Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PHYSICS
Uploaded by
leona jane tamor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 page1) Physics deals with the interaction of matter and energy. It studies motion, especially rectilinear or straight-line motion.
2) Kinematics is the branch of physics that describes and quantifies types of motion such as distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration.
3) Important concepts in kinematics include scalar and vector quantities, where vectors have both magnitude and direction, and standard units are used to measure and compare physical quantities.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Physics deals with the interaction of matter and energy. It studies motion, especially rectilinear or straight-line motion.
2) Kinematics is the branch of physics that describes and quantifies types of motion such as distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration.
3) Important concepts in kinematics include scalar and vector quantities, where vectors have both magnitude and direction, and standard units are used to measure and compare physical quantities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pagePHYSICS
Uploaded by
leona jane tamor1) Physics deals with the interaction of matter and energy. It studies motion, especially rectilinear or straight-line motion.
2) Kinematics is the branch of physics that describes and quantifies types of motion such as distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration.
3) Important concepts in kinematics include scalar and vector quantities, where vectors have both magnitude and direction, and standard units are used to measure and compare physical quantities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
MEASUREMENTS - acts of detemining
PHYSICS - deals w/ the the target’s size, length, weight, RECTILINEAR
interaction of matter and energy.
- “physics” comes from ancient greek ;
capacity or other aspect.
MOTION.
meaning “knowledge of nature” Kilo - thousands
- derived from the greek word Hector - hundred Kinematics from greek word “kinema”
“physica” meaning “nature” Deca - ten which means movement
Deci - tenth
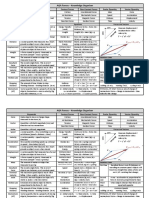
7 FUNDAMENTAL UNITS Centi - hundredth Rectilinear motion (linear motion) -
Length = meter (m) Milli - thousandth specific form of motion ; motion that
Time = seconds (s) occurs in single direction or axis.
Amount of Subtance = mole (mole) - it can also called straight-line motion.
Electric current = ampere (A) VECTOR - quantity or
Temperature = kelvin (A) phenomenom that has two Distance - total distance that covered
Luminous Intensity = candela (cd) independent properties ; magnitude by the moving object or particle.
Mass = Kilogram (kg) and direction. Displacement - Net distance from the
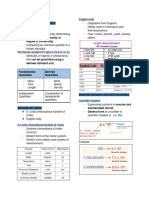
MAGNITUDE - is the length of vector, starting to the end point of motion.
fixed quantity, which physical quantity denoted as “||a||”
is measured called unit. > Starts from orign O reaches point Z
Distance = OZ
Displacement = OZ
TWO MAJOR SYSTEM OF UNITS
> Now he reach the point Y
SI UNITS - known as metric system
Distance = OZ + OY
English Units - known as customary or
Displacement = -OY
imperial system.
( displacement is negative since it is
measured to the left of origin )
DIRECTION - path that something takes
Speed (v) - magnitude of velocity, no
or path that must be taken to reach a
direction and always non-negative.
specific place.
Velocity - rate of change in
displacement, has a direction and this
Scalar Quantities have a magnitude
direction is represented by a negative
but no direction.
or positive sign.
- distance, speed, mass, energy,
density, power, length, areas, volume,
Mathematical Term (defined as
time, temperature, snd work.
STANDARD UNITS - units we usually follows) :
Vector Quantities have magnitude and
use to measure the length, weight, or Speed = Distance Travelled / Time
direction.
capacity of the object. Taken
- displacement, velocity, weight,
SI UNITS are usually used for Velocity = Final Position - Initial
acceleration, force, impulse, pressure,
measuring quantities that accepted Position / Time Taken
momentum, gravity and drag.
worldwide.
COMPONENTS OF VECTOR. Average Speed - denoted by v¯ can
CONVERT BETWEEN MEASUREMENTS Vector quantity - depends on the be given by distance (Delta) covered in
IN PHYSICS direction a given time interval (Δt)
- comparing two vector characteristics Formula : v¯= Δd
1 m = 100 cm = 1,000 mm (millimeters) you have to compare both magnitude Δt
1 km (kilometer) = 1,000 m and direction.
