Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Linear Function
Uploaded by
Marija CvetkovicOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Linear Function
Uploaded by
Marija CvetkovicCopyright:
Available Formats
IM3_Ch08.
fm Page 205 Thursday, January 3, 2008 4:58 PM
them
ma
atic er
Mathematical terms 8
al t
ms
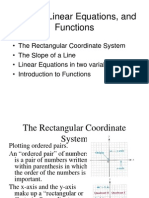
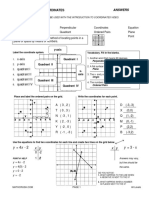
number plane x-coordinate
• A rectangular y • The first of the coordinates. It tells how far 8
4
grid that right (or left) the point is from the origin.
allows the 3
C(–3, 2) 2 A(3, 2) y-coordinate
position of 2
3 1 1 • The second of the coordinates. It tells how
points in a far the point is above (or below) the origin.
plane to be –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 x x-intercept
identified by –1 E(0, –1)
• The point where a line crosses the x-axis.
an ordered –2
pair of B(3, –2) y-intercept
–3
D(–2, –3) • The point where a line crosses the y-axis.
numbers.
plot coefficient
• To mark the position of a point on the • The number that multiplies a pronumeral
number plane. in an equation.
graph (a line) eg 3x − 5y = 6
• All the points on a line coefficient of x is 3
or coefficient of y is −5
• to plot the points that lie on a line. constant
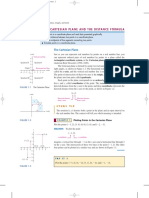
quadrants y • The number part of an equation or
• The four 3 expression.
quarters that 2nd 2 1st eg 3x − 5y = 6
the number quadrant
1
quadrant The constant is 6.
plane is interval
–3 –2 –1 1 2 3 x
divided into –1 • The part of a line between two given
by the x- and 3rd –2 4th points.
y-axes. quadrant quadrant
–3 gradient–intercept form
x-axis • A way of writing the equation of a line.
• The horizontal number line in a number eg y = 2x − 5, y = 1--2- x + 2
plane. See 1 under number plane.
When an equation is rearranged and
y-axis written in the form y = mx + b then m is
• The vertical number line in a number the gradient and b is the y-intercept.
plane. See 2 under number plane.
speed
origin • Relative rate of motion or action.
• The point where the x-axis and y-axis distance
intersect, (0, 0). See 3 under number • Defined as: --------------------
time
plane. • Measuring in units such as km/h or m/s.
coordinates travel graph
• A pair of numbers that gives the position • A line graph where distance travelled is
of a point in a number plane relative to plotted against time taken.
the origin. See (3, 2), (3, −2), (−3, 2), • The gradient (or slope) of the line is an
(−2, −3) and (0, −1) under number indication of the speed of the motion.
plane.
