Professional Documents
Culture Documents
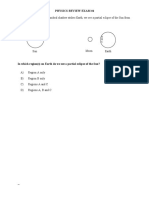
Physics Mechanics Module Workbook
Uploaded by
welcometotheswampOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Mechanics Module Workbook
Uploaded by
welcometotheswampCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYSICS – MECHANICS MODULE WORKBOOK
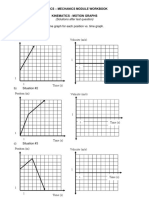
KINEMATICS 1 - UNIFORM MOTION
Unless specified otherwise, all of the following situations involve bodies moving in
rectilinear trajectories in the absence of gravitational fields.
SOLVED PROBLEMS
1. An object is moving along a straight and level track for 3.0 s until it is 12 m from its
initial position. It then stops for 2.1 s, changes direction and travels for 36 m for 2.5 s.
a) Determine the total distance traveled b) Determine the total displacement
c) What was the average speed? d) What was the average velocity?
2. An object is moving along a straight and level track. It moves at 4.2 m/s for 3.0 s. Then,
it changes direction and travels for 5.0 s m at -6.4 m/s.
a) Determine the object’s total distance traveled.
b) Determine the object’s average speed.
c) Determine the object’s total displacement.
d) Determine the object’s average velocity.
3. An airplane is flying along a rectilinear trajectory without changing direction. It travels
1800 km at 900 km/h. It then slows it down to 800 km/h for the next 2400 km.
What was airplane’s average velocity for this trip?
SOLUTIONS
1. An object is moving along a straight and level track for 3.0 s until it is 12 m from its
initial position. It then stops for 2.1 s, changes direction and travels for 36 m for 2.5 s.
a) Determine the total distance traveled b) Determine the total displacement
distance is the total length of the trajectory or displacement is the object's distance from
path (direction is not considered) where it started (direction is considered)
12 + 36 = 48 m (+12) +(- 36) = -24m
c) What was the average speed? d) What was the average velocity?
average speed average velocity
= (total distance) / (total time) = (total displacement) / (total time)
(direction not considered) (direction is considered)
48 / ( 3.0 + 2.1 + 2.5 )= 6.3 m/s -24 / ( 3.0 + 2.1 + 2.5 )= -3.2 m/s
2. An object is moving along a straight and level track. It moves at 4.2 m/s for 3.0 s. Then,
it changes direction and travels for 5.0 s m at -6.4 m/s.
a) Determine the object’s total distance traveled.
Determine distance traveled in each direction
Use Distance = Speed x Time
Positive direction: 4.2 x 3.0 = 12.6 m Negative direction: 6.4 x 5.0 = 32.0 m
Total distance = 12.6 + 32.0 = 44.6 m
b) Determine the object’s average speed.
44.6 / ( 5.0 + 3.0 ) = 5.6 m/s
c) Determine the object’s total displacement.
Total displacement = (+12.6) + (-32.0) = -19.4 m
d) Determine the object’s average velocity.
-19.4 / ( 5.0 + 3.0 ) = - 2.4 m/s
3. An airplane is flying along a rectilinear trajectory without changing direction. It travels
1800 km at 900 km/h. It then slows it down to 800 km/h for the next 2400 km.
What was airplane’s average velocity for this trip?
Determine the total time. Use Time = Distance/Speed
Total time = ( 1800 / 900 ) + ( 2400 / 800 ) = 5 hours
Average velocity = ( 1800 + 2400 ) / 5 = 840 km/h
Note that displacement = distance and velocity = speed
when an object moves in one direction along a straight path
SUPPLEMENTARY EXERCISES
4) A person walks 5.0 metres forward and then 3.0 metres back in 4.0 s.
a) What is the distance the person walked in 4.0 s?
b) What is the displacement of the person’s walk in 4.0 s?
c) What is the average speed of the person during his walk?
d) What is the average velocity of the person during his walk?
5) An airplane that leaves Calgary at 9:05 am and arrives in Grande Prairie at 11:35 am.
The two cities are 350 km apart. Find its average speed (in m/s).
6) How long will it take a bicycle traveling at an average of 8.5 m/s to travel 2.35 km?
7) Two cars have the same initial position and trajectory and are traveling at constant
speeds in the same direction. One car travels at 80 km/h and the other at 100 km/h.
How long will it be before they are 5 km apart?
8) An body travels for 5.0s at 15m/s and then changes direction and travels for 100m at
8.0m/s. What was its average velocity?
ANSWERS
4a) 8 m b) 2 m c) 2 m/s d) 0.5 m/s
5) 38.9 m/s 6) 276.5 s 7) 900 s or 15 min 9) -1.43 m/s
Example Solutions
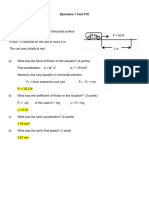
7) Two cars have the same initial position and trajectory and are traveling at constant
speeds in the same direction. One car travels at 80 km/h and the other at 100 km/h.
How long will it be before they are 5 km apart?
There are many ways to solve this problem including making a position graph, using a table of
values or using relative velocity (the easiest method).
The following method is the most general that prepares you for more difficult questions.
Write equations of motion for each car
#⃗
∆"
Start with the velocity equation "⃗ =
v ∆%
"⃗
Isolate ∆d "⃗ = v"⃗ × ∆t
∆d
"⃗ = d
∆d "⃗& − d
"⃗' "⃗ "⃗' = "v⃗ × ∆t
d& − d
Since the two cars have the same initial position, let 𝑑⃗' = 0
(i.e. let both cars have an initial poistion of 0)
"⃗&_)*+' = "v⃗)*+' × ∆t
d "⃗&_)*+& = "v⃗)*+& × ∆t
d
"⃗&_)*+' − d
We are looking for the time when d "⃗&_)*+& = 5 km
"⃗&_)*+' − d
d "⃗&_)*+& = (v
"⃗)*+& × ∆t) − (v
"⃗)*+& × ∆t)
5 = 100∆t − 80∆t
5 = 20∆t
∆t = 0.25 h = 15 minutes
You might also like
- Linear Motion LectureDocument42 pagesLinear Motion LectureTheodore Teddy JNo ratings yet
- Time and DistanceDocument6 pagesTime and DistanceAshish SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ComputationsDocument4 pagesComputationsEthan kale CadienteNo ratings yet
- Most Important Formulas: Speed, Distance and TimeDocument5 pagesMost Important Formulas: Speed, Distance and TimeFight 4 FitnessNo ratings yet
- Solutions To The Problems On Velocity and Speed of Moving ObjectsDocument8 pagesSolutions To The Problems On Velocity and Speed of Moving ObjectsMichelle Diaz DonaireNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Note Ws 2019 UpdatedDocument26 pagesKinematics Note Ws 2019 UpdatedHany WafaNo ratings yet
- Motion in One Dimension ChapterDocument31 pagesMotion in One Dimension ChaptersweetandwildNo ratings yet
- Physics Pre-Test ReviewDocument10 pagesPhysics Pre-Test Reviewcarol janeNo ratings yet
- Physical: ClassworkDocument6 pagesPhysical: ClassworkDianaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 SolutionsDocument10 pagesTutorial 1 SolutionsNicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 NotesDocument68 pagesPhysics 1 NotesMikhael Glen Lataza100% (1)
- Top Q - Kinematics - I - 1700556881394225Document5 pagesTop Q - Kinematics - I - 1700556881394225ilovekpop2023No ratings yet
- H.W-2-Chapter2 With SolutionDocument3 pagesH.W-2-Chapter2 With SolutionLamiaa AlharbeNo ratings yet
- GRK Lurus-RectilinearMotionDocument22 pagesGRK Lurus-RectilinearMotionzaeraNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional KinematicsDocument8 pagesOne Dimensional Kinematicsonyx sallivaramNo ratings yet
- Velocity and SpeedDocument9 pagesVelocity and SpeedJenny Teves DayritNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test Physics (Questions and Answers) : Calculated by Adding or Subtracting Two Measured ValuesDocument10 pagesPre-Test Physics (Questions and Answers) : Calculated by Adding or Subtracting Two Measured ValuesDaisy GamerNo ratings yet
- Ix Physics Question BankDocument4 pagesIx Physics Question BankHanirutha.M 7BNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Worksheet - 1 2Document2 pagesChapter 2-Worksheet - 1 2Aisha AhmedNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 8Document11 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 8shahulNo ratings yet
- Part2 ch05Document14 pagesPart2 ch05api-3705610No ratings yet
- Science 20 Unit B 08Document133 pagesScience 20 Unit B 08api-207957230100% (1)
- Science 7 MotionDocument86 pagesScience 7 MotionappleNo ratings yet
- STD 8 TS1 2022 Position, Time, Distance and Displacement, Air Pressure Test - StudentDocument1 pageSTD 8 TS1 2022 Position, Time, Distance and Displacement, Air Pressure Test - StudentSubrangsu PradhanNo ratings yet
- Using A Graph To Get The General Equation For DisplacementDocument11 pagesUsing A Graph To Get The General Equation For DisplacementAndrea KusickiNo ratings yet
- Classical MechanicsDocument55 pagesClassical MechanicsJoanna Ruth SeproNo ratings yet
- Basic Motion - NotesDocument7 pagesBasic Motion - NotesparneetNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem Speed N VelocityDocument15 pagesSample Problem Speed N VelocityEllen DispoNo ratings yet
- JAH VDT CompleteDocument7 pagesJAH VDT CompleteAli HusnainNo ratings yet
- L01 Average SpeedDocument9 pagesL01 Average SpeedJohn JohnsonNo ratings yet
- ch-8 MotionDocument5 pagesch-8 MotionLohith Chary100% (1)
- CH 1a Motion - Ticker Timers Notes 2024Document27 pagesCH 1a Motion - Ticker Timers Notes 2024andilenbNo ratings yet
- Motion GraphsDocument10 pagesMotion GraphsDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Understanding Motion Through Speed, Velocity and AccelerationDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Motion Through Speed, Velocity and AccelerationSel FortichNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - MotionDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - MotionDani PrimantaraNo ratings yet
