Professional Documents
Culture Documents
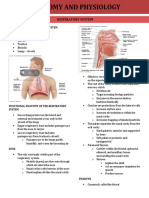
Respiratory System
Uploaded by
Yesha Del Rosario0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views9 pagesmedglo
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentmedglo
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views9 pagesRespiratory System
Uploaded by
Yesha Del Rosariomedglo
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
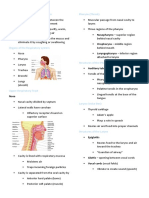
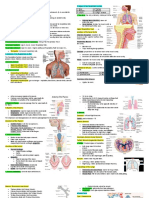
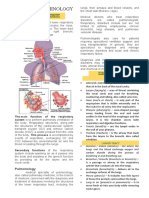
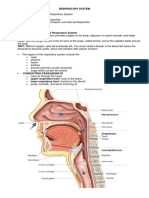
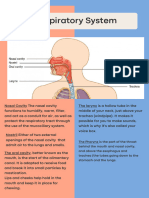
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Expectorant The act of coughing up material from the
respiratory tract; also the material thus
released
1. Normal Structure and Function Expiration The act of breathing out or expelling air
from the lungs exhalation
TERMS MEANING Glottis The opening between the vocal cords
Adenoids Lymphoid tissue located in the nasopharynx Hemoglobin The iron-containing pigment in red blood
the pharyngeal tonsils cells that transports oxygen
Alveoli The tiny air sacs in the lungs through which Inspiration The act of drawing air into the lungs;
gases are exchanged between the atmosphere inhalation
and the blond in respiration (singular: Larynx The enlarged, superior portion of the trachea
alveolus) An alveolus, in general, is a small that contains the vocal cords (root: laryng/o)
hollow or cavity the term also applies to the Lungs Cone-shaped, spongy respiratory organ
bony socket for a tooth contained within the thorax (roots: pneum,
Bronchiole One of the smaller subdivisions of the pulm)
bronchial tubes (root: bronchiol) Mediastinum The space between the lungs together with
Bronchus One of the larger air passageways in the the organs contained in this space
lungs. The bronchi begin as two branches of Nose The organ of the face used for breathing and
the trachea and then subdivide within the for housing receptors for the sense of smell;
lungs (plural: bronchi) (root bronch) includes an external portion and an internal
Carbon dioxide A gas produced by energy metabolism in nasal cavity (roots: nas/o, rhin/o
cells and eliminated through the lungs Oxygen The gas needed by cells to release energy
Carbonic acid An acid formed when carbon dioxide from food during metabolism
dissolves in water Palatine tonsils The paired masses of lymphoid tissue
Compliance A measure of how easily the lungs expand located on either side of the oropharynx;
under pressure. Compliance is reduced in usually meant when the term tonsils is used
many types of respiratory disorders alone
Diaphragm The dome-shaped muscle under the lungs Pharynx The throat; a common passageway for food
that flattens during inspiration (root phren/o) entering the esophagus and air entering the
Epiglottis A leaf-shaped cartilage that covers the larynx (root: paring/o)
larynx during swallowing to prevent food Phrenic nerve The nerve that activates the diaphragm (root:
from entering the trachea phrenic/o)
Pleura A double-layered membrane that lines the vessels and nerves enter
thoracic cavity (parietal pleura) and covers Nares The external openings of the nose; the
the lungs (visceral pleura) (root pleur/o) nostrils (singular: naris)
Pleural space The thin, fluid-filled space between the two Nasal septum The partition that divides the nasal cavity
layers of the pleura; pleural cavity into two parts (root sept/o means "septum")
Pulmonary The movement of air into and out of the 2. Gas Exchange
ventilation lungs
Sinus A cavity or channel; the paranasal sinuses
are located near the nose and drain into the
nasal
Sputum The substance released by coughing or
clearing the throat; expectoration. It may
contain a variety of material from the
respiratory trace
Surfactant A substance that decreases surface tension
within the alveoli and cases lung expansion
Trachea The air passageway that extends from the
larynx to the bronchi (root trache/o)
Turbinate bones The bony projections in the nasal cavity that
contain receptors for the sense of smell. Also
called conchae, singular: concha
Vocal cords Membranous folds on either side of the
larynx that are important in speech
production. Also called vocal folds
Carina A projection of the lowest tracheal cartilage
that forms a ridge between the two bronchi.
