Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evapotranspiration
Uploaded by
Gio Tta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
110 views10 pagesOriginal Title
Evapotranspiration (1).pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
110 views10 pagesEvapotranspiration
Uploaded by
Gio TtaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
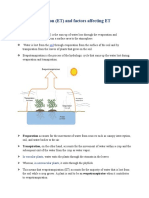
Evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration is the process of evaporating water
from leaves through plant transpiration during
photosynthesis. It varies because of a multitude of
factors like wind, temperature, humidity, and water
availability.
Why do I care?
Evapotranspiration is a main component of the water
cycle and is important in crop maintenance.
Evapotranspiration is an important process in the
water cycle because it is responsible for 15% of the
atmospheres water vapor. Without that input of water
vapor, clouds couldnt form and precipitation would
never fall. Evapotranspiration is the combined name
for the processes of evaporation and transpiration.
When water vapor is released into the atmosphere
both processes are involved, so they have been
combined into one word to cover all bases.
The evaporation in evapotranspiration refers to water
evaporated from over land. This includes evaporation
from soil, wetlands, and standing water from places
like roofs and puddles. It can also refer to direct
evaporation of liquid water from the leaf surface of the
plant.
Transpiration happens when plants release water
vapor from tiny holes, called stomata, in their leaves.
This is caused in part by the chemical and biological
changes that occur as the plant undergoes
photosynthesis and converts carbon dioxide into
oxygen. Transpiration performs the same function as
human sweating because plants do it to cool down
their leaves. Figure A shows the stomata on the
underside of the leaf releasing water vapor (blue
arrow) because of the warmth from the sun.
There are a whole host of factors that affect
evapotranspiration:
Temperature As temperature increases, the rate of
evapotranspiration increases. Evaporation increases
because there is a higher amount of energy available to
convert the liquid water to water vapor. Transpiration
increases because at warmer temperatures plants open
up their stomata and release more water vapor.
There are a whole host of factors that affect
evapotranspiration:
Humidity If the air around the plant is too humid,
the transpiration and evaporation rates drop. Its the
same reason sweat does not evaporate from our skin
when its too humid.
Wind speed If the air is moving, the rate of
evaporation will increase. The wind will also clear the
air of any humidity produced by the plants
transpiration, so the plant will increase its rate of
transpiration.
There are a whole host of factors that affect
evapotranspiration:
Water availability If the soil is dry and there is no
standing water there will be no evaporation. If plants
cant get enough water they will conserve it instead of
transpiring by closing their stoma.
Soil type Soil type determines how much water soil
can hold and how easy it is for the water to be drawn
out of it, either by a plant or by evaporation. For areas
where the ground is covered by vegetation, the rate of
transpiration is considerably higher than the rate of
evaporation from the soil.
There are a whole host of factors that affect
evapotranspiration:
Plant type Some plants, like cacti and other
succulents, naturally hold onto their water and dont
transpire as much. Trees and crops are on the other
end of the spectrum and can release copious amounts
of water vapor in a day. For example, an acre of corn
can release 4,000 gallons of water vapor a day and a
single large oak tree can transpire 40,000 gallons of
water vapor in a year.
