Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PUZZLE1
PUZZLE1
Uploaded by
SeaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PUZZLE1
PUZZLE1
Uploaded by
SeaCopyright:
Available Formats
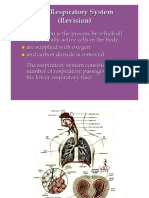
Ventilation, the process of moving air into and out of the lungs
Asthma, characterized by abnormally increased
constriction of the trachea and bronchi in response to various stimuli
Exercise, respiratory adaptations result from this
Alveoli, small, air-filled chambers where the air and the blood come into close contact with each other
Minute Volume, measures the amount of gas moving into and out of the respiratory system per minute
Hering-Breuer Reflex, a reflex that limits the depth of inspiration and prevents overinflation of the lungs
Bronchitis, inflammation of the bronchi caused by irritants
Brainstem, neurons involved with respiration are located here
Oxyhemoglobin, hemoglobin with 02 bound to its heme groups
Nares, external openings of the nose and is also known as nostrils
Partial Pressure, the pressure exerted by a specific gas in a mixture of gases
Surfactant, mixture of lipoprotein molecules produced by secretory cells of the alveolar epithelium
Carbon Dioxide, released into the atmosphere during the process of cellular respiration
Hypoxia, a decrease in blood O2 level below its normal values
Innate Immunity, one of the functions that the respiratory system performs wherein it protects against
microorganisms and pathogensL
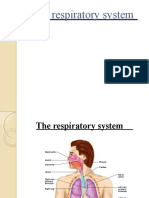
Lungs, principal organs of respiration, and on a volume
basis they are among the largest organs of the body
Ventilation, the process of moving air into and out of the lungs
Asthma, condition in which the airways narrow and swell and may produce extra mucus
Exercise, respiratory adaptations result from this
Alveoli, small, air-filled chambers where the air and the blood come into close contact with each other
Minute Volume, measures the amount of gas moving into and out of the respiratory system per minute
Hering-Breuer Reflex, a reflex that limits the depth of inspiration and prevents overinflation of the lungs
Bronchitis, inflammation of the bronchi caused by irritants
Brainstem, neurons involved with respiration are located here
Oxyhemoglobin, hemoglobin with 02 bound to its heme groups
Nares, external openings of the nose and is also known as nostrils
Partial Pressure, the pressure exerted by a specific gas in a mixture of gases
Surfactant, mixture of lipoprotein molecules produced by secretory cells of the alveolar epithelium
Carbon Dioxide, released into the atmosphere during the process of cellular respiration
Hypoxia, a decrease in blood O2 level below its normal values
Vital Capacity, maximal volume of air that can be expired following maximum inspiration
Lungs, principal organs of respiration, and on a volume basis they are among the largest organs of the
body
You might also like
- Personal and Family Values - Big Life JournalDocument9 pagesPersonal and Family Values - Big Life JournalElona Jane Capangpangan100% (1)
- Respiratory Nursing #1Document19 pagesRespiratory Nursing #1shenric16100% (12)
- Sutures & Suturing: Dr. Sateessh Bhatele Oral & Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument86 pagesSutures & Suturing: Dr. Sateessh Bhatele Oral & Maxillofacial SurgeryShalini SoniNo ratings yet
- L11. Respiratory SystemDocument71 pagesL11. Respiratory SystemLimit FtwNo ratings yet
- The Human Breathing SystemDocument5 pagesThe Human Breathing SystemHarry Cianne Luther Sayon100% (1)
- Respiratory System PhysiologyDocument35 pagesRespiratory System PhysiologySherwan R Shal100% (2)
- 015 Pathology MCQ ACEM Primary General Pathology PDFDocument15 pages015 Pathology MCQ ACEM Primary General Pathology PDFTahseen Jani100% (1)
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument5 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gaseslpc4944No ratings yet
- Introduction To Respiratory PhysiologyDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Respiratory PhysiologyKingsley UdeajaNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemRineshzel WardeNo ratings yet
- Lung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Respiratory SystemDocument63 pagesPathophysiology Respiratory SystemAli Basha QudahNo ratings yet
- Master Rotation Plan For GNMDocument2 pagesMaster Rotation Plan For GNMkuruvagadda sagar100% (4)
- 4 Alveolar Ventilation & Cough, Sneeze ReflexDocument47 pages4 Alveolar Ventilation & Cough, Sneeze ReflexNimra TariqNo ratings yet
- Acclimate To Adapt To Certain ConditionsDocument8 pagesAcclimate To Adapt To Certain ConditionsJuliati JuliatiNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary VentilationDocument24 pagesPulmonary VentilationAreeba KhanNo ratings yet
- Resp Exam PrepDocument75 pagesResp Exam PrepYea Jin SongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 021Document25 pagesChapter 021yukelkelmanNo ratings yet
- 05 RespiratoryDocument38 pages05 Respiratoryglenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- Regulation of RespirationDocument21 pagesRegulation of RespirationSheeraz ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument42 pagesAnatomy of The Respiratory Systempsidra456No ratings yet
- University of Guyana School of Medicine Med 1106 - Physiology I DR Kalima ThompsonDocument66 pagesUniversity of Guyana School of Medicine Med 1106 - Physiology I DR Kalima ThompsonKNo ratings yet
- Human Biology: Respiratory SystemDocument33 pagesHuman Biology: Respiratory SystemSaikrishna RaoNo ratings yet
- Oxygen InsufficiencyDocument16 pagesOxygen Insufficiencydeolzf100% (1)
