - Water Powered CarDocument2 pagesGenepax - Water Powered CarGaurav Kumar100% (1)
- Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons & ElectronsDocument2 pagesAtomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons & ElectronsAdam JensenNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Smart GridDocument4 pagesMCQ On Smart GridJoshi RohitNo ratings yet
- Ingeteam Wind Converter Catalogue 2019Document4 pagesIngeteam Wind Converter Catalogue 2019FBNo ratings yet
- Preface: (Nadeem Irshad Kayani) Programme Director Directorate of Staff Development, PunjabDocument61 pagesPreface: (Nadeem Irshad Kayani) Programme Director Directorate of Staff Development, Punjabsalman khanNo ratings yet
- D4643Document5 pagesD4643Ruddy EspejoNo ratings yet
- EnvisciDocument7 pagesEnvisciPrecious CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Change Over Time - Lesson 1Document14 pagesChange Over Time - Lesson 1Nora ClearyNo ratings yet
- The Birth and Death of Stars: On-Line LessonDocument15 pagesThe Birth and Death of Stars: On-Line Lessonjyotirmoy21No ratings yet
- Petroleum Refinery Lab. Kinematic ViscosityDocument11 pagesPetroleum Refinery Lab. Kinematic ViscositySiyar SaleemNo ratings yet
- TOEFLDocument5 pagesTOEFLNIDA FITHRIANo ratings yet
- R134a TableDocument5 pagesR134a TableAhmed Mahmoud AbouzaidNo ratings yet
- 03 - Case Study - Cherry Hills LandslideDocument8 pages03 - Case Study - Cherry Hills LandslideJoseph Raymund Autor Sumabal100% (1)
- Introduction To PalaeontologyDocument50 pagesIntroduction To PalaeontologyRk PriyaNo ratings yet
- Solar System 9th Edition Seeds Test BankDocument21 pagesSolar System 9th Edition Seeds Test Bankjoshuarussellbmrgzkdeia100% (10)
- EPG EconomicsDocument16 pagesEPG Economicspalitha58No ratings yet
- Green BuildingDocument27 pagesGreen BuildingsaketNo ratings yet
- Powerplant Programme 2012Document100 pagesPowerplant Programme 2012JAFEBY100% (1)
- AQM M1 Ktunotes - inDocument25 pagesAQM M1 Ktunotes - inBala GopalNo ratings yet