Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AMT215 A Aviation Safety (Part 1)
Uploaded by
ricky fluor50Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AMT215 A Aviation Safety (Part 1)
Uploaded by
ricky fluor50Copyright:
Available Formats
AMT215 (Aviation safety)
AAMT 2- 6
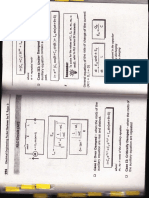
1. Danger signs
Fire - Safety regulations control aircraft materials and the requirements for automated
fire safety systems. Usually these requirements take the form of required tests. The
tests measure flammability of materials and toxicity of smoke. When the tests fail, it is on
a prototype in an engineering laboratory rather than in an aircraft.
2. Caution signs
Bird strike is an aviation term for a collision between a bird and an aircraft.
Fatal accidents have been caused by both engine failure following bird
ingestion and bird strikes breaking cockpit windshields.
The highest risk of a bird strike occurs during takeoff and landing in the vicinity of airports, and
during low-level flying by military aircraft, crop dusters and
helicopters for example. Some airports use active countermeasures,
ranging from a person with a shotgun through recorded sounds of
predators to employing falconers. Poisonous grass can be planted
that is not palatable to birds, nor to insects that
attract insectivorous birds. Passive countermeasures involve
sensible land-use management, avoiding conditions attracting flocks
of birds to the area (e.g. landfills). Another tactic found effective is to
let the grass at the airfield grow taller (approximately 12 inches
(30 cm)) as some species of birds won't land if they cannot see one a
not.
3. Safety instruction signs
The touchdown zone markings identify the touchdown zone for landing operations and are coded
to provide distance information in 500 feet (150m) increments. These markings consist of groups
of one, two, and three rectangular bars symmetrically arranged in pairs about the runway
centerline, as shown in figure, Precision Instrument Runway Markings. For runways having
touchdown zone markings on both ends, those pairs of markings which extend to within 900 feet
(270m) of the midpoint between the thresholds are eliminated.
4. Information signs
Electromagnetic interference - The use of certain electronic equipment is partially
or entirely prohibited as it might interfere with aircraft operation, such as
causing compass deviations.[ Use of some types of personal electronic devices is
prohibited when an aircraft is below 10,000', taking off, or landing. Use of a mobile
phone is prohibited on most flights because in-flight usage creates problems with
ground-based cells.
You might also like
- Bird Strike Prevention PresentationDocument28 pagesBird Strike Prevention PresentationSachintha DilrukshaNo ratings yet
- AMT215 A Aviation Safety (Part 1)Document1 pageAMT215 A Aviation Safety (Part 1)rii amosNo ratings yet
- AMT215 R Aviation Safety (Part 2)Document2 pagesAMT215 R Aviation Safety (Part 2)rii amosNo ratings yet
- Arresting SystemsDocument5 pagesArresting SystemsVishwajeet SinghNo ratings yet
- AAI Intership and Major Project ProposalDocument14 pagesAAI Intership and Major Project ProposalPRAYUSHI KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- Bird StrikesDocument7 pagesBird StrikesBrad MillerNo ratings yet
- Trans Part IDocument11 pagesTrans Part IabhilashjanaNo ratings yet
- Bird Strike Risk and Avoidance PDFDocument2 pagesBird Strike Risk and Avoidance PDFRémi WatineNo ratings yet
- WP27Document28 pagesWP27Worra ThanaNo ratings yet
- Air Carrier Flight Crew Guide - Birdstrike MitigationDocument3 pagesAir Carrier Flight Crew Guide - Birdstrike MitigationFabio MassasogniNo ratings yet
- Aviation SafetyDocument38 pagesAviation SafetyDron ThakurNo ratings yet
- 23-00-00 - COMMUNICATIONS: 23-00-00 PB 001 Conf 00 - Communications - Description and OperationDocument2 pages23-00-00 - COMMUNICATIONS: 23-00-00 PB 001 Conf 00 - Communications - Description and OperationYousefNo ratings yet
- Components of The Aviation Infrastructure - Airport Terminal BuildingsDocument8 pagesComponents of The Aviation Infrastructure - Airport Terminal BuildingsJackielou Marmojada DomaelNo ratings yet
