Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maintaining and Testing Process Instrumentation and Control Devices
Uploaded by
AngelCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maintaining and Testing Process Instrumentation and Control Devices
Uploaded by
AngelCopyright:
Available Formats
SEMPEO239
Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices
Overview This standard covers a broad range of competences covering the
maintenance of process instrumentation and control devices. These
competences will prepare you for entry into the engineering or
manufacturing sectors, creating a progression between education and
employment, or they will provide a basis for the development of
additional skills and occupational competences in the working
environment.
You will be expected to prepare for the instrumentation and control
maintenance activities by obtaining all the necessary information,
documentation, tools and equipment required, and to plan how you
intend to carry out the required maintenance activities and the
sequence of operations you intend to use.
You will be required to select the appropriate equipment to use, based
on the maintenance operations to be carried out and the type of
instrumentation and control equipment being maintained, such as
pressure, flow, level and temperature instruments, fiscal monitoring
equipment, fire and gas detection and alarm systems, industrial
weighing systems, speed measurement and control systems, vibration
monitoring equipment, nucleonics and radiation measurement,
telemetry systems and emergency shutdown systems.
You will be expected to use a variety of maintenance diagnostic
techniques and procedures, such as gathering information from fault
reports, using recognised fault finding techniques and diagnostic aids,
measuring, inspecting and operating the equipment. You will also be
expected to cover a range of maintenance activities, such as isolating
and locking off, disconnecting, removing and reconnecting instruments
and faulty peripheral components, setting and adjusting components,
and testing the equipment, using appropriate techniques and
procedures.
Your responsibilities will require you to comply with health and safety
requirements and organisational policy and procedures for the
instrumentation maintenance activities undertaken. You will need to
take account of any potential difficulties or problems that may arise with
the maintenance activities, and to seek appropriate help and advice in
determining and implementing a suitable solution. You will work under a
high level of supervision, whilst taking responsibility for your own
SEMPEO239 Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices 1
SEMPEO239
Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices
actions and for the quality and accuracy of the work that you carry out.
Your underpinning knowledge will provide an understanding of your
work, and will enable you to apply safely the appropriate maintenance
techniques and procedures for process instrumentation and control
equipment. You will understand the instrumentation maintenance
process, and its application, and will know about the instrumentation
and systems being maintained, and the tools and consumables used, to
the required depth to provide a sound basis for carrying out the
activities to the required specification.
You will understand the safety precautions required when carrying out
the maintenance activities, (especially those for ensuring that the
equipment is correctly isolated), and when using maintenance tools and
equipment. You will be required to demonstrate safe working practices
throughout, and will understand your responsibility for taking the
necessary safeguards to protect yourself and others in the workplace.
Specific Unit Requirements
In order to prove your ability to combine different process
instrumentation and control maintenance operations, at least one of the
instrumentation maintenance activities carried out must be of a
significant nature, and must cover a minimum of eight of the activities
listed in scope 4.
SEMPEO239 Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices 2
SEMPEO239
Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices
Performance criteria
You must be able to:
1. work safely at all times, complying with health and safety
legislation, regulations, directives and other relevant guidelines
2. plan the maintenance activities before you start them
3. obtain all the information you need for the safe removal and
replacement of the instruments and/or sensors