You might also like
- InfiltrationDocument46 pagesInfiltrationglaydelleNo ratings yet
- What is evapotranspirationDocument14 pagesWhat is evapotranspirationerdyNo ratings yet
- Notes On Basics of Hydrology and Meteorology-1-1Document22 pagesNotes On Basics of Hydrology and Meteorology-1-1kapinga0609No ratings yet
- Life ScienceDocument5 pagesLife Sciencegurpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Notes On Basics of Hydrology and Meteorology-1Document28 pagesNotes On Basics of Hydrology and Meteorology-1kapinga0609No ratings yet
- Water Retention Curve Is The Relationship Between The Moisture CharacteristicDocument31 pagesWater Retention Curve Is The Relationship Between The Moisture CharacteristicasprillaNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN PRAKTIKUM PLANT ANATOMY DAN TRANSPIRASIDocument13 pagesLAPORAN PRAKTIKUM PLANT ANATOMY DAN TRANSPIRASIRiskySyahrediNo ratings yet
- Transpiration, Evapotranspiration and SublimationDocument18 pagesTranspiration, Evapotranspiration and SublimationJoseph Noel Coscos100% (2)
- Transpiration - WikipediaDocument27 pagesTranspiration - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Transpiration Evapotranspira TionDocument16 pagesTranspiration Evapotranspira TionLi LiNo ratings yet
- Eva Po TranspirationDocument3 pagesEva Po TranspirationFRANCIS SAMUELNo ratings yet
- Transpiration and Xerophytes by Fumi AwonugaDocument7 pagesTranspiration and Xerophytes by Fumi AwonugatheresafunmiNo ratings yet
- Manage Soil Moisture with Evapotranspiration CalculationsDocument53 pagesManage Soil Moisture with Evapotranspiration CalculationsVatsal AnandNo ratings yet
- Evapotranspiration (ET) and Factors Affecting ET: Transpiration SoilDocument4 pagesEvapotranspiration (ET) and Factors Affecting ET: Transpiration SoilDame NegaroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document7 pagesChapter 5Masithembe Tera DumezweniNo ratings yet
- TranspirationDocument1 pageTranspirationAlicia AugustNo ratings yet
- Biology Project on Transpiration in PlantsDocument29 pagesBiology Project on Transpiration in PlantsDhanush PSNo ratings yet
- Water Regulation in Plant and Stomatal Conductance: Table of ContentDocument5 pagesWater Regulation in Plant and Stomatal Conductance: Table of ContentAmna NasirNo ratings yet
- Agri Environmental InfluencesDocument7 pagesAgri Environmental Influencessmartkid167No ratings yet
- Transpiration E - BookDocument18 pagesTranspiration E - BookAkku Tyagi50% (2)
- What Is Evaporation and How It Occurs?: Bautista, Raymart A. Bsce-3ADocument10 pagesWhat Is Evaporation and How It Occurs?: Bautista, Raymart A. Bsce-3ARaymart BautistaNo ratings yet
- EvapotranspirationDocument49 pagesEvapotranspirationFarid MatovuNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Transport System in Plants: TranspirationDocument27 pages2.3 Transport System in Plants: TranspirationSandera Abdul ManafNo ratings yet
- Eva Po TranspirationDocument16 pagesEva Po TranspirationJanineRianneBagsicNo ratings yet
- Transpiration: The Process of Water Loss in PlantsDocument10 pagesTranspiration: The Process of Water Loss in PlantsMelanie CabforoNo ratings yet
- Trans Piras IDocument14 pagesTrans Piras ILilis SeptianiNo ratings yet
- How Can Cities and Counties Get More Water QuicklyDocument3 pagesHow Can Cities and Counties Get More Water QuicklyRalph Charles Whitley, Sr.No ratings yet
- Hydrology-Report g4Document6 pagesHydrology-Report g4bernie romeroNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument11 pagesTransport in PlantsZahra nooraniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Hydrologic CycleDocument13 pagesChapter 1: The Hydrologic CycledadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Hydrologic CycleDocument13 pagesChapter 1: The Hydrologic CycledadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Hydrology and Hydrologic CycleDocument13 pagesChapter 1: Hydrology and Hydrologic CycledadaNo ratings yet
- CRP 101 Lecture No. 6Document16 pagesCRP 101 Lecture No. 6AnandKuttiyanNo ratings yet
