Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Glossary Respiratory System Terminology
Glossary Respiratory System Terminology
Uploaded by
Ariana MuñozOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Glossary Respiratory System Terminology
Glossary Respiratory System Terminology
Uploaded by
Ariana MuñozCopyright:
Available Formats
CCHI Mini-Glossary Project Glossary #3
Subject: Respiratory
Language: Spanish
# English Spanish Definition
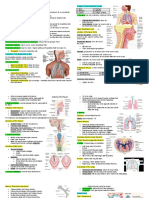
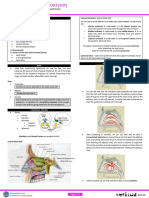
1. Respiratory Adj. (mas, fem) Respiratorio, Relating to, or affecting respiration (breathing) or the
ria. organs used in respiration.
2. ENT doctor (Ear-Nose- Sust. mas. Otorrinolaringólogo A physician who specializes in the disorders of the ear,
Throat) nose, throat.
Syn.
Otorhinolaryngologist
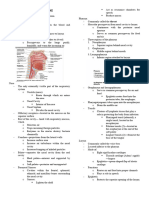
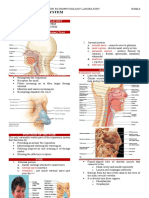
3. Nose Sust. fem. Nariz The part of the face that contains the organs of smell
and is the usual passage for air in breathing.
4. Nostril Sust. fem. Fosa nasal. Either of the two openings in the nose.
Sust. mas. Orificio nasal.
5. Throat Sust. fem. Garganta The passage from the mouth to the stomach or the
lungs.
6. (paranasal) Sinuses Sust. mas. pl. Senos Air cavities in the cranial bones, especially those near
(Pl.) paranasales. the nose (above it and to the sides of it).
(Sing.) Sinus (Sing.) Seno paranasal
7. (palatine) Tonsils (Pl.) Sust. fem pl. Amígdalas Areas of lymphoid tissue on either side of the throat
(palatinas) that can be seen in the back of the throat; organs of
the lymphatic system. The tonsils act as part of the
immune system to help protect against infection.
8. Tonsillectomy Sust. fem. Amigdalectomía Surgical removal of one or both tonsils.
Sust. fem. coloq: Operación de
las amígdalas
9. Adenoids (Pl.) Sust. fem. pl. Adenoides Mass of lymphatic tissue situated in the back of the
nasal cavity, in the roof of the nasopharynx, where the
nose blends into the throat. It often hinders speaking
and breathing in young children.
10. Larynx Sust. fem. Laringe The part of the respiratory tract between the pharynx
Syn. Voice box and the trachea, having walls of cartilage and muscle
and containing the vocal cords enveloped in folds of
mucous membrane.
11. Pharynx Sust. fem. Faringe The throat; a cavity behind the nasal cavity, mouth
and larynx.
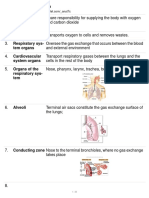
Syn. Throat Sin. Sust. fem. Garganta
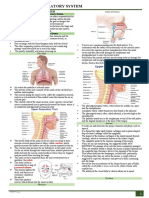
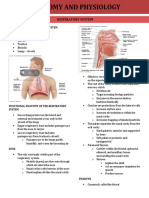
12. Epiglottis Sust. fem. Epiglotis The uppermost cartilage of the larynx; covers the
entrance of the larynx while swallowing.
Certification Commission for Healthcare Interpreters (CCHI)
1725 I Street, NW – Suite 300 / Washington DC 20006
www.cchicertification.org / info@CCHIcertification.org 1
CCHI Mini-Glossary Project Glossary #3, Subject: Respiratory Language: Spanish
13. Trachea Sust. fem. Tráquea The tube that carries inhaled air from the throat to the
lungs.
14. Bronchi (Pl.) Sust. mas. pl. Bronquios The two main branches of the trachea that lead to the
(Sing.) Bronchus (sing) Bronquio lungs, where they divide into smaller branches. They
are part of the lower respiratory tract along with the
lungs.
15. Mucus (n.) Sust. fem. Mucosidad A thick, slippery discharge produced by the mucous
Sust. masc. colq. Moco membranes and glands. Functions to moisten and
protect them.
