Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Schema 3-3
Uploaded by
MariesigOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Schema 3-3
Uploaded by
MariesigCopyright:
Available Formats
..
}
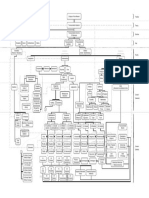
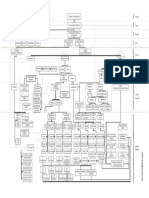
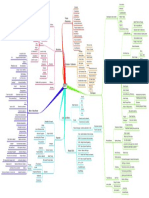
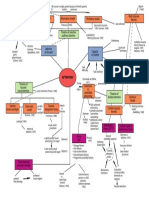
Figure-ground minimum principle
reversal Figure and ground Proximity
..
[Hochberg, 1978]
Similarity
Continuity Gestalt laws
cocktail-party Form perception Grouping . Closure
Part-whole
of perception
(law of Prägnanz)
.
phenomenon
relationship
Gestalt Common fate
qualiität
'The vision problem'= image useful information? (form quality) Gestalt psychology Navon [1977]
and perceptual
Marr's . Computational theory image (grey-level
organisation
Global vs. local features
computational
theory
.. (why? what for?)
Algorithm (how?)
Hardware implementation
description)
primal sketch
2½-D sketch
Segmentation [Marr, 1976]
retinal disparity
Non-pictorial stereopsis
(in what form?) 3-D model representation (primary) cues accommodation
Analysis-by- Depth (monocular)
synthesis model perception convergence
[Neisser, 1967] PERCEPTION: relative size
PROCESSES Pictorial
(secondary) cues relative brightness
Data-driven, Conceptually- and superimposition
bottom-up Theories of driven, top-down THEORIES (overlap)
(direct) visual perception (indirect)
processing motion linear perspective
processing light
parallax
image-retina (dynamic) and
system/eye-head shadow height aerial perspective
texture in
system [Gregory, 1973] gradient horizontal
Gregory's plane
Gibson's theory of constructivist theory long-range, feature-
direct perception tracking system/ size
short-range motion-
'Seeing' Perception of sensing system
vs. real movement [Braddick, 1974] shape
Perceptual Perceptual
Optical 'seeing as' Inference hypotheses
[Fodor & Importance of constancy location
Ecological array ('going
Pylyshyn, 1981] beyond configurational eye movements brightness
optics change
the information superior Cornsweet [1970]
Transactionalism given') Misapplied colliculus colour
size constancy
Optic flow Situational theory Illusions of
patterns variables [Allport, 1955] Illusions (apparent movement)
P-type/ movement
..
Affordances
.
(OFPs) Selector M-type
Perceptual
set ganglion distortions (or autokinetic effect
. ..
{
Texture gradient Interpreter cells geometric illusions) stroboscopic motion
Invariant, + Motivational- phi phenomenon
ambiguous (or
higher-
order
Linear perspective
+
emotional
variables perceptual . reversible) figures
paradoxical figures . induced movement
motion after-effects
.
