Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Selection of Fans
Uploaded by
Mo EmadOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Selection of Fans
Uploaded by
Mo EmadCopyright:
Available Formats
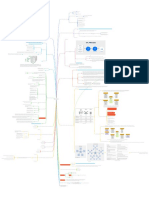
Forward inclined
Backward inclined
four main types
Radial
Backward inclined airfoil.
Although the figure above shows the difference between the different types as the shape and direction of the blades,
there is also another construction difference in the shape of the housing that is needed for each type. The backward
inclined fans require a much stricter housing construction and heavier blades which increases the costs. The airfoil
blades are also more difficult to construct, which also increases the costs of airfoil type fans. .
Efficiency VS Cost comparison
hvacruleofthumbcalculator-37.jpg
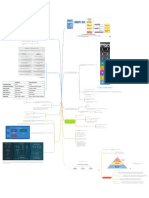
1.Simplicity of construction.
Selection of Fans Fan type Centrifugal fan 2. Absence of valves and
reciprocation parts.
3. Fewer moving parts.
4. Absence of close clearances.
5. Minimum of power transmission
losses.
6. Steady, nonsurging flow.
7. Operation at shutoff condition
without excessive
build-up in pressure.
ADVANTAGES
8. Absence of contact between
liquid pumped and
lubricant.
9. Compactness; light in weight.
10. Adaptability for direct
connection to standard
motors (major types of drive).
Figure-3-PumpRx-0616.jpg 11. Long life.
12. Ease of maintenance and
minimum repair.
13. Reasonable cost.
Selection of Fans
1. Fan type
1.1. Centrifugal fan
1.1.1. four main types
1.1.1.1. Forward inclined
1.1.1.2. Backward inclined
1.1.1.3. Radial
1.1.1.4. Backward inclined airfoil.
1.1.2. Although the figure above shows the difference between the different types as the shape and direction of the blades, there is also another construction difference in the shape of the housing that is needed for each type. The backward inclined fans require a much stricter housing construction and heavier blades which increases the costs. The airfoil blades are also more difficult to construct, which also increases the costs of airfoil type fans. .
1.1.3. Efficiency VS Cost comparison
1.1.3.1. hvacruleofthumbcalculator-37.jpg
1.1.4. ADVANTAGES
1.1.4.1. 1.Simplicity of construction.
1.1.4.2. 2. Absence of valves and reciprocation parts.
1.1.4.3. 3. Fewer moving parts.
1.1.4.4. 4. Absence of close clearances.
1.1.4.5. 5. Minimum of power transmission losses.
1.1.4.6. 6. Steady, nonsurging flow.
1.1.4.7. 7. Operation at shutoff condition without excessive
1.1.4.8. build-up in pressure.
1.1.4.9. 8. Absence of contact between liquid pumped and
1.1.4.10. lubricant.
1.1.4.11. 9. Compactness; light in weight.
1.1.4.12. 10. Adaptability for direct connection to standard
1.1.4.13. motors (major types of drive).
1.1.4.14. 11. Long life.
1.1.4.15. 12. Ease of maintenance and minimum repair.
1.1.4.16. 13. Reasonable cost.
2. Figure-3-PumpRx-0616.jpg
You might also like
- Electric Motors and Drives: Fundamentals, Types and ApplicationsFrom EverandElectric Motors and Drives: Fundamentals, Types and ApplicationsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Digital Communication by Sanjay Sharma Ebook PDFDocument2 pagesDigital Communication by Sanjay Sharma Ebook PDFnikita0% (2)
- US Patent No 5.159.703Document14 pagesUS Patent No 5.159.703ErikTrimarchiNo ratings yet
- Part 8 - Auxiliary Equipment PDFDocument80 pagesPart 8 - Auxiliary Equipment PDFDota Ng75% (4)
- 3196 I FRAME BulletinDocument24 pages3196 I FRAME BulletinGILBERTO YOSHIDANo ratings yet
- Kindexing MechanismsDocument7 pagesKindexing MechanismsSMBEAUTYNo ratings yet
- Me 145 - Machine Design 2: Engr - Harrison R. Flores PME 5072Document56 pagesMe 145 - Machine Design 2: Engr - Harrison R. Flores PME 5072allen eugene vizmanos100% (1)
- Pumps Selection 0703 HandbookDocument12 pagesPumps Selection 0703 Handbookkooljam83% (6)
- Cono RC CedarapidsDocument8 pagesCono RC CedarapidsJesus DugarteNo ratings yet
- Alarm and Fault FindingDocument36 pagesAlarm and Fault Findingmilad100% (2)
- Performance Management (SRAN7.0 01)Document21 pagesPerformance Management (SRAN7.0 01)Petson ChirangaraNo ratings yet