Used as a landmark for endoscopy. Any
ridge or ridge-like structure (from a Latin 3. Roots and Suffixes
word that means "keel")
Hilium An anatomic depression in an organ where Suffixes for Respiration
SUFFIX MEANING EXAMPLE DEFINITION OF bronchiole bronchiole bronchiolestasis Dilation of the
EXAMPLE bronchioles
-pnea breathing orthopnea Breathing difficulty
that is relieved by
assuming an upright Roots for the Lungs and Breathing
(ortho-) position
-oxia Level of hypoxia Decreased amount of ROOT MEANING EXAMPLE DEFINITION OF
oxygen oxygen EXAMPLE
-capnia Level of hypercapnia Increased carbon Phren/o Diaphragm Phrenic Pertaining to the
carbon dioxide in the tissue phrenic
dioxide
Phrenic/o Phrenic phrenicectomy Partial excision of
-phonia voice dysphonia Difficulty in nerve the phrenic nerve
speaking
Pler/o plera pleurodesis Fusion of the
pleura
Pulm/o, lung extrapulmonary Outside the lungs
Roots for the Respiratory Passageway pulmon/o
Pneumon/o lung pneumonitis Inflammation of
ROOT MEANING EXAMPLE DEFINITION OF the lungs;
EXAMPLE pneumonia
Nas/o nose intranasal Within the nose Pneum/o Air, gas; pneumothorax Presence of air in
Rhin/o nose rhinoplasty Plastic repair of also the thorax
the nose respiration,
Pharyng/o pharynx pharyngeal Pertaining to the lung
pharynx Spir/o breathing spirometer Instrument for
Laryng/o larynx laryngospasm Spasm (sudden measuring
contraction) of the breathing volumes
larynx 4. Disorders/Clinical Aspects
Trache/o trachea tracheotome Instrument used to
incise trachea
Bronch/o, bronchus bronchogenic Originating in the Terms Meaning
bronch/i bronchus
Acidosis Abnormal acidity of body fluids.
Respiratory acidosis is caused by (COPD) which includes emphysema, asthma,
abnormally high carbon dioxide levels bronchitis, and bronchiectasis
Acute respiratory Pulmonary edema that can lead rapidly to Cyanosis Bluish discoloration of the skin caused by
distress syndrome fatal respiratory failure; causes include lack of oxygen in the blood (adjective:
(ARDS) trauma, aspiration into the lungs, viral cyanotic)
pneumonia, and drug reactions; shock Cystic fibrosis An inherited disease that affects the
lung (CF) pancreas, respiratory system, and sweat
Acute rhinitis Inflammation of the nasal mucosa with glands. Characterized by mucus
sneezing, tearing, and profuse secretion of accumulation in the bronchi causing
watery mucus, as seen in the common cold obstruction and leading to infection
Alkalosis Abnormal alkalinity of body fluids. Diphtheria Acute infectious disease, usually limited
Respiratory alkalosis is caused by to the upper respiratory tract,
abnormally low carbon dioxide levels characterized by the formation of a surface
Aspiration The accidental inhalation of food or other pseudomembrane. composed of cells and
foreign material into the lungs. Also coagulated material
means the withdrawal of fluid from a Dyspnea Difficult or labored breathing, sometimes
cavity by suction with pain; "air hunger
Asthma A disease characterized by dyspnea and Emphysema A chronic pulmonary disease
wheezing caused by spasm of the characterized by enlargement and
bronchial tubes or swelling their mucous destruction of the alveoli
membranes Empyema Accumulation of pus in a body cavity,
Atelectasis Incomplete expansion of a lung or part of especially the pleural space; pyothorax
a lung; lung collapse. May be present at Hemoptysis The spitting of blood from the mouth or
birth (as in respiratory distress syndrome) respiratory tract (ptysis means spitting
or be caused by bronchial obstruction or Hemothorax Presence of blood in the pleural space
compression of lung tissue (prefix atel/o Hydrothorax Presence of fluid in the pleural space
means "imperfect")
Hyperventilation Increased rate and depth of breathing;
Bronchiectasis Chronic dilatation of a bronchus or increase in the amount of air entering the