features Motion parallax accentuation/
Depth (or impossible objects)
sensitization fictions
perception
[Gregory, 1983]
You might also like
- Schema 3-2Document1 pageSchema 3-2MariesigNo ratings yet
- DFMEA PFMEA Control Plan LinkagesDocument1 pageDFMEA PFMEA Control Plan LinkagesSaul Montiel100% (2)
- CTS Class 1 AugDocument3 pagesCTS Class 1 AugsabeloNo ratings yet
- Post Award Risk RegisterDocument1 pagePost Award Risk RegisterClaim ConsultantNo ratings yet
- Aspect-Impact For LabDocument1 pageAspect-Impact For Labvipulsharma655No ratings yet
- Steps To SuccessDocument1 pageSteps To SuccessSye MasinaNo ratings yet
- Mindmap QUANT - M2Document1 pageMindmap QUANT - M2Quyên ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Vol-I Part-II Section 5.B.3 1 Technical Investigation Report 487Document1 pageVol-I Part-II Section 5.B.3 1 Technical Investigation Report 487mayank dixitNo ratings yet
- dFMEA 4th Edition BlankDocument1 pagedFMEA 4th Edition BlankTom@GGCNo ratings yet
- BLANK Everything You Need To Memorise: Part 3, Statistics PDFDocument1 pageBLANK Everything You Need To Memorise: Part 3, Statistics PDFFrancesco PiazzaNo ratings yet
- PFMEA For Injection Molding ProcessDocument2 pagesPFMEA For Injection Molding ProcessDhananjay Patil100% (2)
- KDRV - EngDocument1 pageKDRV - EngCenker YıldırımNo ratings yet
- Nooscope PDFDocument1 pageNooscope PDFPacoMüllerNo ratings yet
- #5. Inside The Black Box by Rishi K Narang, 2009 - 211 PGDocument1 page#5. Inside The Black Box by Rishi K Narang, 2009 - 211 PGpatar greatNo ratings yet
- (Analytic) (Dialectic) : A Posteriori A PrioriDocument1 page(Analytic) (Dialectic) : A Posteriori A PrioriDas Nichts PvoNo ratings yet
- The Contemporary World - TOS PlateDocument1 pageThe Contemporary World - TOS PlateVivialyn Cordova AsoyNo ratings yet
- ACM ICVGIP 2010 Poster Presentation 14-12-2010Document1 pageACM ICVGIP 2010 Poster Presentation 14-12-2010Ishit MakwanaNo ratings yet
- FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS SampathDocument1 pageFINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS SampathSiddi Sampath Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DNA ReplicationDocument1 pageChapter 2 DNA ReplicationYuume YuuNo ratings yet
- Environmental Scanning The Basic Model: - 30/11/2011 - Prepared by Carl Olav Staff / Rune Fjellvang Page 1 of 1Document1 pageEnvironmental Scanning The Basic Model: - 30/11/2011 - Prepared by Carl Olav Staff / Rune Fjellvang Page 1 of 1Baher WilliamNo ratings yet
- Poster INFIERI Alejandro SopenaDocument1 pagePoster INFIERI Alejandro SopenaTianhan LiuNo ratings yet
- Starting CheetDocument8 pagesStarting Cheetdosani2004No ratings yet
- Seeing The World Through Your EyesDocument1 pageSeeing The World Through Your Eyesdelfinoden.0tNo ratings yet
- AEIOUCanvasDocument1 pageAEIOUCanvasJatin vataliyaNo ratings yet
- FMEADocument1 pageFMEADiego MartínNo ratings yet
- Design Fmea 1 ST Pipe Teflon HoseDocument11 pagesDesign Fmea 1 ST Pipe Teflon HoseSandeep PandeyNo ratings yet
- Fea Unit 4 pg1-26Document25 pagesFea Unit 4 pg1-26SAURAV KOULNo ratings yet
- Scatter Diagram - Merits and Demerits - Correlation Analysis PDFDocument3 pagesScatter Diagram - Merits and Demerits - Correlation Analysis PDFAsif gillNo ratings yet
- Class Diagram Group Final Lab Exercise UML Andrés Burgos, Angélica Cruz, Cristian MéndezDocument1 pageClass Diagram Group Final Lab Exercise UML Andrés Burgos, Angélica Cruz, Cristian MéndezGabriel MoraNo ratings yet
- Princip Les of Space Fomaliz Ation: All Objects)Document3 pagesPrincip Les of Space Fomaliz Ation: All Objects)Wai-Yan HauNo ratings yet