16. Phlegm Sust. fem. Flema Thick, sticky, stringy mucus secreted by the mucous
membrane of the respiratory tract, as during a cold or
other respiratory infection.
17. Sputum Sust. masc. Esputo Matter coughed up and usually ejected from the
mouth, including saliva, foreign material, and
substances such as mucus or phlegm, from the
Sin. Coloq. Sust. masc. Gargajo respiratory tract.
18. Runny nose Expr. coloq. Nariz que escurre, A condition of having excess amount of mucus in the
Nariz que chorrea nose; nasal drainage.
19. Nasal discharge Fem. Secreción nasal Fluids that drain from the nose.
20. Post-nasal drip Masc. Goteo posnasal Excess nasal mucus accumulating in the back of the
nose and sliding down the throat.
21. tTo be congested Expr. Estar congestionado To have the blockage of the nasal passages usually due
oSyn. To have a stuffy Sin. Tener la nariz tapada o to membranes lining the nose becoming swollen from
inflamed blood vessels.
nose tupida (Cuba)
Coloq. Mexicanismo. Estar
mormado, da (de la voz
amormado, da)
22. Watery eyes Masc. pl. Ojos llorosos Persistent or excessive tear draining from the eyes.
23. Itchy eyes Fem. Comezón en los ojos An irritation that leads to a persistent urge to scratch
Sin. Fem. Picazón en los ojos the eyes.
24. To sneeze Estornudar To make a sudden involuntary expulsion of air from
the nose and mouth due to irritation of one's nostrils.
25. (facial) Tissue Sust. masc . Pañuelo A type of thin, soft, disposable paper used for nose-
Syn. Kleenex desechable blowing.
Sin. Kleenex
Certification Commission for Healthcare Interpreters (CCHI)
1725 I Street, NW – Suite 300 / Washington DC 20006
www.cchicertification.org / info@CCHIcertification.org 2
CCHI Mini-Glossary Project Glossary #3, Subject: Respiratory Language: Spanish
26. Allergy Sust. fem. Alergia An immune system reaction to the presence of a
substance that the body "mistakes" for being harmful
(such substance is called allergen).
27. Bacterial infection Sust. fem. Infección Infection caused by bacteria, i.e. microscopic living
bacteriana. organisms, usually one-celled, that can be found
everywhere.
The classic symptoms of a bacterial infection are
localized redness, heat, swelling and pain. One of the
hallmarks of a bacterial infection is local pain, pain
that is in a specific part of the body.
28. Viral infection Sust. fem. Infección viral. Infection caused by a virus, i.e. a small infectious
agent, smaller than a bacterium, that can replicate
only inside the living cells of an organism.
In general, viral infections are systemic. This means
they involve many different parts of the body or more
than one body system at the same time; i.e. a runny
nose, sinus congestion, cough, body aches, etc.
29. Contagious Adj. Contagioso, a Capable of being transmitted from one individual to
Syn. Communicable Sin. Adj. masc, fem. another.
Transmisible
30. (Common) Cold Sust. masc. Resfriado (común). A common viral infection in which the mucous
Sust. Masc. catarro membrane of the nose and throat becomes inflamed,
typically causing a runny nose, sneezing, sore throat,
and other similar symptoms.
31. Flu (Colloq.) Sust. fem. gripe, gripa A highly contagious viral infection that attacks the
respiratory system —nose, throat and lungs.
Syn. Influenza Sin. Sust. fem. Influenza
32. Flu vaccine (La) vacuna contra la gripe A preparation containing inactivated or weakened flu
Syn. Flu shot (Colloq.) virus administered to produce or artificially increase
immunity to flu.
33. Acute upper (La) infección aguda de las vías A contagious infection of the upper respiratory tract
respiratory infection respiratorias superiores which includes the nose, throat, pharynx, larynx, and
bronchi. Types of URIs include the common cold,
(URI) sinusitis, pharyngitis, epiglottitis, and
tracheobronchitis. Influenza is not an upper
respiratory infection because it is a systemic illness.
34. To cough Toser To expel air from the lungs suddenly and noisily, often
to keep the respiratory passages free of irritating
material.