bronchi alveoli
Bronchitis Inflammation of a bronchus Hypoventilation Decreased rate and depth of breathing;
Chronic obstructive Any of a group of chronic, progressive, decrease in the amount of air entering the
pulmonary disease and debilitating respiratory diseases, alveoli
Influenza An acute, contagious respiratory infection surfactant in the lungs. It is treated with
causing fever, chills, headache, and respiratory support and surfactant
muscle pain; "flu administration
Pertussis An acute, infectious disease characterized Sudden infant The sudden and unexplained death of an
by a cough ending in a whooping death syndrome apparently healthy infant; crib death
inspiration; whooping cough (SIDS)
Pleural effusion Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space. Tuberculosis An infectious disease caused by the
The fluid may contain blood (hemothorax) tubercle bacillus, Mycobacterium
or pus (pyothorax or empyema) tuberculosis Often involves the lungs but
Pleurisy Inflammation of the pleura; pleuritis. A may involve other parts of the body as
symptom of pleurisy is sharp pain on well, Miliary tuberculosis is an acute
breathing generalized form of the disease with
Pneumoconiosis Disease of the respiratory tract caused by formation of minute tubercles that
inhalation of dust particles. Named more resemble millet seeds
specifically by the type of dust inhaled, Byssinosis Obstructive airway disease caused by
such as silicosis, anthracosis, asbestosis reaction to the dust in unprocessed plant
Pneumonia Inflammation of the lungs generally fibers
caused by infection. May involve the Sleep apnea Intermittent periods of breathing cessation
bronchioles and alveoli during sleep. Central sleep apnea arises
(bronchopneumonia) or one or more lobes from failure of the brainstem to stimulate
of the lung (lobar pneumonia) breathing. Obstructive sleep apnea results
Pneumonitis Inflammation of the lungs; may be caused from airway obstruction during deep
by infection, asthma, allergy, or inhalation sleep, as from obesity or enlarged tonsils
of irritants Small cell A highly malignant type of bronchial
Pneumothorax Accumulation of air or gas in the pleural carcinoma tumor involving small, undifferentiated
space. May result from injury or disease or cells: "oat cell" carcinoma
may be produced artificially to collapse a 5. Symptom and Conditions
lung
Pyothorax Accumulation of pus in pleural space;
empyema
Respiratory distress A respiratory disorder that affects TERMS MEANING
syndrome (RDS) premature infants born without enough Anoxia Lack or absence of oxygen in the tissues;
often used incorrectly to mean hypoxia Epistaxis Hemorrhage from the nose; nosebleed
Asphyxia Condition caused by inadequate intake of (Greek -staxis means "dripping"
oxygen; suffocation (literally "lack of Fremitus A vibration, especially as felt through the
pulse") chest wall on palpation
Biot respiration Deep, fast breathing interrupted by sudden Kussmaul Rapid and deep gasping respiration
pauses; seen in spinal meningitis and other respiration without pause; characteristic of severe
central nervous system disorders acidosis
Bronchospasm Narrowing of the bronchi caused by Pleural friction rub A sound heard on auscultation that is
smooth muscle spasms; common in cases produced by the rubbing together of the
of asthma and bronchitis two pleural layers; a common sign of
Cheyne-Stoke A repeating cycle of gradually increased pleurisy
respiration and then decreased respiration followed by Rales Abnormal chest sounds heard when air
a period of apnea; caused by depression of enters small airways or alveoli containing
the breathing centers in the brainstem; fluid usually heard during inspiration;
seen cases of coma and in terminally ill singular: rale (rahl). Also called crackles
