Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stub 4.3
Uploaded by
BrcakOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stub 4.3
Uploaded by
BrcakCopyright:
Available Formats
Page: 1/10
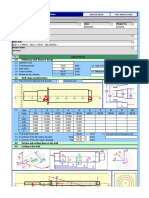
Project: Model: Prosta-greda-4.3 Sheet: 1
Cartesian 1.1 NODES
Node Reference Coordinate Node Coordinates
No. Node Type Node System X [mm] Y [mm] Z [mm] Comment
2 Standard - Cartesian 0.0 0.0 6300.0
3 Standard - Cartesian 0.0 0.0 2500.0 Supported
4 Standard - Cartesian 0.0 0.0 5400.0 Supported
5 Standard - Cartesian 0.0 0.0 4500.0
1.2 LINES
Line Line Length
No. Line Type Nodes No. L [mm] Comment
2 Polyline 4,5 900.0 Z
3 Polyline 2,4 900.0 Z
4 Polyline 5,3 2000.0 Z
1.3 MATERIALS
Matl. Modulus Modulus Poisson's Ratio Spec. Weight Coeff. of Th. Exp. Partial Factor Material
No. E [kN/cm 2] G [kN/cm 2] [-] [kN/m 3] [1/°C] M [-] Model
1 Steel S 235 | EN 10025-2:2004-11
21000.00 8076.92 0.300 78.50 1.20E-05 1.00 Isotropic Linear
Elastic
2 Aluminum EN-AW 6060 (ET,ER/B) T66 | EN 1999-1-1:2007
7000.00 2700.00 0.296 27.00 2.30E-05 1.00 Isotropic Linear
Elastic
1.7 NODAL SUPPORTS
Support Column Support Conditions
No. Nodes No. Axis System in Z uX/uX' uY/uY' uZ/uZ' X/X' Y/Y' Z/Z'
2 3 User Defined X',Y',Z'
3 2 Global X,Y,Z
1.7.10 NODAL SUPPORTS - NONLINEARITIES - SCAFFOLDING - PZ'/PHIX' PHIY',
ABSOLUTE
Support Direction Rotation [°] Coordinate 1st Node 1 Node 2 2nd Referen Member/Line
No. Type Sequence about X about Y about Z System axis No. No. axis Node No.
2 Rotated ZYX 0.00 -90.00 0.00
TO 150/50/2/2/2/2 TO 116/44/5/5/5/5
1.13 CROSS-SECTIONS
Section Matl. J [mm 4] Iy [mm 4] Iz [mm 4] Principal Axes Rotation Overall Dimensions [mm]
No. No. A [mm 2] Ay [mm 2] Az [mm 2] [°] ' [°] Width b Height h
1 TO 150/50/2/2/2/2
TO 150/44/3/3/3/3
2 1030980.3 2132645.3 378245.3 0.00 0.00 50.0 150.0
784.0 104.6 549.5
2 TO 116/44/5/5/5/5
1 1261849.4 2348740.0 476260.0 0.00 0.00 44.0 116.0
1500.0 224.9 1033.7
3 TO 150/44/3/3/3/3
2 1162683.8 2919384.0 406336.0 0.00 0.00 44.0 150.0
1128.0 123.5 818.5
1.17 MEMBERS
Mbr. Line Rotation Cross-Section Hinge No. Ecc. Div. Length
No. No. Member Type [°] Start End Start End No. No. L [mm]
4 4 Beam Angle 0.00 1 1 - - - - 2000.0 Z
5 2 Beam Angle 0.00 1 1 - - - - 900.0 Z
6 3 Beam Angle 0.00 1 1 - - - - 900.0 Z
RFEM 5.25.02 - General 3D structures solved using FEM www.dlubal.com
Page: 2/10
Project: Model: Prosta-greda-4.3 Sheet: 1
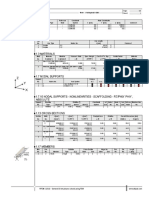
MODEL
Node Numbering Isometric
Member Numbering 2
Cross-Section Description
M6
4
TO 150/50/2/2/2/2
M5
5
TO 150/50/2/2/2/2
3800.0
M4
TO 150/50/2/2/2/2
2.1 LOAD CASES
Load Load Case EN 1990 | CEN Self-Weight - Factor in Direction
Case Description Action Category Active X Y Z
LC1 Permanent 0.000 0.000 -1.000
LC2 Wind Wind
2.1.1 LOAD CASES
Load Load Case
Case Description Calculation Parameters
LC1 Method of analysis : Geometrically linear analysis
Method for solving system of : Newton-Raphson
nonlinear algebraic equations
Activate stiffness factors of: : Cross-sections (factor for J, Iy, I z, A, Ay, Az)
: Members (factor for GJ, EIy, EIz, EA, GA y, GAz)
LC2 Wind Method of analysis : Geometrically linear analysis
Method for solving system of : Newton-Raphson
nonlinear algebraic equations
Activate stiffness factors of: : Cross-sections (factor for J, Iy, I z, A, Ay, Az)
: Members (factor for GJ, EIy, EIz, EA, GA y, GAz)
2.5 LOAD COMBINATIONS
Load Load Combination
Combin. DS Description No. Factor Load Case
CO1 Uls 1 1.35 LC1
2 1.50 LC2 Wind
CO2 1.35*LC1 + 1.5*LC2 1 1.35 LC1
2 1.50 LC2 Wind
2.5.2 LEHR'S DAMPING DIFFERENT FOR EACH LOAD CASE
Load
Combin. Description Calculation Parameters
CO1 Uls Method of analysis : Second order analysis (P-Delta)
