0% found this document useful (0 votes)
876 views16 pagesUnit 2.2 Multivibrator
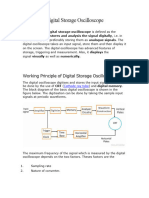
1. Multivibrators are pulse generation circuits that produce square wave output signals.
2. There are three main types of multivibrators - astable, monostable, and bistable. Astable multivibrators continuously switch between two states, monostable have one stable state, and bistables have two stable states.
3. Multivibrators find applications in generating clock signals for sequential logic circuits as well as in applications like timers, missing pulse detectors, and frequency division.
Uploaded by
RohitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
876 views16 pagesUnit 2.2 Multivibrator
1. Multivibrators are pulse generation circuits that produce square wave output signals.
2. There are three main types of multivibrators - astable, monostable, and bistable. Astable multivibrators continuously switch between two states, monostable have one stable state, and bistables have two stable states.
3. Multivibrators find applications in generating clock signals for sequential logic circuits as well as in applications like timers, missing pulse detectors, and frequency division.
Uploaded by
RohitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16