patients Rhonchi Abnormal chest sounds produced in
Cor pulmunate Enlargement of the heart's right ventricle airways with accumulated fluids; more
caused by disease of the lungs or noticeable during expiration (singular:
pulmonary blood vessels rhonchus)
Coryza Acute inflammation of the nasal passages Stridor A harsh, high-pitched sound caused by
with profuse nasal discharge; acute rhinitis obstruction of an upper air passageway
Croup A childhood disease usually caused by a Tussis A cough. An antitussive drug is one that
viral infection that involves upper airway relieves or prevents coughing
inflammation and obstruction. Croup is Wheeze A whistling or sighing sound caused by
characterized by a barking cough, narrowing of a respiratory passageway
difficulty breathing, and laryngeal spasm
Deviated septum A shifted nasal septum; may require
surgical correction
Epiglottitis Inflammation of the epiglottis that may
lead to upper airway obstruction. 6. Diagnosis and Treatment
Commonly seen in croup (also spelled
epiglottiditis) Diagnosis
Terms Meanings accumulate after surgery or as a result of
Arterial blood gasses The concentrations of gases, specifically injury, infection, or cardiovascular
(ABGs) oxygen and carbon dioxide, in arterial problems. Also called thoracocentesis
blood. Reported as the partial pressure Tuberculin test A skin test for tuberculosis. Tuberculin
(P) of the gas in arterial (a) blood, such (PPD), the test material made from
as PaO2, or PACO2, These products of the tuberculosis organism, is
measurements are important in injected below the skin. A hard, raised
measuring acid-base balance lump appearing within 48 to 72 hours
Bronchoscope An endoscope used to examine the indicates an active or inactive TB
tracheobronchial passageways. Also infection. Also called the Mantoux test
allows access for tissue biopsy or Mediastinoscopy Examination of the mediastinum by
removal of a foreign object means of an endoscope inserted through
Lung scan Study based on the accumulation of an incision above the sternum
radioactive isotopes in lung tissue. A Plethysmograpgh An instrument that measures changes in
ventilation scan measures ventilation gas volume and pressure during
after inhalation of radioactive material. respiration
A perfusion Scan measures blood supply Pneumotachometer A device for measuring air flow
to the lungs after injection of radioactive Thoracoscopy Examination of the pleural cavity
material. Also called a pulmonary through an endoscope; pleuroscopy
scintiscan
Pulse oximetry Determination of the oxygen saturation
of arterial blood by means of a
Treatment
photoelectric apparatus (oximeter),
usually placed on the finger or the ear
reported as SpO2, in percent
Pulmonary function Tests done to assess breathing, usually
test by spirometry TERMS MEANING
Spirometer An apparatus used to measure breathing Aerosol therapy Treatment by inhalation of a drug or water
volumes and capacities; record of test is in spray form
a spirogram Continuous Use of a mechanical respirator to maintain
Thoracentesis Surgical puncture of the chest for positive airway pressure throughout the respiratory cycle in
removal of air or fluids, such as may pressure (CPAP) a patient who is breathing spontaneously
Extubation Removal of a previously inserted tube
Intermittent Use of a ventilator to inflate the lungs at TERMS MEANING
positive pressure intervals under positive pressure during Adenoidectomy Surgical removal of the adenoids
breathing (IPPB) inhalation Intubation Insertion of a tube into a hollow organ,
such as into the larynx or trachea for
entrance of air Patients may be intubated
Intermittent Use of a mechanical ventilator to force air during surgery for administration of
positive pressure into the lungs while allowing for passive anesthesia or to maintain an airway.
