Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 4 5 TRIAC P 1 2
Uploaded by
different wayOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 4 5 TRIAC P 1 2
Uploaded by
different wayCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture (4/5)
Triode for Alternating Current (TRIAC)
Part-1 and 2
There are several applications that need to regulate the power fed of the
load. For example: using electrical methods/devices to control the power flow in a
system. But, these devices do not allow a fine control of the power flow.
Additionally, there is an extensive wastage of power. In the present day, such
devices have been developed which can allow a fine control of a large amount of
power flow in a system. These devices perform as controlled switches and can
complete the tasks of controlled rectification, regulation, and inversion of power
in a load. These devices are semiconductor switching devices as BJT, UJT,
JFET, MOSFET, SCR, DIAC, and TRIAC.
Triode for Alternating Current-TRIAC
The TRIAC is a development of the thyristor. While the thyristor can
control the current for one half of an AC waveform only (half-wave device), while
the TRIAC controls it for two halves of an AC waveform (full-wave device).
TRIACs are electronic components that are widely used in AC power
control/switching applications. They are able to switch high voltages and high
levels of current, and over both parts of an AC waveform.
Like other electronic components, the TRIAC has its own circuit symbol for
use on circuit diagrams and this indicates its bi-directional properties. A TRIAC
device comprises two thyristors that are parallel connected in the opposite
direction, but it is controlled by the same gate (the gates merged together).
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 19/26-11-2020
Construction of TRIAC
TRIAC is a three-terminal device; the gate terminal is the control
terminal. The flow of current in the TRIAC is bi-directional which means current
can flow in both directions. The structure of TRIAC is shown in the below figure.
Here, in the structure of TRIAC, two SCRs are connected in the anti-parallel and
it will act as a switch for both directions. The three terminals of the TRIAC are
main terminals 1, 2 ( , ) and gate terminal ( ). The layers closer to the
terminals are the combination of both positive and negative layers, this
combination of both the polarities at the terminals helps in operating the TRIAC in
both directions. Generating pulses are applied between and , using +Ve or
-Ve gate pulses. When the is open, the TRIAC will prevent both the polarities
of the voltage across the and .
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 19/26-11-2020
Characteristics and Operation of TRIAC
The TRIAC is able to conduct in different ways - more than the thyristor.
It can conduct current irrespective of the voltage polarity of terminals and
. It can also be triggered by either positive or negative gate currents,
irrespective of the polarity voltage of the .This means that the TRIAC has
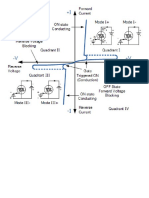
four triggering modes:
Quadrant I (1st quadrant)
Mode (+Ι):
with positive potential (+ve) and with positive potential (+ve), the current
flows as:
Mode (-Ι):
with positive potential (+ve) and with negative potential (-ve), the current
flows as:
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 19/26-11-2020
Quadrant III (3rd quadrant)
Mode (+ΙΙΙ):
with negative potential (-ve) and with positive potential (+ve), the current
flows as:
Mode (-ΙΙΙ):
with negative potential (-ve) and with negative potential (-ve), the current
flows as:
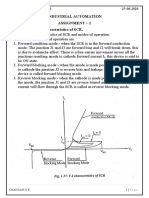
The typical I-V characteristic of a TRIAC can be seen in the diagram below
with the four different quadrants labeled. Operating characteristics of TRIAC in
the 1st and 3rd quadrants are similar but the direction of current and the applied
voltage are reverses. The characteristics of TRIAC in the 1st and 3rd quadrants
are basically the same as those of a thyristor in the 1st quadrant.
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 19/26-11-2020
With no signal to the , the TRIAC will block both halves of the AC
applied voltage, in case of the peak value of this voltage is less than the TRIAC
break-over voltages ( or ).
It is found that the TRIAC sensitivity is greatest when the and
voltages are both in the same polarity (the more common TRIAC triggering).
That means both voltages are positive or both voltages are negative. If the
and voltages are of the opposite polarity then the sensitivity is typically about
half value when they are in the same polarity.
Also, just like thyristor, TRIAC’s also required a minimum Holding
current to maintain conduction. Then even though the two thyristors are
combined into one single TRIAC device, they still display individual electrical
characteristics such as different breakdown voltages and holding currents levels
for each one of them from the other thyristor device.
