100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views4 pagesAstable Multivibrator Overview and Applications
An astable multivibrator uses two transistors connected in a feedback loop to produce a continuous train of pulses without any external triggering. As one transistor turns on, it causes the other to turn off, and vice versa, resulting in a square wave oscillating output. The frequency of oscillations depends on the RC time constants of the circuit and can be controlled by varying the resistor and capacitor values. Astable multivibrators have applications in timer circuits and systems requiring a continuous train of pulses like Morse code generators.
Uploaded by
DaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views4 pagesAstable Multivibrator Overview and Applications
An astable multivibrator uses two transistors connected in a feedback loop to produce a continuous train of pulses without any external triggering. As one transistor turns on, it causes the other to turn off, and vice versa, resulting in a square wave oscillating output. The frequency of oscillations depends on the RC time constants of the circuit and can be controlled by varying the resistor and capacitor values. Astable multivibrators have applications in timer circuits and systems requiring a continuous train of pulses like Morse code generators.
Uploaded by
DaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
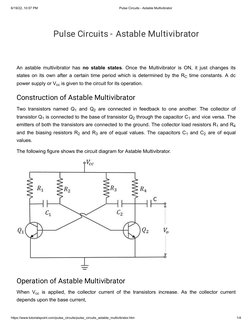
- Construction of Astable Multivibrator: Explains the construction details and components involved in making an astable multivibrator circuit.
- Operation of Astable Multivibrator: Describes the operation and functioning of an astable multivibrator including the role of current and voltage.
- Introduction to Astable Multivibrator: Describes what an astable multivibrator is and introduces the basic concept and its power supply.
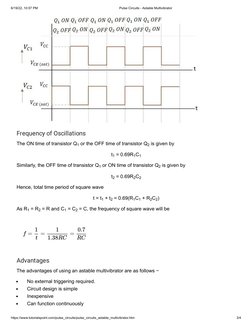
- Waveforms: Discusses the output waveform characteristics at different transistor collectors.
- Advantages: Lists the benefits of using an astable multivibrator, particularly in creating square waves.
- Frequency of Oscillations: Calculates and explains the frequency of oscillations in the astable multivibrator circuit.
- Applications: Describes various applications of astable multivibrators in different electronic systems.
- Disadvantages: Outlines the downsides of using an astable multivibrator including energy aspects.