ventilation exhalation Endotracheal intubation may be used as
(IPPV) an emergency measure when airways are
blocked
Nasal cannula A two-pronged plastic device inserted into Lobectomy Surgical removal of a lobe of the lung or
the nostrils for delivery of oxygen of another organ
Orthopneic An upright or semiupright position that aids Pneumoplasty Plastic surgery of the lung. In reduction
position breathing pneumoplasty, nonfunctional portions of
Positive end- Use of a mechanical ventilator to increase the lung are removed, as in cases of
expiratory the volume of gas in the lungs at the end of advanced emphysema
pressure (PEEP) exhalation, thus improving gas exchange Tracheotomy Incision of the trachea through the neck,
Postural drainage Use of body position to drain secretions usually to establish an airway in cases of
from the lungs by gravity. The patient is tracheal obstruction
placed so that secretions will move Tracheostomy Surgical creation of an opening into the
passively into the larger airways for trachea to form an airway or to prepare
elimination for the insertion of a tube for ventilation;
Thoracic gas The volume of gas in the thoracic cavity also the opening thus created
volume calculated from measurements made with a
body plethysmograph
Drugs
7. Surgery and Drugs
TERMS MEANING
Antihistamine Agent that prevents responses mediated by
Surgery
histamine, such as allergic and
inflammatory reactions
Antitussive Drug that prevents or relieves coughing
Asthma Agent used to prevent asthma attacks and
maintenance drug for chronic treatment of asthma
Bronchodilator Drug that relieves bronchial spasm and
widens the bronchi
Corticosteroid Hormone from the adrenal cortex; used to
reduce inflammation
Decongestant Agent that reduces congestion or swelling
Expectorant Agent that aids in removal of
bronchopulmonary secretions
Isoniazid (INH) Drug used to treat tuberculosis
Leukotriene Drug that prevents or reduces
antagonist inflammation by inhibiting leukotrienes,
substances made in white blood cells that
promote inflammation; they also constrict
the bronchi and increase mucus
production; used in asthma treatment
Mucolytic Agent that loosens mucus to aid in its
removal
Rifampin Drug used to treat tuberculosis
(rifampicin)
You might also like
- Respiratory System - TransesDocument4 pagesRespiratory System - TransesMLS1C - PLARISAN, VALENT DAVENo ratings yet
- O CO O CO O CO: Chapter 15: Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesO CO O CO O CO: Chapter 15: Respiratory SystemPrecious Faith RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy CHP 13 NotesDocument5 pagesAnatomy CHP 13 NotesIsland RaeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument72 pagesRespiratory SystemElaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Joanna Cabuhay 293 Calingacion ST - Poblacion SibulanDocument6 pagesRespiratory System: Joanna Cabuhay 293 Calingacion ST - Poblacion SibulanJoanna :DNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory SystemAlloiza CaguiclaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - GlossaryDocument6 pagesRespiratory System - Glossarynikinagy1No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument27 pagesRespiratory Systemyoga karsendaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory Syste M: DR Arif Chowdhury Opu, MbbsDocument21 pagesThe Respiratory Syste M: DR Arif Chowdhury Opu, MbbsMuntasirNo ratings yet
- 3 2021 05 1012 46 42 AmDocument43 pages3 2021 05 1012 46 42 Amwardahafif00No ratings yet
- Therespiratorysystem Grade 9Document19 pagesTherespiratorysystem Grade 9ClarkBautistaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System ReviewerDocument7 pagesRespiratory System ReviewerVictoria Ellex TiomicoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesRespiratory SystemAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Therespiratorysystem 130524022043 Phpapp01 TestDocument21 pagesTherespiratorysystem 130524022043 Phpapp01 TestMergel GeconcilloNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Larynx EpiglottisDocument12 pagesRespiratory System: Larynx Epiglottisangel sychingNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesRespiratory SystemRichard Castada Guanzon Jr.No ratings yet
