Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Knowledge
Uploaded by
Sandro KobuliaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Knowledge
Uploaded by
Sandro KobuliaCopyright:
Available Formats
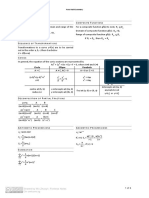
EXP I Winter Term 2021/2022
Useful Knowledge
+1 if (ijk) is (123) or (312) or (231)
(
ϵijk = −1 if (ijk) is (321) or (132) or (213) +1 if i = j
δij =
0 if i = j or j = k or k = i 0 ̸ i
if i =
1. Vectors
q √
ax bx ax + bx |⃗a| = a2x + a2y + a2z = ⃗a⃗a
ay + by = ay + by
az bz az + bz
λax 1 0 0
λ⃗a = λay e⃗x = 0 , e⃗y = 1 , e⃗z = 0
λaz 0 0 1
The skalar product:
⃗a⃗b = ai bi = ax bx + ay by + az bz = |⃗a||⃗b|cos (α)
P
⃗a ⊥ ⃗b : ⃗a⃗b = 0
⃗a⃗b = ⃗b⃗a
⃗a(⃗b + ⃗c) = ⃗a⃗b + ⃗a⃗c
⃗a(⃗b⃗c) = (⃗a⃗b)⃗c
The vector product:
ay bz − by az ⃗a × ⃗b = −⃗b × ⃗a
⃗a × ⃗b =
P
ai bj ϵijk e⃗k = az bx − bz ax
ax by − ay bx ⃗a × (⃗b + ⃗c) = ⃗a × ⃗b + ⃗a × ⃗c
|⃗a × ⃗b| = |⃗a||⃗b| sin (α) ⃗a × (⃗b × ⃗c) ̸= (⃗a × ⃗b) × ⃗c
direction of ⃗c with right-hand-rule ⃗a × (⃗b × ⃗c) = ⃗b(⃗a⃗c) − ⃗c(⃗a⃗b)
e⃗i × e⃗j = ϵijk e⃗k λ(⃗a × ⃗b) = (λ⃗a) × ⃗b = ⃗a × (λ⃗b)
⃗a||⃗b : ⃗a × ⃗b = 0 ⃗a(⃗b × ⃗c) = (⃗a × ⃗b)⃗c
Lecturer: R.Seidel Teaching Assistants: M.Göse, P.Irmisch, D.Kauert
EXP I Winter Term 2021/2022
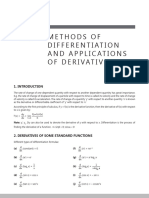
2. Derivatives
δf (x) δ 2 f (x) δ2
Notations: δx = δ
δx f (x) = f˙(x) = f ′ (x), δx2 = δx2 f (x) = f¨(x) = f ′′ (x), . . .
Name of the rule Function Derivative
c 0
Power xn n · xn−1
Constant c · g(x) c · g ′ (x)
Sum g(x) + h(x) g ′ (x) + h′ (x)
Product g(x) · h(x) g ′ (x) · h(x) + g(x) · h′ (x)
g(x) g ′ (x)·h(x)−g(x)·h′ (x)
Quotient h(x) [h(x)]2
′ ′
Chain g(h(x)) g (h(x)) · h (x)
3. Integrals
Rb
f (x)dx = F (x) + c ⇒ F ′ (x) = f (x), f (x)dx = F (x)|ba = [F (x)]ba = F (b) − F (a)
R
Notations: a
Name of the rule Function Integral
Multiplication by constant c c·x
1
Power xn n+1 xn+1
R
Product c · g(x) c · g(x)dx
R R
Sum g(x) + h(x) g(x)dx + h(x)dx
g ′ (x) · h(x) g(x) · h(x) − g(x) · h′ (x)dx
R
Integration by Parts
g(h(u)) · h′ (u)du
R
Substitution g(x)
g ′ (x)
g(x) ln (g(x))
4. Exercises
Derivatives: Calculate the derivative with respect to x of these functions:
1
(a) f (x) = 5x2 + 3bx − 237 (d) f (x) = ( √ )3.5 (g) f (x) = ln (ln (x))
tan(x)
2
(b) f (x) = esin(x ) (e) f (x) = x2 −1
x2 +1
√ (h) f (x) = sin (2x) cos (3x)
5x2 +3
(c) f (x) = 19x−c (f) f (x) = cos ( x)
Integrals: Calculate the following integrals:
(1 + 2x + 3x2 )dx ( x+1
R R R
(a) (c) x )dx (e) (sin (x) cos (x))dx
√
(ex 1 + ex )dx
R R R
(b) (5cos (x))dx (d) (ln (x))dx (f)
Lecturer: R.Seidel Teaching Assistants: M.Göse, P.Irmisch, D.Kauert
You might also like
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Integration of Function: D DX D DXDocument10 pagesIntegration of Function: D DX D DXYeoh HanNo ratings yet
- MATH 2170: Table of Derivatives and IntegralsDocument5 pagesMATH 2170: Table of Derivatives and IntegralsspacejuyNo ratings yet
- Integración Por Sustitución 1Document6 pagesIntegración Por Sustitución 1jose_dino10005190No ratings yet
- Integrals Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesIntegrals Cheat SheetPamela Ricaforte100% (1)
- Formulario para Integrales - SymbolabDocument3 pagesFormulario para Integrales - SymbolabAbraham CandiaNo ratings yet
- Math Summary: Inverse, Composite, Conic SectionsDocument4 pagesMath Summary: Inverse, Composite, Conic SectionsnursyadzwinaNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus Formula SheetDocument4 pagesIntegral Calculus Formula Sheetdaphnegrace villaralvoNo ratings yet
- Common Derivatives IntegralsDocument4 pagesCommon Derivatives IntegralsPhilanderGereenPiniliNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 4Document2 pagesWorksheet 4Kat GoNo ratings yet