- Firefighter Manual 2021Document162 pagesFirefighter Manual 2021Jose GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Agemp Two MarksDocument8 pagesAgemp Two MarksKishore CrazeNo ratings yet
- Cap562 7Document271 pagesCap562 7DavidGarcíaNo ratings yet
- AvionicsDocument108 pagesAvionicsChiranjivi KuthumiNo ratings yet
- Reduction of RiskDocument16 pagesReduction of RiskGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Air Traffic ControlDocument18 pagesAir Traffic ControlBibithaNo ratings yet
- ADD SameeullahDocument4 pagesADD Sameeullahshahbaz naichNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Bird Repeller For AviationDocument4 pagesUltrasonic Bird Repeller For AviationsanketNo ratings yet
- Aula 21Document3 pagesAula 21Leonardo JoseNo ratings yet
- Airport GeometryDocument62 pagesAirport Geometry20BME114Umang KaushalNo ratings yet
- Monitoring: Glass CockpitDocument4 pagesMonitoring: Glass CockpitSealtiel1020100% (1)
- Air Traffic Control SystemDocument20 pagesAir Traffic Control SystemTarun singhNo ratings yet
- Airspace Classification LNDocument47 pagesAirspace Classification LNM S PrasadNo ratings yet
- Ground Vehicle Guide Proof FinalDocument22 pagesGround Vehicle Guide Proof FinalPhanom BoonthanomNo ratings yet
- Security 03Document5 pagesSecurity 03eshNo ratings yet
- APM Session 2Document41 pagesAPM Session 2chuxuan hengNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Rescue and Fire Fighting CommunicationsDocument22 pagesAircraft Rescue and Fire Fighting CommunicationsMelissa Gonzalez TorresNo ratings yet
- To Include Winds and Temperatures Aloft. This Paperwork Is Given To The PilotsDocument12 pagesTo Include Winds and Temperatures Aloft. This Paperwork Is Given To The PilotsMixaelNo ratings yet
- Montaño Activity.Document3 pagesMontaño Activity.harrismontano98No ratings yet
- Airport Operations: By: Zuliana IsmailDocument30 pagesAirport Operations: By: Zuliana Ismailzuliana0% (1)
- Atc PDFDocument17 pagesAtc PDFNick AvisNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: 2 Mark Question and AnswersDocument11 pagesQuestion Bank: 2 Mark Question and Answersraj6062No ratings yet
- Air Traffic Control System 5784 FioanYwDocument29 pagesAir Traffic Control System 5784 FioanYwMamidi Chola SaikiranNo ratings yet
- ATC - Air Traffic Control: K.SasidharDocument29 pagesATC - Air Traffic Control: K.SasidharTeju JagadaleNo ratings yet
- AirtrafficcontrolDocument17 pagesAirtrafficcontrol198W1A0125Sec-A MADIPALLI KRANTHI BHUSHANNo ratings yet
- Air Traffic ManagementDocument7 pagesAir Traffic ManagementHamza MughalNo ratings yet
- Acfrogc Vkul4ir6qjbuygkobnz8h4qbc Fphzkjwu8k1osezbqmhdqz8s Irbx6ts8o2 Uj1dyupotr9p8 Ye7mon9gr9wpaw4tjyjvfxyeu2irwc0wjx4xkspca Zzg3gabjxbkehjrvc7fuciDocument27 pagesAcfrogc Vkul4ir6qjbuygkobnz8h4qbc Fphzkjwu8k1osezbqmhdqz8s Irbx6ts8o2 Uj1dyupotr9p8 Ye7mon9gr9wpaw4tjyjvfxyeu2irwc0wjx4xkspca Zzg3gabjxbkehjrvc7fuciHGAATC OfficeNo ratings yet
- PreviewDocument108 pagesPreviewangelNo ratings yet
- Human Factors and Aviation SafetyDocument20 pagesHuman Factors and Aviation SafetyZai CastroNo ratings yet
- Internship at AAI BarodaDocument24 pagesInternship at AAI BarodaShubham Sehrawat100% (1)
- Techncal SeminarDocument21 pagesTechncal SeminarJanani ankamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 The AirfieldDocument42 pagesChapter 4 The AirfieldAshvariya AishuNo ratings yet
- Air Traffic ControlDocument12 pagesAir Traffic ControlDatta Mks100% (1)
- Basic Concepts of AirportDocument29 pagesBasic Concepts of AirportAravind KPNo ratings yet
- AVM 101-23 W9 YansılarDocument146 pagesAVM 101-23 W9 Yansılarcr7b.gomisNo ratings yet
- Janani Part 2Document14 pagesJanani Part 2Janani ankamNo ratings yet
- Air Traffic ControlDocument24 pagesAir Traffic ControlPrabhakar Kumar Barnwal100% (1)
- Transportation SafetyDocument4 pagesTransportation SafetyApril Vicenta Anacion PambidNo ratings yet
- TCAS AircraftDocument20 pagesTCAS AircraftPrabuddha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Report No. 04: BARUZO, Ian Titus P. Instructor: Date: 8 Mar 2019 Page 1 of 4 Issue No. 1 RatingDocument4 pagesReport No. 04: BARUZO, Ian Titus P. Instructor: Date: 8 Mar 2019 Page 1 of 4 Issue No. 1 RatingCuden JohnmelNo ratings yet
