Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atoms, elements, and subatomic particles
Uploaded by
Jhastine Mhae De VeraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atoms, elements, and subatomic particles
Uploaded by
Jhastine Mhae De VeraCopyright:
Available Formats
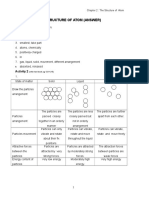
1. Explain the difference between atoms and elements.
An atom is the part of an element. A particular element is composed of only one type of
atom. Atoms are further composed of subatomic particles called electrons, protons and
neutrons. Elements can combine with each other to form molecules via chemical reaction.
2. What are atoms made of?
Atoms are the smallest unit of matter, and are made of three major sub-particles
namely, electrons which are negatively charged, protons, positively charged and neutrons which
are neutrally charged. Protons and neutrons compose the atom’s nucleus and most of the mass
of the atom.
3. Based on Rutherford’s gold foil experiment, explain why it is concluded that an atom has a
positively charged nucleus.
They bombarded very thin sheets of gold foil with fast moving alpha particles.
Rutherford found that a small percentage of alpha particles were deflected at large angles,
which could be explained by an atom with a very small, dense, positively-charged nucleus at its
center.
4. Explain the relationship between the valency and reactivity of an element.
Valence electrons, the electrons in the outermost or valence shell, are important as they
provide insight into an element's chemical properties and are the ones gained, lost, or shared
during a chemical reaction. In general, atoms are most stable and least reactive when their
outermost electron shell is full.
5. Distinguish between electronegativity and electron affinity.
Electronegativity refers to the ability of the atoms to attract electrons from the other
elements. Electron affinity refers to the amount of energy that is liberated whenever a molecule
or a neutral atom tends to acquire an electron from the other elements.
6. Explain the relationship between ionization energy and atomic radius. Cite examples to
support your answer.
Ionization energy is a function of atomic radius; the larger the radius, the smaller the
amount of energy required to remove the electron from the outer most orbital. Helium which
has the lowest atomic radius will have the most ionization energy.
7. Explain what happens to an electron as it moves to and from the nucleus.
Electrons move along energy levels within the atom. The closer an energy level into the
nucleus the lower it is, and electrons tend to absorb energy as they move from lower to high
energy levels, while it emits energy as they move from higher to lower energy levels.
8. Distinguish between Thomson’s and Rutherford’s structure of atom.
The key difference between Thomson and Rutherford model of atom is that Thomson
model of atom does not contain any details about nucleus whereas Rutherford model of atom
explains about the nucleus of an atom.
9. Differentiate metals, non-metals, and metalloids. Cite examples to support your answer.
Metals are found in the left side of the periodic table and has characteristics of being
ductile and malleable and also are good conductors of electricity (e.i. Sodium, Lithium, Iron,
Magnesium), while non-metals are found in the right side of the periodic table and mostly
composed of gases and has characteristics opposite to the metals (e.i. Hydrogen, hekium,
Oxygen, Fluorine, Chlorine), metalloids on the other hands are found in a staircase between
metals and nonmetals, these elements possess characteristics found in both metals and non-
metals (e.i. Boron, Silicon, Germanium, Tellurium)
10. Why do elements acquire a net positive or negative electric charge?
Atoms that lose electrons acquire a positive charge as a result because they are left with
fewer negatively charged electrons to balance the positive charges of the protons in the nucleus.
While atoms that gain electrons becomes negatively charged. Positively charged ions are called
cations while negatively charged ions are called anions.
11. Explain the difference between a molecular and empirical formula.
An empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of various atoms
present in a compound. The molecular formula shows the exact number of different types of
atoms present in a molecule of a compound.
12. How do ionic compounds form? Explain your answer.
Ionic compounds are formed through electron transfer among atoms. Ionic compound is
usually a result of bonding between metal and nonmetal.
13. How do covalent compounds form? Explain your answer.
Covalent compounds are formed through electron sharing of atoms. Covalent compound
is usually a result of bonding between nonmetals.
14. Based on their valence electrons, explain why Alkali Metals and Halogens are the most
reactive elements in the periodic table?
Alkali Metals have only one valence electron which make it more reactive than other
metals, while Halogens have 7 valence electrons, ang having a charge of negative one (-1), they
are the most reactive nonmetals.
15. Why do noble gases remain nonreactive?
Noble gases remain to be nonreactive due to their valence electrons. Noble gases have
already complete valence of eight electrons, thus making the atom stable.