- Wa 600-3 PDFDocument12 pagesWa 600-3 PDFNayla AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal & Axial Compressor - ConstructionDocument16 pagesCentrifugal & Axial Compressor - ConstructionNikesh100% (3)
- HVAC-Fan & Blowers Selection PDFDocument59 pagesHVAC-Fan & Blowers Selection PDFAaron AngNo ratings yet
- The Stability of Frames: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionFrom EverandThe Stability of Frames: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Facebook & WhatsAppDocument10 pagesFacebook & WhatsAppSaqib UsmanNo ratings yet
- Ejectors: Ejectors Have A Wide Range of UsesDocument6 pagesEjectors: Ejectors Have A Wide Range of UsesBaher ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- PM Generator (Installation and Operation Manual) PDFDocument5 pagesPM Generator (Installation and Operation Manual) PDFNkwor MichaelNo ratings yet
- The Hydrocyclone: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandThe Hydrocyclone: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Horizontal Split Case LN TypeDocument38 pagesHorizontal Split Case LN TypeprojashNo ratings yet
- 1 1061GBDocument8 pages1 1061GBPatricio RojasNo ratings yet
- The Unbeatable Furukawa PCR-DTH - Facts Behind Its High Performance. The Unbeatable Furukawa PCR-DTH - Facts Behind Its High PerformanceDocument1 pageThe Unbeatable Furukawa PCR-DTH - Facts Behind Its High Performance. The Unbeatable Furukawa PCR-DTH - Facts Behind Its High PerformanceGerson Pari ChuraNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Split-Case Pumps: Brands You TrustDocument2 pagesHorizontal Split-Case Pumps: Brands You TrustNguyễn Đức CườngNo ratings yet
- Final Term Paper Constraction Machnary Name Abubakkar Su-18-01-149-009Document9 pagesFinal Term Paper Constraction Machnary Name Abubakkar Su-18-01-149-009Hasham khanNo ratings yet
- LF End Suction Pump: A Grundfos CompanyDocument4 pagesLF End Suction Pump: A Grundfos CompanyDya WiNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Roll Bending Machine: April 2018Document3 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Roll Bending Machine: April 2018Manfred GithinjiNo ratings yet
- Selecting A Cooling Fan: Device CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesSelecting A Cooling Fan: Device CharacteristicsGary KerrNo ratings yet
- The Original Dome Valve: Heavy Duty Pneumatic Bulk Solids Cut-Off ValveDocument6 pagesThe Original Dome Valve: Heavy Duty Pneumatic Bulk Solids Cut-Off ValveFelipe Ribeiro da CostaNo ratings yet
- The Design of Axial Shaftless PumpDocument4 pagesThe Design of Axial Shaftless Pumpmouad jaidaneNo ratings yet
- 08 Commercial Vehicle ApplicationsDocument13 pages08 Commercial Vehicle ApplicationsSantoshNo ratings yet
- Propellers NAME: A. Manish Kumar ROLLNO: 319106918066 Overlapping PropellersDocument9 pagesPropellers NAME: A. Manish Kumar ROLLNO: 319106918066 Overlapping Propellersmanish alahariNo ratings yet
- Hydralics Aeroquip - Swivle - JointsDocument20 pagesHydralics Aeroquip - Swivle - JointssunnyartboyNo ratings yet
- Sistem Transmisi TenagaDocument41 pagesSistem Transmisi TenagaPalang Aras RfcNo ratings yet
- Industrial Drives NotesDocument37 pagesIndustrial Drives NotesHitesh ArNo ratings yet
- BA Pump BrochurDocument8 pagesBA Pump Brochurelmer sanchezNo ratings yet
- VT Series Rack and Pinion Pneumatic Actuator: ATEX2014/34/EUDocument8 pagesVT Series Rack and Pinion Pneumatic Actuator: ATEX2014/34/EUMuhammad RidwanNo ratings yet
- Spiralift Catalog 2004-2007Document26 pagesSpiralift Catalog 2004-2007PeterWayNo ratings yet
- Air CompressorsDocument3 pagesAir CompressorsSheraz Abdul HayeeNo ratings yet
- 10 5923 J Mechanics 20120206 01 PDFDocument15 pages10 5923 J Mechanics 20120206 01 PDFsafiraginaNo ratings yet
- Suzuki Df6 4serviceDocument2 pagesSuzuki Df6 4serviceAdrian Hofnăr0% (1)
- Irjet V5i4722Document3 pagesIrjet V5i4722wendiezemene2124No ratings yet
- Install HPC NuTLink SuperTLinkDocument1 pageInstall HPC NuTLink SuperTLinkAndy LNo ratings yet
- Document 9Document9 pagesDocument 9Akshata ShindeNo ratings yet
- Drivepower 2nded 161024201601Document20 pagesDrivepower 2nded 161024201601Eduardo GuidoNo ratings yet
- PSD Pumps PDFDocument12 pagesPSD Pumps PDFUdielh VelezNo ratings yet