4. obtain and prepare the appropriate tools and equipment
5. maintain instrumentation and control devices
6. apply appropriate maintenance diagnostic techniques and
procedures
7. use the appropriate methods and techniques to remove and
replace the required instruments/sensors
8. carry out tests on sensing elements and associated instruments
9. deal promptly and effectively with problems within your control,
and seek help and guidance from the relevant people if you have
problems that you cannot resolve
10. leave the work area in a safe and tidy condition on completion of
the maintenance activities
SEMPEO239 Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices 3
SEMPEO239
Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices
Knowledge and
understanding
You need to know and
1. the health and safety requirements, and safe working practices
understand: and procedures required for the instrumentation maintenance
activities undertaken
2. the isolation and lock-off procedure or permit-to-work procedure
that applies to the system and instruments being worked on, and
how to check that any stored energy in pipework and instruments
has been released
3. the importance of wearing appropriate protective clothing and
equipment (PPE), and keeping the work area safe and tidy
4. hazards associated with carrying out instrumentation and control
maintenance activities (such as live electrical components,
process controller interface, stored pressure/force, misuse of
tools, using damaged or badly maintained tools and equipment,
not following laid-down maintenance procedures), and how to
minimise them
5. what constitutes a hazardous voltage and how to recognise and
deal with victims of electric shock
6. the procedures and precautions to be adopted to eliminate
electrostatic discharge (ESD)
7. how to obtain and interpret information from job instructions and
other documents needed for the maintenance activities (such as
drawings, circuit and physical layouts, charts, specifications,
manufacturers' manuals, history/maintenance reports, symbols
and terminology, BS and ISO wiring regulations)
8. the basic principles of operation of the instrumentation being
maintained (to include pressure, temperature, level and flow
instrument sensors)
9. how to identify the various instrument sensors (including how to
identify their markings, calibration information, component values,
operating parameters and working range)
10. the various maintenance diagnostic techniques and aids that can
be used (such as flow charts, fault reports, visual checks,
measuring, movement and alignment checks, testing)
11. the various fault location techniques that can be used, and how
they are applied (such as half-split, input-to-output, function
testing, unit substitution, and equipment self-diagnostics)
12. how to select and use a range of fault diagnostic equipment to
SEMPEO239 Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices 4
SEMPEO239
Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices
investigate the problem
13. the care, handling and application of instrumentation and control
measuring instruments
14. the reasons for making sure that control systems are isolated or
put into manual control, and that appropriate trip locks or keys are
inserted, before removing any sensors or instruments from the
system, and the consequences of failing to do this
15. the techniques used to dismantle/remove the equipment (such as
release of pressures/force, proof marking to aid assembly,
plugging exposed pipe/component openings, dealing with
soldered joints, screwed, clamped and crimped connections)
16. methods of attaching identification marks/labels to removed
components or cables, to assist with reassembly
17. methods of checking that components are fit for purpose, and the
need to replace batteries, boards and other failed items
18. the correct way of re-fitting instruments to avoid faulty readings
(such as caused by head correction, poor flow past the sensor,
blockages, incorrect wiring, poor insulation or incorrect materials)
19. how to carry out visual checks of the instruments (such as
security of joints and physical damage)
20. the need to carry out tests and calibration checks on the various
sensing elements and stand-alone instruments, and the use of
standard calibration charts and tables
21. the types and application of standard test equipment (such as
pressure sources, deadweight tester, temperature baths, signal
sources and comparators)
22. how to check that tools and equipment are free from damage or