The voltage and current values for a typical TRIAC are given below:
1. On-state current: – 25 A
2. On-state voltage: – 1.5 V
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 19/26-11-2020
3. Average triggering current: – 5 mA
4. Holding current: – 75 mA
Applications of TRIAC
The TRIAC device is the most commonly used for power switching and
power control of AC systems; as the TRIAC can be switched on by either a
positive or negative gate pulse, regardless of the AC supply polarity at that time.
It’s often used in low to medium levels of power switching requirements of AC
systems. But where the large levels of power switching, two thyristors tend to be
used as they can be controlled more easily. Nevertheless, TRIACs are widely
used in many applications:
Lighting control.
Heaters control.
Control of fans and small universal motors.
It is found that because of their slight differences between the two halves of
TRIAC in the internal construction, the results are the non-symmetrical firing of
TRIAC. This results in harmonics being generated; that meaning the less fire
symmetrical of TRIAC, the greater level of harmonics that are produced.
To help in overcoming the problem of the non-symmetrical firing of
TRIAC, and the resulting harmonics; either by using two thyristors instead of
TRIAC or another semiconductor device known as a DIAC with TRIAC, its often
placed in series with the gate of the TRIAC.
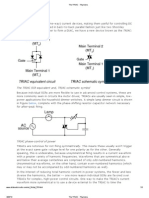
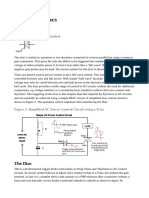
Basic TRIAC Switching Circuit
The circuit below shows a simple AC triggered TRIAC power switching
circuit, using the actual AC supply voltage itself as the gate triggering voltage.
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 19/26-11-2020
As above, if switch is open at position-A, there is no gate current and
the lamp is off.
If the is moved to position-B, the gate current flows at every half cycle
via resistor and the full power is drawn by the lamp as the TRIAC operates in
modes (+Ι) and (–IIΙ).
But in this time when the is connected to position-C, the diode will
prevent the triggering of the gate when is negative as the diode is reversed
biased. Thus the TRIAC only conducts on the positive half-cycles operating in
mode (+Ι) only and the lamp will light at half power.
Then depending upon the position of the switch, the load is ‘Off’ at
position-A, ‘Half Power’ at position-C, or ‘Fully On’ at position-B.
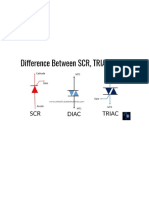
Actual Difference between SCR and TRIAC
SCR and TRIAC are very important semiconductor devices which are used
in power electronics circuits. Here we will discuss the important differences
between SCR and TRIAC.
1- SCR means Silicon Controlled Rectifier and TRIAC means Triode for
Alternating Current.
2- SCR is an uni-directional semiconductor device but TRIAC is a bi-directional
semiconductor device.
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 19/26-11-2020
3- The construction difference between SCR and TRIAC both are four-layer and
three-terminal devices. We can make a TRIAC by connecting two SCR in anti-
parallel and gate terminal connected together.
4- The symbolic difference between SCR and TRIAC as:
5- The SCR can work with only positive gate triggering; TRIAC can work with
both positive and negative gate triggering.
6- The SCR can operate in only one mode; TRIAC can operate in four modes.
7- The SCR mainly used to control DC power, TRIAC mainly used to control AC
power.
8- The SCR mainly requires two heat sinks; TRIAC mainly requires only a single
heat sink.
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 19/26-11-2020
Advantages of TRIAC
Its bi-directional device for conduction.
It requires only a single fuse for protection.
It requires only a single heat sink for cooling.
It can be triggered with positive or negative polarity of gate pulses.
Disadvantages of TRIAC
It doesn’t conduct symmetrically on both sides of the waveforms.
It doesn’t appropriate for the DC power.
It has a very high switching delay.
It doesn’t available in larger rating power.
Reliability of TRIAC is less than that of SCR.
Reference:
1. M. H. Rashid, “Power Electronics: Circuits, Devices and Applications,”
Prentice Hall India, Second Edition, 2006.