Mathematical terms 8
CHAPTER 8 COORDINATE GEOMETRY: GRAPHING STRAIGHT LINES 205
You might also like
- 3.coordinate GeometryDocument14 pages3.coordinate GeometryArush TripathiNo ratings yet
- Graphs, Linear Equations, and FunctionsDocument46 pagesGraphs, Linear Equations, and FunctionsAmit BhararaNo ratings yet
- Coordinate SystemDocument9 pagesCoordinate SystemJojo TakatoNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry WorksheetDocument44 pagesCoordinate Geometry WorksheetCamille ComasNo ratings yet
- Sp'21 Maths III-Lect 3 - Analytical Geometry in 3D-SpaceDocument76 pagesSp'21 Maths III-Lect 3 - Analytical Geometry in 3D-SpaceMuhammad FurqanNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.1 Linear EquationsDocument24 pagesTopic 1.1 Linear EquationsnshoulyNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 - Coordinate Geometry (Activites) Part B-1Document15 pagesGrade 11 - Coordinate Geometry (Activites) Part B-1Kallissa AndersonNo ratings yet
- Systems of Linear Equations. Part IIDocument16 pagesSystems of Linear Equations. Part IIYE KONo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry: Chapter - 6Document16 pagesCoordinate Geometry: Chapter - 6Suvayan MohantyNo ratings yet
- 02 CH 02 Linear Graphs and Simultaneous Linear EquationsDocument7 pages02 CH 02 Linear Graphs and Simultaneous Linear EquationswindaNo ratings yet
- G8 Math Q1 - Week 5 - Slope of A LineDocument43 pagesG8 Math Q1 - Week 5 - Slope of A LineWenilyn MananganNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 8: Graphing A Linear Equation Using Its Slope and A PointDocument5 pagesMathematics 8: Graphing A Linear Equation Using Its Slope and A PointRoella Mae Tudias AlodNo ratings yet
- 7 Post NotesDocument8 pages7 Post Notesabc123asdNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Secondary-Level Maths PresentationDocument15 pagesCambridge Secondary-Level Maths PresentationESC Vietnam fanNo ratings yet
- 02 CH 02 Linear Graphs and Simultaneous Linear EquationsDocument42 pages02 CH 02 Linear Graphs and Simultaneous Linear EquationsNovi Ryanti Siahaan100% (3)
- Appendix BDocument60 pagesAppendix BRJ Wakefield-CarlNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument9 pagesGRADE 8 3rd Quarter ReviewerGracella BurladoNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Unit 3 Lesson 4 Module Graphing Linear.Document10 pagesMath 8 Unit 3 Lesson 4 Module Graphing Linear.mary joy buliagNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS G8 Q1 W5 - Abshalom Legaspi v.2Document13 pagesMATHEMATICS G8 Q1 W5 - Abshalom Legaspi v.2Ochia JustineNo ratings yet
- A. Coordinate SystemDocument16 pagesA. Coordinate SystemIR. TS. DR DARMAWATY MOHD ALINo ratings yet
- UCE Book 4Document134 pagesUCE Book 4Ssonko Martin100% (1)
- Lecture 1.2 LineDocument28 pagesLecture 1.2 LineMohd Haffiszul Bin Mohd SaidNo ratings yet
- What Is A Line?: Y-AxisDocument41 pagesWhat Is A Line?: Y-AxisRoyce Dunhill Fortes DomondonNo ratings yet
- Q2-Coordinate GeometryDocument33 pagesQ2-Coordinate GeometryAkshat ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Lines and Tangent Lines in 3-SpaceDocument4 pagesLines and Tangent Lines in 3-SpaceZulvan AviviNo ratings yet
- Graphing Linear Equations Day 3Document19 pagesGraphing Linear Equations Day 3api-584365435No ratings yet
- Edexcel P1 (已修补 第90页)Document235 pagesEdexcel P1 (已修补 第90页)王硕No ratings yet
- Math 1 - Lines and CirclesDocument13 pagesMath 1 - Lines and CirclespplauNo ratings yet
- Week 19 - LineDocument41 pagesWeek 19 - LineJeff LacasandileNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Linear FunctionsDocument54 pagesGraphs of Linear FunctionsWystan HarripaulNo ratings yet