- Evapotranspiration: Evapotranspiration (ET) Is The Sum ofDocument33 pagesEvapotranspiration: Evapotranspiration (ET) Is The Sum ofBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Soil Plant Water Relationships and Transport ProcessesDocument27 pagesSoil Plant Water Relationships and Transport Processeskharladrian100% (1)
- Define Evapotranspiration ProcessDocument1 pageDefine Evapotranspiration ProcessEkala XuhalxNo ratings yet
- 5175-3-1Cr Aid: 222459 - 5/02/2020Document2 pages5175-3-1Cr Aid: 222459 - 5/02/2020ShekharNo ratings yet
- The Hydrologic CycleDocument2 pagesThe Hydrologic CycleKearly Joy VictorioNo ratings yet
- TranspirationDocument3 pagesTranspirationKENNETH POLONo ratings yet
- Plant Water Relation: Grade 12Document16 pagesPlant Water Relation: Grade 12jovellamNo ratings yet
- Evaporation Causes The Effective Way To Enroll The On AverageDocument9 pagesEvaporation Causes The Effective Way To Enroll The On Averageashok2009cseNo ratings yet
- Effect of Environmental Conditions On The Rate of Transpiration Cbsebiology4uDocument22 pagesEffect of Environmental Conditions On The Rate of Transpiration Cbsebiology4ukumaran30No ratings yet
- 8.2 Transport of WaterDocument11 pages8.2 Transport of Waterzain ul AbideenNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Bio 611Document14 pagesLab 3 Bio 611Zureen SofeaNo ratings yet
- How Light Affects Plant TranspirationDocument7 pagesHow Light Affects Plant TranspirationG100% (1)
- Chapter 11Document3 pagesChapter 11Mahir ShahriyarNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument7 pagesTransport in PlantsMasthankhan PatanNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport System: How Water and Nutrients MoveDocument39 pagesPlant Transport System: How Water and Nutrients MoveChe Sal100% (1)
- Project Report On TranspirationDocument5 pagesProject Report On TranspirationSnehal JoshiNo ratings yet
- Hydrological CycleDocument17 pagesHydrological CycleSakshi TalmaleNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic-reportDocument3 pagesHydrologic-reportlanie mondiaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Factors and Plant GrowthDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Factors and Plant GrowthAlana JamesNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument7 pagesWaterCubbie JayNo ratings yet
- AGATON CEP324 Reaction Paper 2Document1 pageAGATON CEP324 Reaction Paper 2Marco AgatobNo ratings yet
- TranspirationDocument4 pagesTranspirationSaswatNo ratings yet
- Vegetation: Effects On Weather and ClimateDocument20 pagesVegetation: Effects On Weather and ClimateodbayNo ratings yet
- Plant ExcretionDocument25 pagesPlant ExcretionPatrick Tew100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Lesson 2 Transpiration and TranslocationDocument20 pagesChapter 8 Lesson 2 Transpiration and TranslocationAli waleed AbdalmoatyNo ratings yet
- Evaporation, Transpiration and Precipitation | Water Cycle for Kids | Children's Water BooksFrom EverandEvaporation, Transpiration and Precipitation | Water Cycle for Kids | Children's Water BooksNo ratings yet
- The First Plants Grow on Land: The Golden Serie of History: From the First Life Forms to the Latest Humanoid Robot, #3From EverandThe First Plants Grow on Land: The Golden Serie of History: From the First Life Forms to the Latest Humanoid Robot, #3No ratings yet
- P5 03 Barcenas Rainfall Corrections - pdf-729200407Document12 pagesP5 03 Barcenas Rainfall Corrections - pdf-729200407Gio TtaNo ratings yet
- IndonesiaDocument9 pagesIndonesiaGio TtaNo ratings yet
- Types and Characteristics of Precipitation - pdf-395658211 PDFDocument8 pagesTypes and Characteristics of Precipitation - pdf-395658211 PDFGio TtaNo ratings yet
- Shore Protection ManualDocument652 pagesShore Protection Manualrruddick100% (3)
- Design Exam (1) SHFHSDHSDHDocument19 pagesDesign Exam (1) SHFHSDHSDHEmmanuel CristobalNo ratings yet
- Factor MethodDocument5 pagesFactor MethodGio TtaNo ratings yet
- Makingthemostofcommunityresourcesandfield 151003204512 Lva1 App6892Document46 pagesMakingthemostofcommunityresourcesandfield 151003204512 Lva1 App6892Gio TtaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For Civil Service ReviewerDocument3 pagesAnswer Key For Civil Service Reviewervincelord100% (1)