35. To cough up Expectorar (formal) To expel sputum by coughing.
Escupir
36. Wheezing (las) sibilancias A high-pitched whistling sound during breathing. It
occurs when air flows through narrowed breathing
v. silbarle el pecho (a uno)
tubes.
37. Bronchitis (la) bronquitis An inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes,
which carry air to and from the lungs. It typically
causes bronchospasms and coughing.
Certification Commission for Healthcare Interpreters (CCHI)
1725 I Street, NW – Suite 300 / Washington DC 20006
www.cchicertification.org / info@CCHIcertification.org 3
CCHI Mini-Glossary Project Glossary #3, Subject: Respiratory Language: Spanish
38. Sore throat (Colloq.) (el) dolor de garganta A painful or sensitive condition of the throat
aggravated by swallowing or talking, usually caused by
inflammation due to viruses or bacteria.
39. Strep throat (Colloq.) (la) infección por A sore throat caused by streptococcal infection,
estreptococos usually with fever and sometimes with white spots on
the tonsils.
40. Nasal spray (el) atomizador nasal A method of dispensing medicated liquid in the form
(el) espray nasal (anglicismo) of a mist that is inhaled through the nose.
41. Antibiotic (el) antibiótico A medication (such as penicillin) that inhibits the
growth of or destroys microorganisms, especially
bacteria.
42. Antihistamine (el) antihistamínico A medication used to neutralize and inhibit the
physiological effects of histamine (a compound
released in allergic inflammatory reactions), used
especially for treating allergies and colds.
43. Decongestant (el) descongestionante A medication used to relieve nasal congestion, usually
(el) anticongestivo by shrinking the swollen membranes in the nose,
making it easier for a person to breathe.
44. Cough syrup (el) jarabe para la tos A medication in a sugary liquid form used to alleviate
coughing.
45. Cough drop (la) pastilla para la tos A small, sometimes medicated candy or tablet
Syn. Throat lozenge (la) pastlila para la garganta intended to be dissolved slowly in the mouth to
temporarily stop coughs and lubricate and soothe
irritated tissues of the throat (usually due to a sore
throat).
46. Bronchoscopy (la) broncoscopia A procedure in which a hollow, flexible tube called a
bronchoscope is inserted into the airways through the
nose or mouth to provide a view of the
tracheobronchial tree. It can also be used to collect
bronchial and/or lung secretions and to perform tissue
biopsies.
47. Pulmonary pulmonar Relating to, or affecting the lungs.
48. Respiratory therapist (el/la) terapeuta A clinician who provides care for patients who have
respiratorio(a) trouble breathing, including establishing and
maintaining the airways during management of
trauma and intensive care, and may administer
anesthesia for surgery or conscious sedation.
49. Oxygen (el) oxígeno A gas forming part of the air, required for breathing.
50. To inhale Inhaler To breathe in.
Certification Commission for Healthcare Interpreters (CCHI)
1725 I Street, NW – Suite 300 / Washington DC 20006
www.cchicertification.org / info@CCHIcertification.org 4
CCHI Mini-Glossary Project Glossary #3, Subject: Respiratory Language: Spanish
51. To exhale Exhalar To breathe out.
52. Hold your breath. Detener la respiración To voluntarily stop breathing.
Aguantar la respiración
53. Take a deep breath. Respirar profundo To breathe in deeply, filling the lungs with air as full as
possible.
54. Dyspnea (n.) (la) disnea To have difficult or labored breathing that is out of
proportion to the person’s level of physical activity.
Syn. To be short of Tener falta de aire
breath (Colloq.) Faltarle el aire (a uno)
55. Alveoli (Pl.) (los) alvéolos (pl.) Tiny air sacs in the lungs at the end of the bronchioles,
(Sing.) Alveolus (el) alvéolo (sing.) through which oxygen is taken into the blood.
Syn. Air sacs
56. Lung (el) pulmón Either one of two breathing organs, located in the
chest, responsible for introducing oxygen to blood
traveling from the heart, and releasing carbon dioxide
from blood traveling to the heart.
57. Lobe of the lung (el) lóbulo pulmonar One of the five sections of the lungs.
58. Pleural membrane (la) membrana pleural The thin transparent membrane enveloping the lungs
Syn. Pleura (la) pleura and lining the walls of the chest cavity.