- Lec 10Document6 pagesLec 10keteseb131No ratings yet
- Cambridge Physics PhD Tutor IB DSE IGCSE SAT Integration by Parts GuideDocument9 pagesCambridge Physics PhD Tutor IB DSE IGCSE SAT Integration by Parts GuideHin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- Integrarea Functiilor RationaleDocument4 pagesIntegrarea Functiilor RationaleAdriana Pelea BrandasNo ratings yet
- 0 DF DX 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 F (X) G (X) F (X) G (X) F (X) G (X) G (X) 1 G (X) G (X) G (X) 0 0Document4 pages0 DF DX 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 F (X) G (X) F (X) G (X) F (X) G (X) G (X) 1 G (X) G (X) G (X) 0 0Maher MestoNo ratings yet
- Basic Derivatives FormulasDocument2 pagesBasic Derivatives FormulasGeojanni PangibitanNo ratings yet
- Area Under the CurveDocument8 pagesArea Under the CurveWasifNo ratings yet
- Integrals Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesIntegrals Cheat SheetFrostDevs GTNo ratings yet
- Local Center Manifold TheoryDocument4 pagesLocal Center Manifold TheoryAlfredo MartínezNo ratings yet
- Metode de Integrare. Integrarea Functiilor Rationale: 1 2 P p+1 N 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 M 2 M M m+1 2 m+1 m+1 KDocument4 pagesMetode de Integrare. Integrarea Functiilor Rationale: 1 2 P p+1 N 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 M 2 M M m+1 2 m+1 m+1 KVlad IsacNo ratings yet
- Td 2023 Maths 2024Document23 pagesTd 2023 Maths 2024elhilal002No ratings yet
- Definite Integrals 3Document33 pagesDefinite Integrals 3Norol AzurinNo ratings yet
- End of Stage 1/AS Mathematics:: Mathematics A (H230, H240) Paper 2: Pure Mathematics and MechanicsDocument21 pagesEnd of Stage 1/AS Mathematics:: Mathematics A (H230, H240) Paper 2: Pure Mathematics and MechanicsrebeccaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Formulary PDFDocument30 pagesMathematics Formulary PDFfizarimaeNo ratings yet
- Facultad de Ciencias Grado en F IsicaDocument3 pagesFacultad de Ciencias Grado en F IsicaGabryFerGar 11No ratings yet
- Maths Ice 445Document449 pagesMaths Ice 445Ashutosh PatilNo ratings yet
- AddMath Formula SheetDocument5 pagesAddMath Formula SheetHidayah TeacherNo ratings yet
- Calculus 2 14Document51 pagesCalculus 2 14VipanshuNo ratings yet
- Polynomial RingsDocument9 pagesPolynomial RingsN S SujithNo ratings yet
- MATH 259 - Review Sheet (Prerequisite Topics) : (This Is NOT A Comprehensive List!)Document4 pagesMATH 259 - Review Sheet (Prerequisite Topics) : (This Is NOT A Comprehensive List!)Celal KermangilNo ratings yet
- Some Approximations of The Bateman's G: FunctionDocument14 pagesSome Approximations of The Bateman's G: Functionom younesNo ratings yet
- 1551 FinalExam ProblemBankDocument12 pages1551 FinalExam ProblemBankPedro TNo ratings yet
- MATH1231 CALCULUS CHAPTER 2B PARTIAL FRACTIONSDocument27 pagesMATH1231 CALCULUS CHAPTER 2B PARTIAL FRACTIONSmax zebalaNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus: F (X) On I Is Given byDocument32 pagesIntegral Calculus: F (X) On I Is Given byJEYADURGANo ratings yet
- Integration Formulas: 1. Common IntegralsDocument5 pagesIntegration Formulas: 1. Common IntegralsAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Applied Linear Algebra 1st Edition Olver Solutions ManualDocument18 pagesApplied Linear Algebra 1st Edition Olver Solutions Manualthioxenegripe.55vd100% (16)
- Dwnload Full Applied Linear Algebra 1st Edition Olver Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Applied Linear Algebra 1st Edition Olver Solutions Manual PDFeyepieceinexact.4h0h100% (12)
- Basic Integration Methods MaDocument9 pagesBasic Integration Methods MaTOI 1802No ratings yet
