100% found this document useful (1 vote)
558 views2 pagesBattery Charger
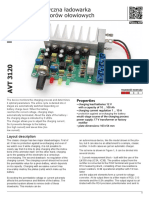
This document describes the construction of a battery charger circuit using an SCR. It lists the required components including a step-down transformer, SCR, diodes, resistor, and potentiometer. The circuit diagram and theory of operation are provided. When powered, the transformer outputs a reduced AC voltage that is rectified and regulated using diodes and a zener diode. The SCR allows current to flow and charge the battery when its gate voltage exceeds the anode voltage. The procedure constructs the circuit and tests the battery voltage before and after a 5 minute charge.
Uploaded by
shameem v.pCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
558 views2 pagesBattery Charger
This document describes the construction of a battery charger circuit using an SCR. It lists the required components including a step-down transformer, SCR, diodes, resistor, and potentiometer. The circuit diagram and theory of operation are provided. When powered, the transformer outputs a reduced AC voltage that is rectified and regulated using diodes and a zener diode. The SCR allows current to flow and charge the battery when its gate voltage exceeds the anode voltage. The procedure constructs the circuit and tests the battery voltage before and after a 5 minute charge.
Uploaded by
shameem v.pCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd