Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transpiration
Uploaded by
Alicia August0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageTranspiration is the process by which plants release water from their leaves into the atmosphere. Water is absorbed by the plant's roots and transported through the xylem tissue to the leaves, where it evaporates through openings called stomata. The rate of transpiration is influenced by temperature, humidity, wind, soil moisture, and the type of plant. Warmer temperatures, lower humidity, more wind, and moister soil cause higher transpiration rates, while adaptations like those in cacti result in less water loss through transpiration.
Original Description:
transpiration
Original Title
transpiration
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTranspiration is the process by which plants release water from their leaves into the atmosphere. Water is absorbed by the plant's roots and transported through the xylem tissue to the leaves, where it evaporates through openings called stomata. The rate of transpiration is influenced by temperature, humidity, wind, soil moisture, and the type of plant. Warmer temperatures, lower humidity, more wind, and moister soil cause higher transpiration rates, while adaptations like those in cacti result in less water loss through transpiration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageTranspiration
Uploaded by
Alicia AugustTranspiration is the process by which plants release water from their leaves into the atmosphere. Water is absorbed by the plant's roots and transported through the xylem tissue to the leaves, where it evaporates through openings called stomata. The rate of transpiration is influenced by temperature, humidity, wind, soil moisture, and the type of plant. Warmer temperatures, lower humidity, more wind, and moister soil cause higher transpiration rates, while adaptations like those in cacti result in less water loss through transpiration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
When water is evaporated from plants, this process is called transpiration.
The surplus water
absorbed by the roots of the plant is released mainly from the leaves into the atmosphere by
this process. The root of the plant allows water to be absorbed into the plant, which is then
transported through the xylem tissue, in the stem, to the leaves due to capillary forces and the
action of cohesion of water molecules. Transpiration occurs when the moisture content of the
atmosphere is lower than that of the moisture inside the leaf. The stomates of the leaves open
and allows the water to be evaporated owing to diffusion. Temperature is one factor that
influence transpiration to occur. As the temperature rises, water transpires due to the stomata
of leaves opening. Warmer conditions cause plants to transpire more. Other crucial elements
include the soil's and the air's amounts of moisture. The rate of transpiration decreases as the
relative humidity of the air rises because there is more moisture in the atmosphere. However,
because they are consuming more water, plants will transpire more if the soil is moister.
Wind reduces the relative humidity in the area around a plant causing an increase rate of
transpiration. Naturally, different plants transpire more than others. Cacti and other arid-
climate plants have evolved to need less water, so they transpire less compared to other
plants. Evapotranspiration is the collective name for the evaporation from Earth's waterways
and from plants through transpiration (Editors, B. D. 2017, January 31).
Editors, B. D. (2017, January 31). Transpiration. Biology Dictionary.
https://biologydictionary.net/transpiration/
You might also like
- Hydroponic Gardening: A Beginner Guide to Learn How to Design and Build Your Own Sustainable Hydroponics System, for Growing Plants and Vegetables at HomeFrom EverandHydroponic Gardening: A Beginner Guide to Learn How to Design and Build Your Own Sustainable Hydroponics System, for Growing Plants and Vegetables at HomeNo ratings yet
- Life ScienceDocument5 pagesLife Sciencegurpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN PRAKTIKUM PLANT ANATOMY DAN TRANSPIRASIDocument13 pagesLAPORAN PRAKTIKUM PLANT ANATOMY DAN TRANSPIRASIRiskySyahrediNo ratings yet
- Trans Piras IDocument14 pagesTrans Piras ILilis SeptianiNo ratings yet
- Transpiration - WikipediaDocument27 pagesTranspiration - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- EvapotranspirationDocument10 pagesEvapotranspirationGio TtaNo ratings yet
- Transpiration and Xerophytes by Fumi AwonugaDocument7 pagesTranspiration and Xerophytes by Fumi AwonugatheresafunmiNo ratings yet
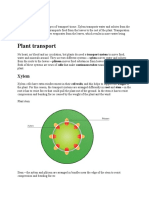
- Plant TransportDocument5 pagesPlant TransportMemona KhalidNo ratings yet
- Biology Research 3Document1 pageBiology Research 3alaaisam25No ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document3 pagesChapter 11Mahir ShahriyarNo ratings yet
- 8.2 Transport of WaterDocument11 pages8.2 Transport of Waterzain ul AbideenNo ratings yet
- InfiltrationDocument46 pagesInfiltrationglaydelleNo ratings yet
- Learning Journal Unit 6 5Document2 pagesLearning Journal Unit 6 5Thobile RevivalNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument7 pagesTransport in PlantsMasthankhan PatanNo ratings yet
- How Light Affects Plant TranspirationDocument7 pagesHow Light Affects Plant TranspirationG100% (1)
- Plants Move Materials Using Xylem and PhloemDocument7 pagesPlants Move Materials Using Xylem and PhloemAshleigh JarrettNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument4 pagesTransport in PlantsrickyNo ratings yet
- The Transport of Water in Plants Involve 3 Interconnected ProcessesDocument3 pagesThe Transport of Water in Plants Involve 3 Interconnected ProcessesJayashree Krishnakumar PillaiNo ratings yet
- TranspirationDocument3 pagesTranspirationKENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- Plant Transport - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Document6 pagesPlant Transport - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Zhi En LeeNo ratings yet
- Transport System in PlantsDocument19 pagesTransport System in PlantsWan Arief SyahmiNo ratings yet
- Water Regulation in Plant and Stomatal Conductance: Table of ContentDocument5 pagesWater Regulation in Plant and Stomatal Conductance: Table of ContentAmna NasirNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Plant TransportDocument28 pagesPart 1 Plant Transportrawan SaketNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants: The Vascular BundleDocument3 pagesTransport in Plants: The Vascular BundleAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- النتحDocument4 pagesالنتحفاطمة الخطيرةNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants (2) .Document43 pagesTransport in Plants (2) .verifyqbytezNo ratings yet
- Effect of Environmental Conditions On The Rate of Transpiration Cbsebiology4uDocument22 pagesEffect of Environmental Conditions On The Rate of Transpiration Cbsebiology4ukumaran30No ratings yet
- TRANSPORT IN PLANTSDocument4 pagesTRANSPORT IN PLANTSdarielleollivierreNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Bio 611Document14 pagesLab 3 Bio 611Zureen SofeaNo ratings yet
- Transpiration: The Process of Water Loss in PlantsDocument10 pagesTranspiration: The Process of Water Loss in PlantsMelanie CabforoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Lesson 2 Transpiration and TranslocationDocument20 pagesChapter 8 Lesson 2 Transpiration and TranslocationAli waleed AbdalmoatyNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Term 2 Support and Transport Systems in Plants 5Document22 pagesGrade 10 Term 2 Support and Transport Systems in Plants 5Abdulah.AbisolaNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument11 pagesTransport in PlantsZahra nooraniNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument3 pagesTransport in PlantsKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport System: How Water and Nutrients MoveDocument39 pagesPlant Transport System: How Water and Nutrients MoveChe Sal100% (1)