- Test Bank For Pediatric Nursing The Critical Components of Nursing Care 2nd Edition Kathryn Rudd Diane KociskoDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Pediatric Nursing The Critical Components of Nursing Care 2nd Edition Kathryn Rudd Diane Kociskolaurencelittlehdcj100% (26)
- Cellular Tower: Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaDocument17 pagesCellular Tower: Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaMonster PockyNo ratings yet
- SAP MM ReportsDocument59 pagesSAP MM Reportssaprajpal95% (21)
- Hierarchical Afaan Oromoo News Text ClassificationDocument11 pagesHierarchical Afaan Oromoo News Text ClassificationendaleNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam Machining (LBM)Document10 pagesLaser Beam Machining (LBM)RAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet
- Ms. Rochelle P. Sulitas – Grade 7 SCIENCE Earth and Space Learning PlanDocument4 pagesMs. Rochelle P. Sulitas – Grade 7 SCIENCE Earth and Space Learning PlanEmelynNo ratings yet
- Aimt ProspectusDocument40 pagesAimt ProspectusdustydiamondNo ratings yet
- Cultural DiffusionDocument2 pagesCultural DiffusionNicole Aguarin SwinNo ratings yet
- Gas Mixtures: Seventh Edition in SI UnitsDocument13 pagesGas Mixtures: Seventh Edition in SI Unitshamed farzanehNo ratings yet
- Grammar Pages 109-112 2 PDFDocument4 pagesGrammar Pages 109-112 2 PDFSteve SernaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Methods in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesTeaching Methods in The PhilippinesTonee Marie Gabriel60% (5)
- Too Early! by Anton Pavlovich ChekhovDocument4 pagesToo Early! by Anton Pavlovich Chekhovapi-19787590No ratings yet
- Drainage Manual: State of Florida Department of TransportationDocument78 pagesDrainage Manual: State of Florida Department of TransportationghoyarbideNo ratings yet
- MPU 2232 Chapter 5-Marketing PlanDocument27 pagesMPU 2232 Chapter 5-Marketing Plandina azmanNo ratings yet
- LTC3108 EnergyHarvestDocument3 pagesLTC3108 EnergyHarvestliawyssbdNo ratings yet
- Handwashing and Infection ControlDocument23 pagesHandwashing and Infection ControlLiane BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Letter of Invitation ESVC 3000 2024 1Document2 pagesLetter of Invitation ESVC 3000 2024 1pradeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Explicit Instruction: A Teaching Strategy in Reading, Writing, and Mathematics For Students With Learning DisabilitiesDocument3 pagesExplicit Instruction: A Teaching Strategy in Reading, Writing, and Mathematics For Students With Learning DisabilitiesKatherineNo ratings yet
- Diesel fuel system for Caterpillar 3208 engineDocument36 pagesDiesel fuel system for Caterpillar 3208 engineLynda CarrollNo ratings yet
- Sample Id: Sample Id: 6284347 Icmr Specimen Referral Form Icmr Specimen Referral Form For For Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2) Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2)Document2 pagesSample Id: Sample Id: 6284347 Icmr Specimen Referral Form Icmr Specimen Referral Form For For Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2) Covid-19 (Sars-Cov2)Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- RCD-GillesaniaDocument468 pagesRCD-GillesaniaJomarie Alcano100% (2)
- FLANSI CAP SONDA CatalogsDocument30 pagesFLANSI CAP SONDA CatalogsTeodor Ioan Ghinet Ghinet DorinaNo ratings yet
- CFPA E Guideline No 2 2013 FDocument39 pagesCFPA E Guideline No 2 2013 Fmexo62No ratings yet
- 1967 2013 PDFDocument70 pages1967 2013 PDFAlberto Dorado Martín100% (1)
- GRL+Prosp - EDocument2 pagesGRL+Prosp - Ethoma111sNo ratings yet
- Elliott Wave Watching Part 2 Rev 1-2600717Document9 pagesElliott Wave Watching Part 2 Rev 1-2600717GateshNdegwahNo ratings yet
- Year 5 Reasoning Test Set 3 Paper A: Q Marks Answer Notes 1a 1b 7 6 4Document2 pagesYear 5 Reasoning Test Set 3 Paper A: Q Marks Answer Notes 1a 1b 7 6 4Amina Zeghar BNo ratings yet
- Gorsey Bank Primary School: Mission Statement Mission StatementDocument17 pagesGorsey Bank Primary School: Mission Statement Mission StatementCreative BlogsNo ratings yet
- Product Catalog Encoders en IM0038143Document788 pagesProduct Catalog Encoders en IM0038143Eric GarciaNo ratings yet