defects and are in a safe, calibrated, tested and usable condition
23. the approved methods of carrying out the tests on each type of
instrument/sensor; setting instrument zero readings; obtaining
instrument readings and comparing them with the circuit
parameters; making adjustments to instrument/circuit components
24. the generation of maintenance documentation and/or reports
following the maintenance activity
25. the problems that can occur during the maintenance of the
instrumentation and control system, and how they can be
overcome
26. the organisational procedure to be adopted for the safe disposal
of waste of all types of materials
27. when to act on your own initiative and when to seek help and
SEMPEO239 Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices 5
SEMPEO239
Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices
advice from others
28. the importance of leaving the work area in a safe and clean
condition on completion of the maintenance activities (such as
returning tools and test equipment to is designated location,
cleaning the work area, and removing and disposing of waste)
SEMPEO239 Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices 6
SEMPEO239
Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices
Scope/range related
1. Carry out all of the following during the instrumentation
to performance
maintenance activities:
criteria 1. adhere to procedures or systems in place for risk
assessment, COSHH, personal protective equipment (PPE)
and other relevant safety regulations
2. where appropriate, ensure the safe isolation of instruments
(such as electrical, pneumatic, process)
3. follow job instructions, maintenance drawings and
procedures
4. check that the tools and test instruments are within
calibration date and are in a safe, tested and usable
condition
5. ensure that the equipment/system is kept free from foreign
objects, dirt or other contamination
6. return all tools and equipment to the correct location on
completion of the maintenance activities
2. Carry out maintenance activities on two of the following types of
instrumentation and control systems:
1. pressure
2. speed measurement
3. fluid level
4. noise
5. fluid flow
6. vibration monitoring
7. temperature measurement
8. nucleonic and radiation measurement
9. fire detection
10. telemetry systems
11. gas detection
12. weight measurement
13. emergency shutdown
14. alarm systems
15. environmental
16. other specific system
3. Use four of the following maintenance diagnostic techniques,
tools and aids:
1. fault finding techniques (such as input/output, half-split, unit
substitution)
SEMPEO239 Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices 7
SEMPEO239
Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices
2. diagnostic aids (such as manuals, flow charts,
troubleshooting guides, maintenance records)
3. information gathered from the person who reported the fault
4. visual checks (such as signs of damage, leaks, missing
parts, wear/deterioration)
5. movement checks (such as loose fittings and connections)
6. monitoring equipment or gauges
7. test instrumentation measurement (such as voltage,
resistance, current)
4. Carry out all of the following instrumentation maintenance
activities:
1. removing excessive dirt and grime
2. replacing all `lifed' and consumable items (such as seals,
gaskets)
3. taking electrostatic discharge (ESD) precautions (where
appropriate)
4. replacing instruments/devices in the system
5. setting, aligning and adjusting components
6. disconnecting supply/signal connections
7. tightening fastenings to the required torque
8. removing instruments from the system
9. re-connecting instrumentation pipework and power supply
10. dismantling equipment to the required level
11. labelling/marking of components
12. checking signal transmission is satisfactory
13. checking components for serviceability
14. replacing or repairing damaged/defective components (such
as electrical, mechanical and back-up batteries)
15. functionally testing the maintained equipment
5. Set up and test sensing elements and/or stand-alone instruments,
to include three of the following:
1. pressure (such as bourdon tube gauge, capsule/diaphragm
gauge, pressure transducers)
2. temperature (such as thermocouple, resistance
thermometers, liquid in steel thermometer)
3. flow (such as differential pressure systems, balanced flow
meters, positive displacement)
4. level (such as displacer systems, purged dip leg,
SEMPEO239 Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices 8
SEMPEO239
Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices
capacitance probes, differential pressure systems, ultrasonic
probes)
5. other instruments/sensing elements (such as fire or gas
detection, noise or vibration, speed or weight)
6. Use four of the following types of instrumentation test and
calibration equipment:
1. signal sources
2. pressure sources
3. logic probes
4. standard test gauges
5. comparators
6. temperature baths
7. analogue or digital meters
8. manometers
9. workshop potentiometers
10. digital pressure indicators
11. current injection devices
12. dead weight testers
13. calibrated flow meters
14. calibrated weights
15. insulation testers
16. special-purpose test equipment
7. Maintain instrumentation and control systems, in accordance with
one of the following:
1. organisational guidelines and codes of practice
2. equipment manufacturer's operation range
3. BS and ISO standards
SEMPEO239 Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices 9
SEMPEO239
Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices
Behaviours
Additional Information
You will be able to apply the appropriate behaviours required in the
workplace to meet the job profile and overall company objectives, such
as:
• strong work ethic
• positive attitude
• team player
• dependability
• responsibility
• honesty
• integrity
• motivation
• commitment
SEMPEO239 Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices 10
SEMPEO239
Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices
Developed by Semta
Version Number 3
Date Approved March 2017
Indicative Review April 2020
Date
Validity Current
Status Original
Originating Semta
Organisation
Original URN SEMPEO2-39
Relevant Engineering; Engineering and manufacturing technologies
Occupations
Suite Performing Engineering Operations Suite 2
Keywords engineering; engineering operations; maintenance; testing; process
instrumentation and control devices; manufacturing; tools; equipment;
diagnostic techniques; fault finding techniques
SEMPEO239 Maintaining and testing process instrumentation and control devices 11
You might also like
- Maintaining and testing process instrumentationDocument9 pagesMaintaining and testing process instrumentationpankaj sharmaNo ratings yet
- Commission Instrumentation and Control EquipmentDocument10 pagesCommission Instrumentation and Control EquipmentYamina DennaNo ratings yet
- Maintaining mechanical devicesDocument9 pagesMaintaining mechanical devicesNico YamatoNo ratings yet
- Maintaining electronic equipmentDocument11 pagesMaintaining electronic equipmentAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Operation and Control PhilosophyDocument2 pagesOperation and Control Philosophyabuzar12533No ratings yet
- Semic339 PDFDocument9 pagesSemic339 PDFUmar UsmanNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Mould, Press Tool or Die Equipment: Semet26Document9 pagesMaintaining Mould, Press Tool or Die Equipment: Semet26CaldwellNo ratings yet
- Unit 355 Carrying Out Fault Diagnosis On Engineering Plant and EquipmentDocument7 pagesUnit 355 Carrying Out Fault Diagnosis On Engineering Plant and EquipmentAbhijeet SableNo ratings yet
- ISA CCST Task List Reference GuideDocument13 pagesISA CCST Task List Reference GuideNaseer HydenNo ratings yet
- Element 9 - Work EquipmentDocument28 pagesElement 9 - Work EquipmentJaveria FatimaNo ratings yet
- Radiation Protection ProceduresDocument40 pagesRadiation Protection ProceduresJie DVNo ratings yet
- PRSTS304A Commission/decommission Security Equipment/system: Release: 1Document19 pagesPRSTS304A Commission/decommission Security Equipment/system: Release: 1arnoldalejadoNo ratings yet
- Safety Measures for OCS TestingsDocument7 pagesSafety Measures for OCS Testingssebastos1982No ratings yet
- Operate Basic Machinery and EquipmentDocument5 pagesOperate Basic Machinery and EquipmentDr-Glen Tapiwa MdangweNo ratings yet
- 0 - Assessment StandardDocument3 pages0 - Assessment StandardMahmoudNo ratings yet
- Modules of Instruction (CSS)Document19 pagesModules of Instruction (CSS)zansue abutamNo ratings yet
- CPCCPB3026 PresentationDocument85 pagesCPCCPB3026 PresentationAbdul HaseebNo ratings yet
- Unit 44 Engineering Maintenance Procedures and Tech 2 PDFDocument10 pagesUnit 44 Engineering Maintenance Procedures and Tech 2 PDFMKPashaPashaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 11 Condition Monitoring On Hydro TurbineDocument4 pagesUNIT 11 Condition Monitoring On Hydro Turbinemuaz_aminu1422100% (1)
- Dkdgs DeploymentDocument5 pagesDkdgs Deploymentsaid.swekNo ratings yet