59. Diaphragm (el) diafragma The large muscle that separates the chest cavity from
the abdominal cavity and is the principal muscle of
respiration. As the diaphragm contracts and moves
downward, the lungs expand and air moves into them.
As the diaphragm relaxes and moves upward, the
lungs contract and air is forced out of them.
60. Thorax (n.) (el) tórax The part of the body between the neck and
Syn. Chest (Colloq.) (el) pecho diaphragm, encased by the ribs.
61. Thoracic (adj.) Torácico Related to the chest area.
62. Pertussis (la) pertussis A contagious disease characterized by spasms of deep,
Syn. Whooping cough (la) tos ferina noisy coughing and a loud "whooping" sound upon
inhalation.
(Colloq.)
63. Pneumonia (la) neumonía Lung inflammation caused by bacterial or viral
(la) pulmonía (coloq.) infection, in which the air sacs fill with fluid or phlegm
and may become solid, causing cough with phlegm,
fever, chills and difficulty breathing. Inflammation may
affect both lungs (double pneumonia), one lung (single
pneumonia), or only certain lobes (lobar pneumonia).
Certification Commission for Healthcare Interpreters (CCHI)
1725 I Street, NW – Suite 300 / Washington DC 20006
www.cchicertification.org / info@CCHIcertification.org 5
CCHI Mini-Glossary Project Glossary #3, Subject: Respiratory Language: Spanish
64. Emphysema (la) enfisema A lung condition featuring an abnormal accumulation
of air due to enlargement and destruction of the lung's
alveoli (air sacs) resulting in the formation of scar
tissue and causing shortness of breath.
65. Chronic Obstructive (la) enfermedad pulmonar A collective name for two conditions causing shortness
Pulmonary Disease obstructiva crónica (EPOC) of breath. There are two main forms of COPD: Chronic
bronchitis, which involves a long-term cough with
(COPD) mucus; Emphysema, which involves destruction of the
lungs over time.
66. Pulmonary edema (el) edema pulmonar Fluid accumulation in the lungs, which collects in air
sacs (alveoli), causing difficulty to breathe.
67. Asthma (el) asma A disorder that causes the airways of the lungs
(bronchi) to swell and narrow and produce more
mucus, leading to wheezing, shortness of breath,
chest tightness, and coughing. It usually results from
an allergic reaction or other forms of hypersensitivity.
68. Asthma attack (el) ataque de asma A sudden worsening of asthma symptoms caused by
o the tightening of muscles around the airways
(bronchospasms). During an asthma attack, the lining
(la) crisis de asma of the airways also becomes swollen or inflamed and
thicker mucus – more than normal – is produced.
69. To trigger Desencadenar To cause something to happen.
Provocar
70. To alleviate Aliviar To relieve, lessen, make easier to endure.
Disminuir
71. Tuberculosis (TB) (la) tuberculosis A contagious and often severe airborne disease
caused by a bacterial infection (Mycobacterium
tuberculosis). TB typically affects the lungs, but it also
may affect any other organ of the body.
72. Chest X-ray (la) radiografía torácica A painless, noninvasive test that creates pictures of
the structures inside your chest, such as your heart,
(del pecho)
lungs, and blood vessels, with the help of
electromagnetic radiation.
73. PPD test (la) prueba de Mantoux The standard method of determining whether a
Syn. Tuberculin Skin (la) prueba cutánea de person is infected with the tuberculosis bacterium,
performed by injecting tuberculin purified protein
Test (TST); tuberculina derivative (PPD) into the inner surface of the forearm.
Mantoux test;
Pirquet test
Syn. (Colloq.) TB skin
test
74. Negative test result (el) resultado negativo The result showing that there is NO infection of a
specific kind in the body.
75. Positive test result (el) resultado positivo The result showing that there IS an infection of a
specific kind in the body.
Certification Commission for Healthcare Interpreters (CCHI)
1725 I Street, NW – Suite 300 / Washington DC 20006
www.cchicertification.org / info@CCHIcertification.org 6
CCHI Mini-Glossary Project Glossary #3, Subject: Respiratory Language: Spanish
76. Latent Latente Existing but dormant or hidden until circumstances are
suitable for development or manifestation.
77. To spit blood Escupir sangre To forcibly eject saliva mixed with blood from the
mouth.