- TOS Template Exam With FormulaDocument1 pageTOS Template Exam With FormulaRuby Esmeralda AndayaNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need To Memorise - Part 3, Statistics PDFDocument1 pageEverything You Need To Memorise - Part 3, Statistics PDFTripleFireWingsNo ratings yet
- Vance Character Tome-Full BleedDocument2 pagesVance Character Tome-Full BleedgnieldNo ratings yet
- Making of Portrait of Graham and Amanda by Ian Spriggs - CG TUTORIALDocument1 pageMaking of Portrait of Graham and Amanda by Ian Spriggs - CG TUTORIALKennedyKisusiNo ratings yet
- Open and Federated Data: DgtaltwnDocument1 pageOpen and Federated Data: DgtaltwnBehlül ÖZKULNo ratings yet
- Carlo Rovelli Seven Brief Lessons On Physics First LessonDocument10 pagesCarlo Rovelli Seven Brief Lessons On Physics First LessonKaleem's CornerNo ratings yet
- NLP SkicaDocument1 pageNLP SkicaKarmen CesarićNo ratings yet
- MinmapDocument1 pageMinmap20 18100% (1)
- L7-526 Exact Comparison ENDocument2 pagesL7-526 Exact Comparison ENvihansNo ratings yet
- Basic Structure DoctrineDocument1 pageBasic Structure DoctrineKesava KumarNo ratings yet
- A Modified Response Spectrum Analysis Procedure: November 2016Document2 pagesA Modified Response Spectrum Analysis Procedure: November 2016Arapat SyamsuddinNo ratings yet
- Contoh Research GapDocument1 pageContoh Research GapDhika AdhityaNo ratings yet
- Blue Planet - Character SheetDocument3 pagesBlue Planet - Character Sheetephatman4288No ratings yet
- Hira DineshDocument11 pagesHira DineshDurai GunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Wellsite Database D - 06Document22 pagesWellsite Database D - 06boimcukNo ratings yet
- Cfa - R2Document1 pageCfa - R2Thanh TuyềnNo ratings yet
- Semiemperical Estimate of Pile Capacity Conforming Aashto Lrfd-2007Document1 pageSemiemperical Estimate of Pile Capacity Conforming Aashto Lrfd-2007civixxNo ratings yet
- Design FMEA Template Rev 1.0Document8 pagesDesign FMEA Template Rev 1.0Lê Hoàn VũNo ratings yet
- English 9 Q1 TOSDocument2 pagesEnglish 9 Q1 TOSJohnfil Ajeno JamolinNo ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document18 pagesWa0000.bookworm12045No ratings yet
- Semiemperical Estimate of Pile Capacity Conforming Aashto Lrfd-2007Document1 pageSemiemperical Estimate of Pile Capacity Conforming Aashto Lrfd-2007civixxNo ratings yet
- 7 Elements of ArtDocument1 page7 Elements of ArtJAPVJ MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Cognitive ProjectDocument1 pageSupply Chain Cognitive ProjectNabia SohailNo ratings yet
- FailureDocument6 pagesFailureWajiha RajaniNo ratings yet
- CrystallographyDocument1 pageCrystallographySUNANDAN PANDANo ratings yet
- Like You To Think About Placement of Facial Features. Use The Oval To Help Guide You With Your Facial Shape. Look at The Examples For HelpDocument1 pageLike You To Think About Placement of Facial Features. Use The Oval To Help Guide You With Your Facial Shape. Look at The Examples For HelpEmma FravigarNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 14-Oct-2023Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 14-Oct-2023Anurag JainNo ratings yet
- Group Name Title of Test Date Time Physics Chemistry Math BiologyDocument1 pageGroup Name Title of Test Date Time Physics Chemistry Math Biologyhariharan PNo ratings yet
- Schema 5-2Document1 pageSchema 5-2MariesigNo ratings yet
- Schema 2-9Document1 pageSchema 2-9MariesigNo ratings yet
- Schema 3-7Document1 pageSchema 3-7MariesigNo ratings yet
- Schema 3-1Document1 pageSchema 3-1MariesigNo ratings yet
- Schema 2-8Document1 pageSchema 2-8MariesigNo ratings yet
- Schema 5-6Document1 pageSchema 5-6MariesigNo ratings yet
- Schema 6-6Document1 pageSchema 6-6MariesigNo ratings yet
