Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Examples Questions
Uploaded by
Anne Marian Anak JOSEPH0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Examples questions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesExamples Questions
Uploaded by
Anne Marian Anak JOSEPHCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
7.
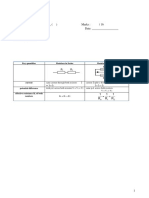
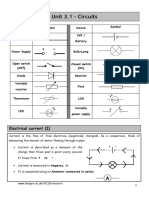
2 Flow of Electric Current in a Series Circuit and Parallel Circuit
Series Circuit Parallel Circuit
The circuit diagram
Arrangement of electrical Components are Components are
components in the circuit connected one after connected side by side in
another from one end of two or more paths to the
the circuit to the other end ends of the battery
of the circuit
Number of pathways for One path only More than one path
electric current to flow
Brightness of bulbs when Dim Bright
switch is turned on. Why? The total voltage supplied Each bulb receives full
by the dry cells is shared voltage from the dry cells.
by the bulbs. Thus, the Thus, the bulbs light more
bulbs light dimly brightly
What happens to the other Cannot light up Can still light up
bulbs when one of the Current cannot flow Current can still follow
bulbs in the circuit is through an incomplete through other paths in the
fused? Why? circuit circuit
The current that flows Each bulb receives the The current from the
through each bulb same amount of current, electrical source is shared
I supplied by the electrical between each bulb
source.
I I1 I 2 I 3 I I1 I 2 I 3
The voltage across each The voltage supplied Each path receives
bulb by the electrical the total voltage
source is shared by all supplied by the
the bulbs electrical source
The sum of voltage Each bulb receives
across each bulb is the same full voltage
the same as the total V V1 V2 V3
voltage supplied by
the electrical source.
V V1 V2 V3
The effective resistance, R The effective resistance The effective resistance
in the circuit increases when the decreases when the
number of bulbs increases. number of bulbs increases.
R R1 R2 R3 1 1 1 1
R R1 R2 R3
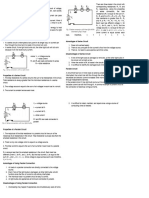
For example;
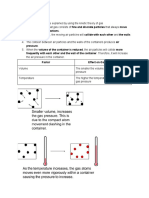
a) Two resistors R1 and R2 are connected in parallel in a circuit as shown in the
following diagram.
I1
R1 3
I2 R2 6
Based on the diagram, calculate the following.
i. Effective resistance, R
1 1 1
R R1 R2
1 1 1
R 3 6
1 1
R 2
2
R
1
R 2
ii. Voltage, V
V V1 V2 V3
Since the voltage of the cell is 6V, therefore , the voltage throughou t the
circuit is 6V.
iii. Current, I in the circuit
V IR
6V I (2)
6V
I
2
I 3 A
b) Two resistors are connected in a series circuit shown in the diagram below.
6V
R1 6 R2 20
V1 V2
Based on the above circuit,
i. Calculate the effective resistance, R
Effective resistance ,
R R1 R2
R 6 20
R 26
ii. Calculate the current, I
V IR
6V I (26)
6V
I
26
I 0.23 A
iii. Calculate the voltage V1 and V2
Voltage for V1
V1 IR
V1 0.23 A 6
V1 1.38V
Voltage for V2
V2 0.23 A 20
V2 4.6V
You might also like
- 7.7 Parallel CircuitDocument13 pages7.7 Parallel CircuitNurul Asnur Farahin MannanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 31: Current & Resistance & Simple CircuitsDocument79 pagesChapter 31: Current & Resistance & Simple CircuitsAno NymousNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Resistance 3.2.1 Ohmic and Non-Ohmic Conductor: Chapter 3 ElectricityDocument12 pages3.2 Resistance 3.2.1 Ohmic and Non-Ohmic Conductor: Chapter 3 ElectricityTan Zhi YunNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Notes and Worksheets 2023Document27 pagesCurrent Electricity Notes and Worksheets 2023kadynnaidoo7No ratings yet
- IGCSE 23 Current&VoltageInCircuitsDocument32 pagesIGCSE 23 Current&VoltageInCircuitsSam JordanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits FETDocument6 pagesElectrical Circuits FETOwamiirh RsaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Electricity and MagnetismDocument44 pagesChapter 7: Electricity and MagnetismRafizal Shafiee82% (11)