- RESPI NotesDocument3 pagesRESPI NotesPatty RomeroNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument40 pagesRespiratory SystemJezebel MolinoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Finals Topic 1 AnaphyDocument5 pagesPre-Finals Topic 1 AnaphyGlenice Joy SenocNo ratings yet
- CHAP13Document8 pagesCHAP13Crystal ARIETANo ratings yet
- 2 - Respiratory SystemDocument9 pages2 - Respiratory SystemHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- NOTES AutoRecoveredDocument4 pagesNOTES AutoRecoveredAngelica BautistaNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Respiratory SystemDocument1 pageStructure of The Respiratory SystemMaxinne Allyssa Cancino RoseñoNo ratings yet
- A.S.a Chapter 12 - The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesA.S.a Chapter 12 - The Respiratory Systemkoshiaiko21No ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument61 pagesThe Respiratory SystemLuna JadeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesRespiratory SystemJed Kachel BugayongNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesLec 1 Respiratory SystemfaiNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 1.2 - Organ System OverviewDocument2 pagesExercise No. 1.2 - Organ System OverviewAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument42 pagesRespiratory SystemKathleen DuenasNo ratings yet
- 11j Caybot Jashjovian Task11Document19 pages11j Caybot Jashjovian Task11Wonder Selene RouxNo ratings yet
- 4 RSDocument16 pages4 RSzabdullahstud1No ratings yet
- 1.oxygenation DisordersDocument8 pages1.oxygenation Disorders2BGrp3Plaza, Anna MaeNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument28 pagesThe Respiratory SystemJuma SammyNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument80 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System PDFDocument62 pagesRespiratory System PDFGayathri SNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Section 9Document9 pagesAnatomy - Section 9Rosinah M KekanaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy RespiratoryDocument14 pagesAnaphy RespiratoryAngellene GraceNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument28 pagesThe Respiratory SystemJuma SammyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesRespiratory SystemTricia CabiliNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Respiratory System & Their FunctionsDocument38 pagesParts of The Respiratory System & Their FunctionsSaajid AmraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesRespiratory SystemQK CLARONo ratings yet
- Amazing Body 1 1661993161713Document28 pagesAmazing Body 1 1661993161713TestNo ratings yet
- CAOLBOY Module 15 Activity Worksheet On Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesCAOLBOY Module 15 Activity Worksheet On Respiratory SystemAnton LeoncitoNo ratings yet
- Module 18 Respiratory FinalDocument15 pagesModule 18 Respiratory FinalJayR MendonesNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 N LECTURE MidtermDocument42 pagesNCM 112 N LECTURE MidtermVivien IgnacioNo ratings yet
- MTPX Care SemiDocument7 pagesMTPX Care SemirusselpageNo ratings yet
- MainRespiratorySystem 20231109081722Document6 pagesMainRespiratorySystem 20231109081722valaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument10 pagesAnaphy ReviewerTsukishima RinNo ratings yet
- Human Respiration HandoutDocument4 pagesHuman Respiration HandoutJulius GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Upper Airway InfectionsDocument5 pagesUpper Airway InfectionsTreesa LouiseNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System AnatomyDocument49 pagesRespiratory System AnatomyHiraya WNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesRespiratory SystemSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Franco L. Razon, RN, Man Divine Word College of LegazpiDocument42 pagesFranco L. Razon, RN, Man Divine Word College of LegazpiFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesOrgans of The Respiratory SystemCrystal Kaye RecasaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Final pt.2Document8 pagesAnatomy Final pt.2Gladys Mae S. BañesNo ratings yet