Method for solving system of : Picard
nonlinear algebraic equations
Options : Consider favorable effects due to tension
: Refer internal forces to deformed system for:
RFEM 5.25.02 - General 3D structures solved using FEM www.dlubal.com
Page: 3/10
Project: Model: Prosta-greda-4.3 Sheet: 1
2.5.2 LEHR'S DAMPING DIFFERENT FOR EACH LOAD CASE
Load
Combin. Description Calculation Parameters
Normal forces N
Shear forces Vy and Vz
Moments My, Mz and MT
Activate stiffness factors of: : Materials (partial factor M)
: Cross-sections (factor for J, Iy, I z, A, Ay, Az)
: Members (factor for GJ, EIy, EIz, EA, GA y, GAz)
CO2 1.35*LC1 + 1.5*LC2 Method of analysis : Second order analysis (P-Delta)
Method for solving system of : Picard
nonlinear algebraic equations
Options : Consider favorable effects due to tension
: Refer internal forces to deformed system for:
Normal forces N
Shear forces Vy and Vz
Moments My, Mz and MT
Activate stiffness factors of: : Materials (partial factor M)
: Cross-sections (factor for J, Iy, I z, A, Ay, Az)
: Members (factor for GJ, EIy, EIz, EA, GA y, GAz)
LC1 3.2 MEMBER LOADS LC1
Reference On Members Load Load Load Reference Load Parameters
No. to No. Type Distribution Direction Length Symbol Value Unit
1 Members 6 Force Concentr. ZL True Length P -0.950 kN
A 350.0 mm
5 Members 5 Force Concentr. ZL True Length P -0.800 kN
A 100.0 mm
6 Members 4 Force Concentr. ZL True Length P -0.950 kN
A 800.0 mm
3.2/2 WIND ON ICE|WI|WI|WIND ON ICE LC1
Reference On Members Absolute Offset Relative Offset
No. to No. eY [mm] eZ [mm] y-Axis z-Axis
1 Members 6 0.0 0.0 Middle Middle
5 Members 5 0.0 0.0 Middle Middle
6 Members 4 0.0 0.0 Middle Middle
3.1 NODAL LOADS - BY COMPONENTS
LC2 - COORDINATE SYSTEM LC2: Wind
Wind On Nodes Coordinate Force [kN] Moment [kNmm]
No. No. System PX / P U PY / PV PZ / P W MX / MU MY / MV MZ / MW
1 2 0 | Global XYZ 0.823 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
3.2 MEMBER LOADS LC2: Wind
Reference On Members Load Load Load Reference Load Parameters
No. to No. Type Distribution Direction Length Symbol Value Unit
1 Members 6 Force Uniform z True Length p 0.600 kN/m
2 Members 4,5 Force Uniform z True Length p 0.600 kN/m
3.2/1 WIND LOADS – FWK – EXECUTION|6.2||WIND LOADS LC2: Wind
Reference On Members Absolute Offset Absolute Offset Relative Offset Relative Offset
No. to No. Mbr. Start Mbr. Start Mbr. End Mbr. End Mbr. Start Mbr. Start Mbr. End Mbr. End
eY [mm] eZ [mm] eY [mm] eZ [mm] y-Axis z-Axis y-Axis z-Axis
1 Members 6 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 Middle Middle Middle Middle
2 Members 4,5 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 Middle Middle Middle Middle
RFEM 5.25.02 - General 3D structures solved using FEM www.dlubal.com
Page: 4/10
Project: Model: Prosta-greda-4.3 Sheet: 1
LC2: WIND
LC2 : Wind Isometric
Loads [kN/m], [kN] 0.823 2
0.600
0.600
3800.0
0.600
RFEM 5.25.02 - General 3D structures solved using FEM www.dlubal.com
Page: 5/10
Project: Model: Prosta-greda-4.3 Sheet: 1
4.0 RESULTS - SUMMARY
Description Value Unit Comment
Load Case LC1
Sum of loads in X 0.000 kN
Sum of support reactions in X 0.000 kN
Sum of loads in Y 0.000 kN
Sum of support reactions in Y 0.000 kN
Sum of loads in Z -2.780 kN
Sum of support reactions in Z -2.780 kN Deviation 0.00%
Resultant of reactions about X 0.000 kNmm At center of gravity of model (X:0.000, Y:0.000, Z:4400.000 mm)
Resultant of reactions about Y 0.000 kNmm At center of gravity of model
Resultant of reactions about Z 0.000 kNmm At center of gravity of model
Max. displacement in X 0.0 mm
Max. displacement in Y 0.0 mm
Max. displacement in Z -0.1 mm Member No. 4, x: 2000.0 mm
Max. vector displacement 0.1 mm Member No. 4, x: 2000.0 mm