1 kg (kilo gram) = 1,000 g (grams) Scalar quantity - does not depend on Average Velocity - given by the
1 J (joule) = 10(7) ergs. the direction. displacement s2-s1 divided by the total
1 P (pascal) = 10 Ba interval of time (t2-t1) it takes cover.
1 A (amp) = 0.1 Bi UNITS OF VECTOR. Formula : v¯= Xf-Xi
- vector that has a magnitude equal to Tf-Ti
Physical Quantites - characteristics or 1, also denoted by the “cap” symbol ;
property of an object that can length of unit vector is 1 Acceleration - the rate of change of
measured or calculated from other velocity, it’s denoted by a.
measurements Acceleration Formula - a = Δv/Δt.
Units are standard for expressing and KINEMATICS :
comparing the measurements of
physical quantities.
MOTION ALONG UNITS OF KINEMATICS
Velocity - m/s
STRAIGHT LINE / Displacement - meter (m)
Acceleration - m/s
You might also like
- SI Units and Unit ConversionsDocument42 pagesSI Units and Unit ConversionsAnthony Quan0% (1)
- CAHSEE Geometry and Measurement Teacher Text - UC Davis - August 2008Document119 pagesCAHSEE Geometry and Measurement Teacher Text - UC Davis - August 2008Dennis Ashendorf100% (1)
- Physics Reviewer PDFDocument6 pagesPhysics Reviewer PDFJam Uly Gasty100% (2)
- Estimation - Costing (Valuation) - BTech Civil Engineering Notes - Ebook PDF DownloadDocument33 pagesEstimation - Costing (Valuation) - BTech Civil Engineering Notes - Ebook PDF DownloadSmitesh AhireNo ratings yet
- CE Board April 2023 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 5Document4 pagesCE Board April 2023 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 5Daryl ArizoNo ratings yet
- The Free High School Science Texts - A Textbook For Highschool Students Studying Physics (Team Nanban) (TPB) PDFDocument397 pagesThe Free High School Science Texts - A Textbook For Highschool Students Studying Physics (Team Nanban) (TPB) PDFAnonymous hYHGFMBJmNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument38 pagesPhysics NotesAlexNo ratings yet
- University Physics I - Mechanics, Sound, Oscillations, WavesDocument936 pagesUniversity Physics I - Mechanics, Sound, Oscillations, WavesFeiFei Sun100% (1)
- ASTM D4429-09aDocument7 pagesASTM D4429-09aGustavo Bances Herrera100% (1)
- CPO Focus On Physical Science Student TextbookDocument399 pagesCPO Focus On Physical Science Student TextbookAmy Doan75% (4)
- Hasan Sayginel: Edexcel IAL Physics Unit 1Document22 pagesHasan Sayginel: Edexcel IAL Physics Unit 1Dusty ClaneNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis PowerpointDocument32 pagesDimensional Analysis PowerpointVijay Sai100% (1)
- Physics ReviewerDocument6 pagesPhysics ReviewerHeart Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Physics wk2Document3 pagesPhysics wk2Pauline Jean Cueto BundaNo ratings yet
- B. Notes (Meas & Motion)Document8 pagesB. Notes (Meas & Motion)Teck TieNo ratings yet
- System of Units Commonly UsedDocument16 pagesSystem of Units Commonly UsedCharlize Lainey Phoemela QuitaligNo ratings yet
- Acfrogb9meunsj Bqhgad4tjprfkaiqpsghbnzstrompbmuvz3m5jjjbwethlgvuqn2vdljovbwv 4sg6o8lcscc0eo55rkb9smxukdhyszzxcahjusvqt 3m5cz7gp2xnfalrjk OckhgllcvntDocument2 pagesAcfrogb9meunsj Bqhgad4tjprfkaiqpsghbnzstrompbmuvz3m5jjjbwethlgvuqn2vdljovbwv 4sg6o8lcscc0eo55rkb9smxukdhyszzxcahjusvqt 3m5cz7gp2xnfalrjk OckhgllcvntYuvraj SinghNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument3 pagesKinematicsCHEOK QI JIA, SOFIE S3-01No ratings yet
- Ch-03 - Motion in A Straight Line - Study ModuleDocument38 pagesCh-03 - Motion in A Straight Line - Study ModuleadityaorhoneyNo ratings yet
- Genphys ReviewerDocument8 pagesGenphys Reviewerjustanony92No ratings yet
- AS Unit G481: Mechanics: Definitions: Scalar: Magnitude Without DirectionDocument7 pagesAS Unit G481: Mechanics: Definitions: Scalar: Magnitude Without DirectionJamaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Rev02Document8 pagesChapter 1 - Rev02Lester KoonNo ratings yet