- Identify Root Hair Cells, As Seen Under The Light Microscope, and Describe Their FunctionsDocument16 pagesIdentify Root Hair Cells, As Seen Under The Light Microscope, and Describe Their FunctionsMandla RebirthNo ratings yet
- Project Report On TranspirationDocument5 pagesProject Report On TranspirationSnehal JoshiNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport Structures and ProcessesDocument15 pagesPlant Transport Structures and ProcessesAbdelrahman GhanimNo ratings yet
- Notes On Basics of Hydrology and Meteorology-1-1Document22 pagesNotes On Basics of Hydrology and Meteorology-1-1kapinga0609No ratings yet
- Note-Chapter 8 Plant TransportDocument4 pagesNote-Chapter 8 Plant Transportzhenrong zhaoNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Transport System in Plants: TranspirationDocument27 pages2.3 Transport System in Plants: TranspirationSandera Abdul ManafNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3Document8 pagesExercise 3Melvy June Balasa100% (1)
- Transpiration For Amateur GardernersDocument3 pagesTranspiration For Amateur Gardernerssurya sureshNo ratings yet
- Trans Piras IDocument14 pagesTrans Piras INurfatimah AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and plant nutritionDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis and plant nutritionBilly FoxNo ratings yet
- Transpiration E - BookDocument18 pagesTranspiration E - BookAkku Tyagi50% (2)
- Transpiration Process ExplainedDocument13 pagesTranspiration Process ExplainedYasmine Alexandra ChuaNo ratings yet
- Air Spaces) Before Diffusing Out of TheDocument12 pagesAir Spaces) Before Diffusing Out of Thetahirah_shukor100% (1)
- Biology Form 5 2.3Document14 pagesBiology Form 5 2.3Ting Hong Lin AnsonNo ratings yet
- Transportation of Food and Minerals in PlantsDocument3 pagesTransportation of Food and Minerals in PlantsRonnith NandyNo ratings yet
- Transport in plant SDADocument5 pagesTransport in plant SDAkmakabe78No ratings yet
- TRANSPIRATIONDocument20 pagesTRANSPIRATIONMelanie LaureanoNo ratings yet
- Plant Water Relation: Grade 12Document16 pagesPlant Water Relation: Grade 12jovellamNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument5 pagesTransport in PlantsAlex LochaiNo ratings yet
- TranspirationDocument22 pagesTranspirationyr44grf94kNo ratings yet
- Surface Area: EVAPOTRANSPIRATION Is The Sum of Evaporation andDocument5 pagesSurface Area: EVAPOTRANSPIRATION Is The Sum of Evaporation andMicah Juguan SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Biology Project on Transpiration in PlantsDocument29 pagesBiology Project on Transpiration in PlantsDhanush PSNo ratings yet
- The First Plants Grow on Land: The Golden Serie of History: From the First Life Forms to the Latest Humanoid Robot, #3From EverandThe First Plants Grow on Land: The Golden Serie of History: From the First Life Forms to the Latest Humanoid Robot, #3No ratings yet
- Hydroponics for Advanced: The Ultimate Hydroponic and Aquaponic Gardening GuideFrom EverandHydroponics for Advanced: The Ultimate Hydroponic and Aquaponic Gardening GuideNo ratings yet
- Disease Ecology IntroDocument1 pageDisease Ecology IntroAlicia AugustNo ratings yet
- Body For 3114 IncompleteDocument4 pagesBody For 3114 IncompleteAlicia AugustNo ratings yet
- Sources of LipidsDocument1 pageSources of LipidsAlicia AugustNo ratings yet
- Bio2205 Lecture NotesDocument1 pageBio2205 Lecture NotesAlicia AugustNo ratings yet
- 2 Functions of ZoosDocument3 pages2 Functions of ZoosAlicia AugustNo ratings yet
- Animal EthicsDocument11 pagesAnimal EthicsAlicia AugustNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Disturbance 2Document14 pagesEcosystem Disturbance 2Alicia AugustNo ratings yet
- Animal ConservationDocument7 pagesAnimal ConservationAlicia AugustNo ratings yet
- A.SIMON - BIO 3112 LAB 2 - Soil Structure and InteractionsDocument6 pagesA.SIMON - BIO 3112 LAB 2 - Soil Structure and InteractionsAlicia AugustNo ratings yet
- PrimatesDocument23 pagesPrimatesAlicia AugustNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Soil-Plant InteractionsDocument2 pagesLecture 6 Soil-Plant InteractionsAlicia AugustNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Introduction To SoilsDocument2 pagesLecture 6 - Introduction To SoilsAlicia AugustNo ratings yet