Max. rotation about X 0.00 °
Max. rotation about Y 0.00 °
Max. rotation about Z 0.00 °
Maximum member strain 0.000 mm/m Member No. 0, x: 0.0 mm
Method of analysis Linear Geometrically linear analysis
Reduction of stiffness Cross-sections, Members, Surfaces
Number of load increments 1
Number of iterations 1
Maximum value of element of stiffness matrix on 1.22E+08
diagonal
Minimum value of element of stiffness matrix on 1.E+03
diagonal
Stiffness matrix determinant 3.544E+113
Infinity Norm 2.439E+08
Load Case LC2 - Wind
Sum of loads in X 3.103 kN
Sum of support reactions in X 3.103 kN Deviation 0.00%
Sum of loads in Y 0.000 kN
Sum of support reactions in Y 0.000 kN
Sum of loads in Z 0.000 kN
Sum of support reactions in Z 0.000 kN
Resultant of reactions about X 0.000 kNmm At center of gravity of model (X:0.000, Y:0.000, Z:4400.000 mm)
Resultant of reactions about Y 1563.700 kNmm At center of gravity of model
Resultant of reactions about Z 0.000 kNmm At center of gravity of model
Max. displacement in X 10.9 mm Member No. 4, x: 0.0 mm
Max. displacement in Y 0.0 mm
Max. displacement in Z 0.0 mm
Max. vector displacement 10.9 mm Member No. 4, x: 0.0 mm
Max. rotation about X 0.00 °
Max. rotation about Y 0.53 ° Member No. 4, x: 2000.0 mm
Max. rotation about Z 0.00 °
Maximum member strain 0.000 mm/m Member No. 0, x: 0.0 mm
Method of analysis Linear Geometrically linear analysis
Reduction of stiffness Cross-sections, Members, Surfaces
Number of load increments 1
Number of iterations 1
Maximum value of element of stiffness matrix on 1.22E+08
diagonal
Minimum value of element of stiffness matrix on 1.E+03
diagonal
Stiffness matrix determinant 3.544E+113
Infinity Norm 2.439E+08
Load Combination CO1 - Uls
Sum of loads in X 4.655 kN
Sum of support reactions in X 4.655 kN Deviation 0.00%
Sum of loads in Y 0.000 kN
Sum of support reactions in Y 0.000 kN
Sum of loads in Z -3.754 kN
Sum of support reactions in Z -3.754 kN Deviation 0.00%
Resultant of reactions about X 0.00 kNmm At center of gravity of model (X:0.00, Y:0.00, Z:4400.00 mm)
Resultant of reactions about Y 2377.03 kNmm At center of gravity of model
Resultant of reactions about Z 0.00 kNmm At center of gravity of model
Max. displacement in X 16.2 mm Member No. 4, x: 200.0 mm
Max. displacement in Y 0.0 mm
Max. displacement in Z -0.1 mm Member No. 4, x: 2000.0 mm
Max. vector displacement 16.2 mm Member No. 4, x: 200.0 mm
Max. rotation about X 0.00 °
Max. rotation about Y 0.78 ° Member No. 4, x: 2000.0 mm
Max. rotation about Z 0.00 °
Maximum member strain 0.000 mm/m Member No. 0, x: 0.0 mm
Method of analysis 2nd Order Second order analysis (Nonlinear, Timoshenko)
Internal forces referred to deformed system for... N, Vy, Vz, My, Mz, M T
Reduction of stiffness Materials, Cross-sections, Members, Surfaces
Consider favorable effects of tensile forces
Divide results by CO factor
Number of load increments 1
Number of iterations 2
Maximum value of element of stiffness matrix on 1.22E+08
diagonal
Minimum value of element of stiffness matrix on 1.E+01
diagonal
Stiffness matrix determinant 5.459E+101
Infinity Norm 2.439E+08
Load Combination CO2 - 1.35*LC1 + 1.5*LC2
Sum of loads in X 4.655 kN
Sum of support reactions in X 4.655 kN Deviation 0.00%
RFEM 5.25.02 - General 3D structures solved using FEM www.dlubal.com
Page: 6/10
Project: Model: Prosta-greda-4.3 Sheet: 1
4.0 RESULTS - SUMMARY
Description Value Unit Comment
Sum of loads in Y 0.000 kN
Sum of support reactions in Y 0.000 kN
Sum of loads in Z -3.754 kN
Sum of support reactions in Z -3.754 kN Deviation 0.00%
Resultant of reactions about X 0.00 kNmm At center of gravity of model (X:0.00, Y:0.00, Z:4400.00 mm)