- NRAG Guidance Temporary Aerial Fibre Wire Rope Camera SystemsDocument2 pagesNRAG Guidance Temporary Aerial Fibre Wire Rope Camera SystemsSophie-Louise MercedesNo ratings yet
- SEMAE3313LDocument11 pagesSEMAE3313LImengga PurwiyanaNo ratings yet
- 23process Eng Maint Instrument Control TechnicianDocument70 pages23process Eng Maint Instrument Control TechnicianRonny Andalas50% (2)
- D2E Guidance On The Use of Permanent SAE v0.1 PDFDocument13 pagesD2E Guidance On The Use of Permanent SAE v0.1 PDFFfttNo ratings yet
- Provision and Use of Work EquipmentDocument13 pagesProvision and Use of Work EquipmentvladNo ratings yet
- E4 Operation ProceduresDocument14 pagesE4 Operation ProceduresEl Sayed Saad ShehataNo ratings yet
- 28 Producing Components Using Hand Fitting TechniquesDocument12 pages28 Producing Components Using Hand Fitting TechniquesjoeNo ratings yet
- Maintain Safe Piling RigsDocument12 pagesMaintain Safe Piling RigsashutoshNo ratings yet
- M05 CommissioningDocument47 pagesM05 CommissioningTariku TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Awareness On Regulation of Occupational Health and SafetyDocument56 pagesAwareness On Regulation of Occupational Health and Safetyjoenediath9345No ratings yet
- Plant & Equipment, WHSPRO-020 CMDocument3 pagesPlant & Equipment, WHSPRO-020 CMJean Claude EidNo ratings yet
- NEWP301D Undertake Commissioning Procedures of Apparatus & Associated Circuits - Instrumentation 3186Document3 pagesNEWP301D Undertake Commissioning Procedures of Apparatus & Associated Circuits - Instrumentation 3186haricytNo ratings yet
- Use Business EqipmentsDocument20 pagesUse Business Eqipmentsnigus100% (1)
- KRA 1.4 Plant and EquipmentDocument13 pagesKRA 1.4 Plant and EquipmentSubburajMechNo ratings yet
- KSU Clinical Research Equipment ProceduresDocument3 pagesKSU Clinical Research Equipment ProceduresThusitha LakpriyaNo ratings yet
- SIAUE3007 Inspect and Service Steering Systems.Document9 pagesSIAUE3007 Inspect and Service Steering Systems.Harry DaogaNo ratings yet
- System Testing: (E.g. Pressure Testing, Electrical Testing, Radiography)Document3 pagesSystem Testing: (E.g. Pressure Testing, Electrical Testing, Radiography)Muhammad Saqib AsifNo ratings yet
- Safety Precautions and Practices in Operation and MaintenanceDocument8 pagesSafety Precautions and Practices in Operation and MaintenanceQwe AsdfNo ratings yet
- ANUP_018020Document10 pagesANUP_018020john.rowleyNo ratings yet
- Scope of WorkDocument3 pagesScope of Work64104641100% (1)
- PEM NOS 10: Minimise Risks To Life, Property and The EnvironmentDocument2 pagesPEM NOS 10: Minimise Risks To Life, Property and The EnvironmentAbdulhameed HamadNo ratings yet
- Commissioning Procedures GuideDocument4 pagesCommissioning Procedures GuideRezky Dian SunartoNo ratings yet
- Care and Control of ToolsDocument22 pagesCare and Control of ToolsRAJ MOHANNo ratings yet
- Care and Control of Tools RecordsDocument22 pagesCare and Control of Tools RecordsRAJ MOHANNo ratings yet
- Plan and Prepare For Maintenance and Repair G10 4QDocument52 pagesPlan and Prepare For Maintenance and Repair G10 4QSchoolNotesArchiveNo ratings yet
- JD Control Room OperatorDocument3 pagesJD Control Room Operatorjamil ahmedNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Equipment ManagementDocument14 pagesLaboratory Equipment Managementtahir UddinNo ratings yet
- System Network Administrator DutiesDocument1 pageSystem Network Administrator DutieseddiebobNo ratings yet
- Learner Guide - AURETR030 - Diagnose and Repair Starting Systems PDFDocument86 pagesLearner Guide - AURETR030 - Diagnose and Repair Starting Systems PDFAakash0% (1)
- Identification and Use of The Correct Instruments - Completion of The Relevant Documentation - Recording of Relevant Data and Information.Document10 pagesIdentification and Use of The Correct Instruments - Completion of The Relevant Documentation - Recording of Relevant Data and Information.MOKAYANo ratings yet
- NIOSH Work Permit System NewDocument92 pagesNIOSH Work Permit System Newsanpkaru100% (1)
- Unit 22 Instrumentation and Control Principles Learning Hours: 60 NQF Level 4: BTEC Higher National - H1Document6 pagesUnit 22 Instrumentation and Control Principles Learning Hours: 60 NQF Level 4: BTEC Higher National - H1jeevanNo ratings yet
- Procedure for Safe Handling and Maintenance of Lab InstrumentsDocument2 pagesProcedure for Safe Handling and Maintenance of Lab InstrumentsGajaNand MallickNo ratings yet
- Maitenance G 8Document12 pagesMaitenance G 8Mariel Jane Mendoza - DucotNo ratings yet