2. P. S. Bimbhra, "Power Electronics," Khanna Publishers, fifth edition, 2012.
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 19/26-11-2020
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- R2 Owner Manual PDFDocument20 pagesR2 Owner Manual PDFRahul RaghuramNo ratings yet
- Why Primary Injection TestsDocument6 pagesWhy Primary Injection TestsEdward Osore100% (2)
- Basic Triac-SCR Projects Circuits TutorialDocument7 pagesBasic Triac-SCR Projects Circuits TutorialAmmar YasserNo ratings yet
- What Is A Diac-TriacDocument26 pagesWhat Is A Diac-TriacChristian Dave Tamparong100% (1)
- Triacs and DiacsDocument4 pagesTriacs and Diacsssami670No ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Checklist 01Document3 pagesEngineering Drawing Checklist 01Inayat HathiariNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle Conductive Charging SystemDocument38 pagesElectric Vehicle Conductive Charging SystemSharath KumarNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Loco Pilot Electric Loco Conventional Book BhusawalDocument276 pagesLoco Pilot Electric Loco Conventional Book BhusawalHarsh Vardhan Singh100% (2)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Triac Symbol and Construction: MT MT G MTDocument2 pagesTriac Symbol and Construction: MT MT G MTRonsonel TajanNo ratings yet
- TRIACDocument5 pagesTRIACSaumil KarnadNo ratings yet
- Case Study (1) Pe Ca1Document10 pagesCase Study (1) Pe Ca1vikas mokasheNo ratings yet
- Triac Tutorial and Triac Switching CircuitsDocument7 pagesTriac Tutorial and Triac Switching CircuitsErick Perez100% (1)
- Triac Tutorial and Triac Switching CircuitsDocument8 pagesTriac Tutorial and Triac Switching CircuitsNikšaNo ratings yet
- TRAICDocument14 pagesTRAICManav JainNo ratings yet
- Triac QuadrantDocument15 pagesTriac QuadrantJohn Paul BaquiranNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 DIACDocument6 pagesLecture 6 DIACdifferent wayNo ratings yet
- Diac - TriacDocument18 pagesDiac - TriacBabe O.No ratings yet
- Liquid Level Controller Using TRIAC: Experiment #5Document7 pagesLiquid Level Controller Using TRIAC: Experiment #5Zeeshan RafiqNo ratings yet
- The University of Jordan School of Engineering Department of Mechatronics Engineering Power Electronics and Drive Lab Instructor: Eng. Nazmi AshourDocument15 pagesThe University of Jordan School of Engineering Department of Mechatronics Engineering Power Electronics and Drive Lab Instructor: Eng. Nazmi AshourMohammad AlbordiniNo ratings yet
- RMAE Notes DIAC TRIACDocument9 pagesRMAE Notes DIAC TRIACPriyanka BhateleNo ratings yet
- Silicon Diode For Alternating CurrentDocument10 pagesSilicon Diode For Alternating CurrentPrincess Dainne Fontanilla DahiligNo ratings yet
- Special Semiconductor Devices: Mr. Jay Mehta Asst. Professor St. Francis Institute of TechnologyDocument35 pagesSpecial Semiconductor Devices: Mr. Jay Mehta Asst. Professor St. Francis Institute of Technologyjay mehtaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Triac-Its Construction and Operation: SCR ControlsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Triac-Its Construction and Operation: SCR ControlsSurendra ChouhanNo ratings yet
- SCR Diac TraicDocument15 pagesSCR Diac TraicEngr. Sarafat KhanNo ratings yet
- Thyristor Triacand DiacDocument12 pagesThyristor Triacand DiacNadin NirvanaNo ratings yet
- Triac Tutorial and Triac Switching CircuitsDocument7 pagesTriac Tutorial and Triac Switching CircuitsBill WhiteNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-: Suresh MohtaDocument14 pagesPresented By:-: Suresh MohtaAmanuel GereziherNo ratings yet
- Rich Text Editor FileDocument1 pageRich Text Editor FilefranchmaverickNo ratings yet
- Triac Tutorial and Triac Switching CircuitsDocument7 pagesTriac Tutorial and Triac Switching Circuitsmarcoms75No ratings yet
- The TRIAC - ThyristorsDocument3 pagesThe TRIAC - Thyristorsge_bdNo ratings yet