Resultant of reactions about Y 2377.03 kNmm At center of gravity of model
Resultant of reactions about Z 0.00 kNmm At center of gravity of model
Max. displacement in X 16.2 mm Member No. 4, x: 200.0 mm
Max. displacement in Y 0.0 mm
Max. displacement in Z -0.1 mm Member No. 4, x: 2000.0 mm
Max. vector displacement 16.2 mm Member No. 4, x: 200.0 mm
Max. rotation about X 0.00 °
Max. rotation about Y 0.78 ° Member No. 4, x: 2000.0 mm
Max. rotation about Z 0.00 °
Maximum member strain 0.000 mm/m Member No. 0, x: 0.0 mm
Method of analysis 2nd Order Second order analysis (Nonlinear, Timoshenko)
Internal forces referred to deformed system for... N, Vy, Vz, My, Mz, M T
Reduction of stiffness Materials, Cross-sections, Members, Surfaces
Consider favorable effects of tensile forces
Divide results by CO factor
Number of load increments 1
Number of iterations 2
Maximum value of element of stiffness matrix on 1.22E+08
diagonal
Minimum value of element of stiffness matrix on 1.E+01
diagonal
Stiffness matrix determinant 5.459E+101
Infinity Norm 2.439E+08
Summary
Max. displacement in X 16.2 mm CO1, Member No. 4, x: 200.0 mm
Max. displacement in Y 0.0
Max. displacement in Z -0.1 mm CO1, Member No. 4, x: 2000.0 mm
Max. vector displacement 16.2 mm CO1, Member No. 4, x: 200.0 mm
Max. rotation about X 0.00
Max. rotation about Y 0.78 ° CO1, Member No. 4, x: 2000.0 mm
Max. rotation about Z 0.00
Other Settings:
Number of 1D finite elements 3
Number of 2D finite elements 0
Number of 3D finite elements 0
Number of FE mesh nodes 4
Number of equations 24
Internal forces referred to deformed system for...:
Max. number of iterations 100
Number of divisions for member results 10
Division of cable/foundation/tapered members 10
Number of member divisions for searching 10
maximum values
Subdivisions of FE mesh for graphical results 3
Percentage of iterations according to Picard 5 %
method in combination with Newton-Raphson
method
Options:
Activate shear stiffness of members (Ay, Az)
Activate member divisions for large deformation or
post-critical analysis
Activate entered stiffness modifications
Ignore rotational degrees of freedom
Check of critical forces of members
Nonsymmetric direct solver if demanded by
nonlinear model
Method for the system of equations Direct
Plate bending theory Mindlin
Solver version 64-bit
Precision and Tolerance:
Change default setting
4.1 NODES - SUPPORT FORCES
Node Support Forces [kN] Support Moments [kNmm]
No. LC/CO PX' PY' PZ' MX' MY' MZ'
2 LC1 0.000 0.000 -2.780 0.000 0.000 0.000
LC2 1.963 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 Wind
CO1 2.953 0.000 -3.754 0.000 0.000 0.000 Uls
CO2 2.953 0.000 -3.754 0.000 0.000 0.000
3* LC1 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
LC2 0.000 0.000 -1.140 0.000 0.000 0.000 Wind
CO1 0.000 0.000 -1.702 0.000 0.000 0.000 Uls
CO2 0.000 0.000 -1.702 0.000 0.000 0.000
Supp. LC1 0.000 0.000 -2.780
Loads LC1 0.000 0.000 -2.780
Supp. LC2 3.103 0.000 0.000
Loads LC2 3.103 0.000 0.000
Supp. CO1 4.655 0.000 -3.754
Supp. CO1 4.655 0.000 -3.754
Supp. CO2 4.655 0.000 -3.754
RFEM 5.25.02 - General 3D structures solved using FEM www.dlubal.com
Page: 7/10
Project: Model: Prosta-greda-4.3 Sheet: 1
4.1 NODES - SUPPORT FORCES
Node Support Forces [kN] Support Moments [kNmm]
No. LC/CO PX' PY' PZ' MX' MY' MZ'
Supp. CO2 4.655 0.000 -3.754
4.12 CROSS-SECTIONS - INTERNAL FORCES
Member Node Location Forces [kN] Moments [kNmm]
No. LC/CO No. x [mm] N Vy Vz MT My Mz
Section No. 1: TO 150/50/2/2/2/2
4 LC1 5 0.0 0.992 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
800.0 0.975 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
800.0 0.025 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
3 2000.0 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