- Security 1Document6 pagesSecurity 1eshNo ratings yet
- Government of India Technical Centre, Opp. Safdurjung Airport, New DelhiDocument9 pagesGovernment of India Technical Centre, Opp. Safdurjung Airport, New DelhimurugeshNo ratings yet
- Guidance Material On Aerodrome ICAO Annex 14 SurfacesDocument21 pagesGuidance Material On Aerodrome ICAO Annex 14 SurfacesAbu Zulkarnain Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Distancias Equipamentos PistaDocument8 pagesDistancias Equipamentos Pistagiant360No ratings yet
- Acp34 2Document141 pagesAcp34 2pilot digitalNo ratings yet
- Controlled and Uncontrolled AirspaceDocument26 pagesControlled and Uncontrolled AirspaceShabrish ShabriNo ratings yet
- Img - 0036 MCQ For Power & Ipe 63aDocument1 pageImg - 0036 MCQ For Power & Ipe 63aricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0034 MCQ For Power & Ipe 59aDocument1 pageImg - 0034 MCQ For Power & Ipe 59aricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0038 MCQ For Power & Ipe 67Document1 pageImg - 0038 MCQ For Power & Ipe 67ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0037 MCQ For Power & Ipe 65Document1 pageImg - 0037 MCQ For Power & Ipe 65ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- IMG - 0111 PSME Code 2008 102Document1 pageIMG - 0111 PSME Code 2008 102ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- IMG - 0119 PSME Code 2008 110Document1 pageIMG - 0119 PSME Code 2008 110ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- IMG - 0117 PSME Code 2008 108Document1 pageIMG - 0117 PSME Code 2008 108ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0039 MCQ For Power & Ipe 69Document1 pageImg - 0039 MCQ For Power & Ipe 69ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0031 MCQ For Power & Ipe 53Document1 pageImg - 0031 MCQ For Power & Ipe 53ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0033 MCQ For Power & Ipe 57aDocument1 pageImg - 0033 MCQ For Power & Ipe 57aricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0040 MCQ For Power & Ipe 71Document1 pageImg - 0040 MCQ For Power & Ipe 71ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- IMG - 0115 PSME Code 2008 106Document1 pageIMG - 0115 PSME Code 2008 106ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0032 MCQ For Power & Ipe 55Document1 pageImg - 0032 MCQ For Power & Ipe 55ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- IMG - 0118 ESAS 2001 Solved Problem Objectives 21-47Document1 pageIMG - 0118 ESAS 2001 Solved Problem Objectives 21-47ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- IMG - 0074 PSME Code 2012 73Document1 pageIMG - 0074 PSME Code 2012 73ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- IMG - 0113 PSME Code 2008 104Document1 pageIMG - 0113 PSME Code 2008 104ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- IMG - 0078 PSME Code 2012 77Document1 pageIMG - 0078 PSME Code 2012 77ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0082 MCQ Ece Board Exam 151Document1 pageImg - 0082 MCQ Ece Board Exam 151ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- IMG - 0072 PSME Code 2012 71Document1 pageIMG - 0072 PSME Code 2012 71ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- IMG - 0080 PSME Code 2012 79Document1 pageIMG - 0080 PSME Code 2012 79ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- IMG - 0076 PSME Code 2012 75Document1 pageIMG - 0076 PSME Code 2012 75ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- IMG - 0071 PSME Code 2012 70Document1 pageIMG - 0071 PSME Code 2012 70ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0086 MCQ Ece Board Exam 159Document1 pageImg - 0086 MCQ Ece Board Exam 159ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0087 MCQ Ece Board Exam 161Document1 pageImg - 0087 MCQ Ece Board Exam 161ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0085 MCQ Ece Board Exam 157Document1 pageImg - 0085 MCQ Ece Board Exam 157ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0100 MCQ Ree Board Exam 193Document1 pageImg - 0100 MCQ Ree Board Exam 193ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0101 MCQ Ree Board Exam 195Document1 pageImg - 0101 MCQ Ree Board Exam 195ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0096 MCQ Ree Board Exam 185Document1 pageImg - 0096 MCQ Ree Board Exam 185ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0083 MCQ Ece Board Exam 153Document1 pageImg - 0083 MCQ Ece Board Exam 153ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- Img - 0098 MCQ Ree Board Exam 189Document1 pageImg - 0098 MCQ Ree Board Exam 189ricky fluor50No ratings yet