- Phy 91171 MechanicshelpDocument4 pagesPhy 91171 MechanicshelpBenedick CruzNo ratings yet
- Topic 1A - NotesDocument1 pageTopic 1A - NotesRausanara FerdoushiNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument2 pagesForceschemphycombNo ratings yet
- CP1a Vectors and Scalars: Word SheetDocument2 pagesCP1a Vectors and Scalars: Word SheetKenneth KnightNo ratings yet
- P6 ReviewerDocument4 pagesP6 ReviewerMisha ArquizaNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Vectors: Vector AdditionDocument4 pagesMeasurement and Vectors: Vector AdditionMARIE GO ROUNDNo ratings yet
- Motion Class 9Document21 pagesMotion Class 9RINA MandalNo ratings yet
- Physics 1ST QuarterDocument7 pagesPhysics 1ST Quarterlcobogne2550antNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Revision PhysicsDocument20 pagesLast Minute Revision PhysicsSwara TendulkarNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: UNIT G481 1.1.3Document9 pagesKinematics: UNIT G481 1.1.3Home Of Math OfficialNo ratings yet
- Genphy Lesson 3 and 4Document2 pagesGenphy Lesson 3 and 4Bhenice AmparoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Our Dynamic Universe Part 1 Notes V1 - 230316 - 232108Document32 pagesUnit 1 - Our Dynamic Universe Part 1 Notes V1 - 230316 - 232108chamikaNo ratings yet
- Motion Merged - Compressed - Edited PDFDocument71 pagesMotion Merged - Compressed - Edited PDFSK KawsarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics 2mohanad Engineering Mechanics DynamicDocument66 pagesEngineering Mechanics 2mohanad Engineering Mechanics DynamicNefer PitouNo ratings yet
- Mere NotesDocument47 pagesMere NotesRakeshKumarNo ratings yet
- Motion: by Sandeep VermaDocument15 pagesMotion: by Sandeep Vermasandeep vermaNo ratings yet
- ME114 Dynamics - Lec 1 - Particle Kinematics - Rectilinear MotionDocument28 pagesME114 Dynamics - Lec 1 - Particle Kinematics - Rectilinear MotionSharique ImamNo ratings yet
- Form Three Physics Handbook-1Document94 pagesForm Three Physics Handbook-1Kisaka G100% (1)
- Kinema TicsDocument45 pagesKinema TicsRakeshKumarNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: UNIT G481 1.1.3Document9 pagesKinematics: UNIT G481 1.1.3Mohammad Jahangir AlamNo ratings yet
- Change in Position W.R.T. Time Speed: Change in Distance W.R.T Time Velocity Change in Displacement W.R.T Time Change in Velocity W.R.T TimeDocument2 pagesChange in Position W.R.T. Time Speed: Change in Distance W.R.T Time Velocity Change in Displacement W.R.T Time Change in Velocity W.R.T TimeNeetu JainNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument13 pagesForcesamnaakmal070No ratings yet
- Albelda - MechanicsDocument19 pagesAlbelda - MechanicsPrince SanjiNo ratings yet
- Unit 03 NocDocument42 pagesUnit 03 NocSaba HashmiNo ratings yet
- Physics IMPDocument36 pagesPhysics IMPTanuNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies NotesDocument2 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies NotesLeighy GalamayNo ratings yet
- Physics STEM 12Document11 pagesPhysics STEM 12Iah VergaraNo ratings yet
- Curvilinear Motion: General & Rectangular Components ApplicationsDocument3 pagesCurvilinear Motion: General & Rectangular Components ApplicationsAngelica NunezNo ratings yet
- Notes On Linear Motion - Physics From 4 Lesson 1Document7 pagesNotes On Linear Motion - Physics From 4 Lesson 1temiNo ratings yet
- Physical Science ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhysical Science ReviewerLea MachadoNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 Study GuideDocument15 pagesPhysics 11 Study GuideMaria DollNo ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument8 pagesPhysics ReviewerSOLIS, John Ernest S.No ratings yet
- AP Physics I EXAM Study Guide - NotesDocument25 pagesAP Physics I EXAM Study Guide - NotesALICENo ratings yet
- 1.2 Motion NotesDocument8 pages1.2 Motion Notestalal150809No ratings yet
- Reviewer in PhysicsDocument8 pagesReviewer in PhysicsKIMLARAANDREA MARIANONo ratings yet