- Diac & Triac: Er. Faruk Bin Poyen Asst. Professor Dept. of Aeie, Uit, BuDocument27 pagesDiac & Triac: Er. Faruk Bin Poyen Asst. Professor Dept. of Aeie, Uit, BuRohit BariNo ratings yet
- Seminar Topic On Speed Control of DC Motor Using TRIACDocument18 pagesSeminar Topic On Speed Control of DC Motor Using TRIACRicha0001100% (1)
- Contents: Diac Triac Other Types of ThyristorDocument24 pagesContents: Diac Triac Other Types of ThyristorKharol A. Bautista100% (1)
- Breakover DevicesDocument37 pagesBreakover DevicesAnnalyn Duculan SoriaNo ratings yet
- Nirma University: Speed Control of Motor Using TriacDocument7 pagesNirma University: Speed Control of Motor Using TriacAman KumarNo ratings yet
- The TRIACDocument3 pagesThe TRIACyudha ainurrokhimNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics Assignment #2 Silicon Controlled Switch (SCS)Document8 pagesIndustrial Electronics Assignment #2 Silicon Controlled Switch (SCS)LM BecinaNo ratings yet
- Nota Unit 6Document19 pagesNota Unit 6F1036No ratings yet
- Midterm-PIT Written-Report Alaba Dano Kabingue Lacanaria-2Document7 pagesMidterm-PIT Written-Report Alaba Dano Kabingue Lacanaria-2IvanAlabaNo ratings yet
- The Triac: Chapter 7 - ThyristorsDocument5 pagesThe Triac: Chapter 7 - ThyristorsDaniel Puentes CorredorNo ratings yet
- The Diac: SCR's TriacsDocument4 pagesThe Diac: SCR's TriacsZaheer Ahmed100% (1)
- Power Report 1Document14 pagesPower Report 1Faustin MailuNo ratings yet
- Ac Phase Control of TriacDocument4 pagesAc Phase Control of Triacjassisc0% (1)
- Power Semiconductor Devices: EE 3036 D: Presented byDocument10 pagesPower Semiconductor Devices: EE 3036 D: Presented byShubham ranjanNo ratings yet
- Triacs and Diac1Document4 pagesTriacs and Diac1Shamsul Haq NtcNo ratings yet
- EE62 Lab 1 - JEFFER N. FALLARCUNADocument8 pagesEE62 Lab 1 - JEFFER N. FALLARCUNAJeffer FallarcunaNo ratings yet
- Triacs and Diacs TechnlogyDocument4 pagesTriacs and Diacs TechnlogyajjjindoreNo ratings yet
- AC Voltage Controller (Using DIAC and TRIAC)Document9 pagesAC Voltage Controller (Using DIAC and TRIAC)Khan Elme100% (2)
- Triac and DiacDocument16 pagesTriac and DiacIan BetosNo ratings yet
- 10.1 S06L06-ThyristorDevices - PDF - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)Document14 pages10.1 S06L06-ThyristorDevices - PDF - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)yotopia horoor gameNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Industrial ReportDocument8 pagesGroup 1 Industrial Reportjoseph5689No ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument9 pagesPower ElectronicsViviana VergelNo ratings yet
- L-4 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 6Document5 pagesL-4 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 6GagneNo ratings yet
- TRIAC LectureDocument2 pagesTRIAC Lecturetinonoy KulitlitNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 in Industrial ElectronicsDocument15 pagesActivity 3 in Industrial ElectronicsFrancis Valdez Lopez100% (1)
- How Does A Thyristor Work?: G A Cathode CDocument10 pagesHow Does A Thyristor Work?: G A Cathode Csamith1No ratings yet
- Triac PDFDocument3 pagesTriac PDFyuj oNo ratings yet
- TriacDocument3 pagesTriacMuhd Zulhusni Ag JaludinNo ratings yet
- TRIACDocument1 pageTRIACGowtham HariNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument201 pagesPower Electronicsdream breakerNo ratings yet
- Industrial Automation AssignmentDocument9 pagesIndustrial Automation AssignmentChandan ChandanNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Linear Induction Machines-P3Document6 pagesLecture-Linear Induction Machines-P3different wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture Synchros P1Document12 pagesLecture Synchros P1different wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Linear Induction Machines-P2Document3 pagesLecture-Linear Induction Machines-P2different wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Linear Induction Machines-P4Document11 