78. Cystic fibrosis (la) fibrosis quística A genetic condition causing poor clearance of mucus
from the bronchi. The accumulated mucus results in
repeated lung infections.
79. Black lung disease (la) neumoconiosis (formal) A condition caused by inhaling coal dust; a form of
Pneumoconiosis.
(Colloq.) (la) enfermedad del pulmón
negro (coloq.)
80. Asbestosis (la) asbestosis A condition caused by inhaling asbestos dust; a form
of Pneumoconiosis.
81. Pulmonary embolism (la) embolia pulmonar A sudden blockage in a lung artery, often causing
(PE) (el) embolismo pulmonar shortness of breath and low blood oxygen levels. The
blockage usually is caused by a blood clot that travels
to the lung from a vein in the leg.
82. Inhaler (el) inhalador A portable device for administering a drug that is to be
breathed in, used for relieving asthma and other
bronchial or nasal congestion.
83. Lung capacity (la) capacidad pulmonar The amount of air that can fill the lungs.
84. Spirometer (el) espirómetro An instrument for measuring the amount of air taken
into and exhaled from the lungs.
85. Oxygen therapy (la) oxigenoterapia A treatment that provides a patient with extra oxygen.
Coloq. Terapia de oxígeno
86. Oxygen face mask (la) mascarilla de oxígeno A device that is placed over the mouth and nose and
through which oxygen is supplied from an attached
(la) mascarilla para
storage tank.
oxigenoterapia
87. Nasal cannula (NC) (la) cánula nasal A plastic tube worn over the ears and inserted into the
nostrils to deliver oxygen.
88. Pulse oximeter (el) oxímetro de pulso A device that indirectly measures the oxygen
Syn. Finger clip saturation of blood and changes in blood volume in
the skin. A sensor device is placed on a thin part of
the patient’s body, usually a fingertip or earlobe, or in
the case of an infant, across a foot.
Certification Commission for Healthcare Interpreters (CCHI)
1725 I Street, NW – Suite 300 / Washington DC 20006
www.cchicertification.org / info@CCHIcertification.org 7
CCHI Mini-Glossary Project Glossary #3, Subject: Respiratory Language: Spanish
89. Acute respiratory (el) síndrome de dificultad A severe, sudden injury to the lungs caused by a
distress syndrome respiratoria aguda serious illness. Life support with mechanical
ventilation is usually needed to survive until the lungs
(ARDS) (SDRA) recover.
90. Respiratory failure (la) insuficiencia respiratoria A condition when not enough oxygen passes from the
lungs into the blood. Respiratory failure also can
happen if the lungs can't remove carbon dioxide (a
waste gas) from the blood.
91. Mechanical ventilation (la) ventilación mecánica A method to mechanically assist or replace
spontaneous breathing, usually involving a machine
called a ventilator.
92. Ventilator (el) respirador artificial A machine for artificial respiration.
93. Intubated (adj.) entubado(a) Most often means tracheal intubation; the placement
of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea to protect a
patient’s airway and provide a means of mechanical
ventilation.