You might also like
- NAME Aneela Aftab Semester Second Subject Fiber Science Submitted To Sir Muhammad QasimDocument22 pagesNAME Aneela Aftab Semester Second Subject Fiber Science Submitted To Sir Muhammad QasimAnila AftabNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1.1Document6 pagesTutorial 1.1FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Atomic Structure - Notes...Document7 pagesGrade 8 Atomic Structure - Notes...Antonita100% (1)
- Pptx5 Chemical BondingDocument39 pagesPptx5 Chemical BondingLumbay, Jolly MaeNo ratings yet
- ATOM Class 7Document23 pagesATOM Class 7Eureka MaterialNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding ExplainedDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure and Chemical Bonding ExplainedSoumya Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 1 Lesson1Document21 pagesBiology Unit 1 Lesson1AvakoalaNo ratings yet
- 1.6 BondingDocument17 pages1.6 BondingMahmoud TahaNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 Book 1 PhysicsDocument41 pagesMod 2 Book 1 Physicsranjit prasadNo ratings yet
- Chem revision essentialsDocument10 pagesChem revision essentialsmaddieNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Chemical BondingarjunvistaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in Electronics ServicingDocument13 pagesBasic Concepts in Electronics ServicingBenjamin FalletNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding and the Formation of IonsDocument6 pagesIonic Bonding and the Formation of IonsNguyenHoangMinhDucNo ratings yet
- GCFGCGCFGFDGDocument15 pagesGCFGCGCFGFDGZabrinaRuizNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Form 2Document70 pagesChemistry Notes For Form 2Charles OtienoNo ratings yet
- A Water Molecule Consists of An Oxygen Atom and Two Hydrogen Atoms, Which Are Attached at An Angle of 105°Document20 pagesA Water Molecule Consists of An Oxygen Atom and Two Hydrogen Atoms, Which Are Attached at An Angle of 105°Kunal LunawatNo ratings yet
- Rutherford's Alpha Particle Scattering ExperimentDocument4 pagesRutherford's Alpha Particle Scattering Experimentboris pocusNo ratings yet
- PeriodictableofelementsDocument6 pagesPeriodictableofelementswoodysseusNo ratings yet
- Bonding Basics: Shells Atom ElectronsDocument7 pagesBonding Basics: Shells Atom ElectronsClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Study Guide Topics Chemistry Elements CompoundsDocument33 pagesAP Bio Study Guide Topics Chemistry Elements CompoundsHayden CaseyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument13 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureVishal MalikNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument23 pagesIonic BondingMark DichosonNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience ReviewerAzel RheadalNo ratings yet
- AtomDocument4 pagesAtomanjaliNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 - General Chemistry-1-Lecture Note - 2023Document36 pagesCHM 101 - General Chemistry-1-Lecture Note - 2023bangysmashiNo ratings yet
- Elements, Atoms, and Chemical BondsDocument9 pagesElements, Atoms, and Chemical BondsAhamadul Islam OnonnoNo ratings yet
- Element Atom: Ion CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesElement Atom: Ion CharacteristicsClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Atomic Structure and BondingDocument27 pagesChapter Two: Atomic Structure and Bondingdawit gashuNo ratings yet
- Atomic Bonding (Metallic, Ionic, Covalent, and Van Der Waals Bonds)Document5 pagesAtomic Bonding (Metallic, Ionic, Covalent, and Van Der Waals Bonds)Aris YusepNo ratings yet
- Punjab Boards 11th Class Chemistry Book English Medium 6368075084588991190 PDFDocument583 pagesPunjab Boards 11th Class Chemistry Book English Medium 6368075084588991190 PDFGulshairNo ratings yet
- Protons: Protons Are The Basis of Atoms. While An Atom CanDocument3 pagesProtons: Protons Are The Basis of Atoms. While An Atom CansaadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document39 pagesChapter 1bilalafzal2323.2323No ratings yet
- 2018 G11 Chemistry EDocument583 pages2018 G11 Chemistry EAsif SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For EngineeringDocument3 pagesChemistry For EngineeringMarcRhyme CalaylayNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atoms and Molecules: Bohr's Atomic ModelDocument4 pagesStructure of Atoms and Molecules: Bohr's Atomic ModelChristianNo ratings yet