- MSDS Indicators 121-125 For Biomedical EquipmentDocument19 pagesMSDS Indicators 121-125 For Biomedical Equipmenthaseeb JuttNo ratings yet
- Magnetic particle testing guideDocument5 pagesMagnetic particle testing guidemohamed fahsNo ratings yet
- Aurt225667a R1Document9 pagesAurt225667a R1Januar Adi NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Operational ControlDocument3 pagesOperational ControlAjas Aju50% (2)
- EUC Appendix EddyCurrentDocument6 pagesEUC Appendix EddyCurrentadmin qaqcNo ratings yet
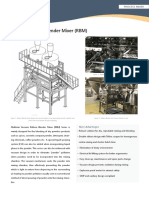
- Ribbon MixerDocument2 pagesRibbon MixerAngelNo ratings yet
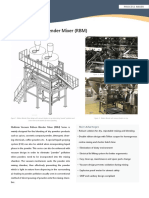
- Vacuum Ribbon Blender Mixer (RBM)Document2 pagesVacuum Ribbon Blender Mixer (RBM)AngelNo ratings yet
- Ribbon Mixer OperationDocument2 pagesRibbon Mixer OperationAngelNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Ribbon Blender Mixer (RBM)Document2 pagesVacuum Ribbon Blender Mixer (RBM)AngelNo ratings yet
- Here are the answers to the questions:1. TRUE2. TRUE 3. TRUE4. FALSE (Boot log stores information from the boot process)5. TRUEDocument18 pagesHere are the answers to the questions:1. TRUE2. TRUE 3. TRUE4. FALSE (Boot log stores information from the boot process)5. TRUELeandro InciongNo ratings yet
- Maintaining SMAW Tools and EquipmentDocument4 pagesMaintaining SMAW Tools and EquipmentRJLifeOfPedzNo ratings yet
- ISO/WD 22400-1: © ISO 2010 - All Rights ReservedDocument12 pagesISO/WD 22400-1: © ISO 2010 - All Rights ReservedHamza HamNo ratings yet
- B200 Training Manual Ata 5Document10 pagesB200 Training Manual Ata 5gupta3070No ratings yet
- Vol IV Price Bid-Wapinfracspuriodisha2019Document117 pagesVol IV Price Bid-Wapinfracspuriodisha2019Gabriel Pratama SebayangNo ratings yet
- FC 02 Instrumentation PDFDocument285 pagesFC 02 Instrumentation PDFDinesh Mehta100% (1)
- Outsourcing Aircraft MaintenanceDocument67 pagesOutsourcing Aircraft MaintenanceEromon Arumemi-IkhideNo ratings yet
- HLeiteDocument6 pagesHLeiteLê Trung DũngNo ratings yet
- Sap PM Tutorial PDFDocument89 pagesSap PM Tutorial PDFAdi UdreaNo ratings yet
- CMM Overpressure Valve 5ha1 PDFDocument81 pagesCMM Overpressure Valve 5ha1 PDFIvan KryskoNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedDocument13 pagesMaintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- Santosh Kumar Dash PDFDocument3 pagesSantosh Kumar Dash PDFSantosh DashNo ratings yet
- CSI 4500 Datasheet PDFDocument16 pagesCSI 4500 Datasheet PDFwretchNo ratings yet
- Sem Wheel LoeaderDocument186 pagesSem Wheel LoeaderJoel RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Guyana LTSA Indicative Price To EPC 8x SGT700 33 MWDocument23 pagesGuyana LTSA Indicative Price To EPC 8x SGT700 33 MWJose FavaNo ratings yet
- KOWA Basics of Oil Analysis Booklet 2020Document32 pagesKOWA Basics of Oil Analysis Booklet 2020AbdoNo ratings yet
- TEM FluidEnds MPDocument15 pagesTEM FluidEnds MPGeorge BuitragoNo ratings yet
- New Holland MH 5 6 EN City Plus PDF (001 312)Document312 pagesNew Holland MH 5 6 EN City Plus PDF (001 312)John Ronald Huacho100% (1)
- Enventure Engineering: Fast, Reliable, Efficient Global Engineering ServicesDocument13 pagesEnventure Engineering: Fast, Reliable, Efficient Global Engineering ServicesAravind MadhuNo ratings yet
- Akhil Joseph CVDocument3 pagesAkhil Joseph CVManu MohanNo ratings yet
- Best Management Practice For Fugitive Emissions ManagementDocument59 pagesBest Management Practice For Fugitive Emissions Managementmihahudea100% (1)
- Computer Operational System PracDocument31 pagesComputer Operational System PracAnushkaNo ratings yet
- TR2381 Rev.7Document158 pagesTR2381 Rev.7Maffone Numerouno0% (1)
- Traction MotorDocument117 pagesTraction Motorbharath100% (1)
- OBS-ONE-PN Installation and Maintenance ManualDocument81 pagesOBS-ONE-PN Installation and Maintenance ManualJaime Guerrero RiañoNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual - Ultra Pompe V16.1Document31 pagesInstruction Manual - Ultra Pompe V16.1AdvanDooremaalNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Engineering (Che-405) : DR Sikander Rafiq Assoc. ProfessorDocument37 pagesMaintenance Engineering (Che-405) : DR Sikander Rafiq Assoc. ProfessorHajra AamirNo ratings yet
- Module For Operations Management and Total Quality ManagementDocument65 pagesModule For Operations Management and Total Quality ManagementKaryll JustoNo ratings yet
- Magnacraft Magnamatch ManualDocument15 pagesMagnacraft Magnamatch ManualJim EngineeringNo ratings yet
- QP-72-01 Maintenance Policy & StrategiesDocument12 pagesQP-72-01 Maintenance Policy & StrategiesSamsudin Ahmad100% (2)