Certification Commission for Healthcare Interpreters (CCHI)
1725 I Street, NW – Suite 300 / Washington DC 20006
www.cchicertification.org / info@CCHIcertification.org 8
You might also like
- Pre-Finals Topic 1 AnaphyDocument5 pagesPre-Finals Topic 1 AnaphyGlenice Joy SenocNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Joanna Cabuhay 293 Calingacion ST - Poblacion SibulanDocument6 pagesRespiratory System: Joanna Cabuhay 293 Calingacion ST - Poblacion SibulanJoanna :DNo ratings yet
- Airway and Its Maintenance Hand Out2Document49 pagesAirway and Its Maintenance Hand Out2agatakassaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesRespiratory SystemJed Kachel BugayongNo ratings yet
- Anaphy RespiratoryDocument14 pagesAnaphy RespiratoryAngellene GraceNo ratings yet
- Upper Nasal Cavity and Chest WallDocument18 pagesUpper Nasal Cavity and Chest WallHessa AlamiraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Section 9Document9 pagesAnatomy - Section 9Rosinah M KekanaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Respiratory System: Gusbakti Prof .DR Physiology University MUHAMMADYAH North SumatraDocument134 pagesPhysiology of Respiratory System: Gusbakti Prof .DR Physiology University MUHAMMADYAH North SumatraIlham KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument26 pagesRespiratory SystemCHESKA LYKA ASILONo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesRespiratory SystemAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Modul Anatomi Blok 11Document40 pagesModul Anatomi Blok 11AyuNo ratings yet
- 2 - Respiratory SystemDocument9 pages2 - Respiratory SystemHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PDFDocument9 pagesRespiratory PDFJoydee Liza MarcoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System-2cgf2Document42 pagesRespiratory System-2cgf2Nzenwa Jedidiah KimizuNo ratings yet
- O CO O CO O CO: Chapter 15: Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesO CO O CO O CO: Chapter 15: Respiratory SystemPrecious Faith RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Nose and Paranasal SinusDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Nose and Paranasal Sinusbayoe_pra100% (1)
- CHAPTER 22 The Respiratory SystemDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 22 The Respiratory System楊畯凱No ratings yet
- 1a. Upper Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument21 pages1a. Upper Anatomy & PhysiologyDliya UlhaqNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesRespiratory SystemAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Pharynx NotesDocument8 pagesPharynx Notesm0rat0r1umNo ratings yet
- External Respiration: Angiotensin-Converting EnzymeDocument4 pagesExternal Respiration: Angiotensin-Converting EnzymeEllä PabustanNo ratings yet
- Scenario 4Document9 pagesScenario 4Syaema MaulidaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesRespiratory SystemHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesLec 1 Respiratory SystemfaiNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesThe Respiratory SysteminitaygracileshayneNo ratings yet
- 002 SPA CCHI Mini - Glossary ENT EarDocument5 pages002 SPA CCHI Mini - Glossary ENT EarfrangomezchirinoNo ratings yet
- Airway Mngt. Module 1.Document11 pagesAirway Mngt. Module 1.marc gorospeNo ratings yet
- ENT - Diseases of The Nose and Paranasal SinusesDocument8 pagesENT - Diseases of The Nose and Paranasal SinusesChristian LantanoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesRespiratory SystemCharlie CharlesNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Respiratory SystemDocument30 pagesANAPHY Respiratory SystemAshley Franceska CansanayNo ratings yet
- MS Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesMS Respiratory Systemarizza ramosNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Respiratory System: Inside-RestDocument7 pagesFunctions of The Respiratory System: Inside-RestRaven LacsonNo ratings yet
- (Week 14) Respiratory SystemDocument3 pages(Week 14) Respiratory SystemDiana Leen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Bio 132 Chapter 23 NotesDocument8 pagesBio 132 Chapter 23 NotesgilissaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Respiratory SystemDocument9 pages2 - Respiratory SystemHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Respiratory SystemDocument75 pagesAnatomy of Respiratory SystemAnonymous aqeaNUn83% (6)
- Nasal Cavity - WikipediaDocument23 pagesNasal Cavity - Wikipediaراوند اعبيدNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory SystemChloe Mae PastranaNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesOrgans of The Respiratory SystemCrystal Kaye RecasaNo ratings yet
- 3 PharyngologyDocument86 pages3 PharyngologyWai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesRespiratory Systemmariel.angeles29No ratings yet
- The Respirator Y System: Mungcal, Dharlynette RTRPDocument158 pagesThe Respirator Y System: Mungcal, Dharlynette RTRPDharlyn MungcalNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument26 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreabctutorNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument26 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreabctutorNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument26 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCNo ratings yet