- Da-Voc-Abe 3.1.1Document25 pagesDa-Voc-Abe 3.1.1godfrey rufusNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: The Atomic Structure of MatterDocument3 pagesUnit 1: The Atomic Structure of MatterDanyel Rodriguez RomeraNo ratings yet
- Grade-11 Chemistry Definitions CollectionDocument65 pagesGrade-11 Chemistry Definitions CollectionMoun Lynn Sythu100% (3)
- Why Do Most Atoms Form Chemical BondsDocument3 pagesWhy Do Most Atoms Form Chemical BondsRUZCHEMISTRYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Student Reading: Parts of The AtomDocument12 pagesChapter 4-Student Reading: Parts of The AtomShimmy LimmyNo ratings yet
- Css Atom StructureDocument20 pagesCss Atom StructureHaris AzizNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Lec 3 MSRDocument25 pagesChemical Bonding Lec 3 MSRsiam137032No ratings yet
- Chem - The Periodic TableDocument20 pagesChem - The Periodic TablePoopNo ratings yet
- Compiled Lecture in General Chemistry (Organic Chemistry) (Midterm) CcjeDocument21 pagesCompiled Lecture in General Chemistry (Organic Chemistry) (Midterm) CcjeEmil Vince T. CumilangNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of an atom and basic chemistryDocument5 pagesAnatomy of an atom and basic chemistryKat OrcinoNo ratings yet
- Brand Chemical BackgroundDocument8 pagesBrand Chemical Backgroundninado92No ratings yet
- Chemical ChangesDocument35 pagesChemical ChangesaafaqnasirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Structure of The Atom Notes Class 9 ScienceDocument47 pagesChapter 4 Structure of The Atom Notes Class 9 ScienceChandan Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 The Structure of MatterDocument19 pagesUnit 4 The Structure of MatterPechito LokoNo ratings yet
- POGIL 01 - Nomenclature 1 - IonsDocument2 pagesPOGIL 01 - Nomenclature 1 - IonsFehmeed AlchemyNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and Ions: Chapter 3 of General ChemistryDocument28 pagesAtoms, Molecules and Ions: Chapter 3 of General ChemistryPauline AdrinedaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument3 pagesChemistryMarc Jonas DiazNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorsDocument17 pagesSemiconductorsHarishNo ratings yet
- IONS, BONDING & PROPERTIESDocument21 pagesIONS, BONDING & PROPERTIESRoshan Jawad ZafirNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Electronic Structure of The Atom Rz29fmDocument17 pagesAtomic Structure and Electronic Structure of The Atom Rz29fmkerri “Kerri” samNo ratings yet
- EnE 250 Air Quality Management and Pollution Control Lecture 03 - 2 Characterizing Air Pollution Oct 2015Document115 pagesEnE 250 Air Quality Management and Pollution Control Lecture 03 - 2 Characterizing Air Pollution Oct 2015Alexis Bryan RiveraNo ratings yet
- Basic Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesBasic Atomic Structureanas subhanNo ratings yet
- CHEM 11/L Module 2 - Atomic Structure and Periodic TableDocument15 pagesCHEM 11/L Module 2 - Atomic Structure and Periodic TableFrancis RecocoNo ratings yet
- About The Periodic Table of The ElementsDocument11 pagesAbout The Periodic Table of The ElementsKal El Dadi100% (2)
- Short 4 Pages PortraitDocument4 pagesShort 4 Pages PortraitJhastine Mhae De VeraNo ratings yet
- Bio 2 1Document11 pagesBio 2 1Jhastine Mhae De VeraNo ratings yet
- Bio 2 1Document11 pagesBio 2 1Jhastine Mhae De VeraNo ratings yet
- Developing My Personal PlanDocument2 pagesDeveloping My Personal PlanJhastine Mhae De VeraNo ratings yet
- Early Life and Evolution Theories ExplainedDocument10 pagesEarly Life and Evolution Theories ExplainedJhastine Mhae De VeraNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH FRAMEWORKSDocument53 pagesRESEARCH FRAMEWORKSJhastine Mhae De VeraNo ratings yet
- Contempo&milDocument4 pagesContempo&milJhastine Mhae De VeraNo ratings yet
- RNWWWWWWDocument1 pageRNWWWWWWJhastine Mhae De VeraNo ratings yet
- Discover Your Inner Superhero StrengthsDocument2 pagesDiscover Your Inner Superhero StrengthsJhastine Mhae De VeraNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Practice Test - 9Document15 pagesJEE Main Practice Test - 9Saravanan BNo ratings yet
- Introduction - Chemistry: Released Test QuestionsDocument24 pagesIntroduction - Chemistry: Released Test QuestionsJo CesNo ratings yet
- Discovery of The Hot Big Bang - What Happened in 1948 - P.J.E PeeblesDocument24 pagesDiscovery of The Hot Big Bang - What Happened in 1948 - P.J.E PeeblesLucas OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment Questions OneDocument3 pagesSelf Assessment Questions OneTendus StephanNo ratings yet