LC2 5 0.0 0.000 0.000 -0.060 0.000 -1080.000 0.000
3 2000.0 0.000 0.000 1.140 0.000 0.000 0.000
CO1 5 0.0 1.340 0.000 -0.097 0.000 -1594.680 0.000
800.0 1.321 0.000 0.616 0.000 -1385.410 0.000
800.0 0.039 0.000 0.616 0.000 -1385.400 0.000
3 2000.0 0.023 0.000 1.702 0.000 0.000 0.000
CO2 5 0.0 1.340 0.000 -0.097 0.000 -1594.680 0.000
800.0 1.321 0.000 0.616 0.000 -1385.410 0.000
800.0 0.039 0.000 0.616 0.000 -1385.400 0.000
3 2000.0 0.023 0.000 1.702 0.000 0.000 0.000
5 LC1 4 0.0 1.811 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
100.0 1.809 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
100.0 1.009 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
5 900.0 0.992 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
LC2 4 0.0 0.000 0.000 -0.600 0.000 -783.000 0.000
5 900.0 0.000 0.000 -0.060 0.000 -1080.000 0.000
CO1 4 0.0 2.454 0.000 -0.884 0.000 -1149.220 0.000
100.0 2.450 0.000 -0.798 0.000 -1233.850 0.000
100.0 1.370 0.000 -0.798 0.000 -1233.870 0.000
5 900.0 1.340 0.000 -0.097 0.000 -1594.680 0.000
CO2 4 0.0 2.454 0.000 -0.884 0.000 -1149.220 0.000
100.0 2.450 0.000 -0.798 0.000 -1233.850 0.000
100.0 1.370 0.000 -0.798 0.000 -1233.870 0.000
5 900.0 1.340 0.000 -0.097 0.000 -1594.680 0.000
6 LC1 2 0.0 2.780 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
350.0 2.773 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
350.0 1.823 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
4 900.0 1.811 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
LC2 2 0.0 0.000 0.000 -1.140 0.000 0.000 0.000
4 900.0 0.000 0.000 -0.600 0.000 -783.000 0.000
CO1 2 0.0 3.777 0.000 -1.667 0.000 0.000 0.000
350.0 3.761 0.000 -1.361 0.000 -532.270 0.000
350.0 2.479 0.000 -1.361 0.000 -532.298 0.000
4 900.0 2.454 0.000 -0.884 0.000 -1149.220 0.000
CO2 2 0.0 3.777 0.000 -1.667 0.000 0.000 0.000
350.0 3.761 0.000 -1.361 0.000 -532.270 0.000
350.0 2.479 0.000 -1.361 0.000 -532.298 0.000
4 900.0 2.454 0.000 -0.884 0.000 -1149.220 0.000
RFEM 5.25.02 - General 3D structures solved using FEM www.dlubal.com
Page: 8/10
Project: Model: Prosta-greda-4.3 Sheet: 1
GLOBAL DEFORMATIONS uX, SUPPORT REACTIONS
LC2 : Wind Isometric
Support Reactions[kN] 2
1.963
M6
4
TO 150/50/2/2/2/2
M5
5
TO 150/50/2/2/2/2
10.9
3800.0
M4
TO 150/50/2/2/2/2
3
1.140
Factor of deformations: 35.00
Max P-X': 1.963, Min P-X': 0.000 kN
Max P-Y': 0.000, Min P-Y': 0.000 kN
Max P-Z': 0.000, Min P-Z': -1.140 kN
Max u-X: 10.9, Min u-X: 0.0 mm
RFEM 5.25.02 - General 3D structures solved using FEM www.dlubal.com
Page: 9/10
Project: Model: Prosta-greda-4.3 Sheet: 1
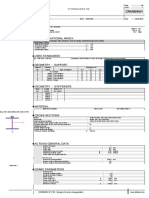
RF-ALUMINUM
CA1
Design of aluminum 1.1 GENERAL DATA
members according to Members to design: All
Eurocode 9 Sets of members to design:
National Annex: CEN
Ultimate Limit State Design
Load combinations to design: CO2 1.35*LC1 + 1.5*LC2
1.2 MATERIALS
Matl. Material E- Modulus Shear Modulus Poisson's Ratio Proof Strength Max. Thickness
No. Description E [ksi] G [ksi] [-] fo [ksi] t [mm]
2 Aluminum EN-AW 6060 (ET, 10152.600 3916.020 0.300 23.206 3.0
ER/B) T66 | EN 1999-1-1:2007
TO 150/50/2/2/2/2 1.3 CROSS-SECTIONS
Sect. Matl. Cross-Section Cross-Section Max Design
No. No. Description Type Ratio Comment
1 2 TO 150/50/2/2/2/2 Box welded 0.39
1.6 EFFECTIVE LENGTHS - MEMBERS
Member Buckling Buckling About Axis y Buckling About Axis z Lateral-Torsional Buckling
No. Possible Possible k cr,y Lcr,y [mm] Possible kcr,z Lcr,z [mm] Possible kz kw Lw [mm] LT [mm]
4 1.00 2000.0 1.00 2000.0 1.0 1.0 2000.0 2000.0
5 1.00 900.0 1.00 900.0 1.0 1.0 900.0 900.0
6 1.00 900.0 1.00 900.0 1.0 1.0 900.0 900.0
2.4 DESIGN BY MEMBER
Member Location LC/CO/ Design Equation Description
No. x [mm] RC No.
