Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Schema 3-2
Uploaded by
MariesigOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Schema 3-2
Uploaded by
MariesigCopyright:
Available Formats
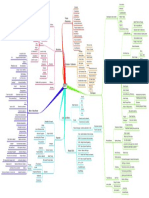
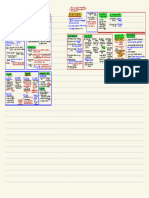
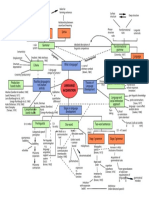
Case of Keith (geon =
Unilateral 'geometrical icon')
neglect Case of
Case of Arthur
W.J. Prosopagnosia Bar codes Geon theory [Biederman, 1987]
Capgras' delusion/
syndrome ('recognition-by-components'
(delusional mis- model)
Disorders identification Template-
of face processing matching hypothesis
Faces = greater than the sum Prototype theories
Serial
of their parts (i.e. 'configural') processing
= the process by which we assign
Part of face perception meaning to visual input, by identifying
the objects in the visual field
Upright and inverted [Eysenck, 1993]
faces are processed Face PATTERN Theories of Feature-detection
differently recognition RECOGNITION PR theories
(PR)
visual
e.g. Thatcher illusion scanning
..
[Thompson, 1980] tasks
Face-specific
Simple
.
cells in
Face recognition Parallel infero-temporal Complex
Models of and the brain processing monkey cortex Hypercomplex
face recognition [Ono et al., 1993] cortical cells
[Selfridge, [Hubel & Wiesel, 1968]
1959] Pandemonium model
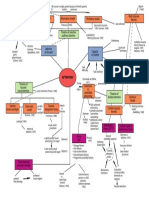
[Young Model of functional Revised Functional model [Bruce &
Young, .. image demons
et al.,
1985]
components in person
identification
for face recognition 1986]
orienting
response
.. feature demons
cognitive demons
decision demons
Cells responsive to
specific aspects of
Recognition Stages of person temporal human face/set of features
units identification put into lobe crucial [Perrett]
broader context of their for face
relationship with the recognition prepare us for
Diary study of other uses made of facial ('what pathway') what is likely
everyday failures information to happen top-down/conceptually-driven
in person processing
Person vs.
identification identity nodes influence bottom-up/data-driven
(PINs) amygdala of context/ processing
several processing (helps generate expectation
'modules' linked in emotional responses)
sequence/in parallel to particular faces
e.g. face recognition
units/FRUs tip-of-the-tongue
(TOT) phenomenon
[e.g. Brennan et al., 1990]
You might also like
- BDSM Negotiation Checklist PDFDocument2 pagesBDSM Negotiation Checklist PDFJulia Marie Flautt80% (5)
- Potential Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (DESIGN FMEA) : Disk Brake Sub-AssemblyDocument6 pagesPotential Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (DESIGN FMEA) : Disk Brake Sub-AssemblyLuis Carlos SuarezNo ratings yet
- 4 HIRA Format - Sand Blasting ActivityDocument2 pages4 HIRA Format - Sand Blasting ActivityMD Abdullah100% (1)
- Design Fmea 1 ST Pipe Teflon HoseDocument11 pagesDesign Fmea 1 ST Pipe Teflon HoseSandeep PandeyNo ratings yet
- MinmapDocument1 pageMinmap20 18100% (1)
- Mind Domination Mind MapDocument1 pageMind Domination Mind MapAndrea BertocchiNo ratings yet
- Controlling Sex and Decency in Advertising Around The WorldDocument12 pagesControlling Sex and Decency in Advertising Around The WorldShwetha ShekharNo ratings yet
- #5. Inside The Black Box by Rishi K Narang, 2009 - 211 PGDocument1 page#5. Inside The Black Box by Rishi K Narang, 2009 - 211 PGpatar greatNo ratings yet
- Cambridge University Press Richard Rorty JulDocument223 pagesCambridge University Press Richard Rorty JulGulantat100% (5)
- Vedic Maths PDFDocument2 pagesVedic Maths PDFbikash chandra haldarNo ratings yet
- Final Demo Lesson Plan in MAPEH 9Document10 pagesFinal Demo Lesson Plan in MAPEH 9Giezelle Leopando100% (4)
- NLP SkicaDocument1 pageNLP SkicaKarmen CesarićNo ratings yet
- NCP IcuDocument2 pagesNCP Icujennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Hermeneutical PhenomenologyDocument12 pagesHermeneutical PhenomenologySean Wasil100% (4)
- Maria Montessori QuotesDocument93 pagesMaria Montessori Quotesqwertz_mNo ratings yet
- Java Self-Evaluation FormDocument5 pagesJava Self-Evaluation FormYurii ProrokNo ratings yet
- Occupational Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment Rating SheetDocument4 pagesOccupational Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment Rating SheetSir ZenNo ratings yet