- Sample Chapter ch17 PDFDocument37 pagesSample Chapter ch17 PDFMaitraNo ratings yet
- Igcse 9-1Document14 pagesIgcse 9-1kashif mohammedNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY NO. 6: The Discovery of The Structure of The Atom and Its Subatomic Particles Name: Date: Year & Section: Score: Concept NotesDocument2 pagesACTIVITY NO. 6: The Discovery of The Structure of The Atom and Its Subatomic Particles Name: Date: Year & Section: Score: Concept NotesDexter DizonNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument57 pagesEnvironmental Science Chapter 1 IntroductionZura UmarNo ratings yet
- Waja Chemistry The Structure of The AtomDocument8 pagesWaja Chemistry The Structure of The AtomChewfun KhooNo ratings yet
- Ch02 - Lecture (Atom, Ion, Molecule)Document26 pagesCh02 - Lecture (Atom, Ion, Molecule)Shir0 NobiNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom Class IXDocument33 pagesStructure of Atom Class IXAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- CHE 105 Exam 1 ReviewDocument22 pagesCHE 105 Exam 1 ReviewRamenKing12No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLesson Planapi-239702286No ratings yet
- Key Definitions AS PhysicsDocument6 pagesKey Definitions AS Physicshaya waqrNo ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document9 pagesWa0000.Ramya. RNo ratings yet
- Questions 1 - 4 Are Worth Two Points Each. Questions 5 - 28 Are Worth Four Points EachDocument5 pagesQuestions 1 - 4 Are Worth Two Points Each. Questions 5 - 28 Are Worth Four Points EachLouis ParrNo ratings yet
- After The First Three Minutes - The Story of Our Universe (PDFDrive)Document228 pagesAfter The First Three Minutes - The Story of Our Universe (PDFDrive)Divyanshi DubeyNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Geology 13th Edition Lutgens Test BankDocument19 pagesEssentials of Geology 13th Edition Lutgens Test Bankstephenbarnesdtinzqxkbm100% (15)
- Comparing Masses of Subatomic ParticlesDocument8 pagesComparing Masses of Subatomic ParticlesMa. Elizabeth CusiNo ratings yet
- DPPS 1 Coulomb's LawDocument1 pageDPPS 1 Coulomb's LawRakesh Ranjan MishraNo ratings yet
- Systematic Inorganic Chemistry 1946Document452 pagesSystematic Inorganic Chemistry 1946omansuNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument24 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelSzeYee OonNo ratings yet
- Electricity Sensing Waves and Quantum Physics MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementDocument35 pagesElectricity Sensing Waves and Quantum Physics MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson Elementbob matthewNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 LAS Quarter 3Document428 pagesGeneral Physics 2 LAS Quarter 3Dkaye GorospeNo ratings yet
- Test Topic 2Document4 pagesTest Topic 2Ashutosh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Iit - JEE Syllabus: RSM79 PH I AS CH 1Document48 pagesIit - JEE Syllabus: RSM79 PH I AS CH 1MD IMRAN100% (1)
- Nucleus Decay and Radiation PropertiesDocument12 pagesNucleus Decay and Radiation Propertiesnikhilpatel1986No ratings yet
- Physical Science: Quarter 1 - Module 2: The Atomic Number and The Synthesis of New ElementsDocument24 pagesPhysical Science: Quarter 1 - Module 2: The Atomic Number and The Synthesis of New ElementsArthur LaurelNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Atomic Structure and BondingDocument27 pagesChapter Two: Atomic Structure and Bondingdawit gashuNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PHYSICSDocument195 pagesNuclear PHYSICSAugustte StravinskaiteNo ratings yet
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Meltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalFrom EverandMeltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Transformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathFrom EverandTransformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsFrom EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireFrom EverandA Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (129)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Chemistry: 1001 Practice Problems For Dummies (+ Free Online Practice)From EverandChemistry: 1001 Practice Problems For Dummies (+ Free Online Practice)No ratings yet
- Stuff Matters: Exploring the Marvelous Materials That Shape Our Man-Made WorldFrom EverandStuff Matters: Exploring the Marvelous Materials That Shape Our Man-Made WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (289)