- Gender SimilaritiesDocument12 pagesGender SimilaritiesMariesigNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan (Deductive Teaching Method)Document4 pagesLesson Plan (Deductive Teaching Method)Angelene Mae MolinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Form: Recognize and Produce Rhyming WordsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Form: Recognize and Produce Rhyming Wordsapi-456828286No ratings yet
- Colours As Emotion Conceptual MetaphorsDocument29 pagesColours As Emotion Conceptual MetaphorsChatchawadee SaralambaNo ratings yet
- 7 Critical Thinking Skills: Examples and Ways To ImproveDocument3 pages7 Critical Thinking Skills: Examples and Ways To ImproveCalvin YeohNo ratings yet
- Individual Project Management: Von Steven O. Ortiz 201D T/F 12:00pm - 1:30pm Sir Pete VillarDocument12 pagesIndividual Project Management: Von Steven O. Ortiz 201D T/F 12:00pm - 1:30pm Sir Pete VillarVon Steven OrtizNo ratings yet
- Division of Bohol: Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VII, Central VisayasDocument4 pagesDivision of Bohol: Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VII, Central VisayasJaime Curag Jr.No ratings yet
- ASTM E2299-11 Standard Guide For Sensory Evaluation of Products by ChildrenDocument12 pagesASTM E2299-11 Standard Guide For Sensory Evaluation of Products by ChildrenGuillermo Balseiro100% (3)
- Consent Form Assessment and TreatmentDocument1 pageConsent Form Assessment and TreatmentSaroja RoyNo ratings yet
- Om Kothari Institute of Management & Research: Presentation OnDocument56 pagesOm Kothari Institute of Management & Research: Presentation OnpoonicelikeNo ratings yet
- Learning and Teaching PDFDocument75 pagesLearning and Teaching PDFSayali Bhojane0% (1)
- Suggestology - Lozanov PDFDocument393 pagesSuggestology - Lozanov PDFcharset12100% (2)
- Ge6075 Scad MSM PDFDocument89 pagesGe6075 Scad MSM PDFlogamaniNo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument5 pagesArgumentative Essayapi-388945643No ratings yet
- CONFERENCEDocument12 pagesCONFERENCETHONDYNALUNo ratings yet
- .LSHDB Foy Y..k.rjg IouttDocument1 page.LSHDB Foy Y..k.rjg IouttmeekoangelaNo ratings yet
- Mythological CriticismDocument8 pagesMythological CriticismDanielle AkutagawaNo ratings yet
- 5 Principles of LearningDocument4 pages5 Principles of LearningSatish UlliNo ratings yet
- Document Art AppreciationDocument2 pagesDocument Art AppreciationMohaimen G. EsmailNo ratings yet
- Creating Authentic CommunityDocument30 pagesCreating Authentic CommunityRicardo Marquez100% (2)
- CBSE Class 12 Psychology Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 12 Psychology Worksheet PDFishwar singh100% (1)
- Planning A Narrative EssayDocument4 pagesPlanning A Narrative EssayAparna RameshNo ratings yet
- Begin With The End in Mind Habit 2Document3 pagesBegin With The End in Mind Habit 2fiduNo ratings yet
- Pe Action Plan - Template Action Plan For Quality Physical Education and Schools SportDocument1 pagePe Action Plan - Template Action Plan For Quality Physical Education and Schools SportElisha TanNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence: Dr. Praveen SrivastavaDocument33 pagesEmotional Intelligence: Dr. Praveen SrivastavaSamaycallingNo ratings yet
- Jamapsychiatry Ashar 2021 Oi 210060 1632764319.53348Document12 pagesJamapsychiatry Ashar 2021 Oi 210060 1632764319.53348FideoPereNo ratings yet
- Personality DevelopmentDocument2 pagesPersonality Developmentjanniah romanceNo ratings yet
- Developing Critical ApproachesDocument9 pagesDeveloping Critical ApproachesSyam Sugama PutraNo ratings yet
- Preparing Questions For A Qualitative Research InterviewDocument9 pagesPreparing Questions For A Qualitative Research InterviewEmman RevillaNo ratings yet
- Final Report Card CommentsDocument3 pagesFinal Report Card CommentsTracyDianeSides33% (6)
- FS2 Ep5 (PACATANG, EVELYN)Document4 pagesFS2 Ep5 (PACATANG, EVELYN)Pacatang Evelyn50% (2)