- 7.Methods of Differentiation and Applications of DerivativesTheoryDocument27 pages7.Methods of Differentiation and Applications of DerivativesTheoryDevansh ParasharNo ratings yet
- Summary: Techniques of IntegrationDocument2 pagesSummary: Techniques of IntegrationStart 2 GamingNo ratings yet
- MATH 175 Calculus I - 2020-2021 Fall Worksheet 2Document2 pagesMATH 175 Calculus I - 2020-2021 Fall Worksheet 2malafikokamilNo ratings yet
- Integration by SubstitutionDocument3 pagesIntegration by Substitutiongodforalways20092411No ratings yet
- Techniques for Finding Integrals of Algebraic and Transcendental FunctionsDocument27 pagesTechniques for Finding Integrals of Algebraic and Transcendental Functionsramathan reignsNo ratings yet
- Edexcel C3 Revision SheetDocument3 pagesEdexcel C3 Revision SheetAshfaaq SkadamNo ratings yet
- x→∞ x→0 x→0 βx αβ x→0 αβ x→0Document9 pagesx→∞ x→0 x→0 βx αβ x→0 αβ x→0ana PlejicNo ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics MAL 110 (Mathematics I) Tutorial Sheet No. 1 Taylors Theorem and Integral CalculusDocument2 pagesDepartment of Mathematics MAL 110 (Mathematics I) Tutorial Sheet No. 1 Taylors Theorem and Integral CalculusKushagra GuptaNo ratings yet
- FormulaDocument1 pageFormulabrentbasha17No ratings yet
- Calculus Common Derivatives IntegralsDocument2 pagesCalculus Common Derivatives IntegralsMarissa CurryNo ratings yet
- Unknown 15Document27 pagesUnknown 15Pragya PanwarNo ratings yet
- Some Fundamental Types of FunctionsDocument12 pagesSome Fundamental Types of Functionsdana alharbiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Methods Formula Sheet 2017Document4 pagesMathematics Methods Formula Sheet 2017Zeba ZiaNo ratings yet
- Common Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFDocument2 pagesCommon Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFAyat FikNo ratings yet
- Common Derivatives Integrals ReducedDocument2 pagesCommon Derivatives Integrals ReducedJoshua ValentiNo ratings yet
- Common Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFDocument2 pagesCommon Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFJayWinnerNo ratings yet
- Common Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFDocument2 pagesCommon Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFJonalyn FuNo ratings yet
- Common Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFDocument2 pagesCommon Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFAyat FikNo ratings yet
- Formula Deri & IntDocument2 pagesFormula Deri & IntlondonNo ratings yet
- Common Derivatives Integrals Reduced 2Document2 pagesCommon Derivatives Integrals Reduced 2216435964No ratings yet
- Common Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFDocument2 pagesCommon Derivatives Integrals Reduced PDFei-888646No ratings yet
- Common Derivatives Integrals ReducedDocument2 pagesCommon Derivatives Integrals ReducedNatasha PandaNo ratings yet
- TP1HW Dimanalysis-PhasespaceDocument3 pagesTP1HW Dimanalysis-PhasespaceSandro KobuliaNo ratings yet
- BSC IPSP 3years - Module DescriptionsDocument52 pagesBSC IPSP 3years - Module DescriptionsSandro KobuliaNo ratings yet
- Results PublishDocument1 pageResults PublishSandro KobuliaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 1Document1 pageProblem Sheet 1Sandro KobuliaNo ratings yet
- ADAC health insurance details for Bela IashviliDocument3 pagesADAC health insurance details for Bela IashviliSandro KobuliaNo ratings yet
- Chetan Tour and Travel: Pickup Spot: Destination SpotDocument2 pagesChetan Tour and Travel: Pickup Spot: Destination SpotRahulNo ratings yet
- Ch06 Allocating Resources To The ProjectDocument55 pagesCh06 Allocating Resources To The ProjectJosh ChamaNo ratings yet
- Big Kaiser2019 PDFDocument624 pagesBig Kaiser2019 PDFGoto SamNo ratings yet