- Aptitude Day05Document65 pagesAptitude Day05AKSHAY ANDURENo ratings yet
- Phys11 C01 HomeworkDocument4 pagesPhys11 C01 HomeworkAynaticNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line: Distance, Displacement, Speed and VelocityDocument6 pagesMotion in A Straight Line: Distance, Displacement, Speed and VelocityMAG MarvelNo ratings yet
- Physics 2414 - Strauss Chapter 2 Lecture Notes: V V X X T + (1/2) at X X V V V VDocument7 pagesPhysics 2414 - Strauss Chapter 2 Lecture Notes: V V X X T + (1/2) at X X V V V VansarixxxNo ratings yet
- MARY JOSETTE ACADEMY PHYSICS MODULEDocument7 pagesMARY JOSETTE ACADEMY PHYSICS MODULEleslie mermeloNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Gen Physics Module Week 3Document7 pagesGrade 12 Gen Physics Module Week 3leslie mermeloNo ratings yet
- Concept Check #2Document4 pagesConcept Check #2zhan sunNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Mod1 Q3Document12 pagesScience 7 Mod1 Q3Roselyn B. BitareNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document4 pagesQuiz 2Ijaz Talib Classical MechanicsNo ratings yet
- Tutorial KinematicsDocument3 pagesTutorial KinematicsAimeenul AzfarNo ratings yet
- Assignment EoM EasyDocument3 pagesAssignment EoM EasySohan KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Problem 1Document4 pagesProblem 1Joan AlfarasNo ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument63 pagesKinema TicsTutor JamesNo ratings yet
- Physics Kinematics Test AnalysisDocument9 pagesPhysics Kinematics Test AnalysisBabbi SinghNo ratings yet
- 1 - Linear MotionDocument10 pages1 - Linear Motionapi-242844746No ratings yet
- Ch2 MCQuestions - Blank 2016Document13 pagesCh2 MCQuestions - Blank 2016utheinsweNo ratings yet
- Aptitude Day04 125327Document94 pagesAptitude Day04 125327SOURAV KAMBLENo ratings yet
- 2.1 Motion PDFDocument73 pages2.1 Motion PDFsanad boshehNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document4 pagesCH 2Civil NutNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 10Document12 pagesChapter 2 10FawadAkhtarNo ratings yet
- More Projectile Motion Practice Problems and SolutionsDocument3 pagesMore Projectile Motion Practice Problems and SolutionsJocelyn Yemyem Mantilla Veloso100% (1)
- Physics - Vectors - Basic Kinematics - Exercise Workbook 2023Document2 pagesPhysics - Vectors - Basic Kinematics - Exercise Workbook 2023welcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Physics - Vectors - Basic Kinematics - Exercise Workbook 2023Document2 pagesPhysics - Vectors - Basic Kinematics - Exercise Workbook 2023welcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 1 Test V2ADocument2 pagesDynamics 1 Test V2AwelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Physics - Mechanics - Vectors - ReviewDocument5 pagesPhysics - Mechanics - Vectors - ReviewwelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Vector Theory ExercisesDocument9 pagesVector Theory ExerciseswelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Physics Review 4Document23 pagesPhysics Review 4welcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Physics Review 3Document19 pagesPhysics Review 3welcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 1 Test V1CDocument2 pagesDynamics 1 Test V1CwelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Physics - Kinematics - Exercises 4Document2 pagesPhysics - Kinematics - Exercises 4welcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Science Exam Information DocumentDocument2 pagesScience Exam Information DocumentwelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Physics - Kinematics - Exercises 3Document6 pagesPhysics - Kinematics - Exercises 3welcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Physics - Kinematics - Exercises 5Document2 pagesPhysics - Kinematics - Exercises 5welcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 1 Test V2ADocument2 pagesDynamics 1 Test V2AwelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 1 Test V1CDocument2 pagesDynamics 1 Test V1CwelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Basic Neurogenesis ImagesDocument3 pagesBasic Neurogenesis ImageswelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 1 Test V1ADocument2 pagesDynamics 1 Test V1AwelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Graphical LearningDocument8 pagesGraphical LearningwelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Nervous System WorksheetDocument1 pageAnatomy of The Nervous System WorksheetwelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1 - Rules of DerivativesDocument7 pagesCalculus 1 - Rules of DerivativeswelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Physics - Kinematics - Exercises 1Document11 pagesPhysics - Kinematics - Exercises 1welcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Related RatesDocument1 pageCalculus - Related RateswelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Credit Plus Calculus - Optimization 2019Document3 pagesCredit Plus Calculus - Optimization 2019welcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Commerce Word ProblemsDocument2 pagesCalculus - Commerce Word ProblemswelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Kinematics ApplicationsDocument2 pagesCalculus - Kinematics ApplicationswelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Basic ApplicationsDocument2 pagesCalculus - Basic ApplicationswelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Cost Function: Price Function: Do Not Simplify Your Answer: Credit+ Calculus Test 2 - WHITE Question 1aDocument4 pagesCost Function: Price Function: Do Not Simplify Your Answer: Credit+ Calculus Test 2 - WHITE Question 1awelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Economics-Kinematics Problem SetDocument2 pagesEconomics-Kinematics Problem SetwelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Step Function NotesDocument5 pagesStep Function NoteswelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- A An Some Any Jamie Oliver Pancake With Answer KeyDocument8 pagesA An Some Any Jamie Oliver Pancake With Answer Keygcciprian66570% (3)
- SW - Simulation - Product MatrixDocument2 pagesSW - Simulation - Product Matrixsamar2011No ratings yet
- Module 1Document12 pagesModule 1Ajhay Torre100% (1)
- MOA of Actuarial Societ of BangladeshDocument22 pagesMOA of Actuarial Societ of BangladeshActuarial Society of BangladeshNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Bugs Lesson 2Document1 pageYear 7 Bugs Lesson 2api-293503824No ratings yet
- Panasonic SA-HT878Document82 pagesPanasonic SA-HT878immortalwombatNo ratings yet
- Q3 SolutionDocument5 pagesQ3 SolutionShaina0% (1)
- Black Veil BridesDocument2 pagesBlack Veil BridesElyza MiradonaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Google SheetDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Google SheetJohn Rey Radoc100% (1)
- List of Candidates for BUDI Scholarship 2016Document9 pagesList of Candidates for BUDI Scholarship 2016Andriawan Mora Anggi HarahapNo ratings yet
- Online Student Enrollment SystemDocument29 pagesOnline Student Enrollment SystemajidonsonNo ratings yet
- Hierarchical Afaan Oromoo News Text ClassificationDocument11 pagesHierarchical Afaan Oromoo News Text ClassificationendaleNo ratings yet
- Ultra Structure of Plant Cell 1Document18 pagesUltra Structure of Plant Cell 1Kumaran JothiramNo ratings yet
- 5e3 Like ApproachDocument1 page5e3 Like Approachdisse_detiNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower FundamentalsDocument17 pagesCooling Tower FundamentalsGaurav RathoreNo ratings yet
- Aimt ProspectusDocument40 pagesAimt ProspectusdustydiamondNo ratings yet
- Adafruit Color SensorDocument25 pagesAdafruit Color Sensorarijit_ghosh_18No ratings yet
- Dental Pulp TissueDocument77 pagesDental Pulp TissueJyoti RahejaNo ratings yet
- Telegram Log File Details Launch Settings Fonts OpenGLDocument5 pagesTelegram Log File Details Launch Settings Fonts OpenGLThe nofrizalNo ratings yet
- A Grammar of Awa Pit (Cuaiquer) : An Indigenous Language of South-Western ColombiaDocument422 pagesA Grammar of Awa Pit (Cuaiquer) : An Indigenous Language of South-Western ColombiaJuan Felipe Hoyos García100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in TechnologyDocument11 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in TechnologyReshiela OrtizNo ratings yet
- Asian Paint FMVRDocument20 pagesAsian Paint FMVRdeepaksg787No ratings yet
- USA Gas TurbineDocument4 pagesUSA Gas TurbineJustin MercadoNo ratings yet
- The History of Coins and Banknotes in Mexico: September 2012Document35 pagesThe History of Coins and Banknotes in Mexico: September 2012Mladen VidovicNo ratings yet
- Gender Support Plan PDFDocument4 pagesGender Support Plan PDFGender SpectrumNo ratings yet
- Distillation Lab ReportDocument6 pagesDistillation Lab ReportSNo ratings yet
- Configuration Management and ISO 9001Document7 pagesConfiguration Management and ISO 9001Simone MeschinoNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On Incepta PharmaceutiDocument31 pagesInternship Report On Incepta PharmaceutihhaiderNo ratings yet
- Abbadvant 800 XaDocument9 pagesAbbadvant 800 XaAlexNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam Machining (LBM)Document10 pagesLaser Beam Machining (LBM)RAMAKANT RANANo ratings yet