- British Midland Flight ADocument2 pagesBritish Midland Flight AattiqueNo ratings yet
- Accidenta Study and Analysis: Presented by Ravindra CDocument33 pagesAccidenta Study and Analysis: Presented by Ravindra CEng-Mohammed TwiqatNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare For Your Skills / "Behind-the-Wheel" Test For A Non-Commercial Class C Driver's LicenseDocument5 pagesHow To Prepare For Your Skills / "Behind-the-Wheel" Test For A Non-Commercial Class C Driver's LicenseCristian C. OlayaNo ratings yet
- Collision Avoidance System ProjectDocument20 pagesCollision Avoidance System ProjectMeharaj MehaNo ratings yet
- Helicopter OperationDocument15 pagesHelicopter OperationNguyễnBìnhPhương100% (1)
- COP For Road Opening WorkDocument60 pagesCOP For Road Opening WorkSun QuanNo ratings yet
- 10 AmperDocument54 pages10 AmperPy LabNo ratings yet
- C003 Forklifts ADocument1 pageC003 Forklifts Appimaintenance23No ratings yet
- JHA Sewer Drain Example Full Report JSEAsy 2021Document15 pagesJHA Sewer Drain Example Full Report JSEAsy 2021Alexander B. ApanNo ratings yet
- Balancesheet B737-300 InstruccionDocument1 pageBalancesheet B737-300 InstruccionCarlos JaldinNo ratings yet
- Aviation - Model TemplateDocument1 pageAviation - Model TemplateJagadeep MNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper Edited AssignmentDocument13 pagesConcept Paper Edited AssignmentOmar NabilNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Crashes Involving QLINE 2017-2021Document48 pagesVehicle Crashes Involving QLINE 2017-2021Malachi BarrettNo ratings yet
- Bulletin-Inspection Engine MountDocument3 pagesBulletin-Inspection Engine MountdianaNo ratings yet
- Road Safety BrochureDocument2 pagesRoad Safety BrochureOlango Joy COOPNo ratings yet
- 3 1 Road Accidents in Tamil NaduDocument20 pages3 1 Road Accidents in Tamil NaduKRISHNA RAJ JNo ratings yet
- 5 - Highway Functional ClassificationDocument16 pages5 - Highway Functional ClassificationPenelope MalilweNo ratings yet
- Tugade vs. CA 85 SCRA 226Document6 pagesTugade vs. CA 85 SCRA 226Aerith AlejandreNo ratings yet
- Traffic Accident ThesisDocument6 pagesTraffic Accident ThesisKatie Naple100% (2)
- Fuel Tank Safety (FTS) & Critical Design Configuration Control Limitations (CDCCL)Document44 pagesFuel Tank Safety (FTS) & Critical Design Configuration Control Limitations (CDCCL)Suman BajracharyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Problem IdentificationDocument1 pageAssignment 1 - Problem IdentificationYAHAMPATH ARACHCHIGE PASAN MADURA YahampathNo ratings yet
- Safety Alert Monkeys Fists On Heaving LinesDocument1 pageSafety Alert Monkeys Fists On Heaving LinesMagrillonNo ratings yet
- Texting While Walking ListeningDocument2 pagesTexting While Walking ListeningIrene TamayNo ratings yet
- Liva MRTA FormDocument1 pageLiva MRTA FormBharat SinghNo ratings yet
- Road AccidentDocument2 pagesRoad AccidentRAKESH YADAVNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Check ListDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Check ListSalman EidNo ratings yet
- 4-HOUR Course: National Traffic Incident Management (Tim) Responder Training Program: North Carolina-SpecificDocument21 pages4-HOUR Course: National Traffic Incident Management (Tim) Responder Training Program: North Carolina-SpecificKevin Christ PadilloNo ratings yet
- Upset RecoveryDocument28 pagesUpset RecoveryricardotorresNo ratings yet
- Focus XR5Document173 pagesFocus XR5guff01No ratings yet
- Henri Coanda International Airport Bucharest (OTP) August 26, 2020 Istanbul Airport Istanbul (IST)Document1 pageHenri Coanda International Airport Bucharest (OTP) August 26, 2020 Istanbul Airport Istanbul (IST)Mariana AndroneNo ratings yet