- Ejercicios Practicos Electricidad 2 EsoDocument7 pagesEjercicios Practicos Electricidad 2 EsoJOSE RAMONNo ratings yet
- DC CircuitDocument46 pagesDC CircuitMohammad Wajeeh MohsinNo ratings yet
- Electricityppt 120307204317 Phpapp02Document64 pagesElectricityppt 120307204317 Phpapp02Nunag Mary AnnNo ratings yet
- GR 8 Electric CircuitsDocument6 pagesGR 8 Electric Circuitskadynnaidoo7No ratings yet
- Current and Voltage in CircuitsDocument31 pagesCurrent and Voltage in CircuitsChalitha RanasingheNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Science Notes Chapter 7 Electricity: 7.1 ElectrostaticsDocument10 pagesForm 3 Science Notes Chapter 7 Electricity: 7.1 ElectrostaticsJu Li TanNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsDocument8 pagesElectricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsQuinto Jaypee SeinseiNo ratings yet
- Batteries & Bulbs: Open CircuitDocument7 pagesBatteries & Bulbs: Open CircuitVinujah SukumaranNo ratings yet
- Segment 2 QB - AnswersDocument14 pagesSegment 2 QB - Answersavp sNo ratings yet
- Internal Resistance and Matching in Voltage SourceDocument8 pagesInternal Resistance and Matching in Voltage SourceAsif Rasheed Rajput100% (1)
- Electricity 4 Series and ParallelDocument36 pagesElectricity 4 Series and ParallelJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- 2022 16A DC AnsDocument15 pages2022 16A DC AnsPk PlooNo ratings yet
- Physics PresentationDocument24 pagesPhysics PresentationGrace jereNo ratings yet
- S2 Science SSS - 16 Electrical SystemsDocument6 pagesS2 Science SSS - 16 Electrical SystemsSHANNON TAN S2-02No ratings yet
- Cea 223 Mod 2Document2 pagesCea 223 Mod 2PhoemelaNo ratings yet
- Serway PSE Quick ch27Document15 pagesSerway PSE Quick ch27Julio S. RendónNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Electricity (Form 5)Document28 pagesChapter 2 - Electricity (Form 5)kcnjojo88% (16)
- Portfolio in TleDocument16 pagesPortfolio in TleAileen Javines50% (2)
- Ohms Law: Mitsuko J. Osugi Physics 409D Winter 2004 UBC Physics OutreachDocument34 pagesOhms Law: Mitsuko J. Osugi Physics 409D Winter 2004 UBC Physics OutreachRyne MontoyaNo ratings yet
- WorksheetsssDocument2 pagesWorksheetsssRyrl ShinNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision 1Document37 pagesPhysics Revision 1kokobame003No ratings yet
- 1d Current and P.D in Electrical CircuitDocument34 pages1d Current and P.D in Electrical CircuitninaNo ratings yet
- (L11) - (JLD 3.0) - Current Electricity - 7th June.Document52 pages(L11) - (JLD 3.0) - Current Electricity - 7th June.BabithNo ratings yet
- Circuits in Parallel and in Series-Simulation and Hands OnDocument15 pagesCircuits in Parallel and in Series-Simulation and Hands OnvalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ElectricityDocument48 pagesIntroduction To ElectricitytuNo ratings yet
- Phy Unit 4-ElectricityDocument84 pagesPhy Unit 4-ElectricityportaliteNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Technology (ESC 101-A) Module 1: DC Circuits Electric PotentialDocument8 pagesBasic Electrical Technology (ESC 101-A) Module 1: DC Circuits Electric PotentialtusharNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Physics ElectricityDocument326 pagesiGCSE Physics ElectricityKt TristopNo ratings yet
- DC TheoryDocument37 pagesDC TheoryAyyub AchilevNo ratings yet
- Circuits LabDocument3 pagesCircuits LabEric NoriegaNo ratings yet
- Reading Quiz: - A Light Bulb Is Connected To A Battery So ThatDocument32 pagesReading Quiz: - A Light Bulb Is Connected To A Battery So ThatMohammad RidwanNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - Current in Simple DC CircuitDocument6 pagesLab 4 - Current in Simple DC CircuitAbdoul BinJim100% (1)