- Training PresentationDocument7 pagesTraining PresentationMagda AryaniNo ratings yet
- Chcmgt005 Course Hero Case StudyDocument18 pagesChcmgt005 Course Hero Case StudySandeep Kaur100% (3)
- Italian Vocabulary-Asking and Giving DirectionsDocument7 pagesItalian Vocabulary-Asking and Giving Directionsswatson033100% (1)
- Units of Time LessonDocument5 pagesUnits of Time Lessonapi-245595227No ratings yet
- Schema 3-3Document1 pageSchema 3-3MariesigNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-12-11 at 19.29.39Document11 pagesScreenshot 2023-12-11 at 19.29.39criveira.ieu2023No ratings yet
- Seeing The World Through Your EyesDocument1 pageSeeing The World Through Your Eyesdelfinoden.0tNo ratings yet
- Sphereface: Deep Hypersphere Embedding For Face RecognitionDocument13 pagesSphereface: Deep Hypersphere Embedding For Face RecognitionShazzad Sakim Sourav 1510719642No ratings yet
- Aula T4Document1 pageAula T4Raul LeitaoNo ratings yet
- Nursery 1A ANNUAL PLAN Mulungi AllenDocument20 pagesNursery 1A ANNUAL PLAN Mulungi AllenKansiime JonasNo ratings yet
- Vance Character Tome-Full BleedDocument2 pagesVance Character Tome-Full BleedgnieldNo ratings yet
- 1E - Parcial 4Document16 pages1E - Parcial 4SOL AMARILLONo ratings yet
- HciDocument25 pagesHcibeleharshwardhanNo ratings yet
- Dark Heresy 2e CS Priest Snope's World (Unfinished)Document2 pagesDark Heresy 2e CS Priest Snope's World (Unfinished)Alasdair GoudieNo ratings yet
- 01 Sept 2022-Update Candidate Summary Pengawas Team Project AHM-1Document1 page01 Sept 2022-Update Candidate Summary Pengawas Team Project AHM-1CiyaNo ratings yet
- RA-T&C Plumbing SystemDocument10 pagesRA-T&C Plumbing System721917114 47No ratings yet
- Sphere FaceDocument9 pagesSphere FaceSkarica En RedNo ratings yet
- Dark Heresy Character Sheet - Psyker Character (Almost Finished)Document2 pagesDark Heresy Character Sheet - Psyker Character (Almost Finished)Alasdair GoudieNo ratings yet
- Ficha D&D 5e PrismaDocument2 pagesFicha D&D 5e PrismaMurillo VazNo ratings yet
- Aspect-Impact For LabDocument1 pageAspect-Impact For Labvipulsharma655No ratings yet
- Pt. Abcd Indonesia: Identification Base Risk Current ControlDocument2 pagesPt. Abcd Indonesia: Identification Base Risk Current ControlPheNol LOve PeaCeNo ratings yet
- Construction ModelDocument1 pageConstruction Modelmirna ojedaNo ratings yet
- Peripherals (Sedition, Reservation)Document1 pagePeripherals (Sedition, Reservation)Kesava KumarNo ratings yet
- Sphereface: Deep Hypersphere Embedding For Face RecognitionDocument9 pagesSphereface: Deep Hypersphere Embedding For Face RecognitionCẩm Tú CầuNo ratings yet
- Final Resume 2022Document1 pageFinal Resume 2022flor johnNo ratings yet
- Dark Heresy Character Sheet - Warrior (Unfinished)Document2 pagesDark Heresy Character Sheet - Warrior (Unfinished)Alasdair GoudieNo ratings yet
- Test ParkingDocument1 pageTest ParkingBrando MartinezNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - PCMDocument7 pagesFormula Sheet - PCMRonit MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Dark Heresy 2e Character Sheet - Desperado CharlatanDocument2 pagesDark Heresy 2e Character Sheet - Desperado CharlatanAlasdair GoudieNo ratings yet
- Aapdamitra Volunteers DetailsDocument8 pagesAapdamitra Volunteers Detailssiva santhosh100% (1)
- READING TOEFL STRATEGY (Fix)Document7 pagesREADING TOEFL STRATEGY (Fix)Saefull OhNo ratings yet
- 10 STR DEX CON INT WIS CHA: LevelDocument4 pages10 STR DEX CON INT WIS CHA: LevelHerobrine CompanyNo ratings yet
- Nooscope PDFDocument1 pageNooscope PDFPacoMüllerNo ratings yet
- Mindmap QUANT - M2Document1 pageMindmap QUANT - M2Quyên ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Series of LecturesDocument136 pagesSeries of LecturesIrfan SaeedNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Table of SpecificationsDocument4 pagesScience 8 Table of SpecificationsAngelyn CanonizadoNo ratings yet
- Mind MapsDocument14 pagesMind MapsRushil ReddyNo ratings yet
- Empty SR6 SheetDocument6 pagesEmpty SR6 Sheetcruelangel1324No ratings yet
- ShearInBeams CE153 2Document54 pagesShearInBeams CE153 2Simon IssNo ratings yet
- Scatter Diagram - Merits and Demerits - Correlation Analysis PDFDocument3 pagesScatter Diagram - Merits and Demerits - Correlation Analysis PDFAsif gillNo ratings yet
- Dark Heresy 2e Adeptus Mechanicus Character - UnfinishedDocument2 pagesDark Heresy 2e Adeptus Mechanicus Character - UnfinishedAlasdair GoudieNo ratings yet