- 06 Plastic Model KitsDocument1 page06 Plastic Model KitsLeonidas MianoNo ratings yet
- Tourism and Development Planning: Slide 9.1Document19 pagesTourism and Development Planning: Slide 9.1English TimeNo ratings yet
- Standards in Nursing Education ProgrammeDocument13 pagesStandards in Nursing Education ProgrammeSupriya chhetryNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory - Audit ReportDocument26 pagesAuditing Theory - Audit ReportCarina Espallardo-RelucioNo ratings yet
- ANGCOS - The Challenge and The Future For OrganizationsDocument28 pagesANGCOS - The Challenge and The Future For Organizationshoney beeNo ratings yet
- April 2016Document4 pagesApril 2016Albert CorderoNo ratings yet
- BiomassGasificationFoam: OpenFOAM solver for biomass gasificationDocument29 pagesBiomassGasificationFoam: OpenFOAM solver for biomass gasificationbinho58No ratings yet
- 11 Ways To Encourage Stakeholder Participation:: Writing Good Consultation QuestionsDocument1 page11 Ways To Encourage Stakeholder Participation:: Writing Good Consultation QuestionsLuz Alinsunurin DulogNo ratings yet
- Federal Ombudsmen Institutional Reforms Act, 2013Document8 pagesFederal Ombudsmen Institutional Reforms Act, 2013Adv HmasNo ratings yet
- GCSE History Revision Guide and Workbook Examines Henry VIII's Reign 1509-1540Document23 pagesGCSE History Revision Guide and Workbook Examines Henry VIII's Reign 1509-1540Haris KhokharNo ratings yet
- S3 Unseen PracticeDocument7 pagesS3 Unseen PracticeTanush GoelNo ratings yet
- (GUIDE) Advanced Interactive Governor Tweaks Buttery Smooth and Insane Battery Life! - Page 519 - Xda-DevelopersDocument3 pages(GUIDE) Advanced Interactive Governor Tweaks Buttery Smooth and Insane Battery Life! - Page 519 - Xda-Developersdadme010% (2)
- Communicate With S7-1200 Via EhernetDocument6 pagesCommunicate With S7-1200 Via EhernetRegisNo ratings yet
- ICICI Health Insurance Policy DetailsDocument3 pagesICICI Health Insurance Policy DetailsarjunNo ratings yet
- SPE Estimating Fracture Gradient in Gulf of Mexico Deepwater, Shallow, Massive Salt SectionsDocument9 pagesSPE Estimating Fracture Gradient in Gulf of Mexico Deepwater, Shallow, Massive Salt SectionsTHiago LOpesNo ratings yet
- COURSE Strucure - M.tech (S.E) I & II Sem (Autonomous)Document40 pagesCOURSE Strucure - M.tech (S.E) I & II Sem (Autonomous)Fresherjobs IndiaNo ratings yet
- Java Programming: Lab Assignment 2Document17 pagesJava Programming: Lab Assignment 2Sanjana chowdary50% (4)
- Samahan NG Manggagawa NG Hanjin Vs BLRDocument11 pagesSamahan NG Manggagawa NG Hanjin Vs BLRPhrexilyn PajarilloNo ratings yet
- AESO ENERGY TRADING SYSTEM TRAINING Course Net Settlement Instructions VersionDocument19 pagesAESO ENERGY TRADING SYSTEM TRAINING Course Net Settlement Instructions VersionJustyna LipskaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Semester SchemeDocument35 pagesMechanical Engineering Semester Schemesantvan jagtapNo ratings yet
- 2003 June Calc Paper 6 (H)Document20 pages2003 June Calc Paper 6 (H)abbasfazilNo ratings yet
- Report of Six Months Industrial TrainingDocument38 pagesReport of Six Months Industrial TrainingJibran BashirNo ratings yet
- 12.CEH Module 3 Assignment 3.1Document7 pages12.CEH Module 3 Assignment 3.1piyuhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Earth WorkDocument39 pagesChapter 4 Earth WorkYitbarek BayieseNo ratings yet
- Iwan Lab Guide v1.1 FinalDocument63 pagesIwan Lab Guide v1.1 FinalRicardo SicheranNo ratings yet
- Meita Juniar - 41921200002 - Teknik Sipil Reg b2 Uas English For EngineerDocument18 pagesMeita Juniar - 41921200002 - Teknik Sipil Reg b2 Uas English For EngineerREG.B/41921200002/MEITA JUNIARNo ratings yet