- Physics - NotesDocument12 pagesPhysics - Notesdagakabbier1718No ratings yet
- Edexcel Igcse Physics 4ph1 Theory v1Document18 pagesEdexcel Igcse Physics 4ph1 Theory v1farhadmustafa128No ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - KinematicsDocument65 pagesSheet - 01 - KinematicsLakshya Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Physics Mind MapsDocument38 pagesEdexcel GCSE Physics Mind MapsDanmin YuNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument3 pagesPhysics FormulasBarbie JooNo ratings yet
- Physics FinalDocument5 pagesPhysics FinalFiery RoseyNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter 3 Review SheetDocument4 pagesScience Quarter 3 Review SheetEljohn MarquezNo ratings yet
- Uplink Nmat Physics Lecture 2017Document73 pagesUplink Nmat Physics Lecture 2017Madhu MithaNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Physics 0625 Theory v3Document20 pagesCaie Igcse Physics 0625 Theory v3shravanthsennimalaiNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Handouts Vector and ScalarDocument3 pagesGrade 7 Handouts Vector and ScalarLovieAlfonsoNo ratings yet
- LAS 1 Units Physical Quantities Measurement Errors and UncertaintiesDocument19 pagesLAS 1 Units Physical Quantities Measurement Errors and UncertaintiesFlor de AldaNo ratings yet
- Chap-2 PropertiesDocument82 pagesChap-2 PropertieskushNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept Notes 2Document43 pagesMole Concept Notes 2Gupta's StudioNo ratings yet
- Wind Is A Mass of Air That Moves in A Mostly Horizontal Direction From An Area of High Pressure To An Area With Low PressureDocument10 pagesWind Is A Mass of Air That Moves in A Mostly Horizontal Direction From An Area of High Pressure To An Area With Low Pressurehimanshu tonkNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Topics Covered: Basic and Derived Units Use of Different System of Units in Process CalculationsDocument14 pagesUnit 1 Topics Covered: Basic and Derived Units Use of Different System of Units in Process CalculationsASHADEVI UNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantity - DataDocument53 pagesPhysical Quantity - DataDeogratias LaurentNo ratings yet
- Quantities, Measurements, and VectorsDocument34 pagesQuantities, Measurements, and VectorsDiane RosarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Electrical MeasurementDocument38 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Electrical MeasurementAdli IkramNo ratings yet
- 2 - Units and MeasurementDocument12 pages2 - Units and MeasurementPhysics with GurmeetNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 PPT Science Q3 W2 Day 1-5Document85 pagesGrade 5 PPT Science Q3 W2 Day 1-5FarahJaneBonusNo ratings yet
- HW1 ScannedDocument3 pagesHW1 ScannedchennkitNo ratings yet
- Customary Units MeasurmentDocument7 pagesCustomary Units MeasurmentKeyania MurrayNo ratings yet
- Fluid Properties and UnitsDocument33 pagesFluid Properties and UnitsFariha RasulNo ratings yet
- 1920 Unit 4 Length, Mass and Capacity (Worksheet)Document7 pages1920 Unit 4 Length, Mass and Capacity (Worksheet)Kogilan Bama DavenNo ratings yet
- 1 - Physical Quantities and MeasurementsDocument47 pages1 - Physical Quantities and MeasurementsShivaranjini RamendranNo ratings yet
- Measurement and ExperimentationDocument6 pagesMeasurement and ExperimentationSarvashreshthaPatelNo ratings yet
- 2 Physics-Module 1-INTRODUCTION - Student PDFDocument14 pages2 Physics-Module 1-INTRODUCTION - Student PDFSarah Sophia AragonNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 Chapter 1 (1.3)Document5 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 1 (1.3)yasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Measurements and CalculationsDocument39 pagesChapter 2-Measurements and CalculationsAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Physics G12 HW 1Document7 pagesPhysics G12 HW 1PegoNo ratings yet
- 9th ScienceDocument220 pages9th Sciencejpbabu68No ratings yet