- Solution 07Document6 pagesSolution 07Narendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Circuit Compound Symbol Use: 7.5 Parallel and Series Circuits Symbols of Electric Circuit ComponentsDocument7 pagesCircuit Compound Symbol Use: 7.5 Parallel and Series Circuits Symbols of Electric Circuit ComponentsShi MingNo ratings yet
- New Energy Technologies Issue 13Document78 pagesNew Energy Technologies Issue 13blameitontherain9877No ratings yet
- Physic DemoDocument26 pagesPhysic DemoMaungwae WaeNo ratings yet
- Régime VariableDocument6 pagesRégime VariableSalah IdrNo ratings yet
- LXL - Gr11PhysicalSciences - 23 - Ohms Law - 05aug2014Document6 pagesLXL - Gr11PhysicalSciences - 23 - Ohms Law - 05aug2014HNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's LawsDocument31 pagesKirchhoff's Lawsezrah ogoriNo ratings yet
- Year 10 D & T Physics Revision Guide.186924746Document58 pagesYear 10 D & T Physics Revision Guide.186924746MonginWeissAgnèsNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 MaterialDocument88 pagesUnit-1 Materialkushalvemula07No ratings yet
- Single-Wire Electric Power Transmission: N.V. Kosinov, V.I. Garbaruk, UkraineDocument6 pagesSingle-Wire Electric Power Transmission: N.V. Kosinov, V.I. Garbaruk, UkraineDavide Tanner TainiNo ratings yet
- 2013 Revision Document Electric CircuitsDocument11 pages2013 Revision Document Electric Circuitsrowan chibiNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit AnalysisDocument21 pagesBasic Circuit AnalysisDei PehNo ratings yet
- Transformers and Logic GatesDocument4 pagesTransformers and Logic GatesCåłłmėĎäddyNo ratings yet
- Electricity SummaryDocument8 pagesElectricity Summarya kamranNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 12: ElectricityDocument18 pagesChapter - 12: Electricitysachin121083No ratings yet
- 13 Electric Circuits Batteries and ResistorsDocument10 pages13 Electric Circuits Batteries and ResistorsrezhabloNo ratings yet
- Physics Dept at Ghs S.2 Introduction To Electricity Part Ii Notes 2020Document9 pagesPhysics Dept at Ghs S.2 Introduction To Electricity Part Ii Notes 2020Dahanyakage WickramathungaNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit TheoryDocument6 pagesElectric Circuit TheoryPaula ZofioNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Quick Notes PDFDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 7 Quick Notes PDFEmmy NurulazwanaNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 6 Periodic TableDocument27 pagesScience Chapter 6 Periodic TableAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- F1 Chapter 3 TestDocument5 pagesF1 Chapter 3 TestAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Characterisation Study For Halal Abattoir Wastewater Treatment Plant in Siburan SarawakDocument35 pagesWastewater Characterisation Study For Halal Abattoir Wastewater Treatment Plant in Siburan SarawakAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Classes of FoodDocument8 pages3.1 Classes of FoodAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Summative PracticeDocument4 pagesSummative PracticeAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Digestive SystemAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- F3 Compulsory ExperimentsDocument4 pagesF3 Compulsory ExperimentsAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Date: Name Time Out Time inDocument3 pagesDate: Name Time Out Time inAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Science Is Part of Daily LifeDocument1 page1.1 Science Is Part of Daily LifeAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- HypermetropiaDocument5 pagesHypermetropiaAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Gas PressureDocument2 pagesGas PressureAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 AirDocument31 pagesChapter 7 AirAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- F2 Chapter 9 - HeatDocument6 pagesF2 Chapter 9 - HeatAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- F2 Mid-Year Exam Section BDocument3 pagesF2 Mid-Year Exam Section BAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- RPT