- Konst & Stab SMT 3 2020 PPT Rev 2 Meet 6Document31 pagesKonst & Stab SMT 3 2020 PPT Rev 2 Meet 6Yufansza RayhanNo ratings yet
- GC6000-0-1-0 Principles of Bearing Selection and ApplicationDocument6 pagesGC6000-0-1-0 Principles of Bearing Selection and ApplicationFrancisco AlessandriNo ratings yet
- Bladder Accumulators Standard: 1. DescriptionDocument7 pagesBladder Accumulators Standard: 1. DescriptionAalap DerasaryNo ratings yet
- Senthia Ahmed - Vip Hyperloop JournalDocument17 pagesSenthia Ahmed - Vip Hyperloop Journalapi-557424888No ratings yet
- حل اسيمنت الفلويد 2Document4 pagesحل اسيمنت الفلويد 2nwg6ssdm8rNo ratings yet
- GSD General Service Centrifugal Pump Brochure EN Oct18Document4 pagesGSD General Service Centrifugal Pump Brochure EN Oct18rafaelberaldiNo ratings yet
- GEOTHERMAL DIRECT USE - Well PumpsDocument29 pagesGEOTHERMAL DIRECT USE - Well PumpsDinda NovitaNo ratings yet
- Installation and Maintenance: Novenco Zerax® Fan Types Azl-Azn-AzwDocument17 pagesInstallation and Maintenance: Novenco Zerax® Fan Types Azl-Azn-AzwYorlevy J. Chirinos M.No ratings yet
- 3 - Module 6Document20 pages3 - Module 6Pinaki SankarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 PROPULSION SYSTEM - Marine Propellers and Propulsion - JOHN CARLTONDocument20 pagesCHAPTER 2 PROPULSION SYSTEM - Marine Propellers and Propulsion - JOHN CARLTONNur Salim100% (1)
- Hayes Proceedings PaperDocument21 pagesHayes Proceedings Papers4halaNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Improved Pneumatic Glass Cutting MachineDocument3 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Improved Pneumatic Glass Cutting MachineHarshal PatilNo ratings yet
- Technical Information Kalmar Container Handler, DRF.: Reachstackers 42 - 45 TonnesDocument12 pagesTechnical Information Kalmar Container Handler, DRF.: Reachstackers 42 - 45 TonnesIlija MiosevicNo ratings yet
- E26 Body ReportDocument16 pagesE26 Body ReportMatthew NelsonNo ratings yet
- D-Appendix BDocument22 pagesD-Appendix BadrianramNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Optimal Structural Design: Minimum Weight StructuresFrom EverandMechanics of Optimal Structural Design: Minimum Weight StructuresNo ratings yet
- Data QuestionsDocument3 pagesData QuestionsMo EmadNo ratings yet
- ERDDocument3 pagesERDMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Big DataDocument3 pagesBig DataMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis ConceptsDocument3 pagesData Analysis ConceptsMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Data MiningDocument3 pagesData MiningMo EmadNo ratings yet
- VIEWSDocument3 pagesVIEWSMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Tables of DesignDocument3 pagesTables of DesignMo EmadNo ratings yet
- PUMPSDocument3 pagesPUMPSMo EmadNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between A Data Warehouse and Big DataDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between A Data Warehouse and Big DataMo EmadNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument4 pagesDBMSMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Steps of Hvac DesginDocument3 pagesSteps of Hvac DesginMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Chiller Plant ExplainedDocument3 pagesChiller Plant ExplainedMo EmadNo ratings yet
- SELECTION Parameters OF COOLING UNITDocument3 pagesSELECTION Parameters OF COOLING UNITMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Optimization of A Battery Manufacturing Line Using Computer SimulationDocument107 pagesOptimization of A Battery Manufacturing Line Using Computer SimulationMo EmadNo ratings yet