pagesLecture-Linear Induction Machines-P4different wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 DIACDocument6 pagesLecture 6 DIACdifferent wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture Synchros P2Document7 pagesLecture Synchros P2different wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3 - SCRDocument7 pagesLecture-3 - SCRdifferent wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - BJTDocument10 pagesLecture 2 - BJTdifferent wayNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document1 pageSheet 1different wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1-Revision On Basic of Power Electronic ComponentsDocument11 pagesLecture-1-Revision On Basic of Power Electronic Componentsdifferent wayNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy 2021Document4 pagesEngineering Economy 2021different wayNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy 2021Document4 pagesEngineering Economy 2021different wayNo ratings yet
- Level Control Relay: Wiring DiagramDocument1 pageLevel Control Relay: Wiring DiagramRamius HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Nirma University: InstructionsDocument3 pagesNirma University: InstructionsBHENSDADIYA KEVIN PRABHULALNo ratings yet
- Common Tools and Equipment For Computer System ServicingDocument17 pagesCommon Tools and Equipment For Computer System ServicingEchelle OgatisNo ratings yet
- Cascada Co2 Con HFCDocument34 pagesCascada Co2 Con HFCjuan leyyonNo ratings yet
- On IgbtDocument19 pagesOn IgbtSayanta Saha100% (1)
- 7MBR15SA120 IGBT ModuleDocument7 pages7MBR15SA120 IGBT ModuleDario BessoneNo ratings yet
- I. How Do You Use An Adjective in English?Document2 pagesI. How Do You Use An Adjective in English?Juvenal UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Lab Summing AmplifierDocument2 pagesLab Summing AmplifierShahzad Raza JalbaniNo ratings yet
- QoneDocument3 pagesQoneHv TopNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Sem 1 20202021 BDA30703Document3 pagesAssignment 1 Sem 1 20202021 BDA30703Izzat Khair Bin MahmudNo ratings yet
- 412SI412SI72Document28 pages412SI412SI72storgemateoNo ratings yet
- MST For Roof Slab WaterproofingDocument6 pagesMST For Roof Slab Waterproofingdina gunasekeraNo ratings yet
- Transistor DC Biasing 1Document38 pagesTransistor DC Biasing 1farhan jalaludinNo ratings yet
- Exp No 1 - FWR, Vtu17455 PDFDocument9 pagesExp No 1 - FWR, Vtu17455 PDFAnudeep ThanikondaNo ratings yet
- DOMINODocument16 pagesDOMINOBerat DalyabrakNo ratings yet
- Esab - rt62 TorchDocument50 pagesEsab - rt62 TorchZMCNo ratings yet
- Cascode High Swing PreciseDocument2 pagesCascode High Swing PreciselorisNo ratings yet
- Control Integrated Power System (Cipos™) : Igcm04G60HaDocument17 pagesControl Integrated Power System (Cipos™) : Igcm04G60Hafredy guevara oNo ratings yet
- Lista Chint Sep 18Document10 pagesLista Chint Sep 18Daygo BarcoNo ratings yet
- Valve (Tube) Regulated Power Supplies (AudioXpress 2008)Document6 pagesValve (Tube) Regulated Power Supplies (AudioXpress 2008)Kemboya LuigiNo ratings yet
- Solar Based Mobile Charger: Mr. Betallu Abhishek Rajendra Roll No 09 EXAM SEAT NO:71903353FDocument26 pagesSolar Based Mobile Charger: Mr. Betallu Abhishek Rajendra Roll No 09 EXAM SEAT NO:71903353FDadaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Short Circuited DC Link Capacitor of An AC-DC-AC Inverter On The Performance of Induction MotorDocument8 pagesEffect of Short Circuited DC Link Capacitor of An AC-DC-AC Inverter On The Performance of Induction MotorOSAMANo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 Electrical Power: 24 ContentsDocument8 pagesChapter 24 Electrical Power: 24 ContentsatrflyerNo ratings yet
- Watertight High Power Horn IMCOS 5217v6Document1 pageWatertight High Power Horn IMCOS 5217v6Sam ZhangNo ratings yet
- Subcontractor Strategy Dated 28thjuly'21Document12 pagesSubcontractor Strategy Dated 28thjuly'21SyedFarhanNo ratings yet