- Sinuses and Nasal Cavity PDFDocument4 pagesSinuses and Nasal Cavity PDFChristopher PhilipsNo ratings yet
- 1.anatomy of Respiratory SystemDocument73 pages1.anatomy of Respiratory Systemokoti.omutanyi22No ratings yet
- Topic 11Document15 pagesTopic 11Lorraine RiegoNo ratings yet
- Catatan Koas THT 1Document5 pagesCatatan Koas THT 1MEDS easyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of AirwayDocument50 pagesAnatomy of AirwayHari Om ChaurasiyaNo ratings yet
- Sistem RespirasiDocument39 pagesSistem RespirasiBestariayuNo ratings yet
- CHAP13Document8 pagesCHAP13Crystal ARIETANo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory SystemAlloiza CaguiclaNo ratings yet
- PharynxDocument18 pagesPharynxzenith parmarNo ratings yet
- 11j Caybot Jashjovian Task11Document19 pages11j Caybot Jashjovian Task11Wonder Selene RouxNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Upper Respiratory Tract: Guyton Ed 12 THDocument22 pagesPhysiology of Upper Respiratory Tract: Guyton Ed 12 THauliaNo ratings yet
- 12 - Anatomy of The NoseDocument32 pages12 - Anatomy of The Nosehanizulfani13No ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesThe Respiratory SystemVernice LopezNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesRespiratory SystemYesha Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Treatise on the Anatomy and Physiology of the Mucous Membranes: With Illustrative Pathological ObservationsFrom EverandTreatise on the Anatomy and Physiology of the Mucous Membranes: With Illustrative Pathological ObservationsNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Merokok Dengan Asma Pada Usia LanjutDocument20 pagesHubungan Merokok Dengan Asma Pada Usia LanjutPuput Indah PratiwiNo ratings yet
- RatDocument2 pagesRatAriel ChouNo ratings yet
- Lung SoundDocument2 pagesLung SoundRJay AlavazoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Pogil HonorsDocument11 pagesCellular Respiration Pogil Honorsapi-323720899100% (1)
- Pediarespi QuizDocument1 pagePediarespi QuizAlessa Mikkah BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Grade Four Consolidated Worksheeets: ScienceDocument12 pagesGrade Four Consolidated Worksheeets: Scienceezerah nuwagabaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Week 6 - ANSWERSDocument6 pagesWorksheet - Week 6 - ANSWERSstudent4007No ratings yet
- Respiratory MechanicsDocument27 pagesRespiratory MechanicsKarla Hernandez100% (1)
- Oxygen TransportDocument3 pagesOxygen TransportLovely RoseNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearanceapi-253288732No ratings yet
- Oxygen InhalationDocument26 pagesOxygen InhalationdaisyNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans (Multiple Choice) QPDocument12 pagesGas Exchange in Humans (Multiple Choice) QPBudi LindrawatiNo ratings yet
- Interpret Your CapnogramDocument5 pagesInterpret Your CapnogramMayHnin KhaingNo ratings yet
- DLP-Bohol - Science9 Q1 W1 D1Document3 pagesDLP-Bohol - Science9 Q1 W1 D1Jen Lorejas100% (1)
- Biology TestDocument8 pagesBiology TestArmanai KhamzinaNo ratings yet
- FDA Approved ListDocument25 pagesFDA Approved ListAli UnitedHospitalNo ratings yet
- Tension PneumothoraxDocument13 pagesTension PneumothoraxAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chain - Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesElectron Transport Chain - Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisJan Go100% (1)
- Copd and Equal Pressure PointDocument3 pagesCopd and Equal Pressure Pointleh.mo9315No ratings yet
- Physical Exam - Chest 2006Document84 pagesPhysical Exam - Chest 2006api-19916399No ratings yet
- BioK 8.2 Cell Respiration AHLDocument71 pagesBioK 8.2 Cell Respiration AHLSoham JaybhayNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Assessment PDFDocument53 pagesRespiratory System Assessment PDFJay RomeNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: AsthmaDocument21 pagesCase Presentation: AsthmaCalingalan Hussin CaluangNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Practical Lecture StudentsDocument9 pagesRespiratory System Practical Lecture StudentsAmwaj MohammedNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation - Initial SettingsDocument57 pagesMechanical Ventilation - Initial SettingsabdallahNo ratings yet
- Critical Care DNB Q & ADocument262 pagesCritical Care DNB Q & AmeddocNo ratings yet
- Understanding Ventilator Waveforms-And How To Use Them in Pa... - Nursing2020 Critical CareDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Ventilator Waveforms-And How To Use Them in Pa... - Nursing2020 Critical Caremahbub alamNo ratings yet
- Cu 10 (Ncma111)Document2 pagesCu 10 (Ncma111)Arjay VerdejoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan 4Document2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan 4Fria mae AbellanoNo ratings yet
- Administering O2 TherapyDocument22 pagesAdministering O2 TherapyWilbert Andrew FlojemonNo ratings yet