- Functions and Their GraphsDocument148 pagesFunctions and Their GraphsLi YuNo ratings yet
- DGDGDocument66 pagesDGDGmeenuNo ratings yet
- Equations of Linear Graphs: Edexcel GCSEDocument8 pagesEquations of Linear Graphs: Edexcel GCSED SNo ratings yet
- bpc5 ch08-04Document13 pagesbpc5 ch08-04Flor CarononganNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 PPT .Document75 pagesWEEK 4 PPT .Dame YooheeNo ratings yet
- Slope of A LineDocument43 pagesSlope of A LineDenielNo ratings yet
- Intro To Coordinates Answers PDFDocument2 pagesIntro To Coordinates Answers PDFKeri-ann MillarNo ratings yet
- Review of Matrices: 1.1 DefinitionsDocument17 pagesReview of Matrices: 1.1 DefinitionsAlexander ChenNo ratings yet
- ICSE-X Mathematics - Chap-12 (Equation of A Line)Document12 pagesICSE-X Mathematics - Chap-12 (Equation of A Line)mohammedumar7864521No ratings yet
- The Real Space: MATH 38. Mathematical Analysis III Imsp, Cas, UplbDocument38 pagesThe Real Space: MATH 38. Mathematical Analysis III Imsp, Cas, UplbFelicidad Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry RevisionDocument11 pagesCoordinate Geometry Revisionhehe heheNo ratings yet
- Busana2 - Chapter 1, Part 1Document29 pagesBusana2 - Chapter 1, Part 1Odult ChanNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Analytical Geometry : 5.0 ObjectivesDocument18 pagesUnit 5 Analytical Geometry : 5.0 ObjectivesFaroq MaraqaNo ratings yet
- r2 - Lecture - CO2 - Math 21-1Document38 pagesr2 - Lecture - CO2 - Math 21-1Benmar N. OcolNo ratings yet
- G8 Math Q1 - Week 5 - Slope of A LineDocument43 pagesG8 Math Q1 - Week 5 - Slope of A LineSarahglen Ganob LumanaoNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 1: Engr. Reynilan Lopez DimalDocument37 pagesAnalytic Geometry 1: Engr. Reynilan Lopez Dimalkyle samsonNo ratings yet
- Graphs and Variations IDocument34 pagesGraphs and Variations IA.BensonNo ratings yet
- Slope Linear EquationDocument38 pagesSlope Linear EquationAlondra Marie E BaradasNo ratings yet
- Book 30 Jan 2024Document14 pagesBook 30 Jan 2024Navpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry of The Straight LineDocument6 pagesCoordinate Geometry of The Straight Linereeta ramNo ratings yet
- Graphs and TransformationsDocument12 pagesGraphs and TransformationsMariam AhmedNo ratings yet
- CCGPS Math 6 Grade Unit 7 Study Guide-Rational Explorations: Numbers and Their Opposites. Show All Work On A Separate Sheet of PaperDocument6 pagesCCGPS Math 6 Grade Unit 7 Study Guide-Rational Explorations: Numbers and Their Opposites. Show All Work On A Separate Sheet of Paperapi-366304862No ratings yet
- MTH 101 CH 3Document56 pagesMTH 101 CH 3Suli FlamencoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Matrix Algebra I: 1 Definition of Matrices and VectorsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Matrix Algebra I: 1 Definition of Matrices and VectorsholiNo ratings yet
- Algebra Unidad 2Document84 pagesAlgebra Unidad 2Paula MorenoNo ratings yet
- P5 Straight Line GraphsDocument24 pagesP5 Straight Line GraphsRNGtypicalNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Level - 1 (Practice Questions Based On Fundamentals)Document17 pagesExercises: Level - 1 (Practice Questions Based On Fundamentals)Devesh TripathiNo ratings yet
- 3 Dimension GB Sir Module PDFDocument17 pages3 Dimension GB Sir Module PDFPriyanshu GNo ratings yet
- MYP Unit Planner - MathDocument5 pagesMYP Unit Planner - MathMarija CvetkovicNo ratings yet
- Graphing Linear Functions - With A TableDocument2 pagesGraphing Linear Functions - With A TableMarija CvetkovicNo ratings yet