4 Cross-section No. 1 - TO 150/50/2/2/2/2
800.0 CO2 0.34 1 106) Cross-section check - Bending about y-axis acc. to 6.2.5
2000.0 CO2 0.03 1 111) Cross-section check - Shear force in z-axis acc. to 6.2.6
2000.0 CO2 0.05 1 122) Cross-section check - Shear buckling acc. to 6.7.4.1 - Shear force in
z-axis
2000.0 CO2 0.05 1 124) Cross-section check - Shear buckling acc. to 6.5.5 - Shear force in
z-axis
800.0 CO2 0.34 1 141) Cross-section check - Bending and shear force acc. to 6.2.5 and
6.2.8
800.0 CO2 0.34 1 150) Cross-section check - Bending, shear force and torsion acc. to 6.7 -
Plate girders
200.0 CO2 0.39 1 171) Cross-section check - Bending, shear and axial force acc. to 6.2.9
200.0 CO2 0.39 1 180) Cross-section check - Bending, shear, axial force and torsion acc.
to 6.7 - Plate girders
5 Cross-section No. 1 - TO 150/50/2/2/2/2
0.0 CO2 0.02 1 111) Cross-section check - Shear force in z-axis acc. to 6.2.6
0.0 CO2 0.03 1 122) Cross-section check - Shear buckling acc. to 6.7.4.1 - Shear force in
z-axis
0.0 CO2 0.03 1 124) Cross-section check - Shear buckling acc. to 6.5.5 - Shear force in
z-axis
900.0 CO2 0.39 1 171) Cross-section check - Bending, shear and axial force acc. to 6.2.9
900.0 CO2 0.39 1 180) Cross-section check - Bending, shear, axial force and torsion acc.
to 6.7 - Plate girders
6 Cross-section No. 1 - TO 150/50/2/2/2/2
0.0 CO2 0.03 1 101) Cross-section check - Tension acc. to 6.2.3
0.0 CO2 0.03 1 111) Cross-section check - Shear force in z-axis acc. to 6.2.6
0.0 CO2 0.05 1 122) Cross-section check - Shear buckling acc. to 6.7.4.1 - Shear force in
z-axis
0.0 CO2 0.05 1 124) Cross-section check - Shear buckling acc. to 6.5.5 - Shear force in
z-axis
900.0 CO2 0.28 1 171) Cross-section check - Bending, shear and axial force acc. to 6.2.9
900.0 CO2 0.28 1 180) Cross-section check - Bending, shear, axial force and torsion acc.
to 6.7 - Plate girders
RFEM 5.25.02 - General 3D structures solved using FEM www.dlubal.com
Page: 10/10
Project: Model: Prosta-greda-4.3 Sheet: 1
DESIGN RATIO
RF-ALUMINUM CA1 Isometric
Ultimate Limit State: Cross-Section Design, Stability Design
2
Max
Design Ratio [-] 0.05
0.39
0.28 4
0.00
Max : 0.39
Min : 0.00
0.39 5
0.39
3
0.05
Max Design Ratio: 0.39
RFEM 5.25.02 - General 3D structures solved using FEM www.dlubal.com
You might also like
- Advaita Vedanta and Modern ScienceDocument63 pagesAdvaita Vedanta and Modern ScienceKaushik Saha100% (1)
- Abs 0056Document17 pagesAbs 0056darrow dori100% (1)
- Stress Analysis Methods For Underground Pipe Lines Part 1 - Basic CalculationsDocument5 pagesStress Analysis Methods For Underground Pipe Lines Part 1 - Basic Calculationskumaran__k100% (3)
- Biaxial Bending in ColumnsDocument14 pagesBiaxial Bending in Columnsnvnrev100% (1)
- MItcal - Ejemplo de ClaseDocument102 pagesMItcal - Ejemplo de ClasedaagiraldogoNo ratings yet
- Schüco Fassade FW 50+ - FW 60+Document112 pagesSchüco Fassade FW 50+ - FW 60+BrcakNo ratings yet
- Allplan 2015 BasicsTutl PDFDocument269 pagesAllplan 2015 BasicsTutl PDFSirHumptyDumptyNo ratings yet
- Lateral Bracing of Beams Provided by Standing Seam Roof System Concepts and Case StudyDocument11 pagesLateral Bracing of Beams Provided by Standing Seam Roof System Concepts and Case Studyjackcan501No ratings yet
- ch4 Mechanical Properties of Wood PDFDocument46 pagesch4 Mechanical Properties of Wood PDFdan-gabiNo ratings yet
- Unbalance: Dew/Cbpm Lab/JvDocument27 pagesUnbalance: Dew/Cbpm Lab/JvNaveen ChodagiriNo ratings yet
- Stub 1.1Document9 pagesStub 1.1BrcakNo ratings yet
- Stub 3Document9 pagesStub 3BrcakNo ratings yet
- Pipe Support - Calculation ReportDocument33 pagesPipe Support - Calculation ReportIkramNo ratings yet
- 03-Conn-102 - Glass RailingDocument5 pages03-Conn-102 - Glass RailingReysan Caballero GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Duct Working LayoutDocument1 pageDuct Working LayoutAlps EngineeringNo ratings yet
- PTR90 777814Document5 pagesPTR90 777814Sgly ZemogNo ratings yet
- Frame UnitDocument27 pagesFrame UnitVN MÁY TỰ ĐỘNGNo ratings yet
- Specification For Fixed, Insulated, Hermetically Sealed Tantalum Capacitors With Solid ElectrolyteDocument5 pagesSpecification For Fixed, Insulated, Hermetically Sealed Tantalum Capacitors With Solid ElectrolytepadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- SAW Components: SAW RX 2in1 FilterDocument12 pagesSAW Components: SAW RX 2in1 Filterdiagnoz7auto7carsvanNo ratings yet
- TACT Switch TDSDocument3 pagesTACT Switch TDSHareram ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Calculo de Bus BarraDocument8 pagesCalculo de Bus BarraJohn AnguloNo ratings yet
- Part Number 22232KEJW33, Spherical Roller Bearings - Steel CageDocument4 pagesPart Number 22232KEJW33, Spherical Roller Bearings - Steel CageXiaoYaiZiZaiNo ratings yet