Science Form 1 2019Document17 pagesRPT Science Form 1 2019Anne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument50 pagesCombinepdfAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Study Guide KeyDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table Study Guide KeyAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Pressure (Part 2)Document2 pagesPressure (Part 2)Anne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- F1 Quiz Chapter 1Document3 pagesF1 Quiz Chapter 1Anne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- STR Mpa-MpmDocument8 pagesSTR Mpa-MpmBANGGANo ratings yet
- Etap - Relay CoordinationDocument311 pagesEtap - Relay CoordinationManohar Potnuru100% (1)
- Cs9152 DBT Unit IV NotesDocument61 pagesCs9152 DBT Unit IV NotesNivithaNo ratings yet
- Turning Circles and Stopping DistancesDocument7 pagesTurning Circles and Stopping DistancesBisrat100% (1)
- Government College of Engineering SALEM 636011.: Electronics and Communication Engineering Curriculum and SyllabusDocument111 pagesGovernment College of Engineering SALEM 636011.: Electronics and Communication Engineering Curriculum and SyllabusSalma Mehajabeen ShajahanNo ratings yet
- Fiocchi USA Catalogue 2010Document60 pagesFiocchi USA Catalogue 2010Mario LopezNo ratings yet
- Arun Et al-2019-ChemistrySelectDocument8 pagesArun Et al-2019-ChemistrySelectRavi Kumar ARunNo ratings yet
- Identifying Solutions: 1 - 2 0 1 1 Sick'S Customer MagazineDocument58 pagesIdentifying Solutions: 1 - 2 0 1 1 Sick'S Customer MagazineNicuVisanNo ratings yet
- Face Recognition Using Back Propagation Neural NetworkDocument1 pageFace Recognition Using Back Propagation Neural NetworkMayank OnkarNo ratings yet
- Patrick C Hall@yahoo - com-TruthfinderReportDocument13 pagesPatrick C Hall@yahoo - com-TruthfinderReportsmithsmithsmithsmithsmithNo ratings yet
- 01.2 Small-Cell Report - Full ReportDocument31 pages01.2 Small-Cell Report - Full Reportwalia_anujNo ratings yet
- G3508 - 600kvaDocument7 pagesG3508 - 600kvaJim Patrick ChombaNo ratings yet
- LPPC Preliminary Work Schedule 12-11-21Document2 pagesLPPC Preliminary Work Schedule 12-11-21DMNo ratings yet
- Applies To:: The Beginner's Guide To Oracle Solaris Patching (ID 1005835.1)Document5 pagesApplies To:: The Beginner's Guide To Oracle Solaris Patching (ID 1005835.1)apletonprinceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To PSoCDocument32 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To PSoCtptuyen2246No ratings yet
- Water Tank Seat Slab DesignDocument2 pagesWater Tank Seat Slab DesignMesfin Derbew100% (2)
- Kalkhoff Users ManualDocument148 pagesKalkhoff Users Manualanonms_accNo ratings yet
- Injection Moulding - Quality Molded PartsDocument28 pagesInjection Moulding - Quality Molded PartsQuản Lê Đình100% (3)
- Chapter 2 A Guide To Using UnixDocument53 pagesChapter 2 A Guide To Using UnixAntwon KellyNo ratings yet
- Pressure Flow and Temperature SwitchesDocument16 pagesPressure Flow and Temperature SwitchesMD SAMANNo ratings yet
- CAM Charges Working For The Month of May 2023Document1 pageCAM Charges Working For The Month of May 2023adnandani2882No ratings yet
- Commodity Sourcing Strategy ProjectDocument5 pagesCommodity Sourcing Strategy ProjectMohit TalwarNo ratings yet
- Oral Presentations Ormrod 2015 06Document23 pagesOral Presentations Ormrod 2015 06Miguel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Palfinger PK 15500 Load ChartDocument2 pagesPalfinger PK 15500 Load ChartD Chandra Sekhar100% (2)
- Lab Manual No 13Document3 pagesLab Manual No 13Hammad JawadNo ratings yet
- 6400t Rev-BDocument4 pages6400t Rev-BGloria HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Solar Storage System Comp GUIDEGTM 2 1Document10 pagesSolar Storage System Comp GUIDEGTM 2 1harosalesvNo ratings yet
- CMVR ProcedureDocument14 pagesCMVR ProcedureSoumil GuptabhayaNo ratings yet
- Community Building PDFDocument2 pagesCommunity Building PDFLauren100% (1)