- Head & Heart Together: Essays On The Buddhist PathDocument81 pagesHead & Heart Together: Essays On The Buddhist PathMarija CvetkovicNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 Ch.3 TESTDocument3 pagesAlgebra 1 Ch.3 TESTMarija CvetkovicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Test (Newton's Laws A)Document3 pagesChapter 2 Test (Newton's Laws A)Marija CvetkovicNo ratings yet
- Lectures On Groups of Transformations: J. L. KoszulDocument85 pagesLectures On Groups of Transformations: J. L. KoszulMiguel Sánchez ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document8 pagesAssignment 5Gloria HuNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Exam Math 8Document4 pages2nd Quarter Exam Math 8Salgie SernalNo ratings yet
- Fairing Methods of Planar and Space Curves Under Design Constraints - Applications in Computer-Aided Ship DesignDocument124 pagesFairing Methods of Planar and Space Curves Under Design Constraints - Applications in Computer-Aided Ship DesignKostis PigounakisNo ratings yet
- 2006 Usamo SDocument10 pages2006 Usamo SZahra ZahraNo ratings yet
- MSM 111 - Quadratic Functions - T3Document2 pagesMSM 111 - Quadratic Functions - T3Chileshe SimonNo ratings yet
- Sec D CH 12 Regression Part 2Document66 pagesSec D CH 12 Regression Part 2Ranga SriNo ratings yet
- Worksheet ConvergenceDocument3 pagesWorksheet ConvergenceValeria Vargas LaverdeNo ratings yet
- IT1T1Document2 pagesIT1T1Vyshnavi ThottempudiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics SQP-01 2024Document8 pagesMathematics SQP-01 2024vishalnirmala.vkvNo ratings yet
- Homework - QuestionsDocument14 pagesHomework - Questionsaurora borealissNo ratings yet
- Problem B: Standard:Hs-Ps2-1 Determining Net Force ProblemDocument2 pagesProblem B: Standard:Hs-Ps2-1 Determining Net Force ProblemMona Mohamed SafwatNo ratings yet
- C12 Oct 2017Document25 pagesC12 Oct 2017Michael Farajian100% (1)
- Eee407 Fa09 DSPDocument2 pagesEee407 Fa09 DSPDavidsiño Andresiño VarelaNo ratings yet
- UMLDocument24 pagesUMLbirrajNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument283 pagesNotescristhian aaron vigo villarNo ratings yet
- Appendix A. Linear AlgebraDocument15 pagesAppendix A. Linear AlgebraFrederico AntoniazziNo ratings yet
- 2008 Seemous Problems SolutionsDocument4 pages2008 Seemous Problems SolutionsHipstersdssadadNo ratings yet
- Computational Physics Exam 02: 1. Types of EquationsDocument4 pagesComputational Physics Exam 02: 1. Types of EquationsBradley AndrewNo ratings yet
- IE 325 - Recitation 3 Partial SolutionsDocument4 pagesIE 325 - Recitation 3 Partial SolutionsAE ENo ratings yet
- 7 LP Sensitivity AnalysisDocument9 pages7 LP Sensitivity AnalysiszuluagagaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 MMW Arithmetic SeriesDocument20 pagesTopic 2 MMW Arithmetic SeriesMarlyn CuregNo ratings yet
- ENGR 516 Assignment 1 DuongLeDocument20 pagesENGR 516 Assignment 1 DuongLeRock RáchNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument2 pagesThesisammarah sanwalNo ratings yet
- Deriving Simpsons Rule Using Newton InterpolationDocument4 pagesDeriving Simpsons Rule Using Newton InterpolationVinjkNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Matrices by P. Lancaster and M. TismenetskyDocument292 pagesThe Theory of Matrices by P. Lancaster and M. TismenetskyzakwanaslamNo ratings yet
- Roark's Formula 0 33Document1 pageRoark's Formula 0 33Jay CeeNo ratings yet
- Maths ContinuityDocument38 pagesMaths ContinuityHimanjal NathNo ratings yet
- 2022 MATENA1 Semester Test 1 MemoDocument11 pages2022 MATENA1 Semester Test 1 MemoEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (T) : SMJK Hua Lian Taiping, PerakDocument5 pagesMathematics (T) : SMJK Hua Lian Taiping, PerakMelody OngNo ratings yet