- Nama: Ely Marliyana NIM: P00620219013 TK: 2ADocument12 pagesNama: Ely Marliyana NIM: P00620219013 TK: 2AelyNo ratings yet
- Bio1 Respiratory System 1Document41 pagesBio1 Respiratory System 1Camela Kim Domider TenorioNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesRespiratory SystemamirehmoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory SystemJay QuilnetNo ratings yet
- Buy Lizol Floor Cleaner 5000 ML Online - GeMDocument4 pagesBuy Lizol Floor Cleaner 5000 ML Online - GeMHimanshu ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Octavia Tour BrochureDocument9 pagesOctavia Tour BrochureOvidiuIONo ratings yet
- Midterm Requirement-Green BuildingDocument7 pagesMidterm Requirement-Green BuildingJo-anne RiveraNo ratings yet
- Access To JusticeDocument9 pagesAccess To JusticeprimeNo ratings yet
- Calinescu2017 PDFDocument38 pagesCalinescu2017 PDFElizabeth UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Chennai City Disaster Management Plan GCC 2021Document772 pagesChennai City Disaster Management Plan GCC 2021Disability Rights AllianceNo ratings yet
- WaveLab - BUC Datasheet - Ku Band 80W 100WDocument4 pagesWaveLab - BUC Datasheet - Ku Band 80W 100WLeonNo ratings yet
- FM 200Document3 pagesFM 200raviNo ratings yet
- FilterFlow Cartridge Installation GuideDocument8 pagesFilterFlow Cartridge Installation GuideSilver FoxNo ratings yet
- Cord Care Evaluation ToolDocument1 pageCord Care Evaluation ToolCherry AnnNo ratings yet
- ASME Single Certification MarkDocument3 pagesASME Single Certification MarkahmadghasusNo ratings yet
- CyberPunk 2020 - Unofficial - Reference Book - Ammo and Add-OnsDocument6 pagesCyberPunk 2020 - Unofficial - Reference Book - Ammo and Add-Onsllokuniyahooes100% (1)
- First Quarter Examination For AP 10Document4 pagesFirst Quarter Examination For AP 10Reynan Orillos HorohoroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Fitness Training PrinciplesDocument80 pagesChapter 10 Fitness Training Principlesapi-115744109No ratings yet
- Physical, Biology and Chemical Environment: Its Effect On Ecology and Human HealthDocument24 pagesPhysical, Biology and Chemical Environment: Its Effect On Ecology and Human Health0395No ratings yet
- Compact Water Treatment 200 m3Document3 pagesCompact Water Treatment 200 m3civil eng915No ratings yet
- Directory of Acredited Medical Testing LaboratoriesDocument93 pagesDirectory of Acredited Medical Testing LaboratoriesCALIDAD METROMEDICA E.UNo ratings yet
- Dont Sweat The Small Stuff For Men - Richard CarlsonDocument226 pagesDont Sweat The Small Stuff For Men - Richard CarlsonAaliyah Csmrt100% (1)
- 1often Wonder About My Future As I Am About To Finish Secondary SchoolDocument2 pages1often Wonder About My Future As I Am About To Finish Secondary SchoolMidz Santayana100% (1)
- The Thermodynamic Principles of Isochoric Cryopreservation.Document18 pagesThe Thermodynamic Principles of Isochoric Cryopreservation.Boris RubinskyNo ratings yet
- Interpretacion Curso Cat CoolantDocument39 pagesInterpretacion Curso Cat Coolanthouston machacaNo ratings yet
- Material Data Sheet Durapro Asa: DescriptionDocument1 pageMaterial Data Sheet Durapro Asa: DescriptionAlexandru NeacsuNo ratings yet
- Biolis 24i PDFDocument43 pagesBiolis 24i PDFMohamed Ben MohamedNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Operation Slurry TransportDocument113 pagesMechanical Operation Slurry TransportIsrarulHaqueNo ratings yet
- Social Science Assignment Class 8 CBSEDocument3 pagesSocial Science Assignment Class 8 CBSEgurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- IOC CoachingResearchStudiesList PDFDocument87 pagesIOC CoachingResearchStudiesList PDFJeane LucenaNo ratings yet
- To: Head of Sea Training Department PT Gemilang Bina Lintas Tirta Ship ManagementDocument1 pageTo: Head of Sea Training Department PT Gemilang Bina Lintas Tirta Ship ManagementtarNo ratings yet
- Anexate IVsolnDocument7 pagesAnexate IVsolnJelena Obrenovic StankovicNo ratings yet
- Banana Disease 2 PDFDocument4 pagesBanana Disease 2 PDFAlimohammad YavariNo ratings yet
- CoC VampireCharacterPrimerPDFDocument5 pagesCoC VampireCharacterPrimerPDFDavid Alexander TomblinNo ratings yet