- Le Cle I Re Foucault Final BDocument6 pagesLe Cle I Re Foucault Final BdanyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2: Submitt Ed by Hassan AhmedDocument11 pagesAssignment 2: Submitt Ed by Hassan AhmedHasan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Flexible Pavement DesignDocument39 pagesFlexible Pavement DesignSaurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Material: DesignDocument26 pagesMaterial: DesignDavor IlicNo ratings yet
- ASNA2050 - Solid Rivet - Aluminium&UniversalHead PDFDocument9 pagesASNA2050 - Solid Rivet - Aluminium&UniversalHead PDFAnonymous mq0U43UsP100% (1)
- Power Scaling of Kw-Diode Lasers Optimized For Material Processing ApplicationsDocument9 pagesPower Scaling of Kw-Diode Lasers Optimized For Material Processing ApplicationsDu RoyNo ratings yet
- Craneway: Design of Crane RunwayDocument5 pagesCraneway: Design of Crane RunwayHamdi AslanNo ratings yet
- Post TensionDocument8 pagesPost Tensionedc1312No ratings yet
- Portal 1 PDFDocument21 pagesPortal 1 PDFAyodele Oluwaseyi DinaNo ratings yet
- Connector: 0.5mm Pitch/connectors For FPCDocument2 pagesConnector: 0.5mm Pitch/connectors For FPCJoão Paulo Da S NogueiraNo ratings yet
- Radio SIAE (Dia 0,6 M)Document8 pagesRadio SIAE (Dia 0,6 M)indra_uhuiiNo ratings yet
- E ACH1Document2 pagesE ACH1JamesNo ratings yet
- Part Number 2875 - 2820, Tapered Roller Bearings - TS (Tapered Single) ImperialDocument5 pagesPart Number 2875 - 2820, Tapered Roller Bearings - TS (Tapered Single) ImperialGỗ MộcNo ratings yet
- Navi Mumbai Metro Line 1: Mast Calculation - Panchanand DepotDocument3 pagesNavi Mumbai Metro Line 1: Mast Calculation - Panchanand DepotAnkit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- MICROJDocument12 pagesMICROJalexanderNo ratings yet
- RECOM Rev BDocument1 pageRECOM Rev Be.montgomeryNo ratings yet
- WL24Document23 pagesWL24alex robinNo ratings yet
- 2D Plane Strain PlasticityDocument4 pages2D Plane Strain PlasticitySebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Detail 02 L Vinkel Var 1Document14 pagesDetail 02 L Vinkel Var 1BrcakNo ratings yet
- SurlokPlusRighAnglePlug3 6Document47 pagesSurlokPlusRighAnglePlug3 6ayesNo ratings yet
- Innershield NS-3M: Welding Positions Key FeaturesDocument2 pagesInnershield NS-3M: Welding Positions Key FeaturesGiancarlo BlandinoNo ratings yet
- Pg240128a DisplayDocument1 pagePg240128a Displaybancadasol03No ratings yet
- 1500 SLC DS-1Document2 pages1500 SLC DS-1Soup PongsakornNo ratings yet
- Catalog Low Voltage Armour Cable XLPE CableDocument39 pagesCatalog Low Voltage Armour Cable XLPE Cableteguh prasetyoNo ratings yet
- Description of The ProjectDocument8 pagesDescription of The ProjectCompass GreenNo ratings yet
- Examples of ConductorsDocument16 pagesExamples of ConductorsJubert PerezNo ratings yet
- Part Number 22211KEJW33, Spherical Roller Bearings - Steel CageDocument4 pagesPart Number 22211KEJW33, Spherical Roller Bearings - Steel CageXiaoYaiZiZaiNo ratings yet
- Resistencia 680Document3 pagesResistencia 680Rafael Román García-sec DNo ratings yet
- Supreme Kabel NYYDocument2 pagesSupreme Kabel NYYIntanNo ratings yet
- 248, 249 1/2" (12.7 MM) Conductive Plastic and Cermet PotentiometersDocument20 pages248, 249 1/2" (12.7 MM) Conductive Plastic and Cermet PotentiometersRahmat Nur IlhamNo ratings yet
- WL21Document11 pagesWL21alex robinNo ratings yet
- SJ Mepla Calculation Protocol: Geometry:: Project: 03-Jlt Case-3 - Wl-1.72Kpa Back Support 03-04-2024Document9 pagesSJ Mepla Calculation Protocol: Geometry:: Project: 03-Jlt Case-3 - Wl-1.72Kpa Back Support 03-04-2024alex robinNo ratings yet
- WL02Document9 pagesWL02alex robinNo ratings yet
- SJ Mepla Calculation Protocol: Geometry:: Project: 03-Jlt Case-3 - Wl-1.72Kpa Back Support 03-04-2024Document10 pagesSJ Mepla Calculation Protocol: Geometry:: Project: 03-Jlt Case-3 - Wl-1.72Kpa Back Support 03-04-2024alex robinNo ratings yet
- Project Data: Project Name Project Number Author Description Date 26-Dec-23 Design Code AISC 360-16Document21 pagesProject Data: Project Name Project Number Author Description Date 26-Dec-23 Design Code AISC 360-16kheang amgNo ratings yet
- Program Discerption & VerificationDocument45 pagesProgram Discerption & VerificationMohammed Haitham ElShafieNo ratings yet
- ZJYS81 - CanCommon Mode FiltersDocument2 pagesZJYS81 - CanCommon Mode Filters40818248No ratings yet
- 120 X 120 X 38 MM SERIES: Dimensions DrawingDocument1 page120 X 120 X 38 MM SERIES: Dimensions DrawingrseheNo ratings yet
- Rf/Pulse Transformers: Electrical Specifications @25 CDocument1 pageRf/Pulse Transformers: Electrical Specifications @25 CzakreaNo ratings yet
- Kajian Teknis Untuk Perubahan Kabel Feeder Trafo To LVMDPDocument4 pagesKajian Teknis Untuk Perubahan Kabel Feeder Trafo To LVMDPHendrias ari sujarwoNo ratings yet
- Magnet Selection Homogenous Field Application Note MelexisDocument8 pagesMagnet Selection Homogenous Field Application Note MelexisCelis CedeñoNo ratings yet
- Analisys Panel Support Arah PendekDocument150 pagesAnalisys Panel Support Arah PendekWANSNo ratings yet