- BODR For HVACDocument3 pagesBODR For HVACMo EmadNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument3 pagesDBMSMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Autocad MepDocument3 pagesAutocad MepMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Carrier Corporation: Limited Warranty For Condensing Gas Furnace With Clamshell Secondary Heat ExchangerDocument2 pagesCarrier Corporation: Limited Warranty For Condensing Gas Furnace With Clamshell Secondary Heat ExchangerMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Autocad Mep FeaturesDocument3 pagesAutocad Mep FeaturesMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Precast Concrete: Custom Built Solutions From Design To InstallationDocument6 pagesPrecast Concrete: Custom Built Solutions From Design To InstallationMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Precast Products - Declaration of Performance: Hallowcore FlooringDocument2 pagesPrecast Products - Declaration of Performance: Hallowcore FlooringMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Research AT Carnegie-Mellon UniversityDocument6 pagesArtificial Intelligence Research AT Carnegie-Mellon UniversityMo EmadNo ratings yet
- HandbookDocument206 pagesHandbookMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Roadstone: Thermal Liteblock SystemDocument24 pagesRoadstone: Thermal Liteblock SystemMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Oman - Ophiolite Hollow Block U-ValueDocument32 pagesOman - Ophiolite Hollow Block U-ValueMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Conformity of The Factory Production ControlDocument2 pagesCertificate of Conformity of The Factory Production ControlMo EmadNo ratings yet
- Handbook 2016 2017Document59 pagesHandbook 2016 2017Mo EmadNo ratings yet
- DVS VRTX Repair GuideDocument29 pagesDVS VRTX Repair GuideLuke RenzNo ratings yet
- SEW AC Motors 2009 PDFDocument496 pagesSEW AC Motors 2009 PDFwickedness100% (1)
- Aquarius Engineers Pvt. Ltd.Document18 pagesAquarius Engineers Pvt. Ltd.pranshamiNo ratings yet
- Pololu 3pi Robot User's Guide © 2001-2011 Pololu CorporationDocument68 pagesPololu 3pi Robot User's Guide © 2001-2011 Pololu CorporationMarcos LimaNo ratings yet
- Feistel CipherDocument11 pagesFeistel CipherManarNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi Aviation Univ HostelDocument1 pageRajiv Gandhi Aviation Univ HostelAditi MishraNo ratings yet
- Preventa Xps Xpsac5121Document2 pagesPreventa Xps Xpsac5121pedro torresNo ratings yet
- Resources - Sites - SCHNEIDER - ELECTRIC - Content - Live - FAQS - 167000 - FA167384 - en - US - TRIP Curve Zs CD, CN, DH PDFDocument6 pagesResources - Sites - SCHNEIDER - ELECTRIC - Content - Live - FAQS - 167000 - FA167384 - en - US - TRIP Curve Zs CD, CN, DH PDFmostafabasionyNo ratings yet
- Voltage Control in Power System Using Expert System Based On SCADA SystemDocument5 pagesVoltage Control in Power System Using Expert System Based On SCADA SystemFABIANCHO2210100% (1)
- Technical English Vocabulary and Grammar Alison Pohl Nick Brieger 2002 PDF FreeDocument148 pagesTechnical English Vocabulary and Grammar Alison Pohl Nick Brieger 2002 PDF FreeDima IlyinNo ratings yet
- Your Traction Inverter DesignDocument15 pagesYour Traction Inverter DesigndinhquangcdtbkNo ratings yet
- CodegiaodienDocument4 pagesCodegiaodienKhôi Nguyễn ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- Prefix Stereo Blender User GuideDocument12 pagesPrefix Stereo Blender User GuideScott HinsonNo ratings yet
- Activemq Broker Camel Connector Jms Client 5.15.8 5.15.9 5.15.10 5.15.12Document4 pagesActivemq Broker Camel Connector Jms Client 5.15.8 5.15.9 5.15.10 5.15.12MassiNo ratings yet
- Cim Model Unit 1 QB With AnsDocument18 pagesCim Model Unit 1 QB With AnsSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- SimpleTech 64 MB Industrial Flash DrivaDocument21 pagesSimpleTech 64 MB Industrial Flash DrivabplaNo ratings yet
- The Ethics of Artificial IntelligenceDocument2 pagesThe Ethics of Artificial Intelligencedragon knightNo ratings yet
- Quality Gururs Total Quality ManagementDocument11 pagesQuality Gururs Total Quality ManagementMaisha AnzumNo ratings yet
- SuperMax Receiver Biss EnglishDocument7 pagesSuperMax Receiver Biss EnglishStelios ZoitNo ratings yet
- Agilent Haim SDocument54 pagesAgilent Haim Ssepe999No ratings yet
- QTP CodesDocument172 pagesQTP CodesRajeev SinghNo ratings yet
- Ic 616ece484 - Lab - 2020Document116 pagesIc 616ece484 - Lab - 2020wang zhaoNo ratings yet
- MUHAMMAD AFFAN BASHIR (SR Reliability Engineer)Document2 pagesMUHAMMAD AFFAN BASHIR (SR Reliability Engineer)darff45No ratings yet
- Case Study On Sears Logistics Management PracticesDocument10 pagesCase Study On Sears Logistics Management PracticesRuby Chanda0% (1)