- Organization & Design. Acetate Department Case.Document2 pagesOrganization & Design. Acetate Department Case.sudipto rajNo ratings yet
- Chujch - Orc ThaumaturgeDocument8 pagesChujch - Orc ThaumaturgeAlasdair GoudieNo ratings yet
- Lecture-05 (General Complex Exponentials For CT and DT)Document15 pagesLecture-05 (General Complex Exponentials For CT and DT)The LifeNo ratings yet
- English 9 Q1 TOSDocument2 pagesEnglish 9 Q1 TOSJohnfil Ajeno JamolinNo ratings yet
- Board PosterDocument1 pageBoard PosterEmilda IzhnyNo ratings yet
- English 3.1 - Vocabulary: Business & School Nature OtherDocument6 pagesEnglish 3.1 - Vocabulary: Business & School Nature OtherVargas LaloNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map Q1Document3 pagesCurriculum Map Q1Jerwin DiazNo ratings yet
- L7-526 Exact Comparison ENDocument2 pagesL7-526 Exact Comparison ENvihansNo ratings yet
- Vision, Result and Sustainable SuccessDocument16 pagesVision, Result and Sustainable SuccesszeyinuNo ratings yet
- Divine Light Academy: Table of SpecificationsDocument5 pagesDivine Light Academy: Table of SpecificationsRussel AraniegoNo ratings yet
- Ad Soyad Taraf Mevki: Hit Points RecoveriesDocument2 pagesAd Soyad Taraf Mevki: Hit Points RecoveriesSelam CanımNo ratings yet
- Schema 5-2Document1 pageSchema 5-2MariesigNo ratings yet
- Schema 2-9Document1 pageSchema 2-9MariesigNo ratings yet
- Schema 3-7Document1 pageSchema 3-7MariesigNo ratings yet
- Schema 3-1Document1 pageSchema 3-1MariesigNo ratings yet
- Schema 5-6Document1 pageSchema 5-6MariesigNo ratings yet
- Schema 2-8Document1 pageSchema 2-8MariesigNo ratings yet
- Gender SimilaritiesDocument12 pagesGender SimilaritiesMariesigNo ratings yet
- Schema 6-6Document1 pageSchema 6-6MariesigNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Emma by Jane AustenDocument10 pagesWorksheet On Emma by Jane AustenRaylla AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- What Motivates Employees To Participate in Continuous Improvement ActivitiesDocument21 pagesWhat Motivates Employees To Participate in Continuous Improvement ActivitiesAnonymous 9YkkjPNo ratings yet
- PMP Lesson1 (Cert Review and PMI-Isms)Document36 pagesPMP Lesson1 (Cert Review and PMI-Isms)L_ErosNo ratings yet
- Reframing Organizations Power PointDocument50 pagesReframing Organizations Power PointjoeybriggsNo ratings yet
- 1ms Sequence 5 Me My Country and The World by Teacher Djamal Djamal1650673330Document14 pages1ms Sequence 5 Me My Country and The World by Teacher Djamal Djamal1650673330Karim HaciniNo ratings yet
- Amivalences of The Mass Ornament in King Vidor's The CrowdDocument19 pagesAmivalences of The Mass Ornament in King Vidor's The Crowdjames joyceNo ratings yet
- Drugs Take You To Hell, Disguised As HeavenDocument2 pagesDrugs Take You To Hell, Disguised As HeavenJust Tine100% (2)
- Assessment 2Document55 pagesAssessment 2Danica Joy MendozaNo ratings yet
- Applying Lenses To Short StoriesDocument3 pagesApplying Lenses To Short Storiesapi-239518128No ratings yet
- What Is Political ScienceDocument3 pagesWhat Is Political ScienceZion TesalonaNo ratings yet
- B Ed Program StructureDocument11 pagesB Ed Program StructureLinta ChandyNo ratings yet
- Course Learning OutcomesDocument4 pagesCourse Learning OutcomesprakashkerurNo ratings yet
- Worksheet MomentumDocument5 pagesWorksheet MomentumSiti RohmahNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Travails of A Training ManagerDocument3 pagesHuman Resource Management: Travails of A Training ManagerTahiratul Elma0% (1)
- Beginning Sentence CorrectionDocument1 pageBeginning Sentence CorrectionJaya SugantiniNo ratings yet
- Leo Liu Assignment 3 Leo Ningzhuo LiuDocument13 pagesLeo Liu Assignment 3 Leo Ningzhuo Liuapi-483734281No ratings yet
- Sociology Project: Topic - A Discourse On Theories of SocializationDocument19 pagesSociology Project: Topic - A Discourse On Theories of SocializationSumukh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Preventing Teenage Drug Abuse With Drug TestingDocument11 pagesPreventing Teenage Drug Abuse With Drug TestingJohn ArkinNo ratings yet
- The Art of Atomic HabitsDocument32 pagesThe Art of Atomic Habitsazmi hayazaNo ratings yet
- Erich Fromm Art Loving Free PDF DownloadDocument2 pagesErich Fromm Art Loving Free PDF DownloadOsama Jamshaid JamshaidNo ratings yet