- Antenna Product Specifications: SLU1278S6Document8 pagesAntenna Product Specifications: SLU1278S6camilo andres ToroNo ratings yet
- Componon S4-0 80Document5 pagesComponon S4-0 80Никита КуратовNo ratings yet
- Millimetre Wave Antennas for Gigabit Wireless Communications: A Practical Guide to Design and Analysis in a System ContextFrom EverandMillimetre Wave Antennas for Gigabit Wireless Communications: A Practical Guide to Design and Analysis in a System ContextNo ratings yet
- Detail 02 L Vinkel Var 1Document14 pagesDetail 02 L Vinkel Var 1BrcakNo ratings yet
- Post-Installed Rebar Connections Technical Information ASSET DOC LOC 5018489Document77 pagesPost-Installed Rebar Connections Technical Information ASSET DOC LOC 5018489BrcakNo ratings yet
- Industrial Profiles 2018 Bros enDocument28 pagesIndustrial Profiles 2018 Bros enBrcakNo ratings yet
- List of Standards in SerbiaDocument51 pagesList of Standards in SerbiaBrcakNo ratings yet
- Allplan TutorialDocument330 pagesAllplan TutorialOana ScutarasuNo ratings yet
- GmizavciDocument19 pagesGmizavciBrcakNo ratings yet
- GmizavciDocument19 pagesGmizavciBrcakNo ratings yet
- 16.zidovi 3.SP. List4-Spec - ArmDocument1 page16.zidovi 3.SP. List4-Spec - ArmBrcakNo ratings yet
- Krek Revit 2014Document1 pageKrek Revit 2014BrcakNo ratings yet
- 001-LIM 20mmDocument1 page001-LIM 20mmBrcakNo ratings yet
- Instalacija Tower Build 1350 I ArmCAD-A Build 1763 Na Win 7 x64 UltimateDocument2 pagesInstalacija Tower Build 1350 I ArmCAD-A Build 1763 Na Win 7 x64 UltimateNikola Zecevic100% (2)
- Monarplan FMDocument1 pageMonarplan FMBrcakNo ratings yet
- tg53 Model PDFDocument1 pagetg53 Model PDFBrcakNo ratings yet
- Tg53 ModelDocument1 pageTg53 ModelBrcakNo ratings yet
- Nads Adic 1 - 1Document2 pagesNads Adic 1 - 1BrcakNo ratings yet
- Instructions For Europass CVDocument12 pagesInstructions For Europass CVKasia KowalskaNo ratings yet
- 2foundation Moments Hydraulics and CM Self Study QuestionsDocument40 pages2foundation Moments Hydraulics and CM Self Study QuestionsAngel TeyNo ratings yet
- Thermal MCQDocument42 pagesThermal MCQRanjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Week II FlotationDocument23 pagesWeek II FlotationAamir SirohiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SensorsDocument17 pagesIntroduction To SensorsHossam AbdelmoneimNo ratings yet
- Netting Analysis of Composite Pressure VesselsDocument3 pagesNetting Analysis of Composite Pressure VesselsPratyu Ch100% (1)
- Types of Fluid FlowDocument7 pagesTypes of Fluid FlowVinoth PandiNo ratings yet
- SHM Full NotesDocument11 pagesSHM Full Notessrashtikumariclass9No ratings yet
- Development Length - Difference Between Development Length and Lap LengthDocument6 pagesDevelopment Length - Difference Between Development Length and Lap LengthFeraidoon zamani najiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Foundation Design D.BDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Foundation Design D.BDavid BaltazaryNo ratings yet
- Lecture-2 Module-1 Structural Analysis-IIDocument26 pagesLecture-2 Module-1 Structural Analysis-IIHira WahabNo ratings yet
- Magnetism (Solved Ex. & Exciese)Document22 pagesMagnetism (Solved Ex. & Exciese)Chandradeep MandalNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Force On Plane SurfacesDocument3 pagesHydrostatic Force On Plane SurfaceskarthikNo ratings yet
- SimXpert R3.2 Motion Workspace GuideDocument262 pagesSimXpert R3.2 Motion Workspace GuidepaulkastleNo ratings yet
- Diseño de Maquinas - Estabilidad 2Document451 pagesDiseño de Maquinas - Estabilidad 2Rodrii RoblesNo ratings yet
- Dme Imp QuestionsDocument9 pagesDme Imp QuestionsCAD With RaoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - Theory of FailureDocument38 pagesCHAPTER 4 - Theory of FailureMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- Vortex Drop ShaftDocument9 pagesVortex Drop ShaftMarco PazNo ratings yet
- Strain Rate and Temperature Effects On Tensile Properties of Monocrystaline Cu6Sn5 by Molecule Dynamic SimulationDocument4 pagesStrain Rate and Temperature Effects On Tensile Properties of Monocrystaline Cu6Sn5 by Molecule Dynamic SimulationMd Sihan KhanNo ratings yet
- MSC Mechanical BUET-All QuestionsDocument13 pagesMSC Mechanical BUET-All QuestionsTahsin IbtidaNo ratings yet
- Bluebook (EN1993 1 1, HyperBeam, 17 Dec 2013)Document138 pagesBluebook (EN1993 1 1, HyperBeam, 17 Dec 2013)Peyman MznNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 FluentDocument56 pagesTutorial 5 FluentCrisner ToicenNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Twin-Rudders at Small Attack AnglesDocument13 pagesHydrodynamic Characteristics of Twin-Rudders at Small Attack Anglesebey_endunNo ratings yet
- Friction Coefficient in PipesDocument16 pagesFriction Coefficient in PipesVanessa AyalaNo ratings yet
- M1 As-Level Past PaperDocument6 pagesM1 As-Level Past PaperTimur ChirkovNo ratings yet