- Respiratory Physiology PostedDocument25 pagesRespiratory Physiology PostedYeni PuspitaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory SystemconnievelardeNo ratings yet
- 1-Mechanism and Regulation of Respiration ModifiedDocument10 pages1-Mechanism and Regulation of Respiration Modifiedخالد القرشيNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument21 pagesThe Respiratory SystemdeepakNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 3Document16 pagesRespiratory System 3rueNo ratings yet
- ch18 RespiratoryDocument49 pagesch18 RespiratoryHazelynne MamucudNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesRespiratory SystemsanathNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System PDFDocument21 pagesThe Respiratory System PDFhechi_zeroNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Ventilation: Dr. Mohamed HassanDocument29 pagesPulmonary Ventilation: Dr. Mohamed HassanSAKARIYE MAXAMEDNo ratings yet
- Hypo/HyperventilationDocument7 pagesHypo/Hyperventilationfaisal alharbiNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesFunctional Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemRica Mae TingcoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System: A. NormalDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System: A. NormalCherrie CatingubNo ratings yet
- Biophysics of The Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesBiophysics of The Respiratory SystemIfe AzeezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Regulation of Breathing and Cough0Document15 pagesLecture 1 Regulation of Breathing and Cough0KelvinNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Respiratory PrelabDocument23 pagesLab 6 Respiratory Prelabkkk13whyNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesThe Respiratory SystemmvslikavNo ratings yet
- MLS221 Respiratory System PhysiologyDocument37 pagesMLS221 Respiratory System PhysiologyAbdirazak AliNo ratings yet
- I.C.T ASSIGNMENT On Human RespirationDocument48 pagesI.C.T ASSIGNMENT On Human RespirationjeetudongreNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Dr. Agung Kurniawan, MkesDocument31 pagesRespiratory System: Dr. Agung Kurniawan, MkesJojo BodhoNo ratings yet
- 16 Pulmonary Ventsilation CH16 2Document34 pages16 Pulmonary Ventsilation CH16 2Brodsky MacedoNo ratings yet
- Breathing & Exchange of Gases NotesDocument7 pagesBreathing & Exchange of Gases NotesKankana Biswas100% (1)
- Respira SiDocument80 pagesRespira SiIlaJako StefanaticNo ratings yet
- 3-ch 23 - Respiratory BDocument106 pages3-ch 23 - Respiratory Blouise navorNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument18 pagesIntroductionsamar yousif mohamedNo ratings yet
- The Pathophysiology of COPDDocument1 pageThe Pathophysiology of COPDJay. SelNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in MammalsDocument35 pagesGaseous Exchange in Mammalsmahanswarnima08No ratings yet
- Lecture 6 (Respiratory System)Document10 pagesLecture 6 (Respiratory System)Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNo ratings yet
- H.circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesH.circulatory SystemElleNo ratings yet
- Prologue 1.1 BackgroundDocument9 pagesPrologue 1.1 BackgroundWulan Yulia DintasariNo ratings yet
- Control of RespirationDocument26 pagesControl of RespirationAhmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystempptDocument26 pagesRespiratory SystempptRinaliza BogsulenNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 6 - Airflow Breathing Mechanism - LectureDocument31 pagesLecture - 6 - Airflow Breathing Mechanism - LectureAmr KasemNo ratings yet
- Airflow: Group 4 - Respiratory System VentilationDocument18 pagesAirflow: Group 4 - Respiratory System VentilationNathalieCaracaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology ReviewDocument8 pagesRespiratory Physiology ReviewMeccanazaren Susvilla BojorqueNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument74 pagesThe Respiratory SystemRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Exchange of Gases: Powerpoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Robert J. Sullivan, Marist CollegeDocument13 pagesRespiratory System Exchange of Gases: Powerpoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Robert J. Sullivan, Marist CollegeJoan Rescate Rigodon-AgustinNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- THE BUTEYKO METHOD (Translated): The secret of controlled breathing for health, well-being and vitalityFrom EverandTHE BUTEYKO METHOD (Translated): The secret of controlled breathing for health, well-being and vitalityNo ratings yet
- PUZZLEDocument4 pagesPUZZLESeaNo ratings yet
- Special-Senses FormatDocument5 pagesSpecial-Senses FormatSeaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic Structures All All MCDocument2 pagesLymphatic Structures All All MCSeaNo ratings yet
- Common Bone MarkingsDocument1 pageCommon Bone MarkingsSeaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 ActivityDocument3 pagesModule 7 ActivitySeaNo ratings yet
- UrinaryDocument3 pagesUrinarySeaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ActivityDocument2 pagesEndocrine ActivitySeaNo ratings yet
- LymphaticDocument2 pagesLymphaticSeaNo ratings yet
- Activity 10Document6 pagesActivity 10SeaNo ratings yet
- Ap LabDocument3 pagesAp LabSeaNo ratings yet
- AP LabDocument1 pageAP LabSeaNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Complete/partial Dentures (Different Final Impression Techniques and Materials) For Treating Edentulous Patients (Protocol)Document18 pagesFabrication of Complete/partial Dentures (Different Final Impression Techniques and Materials) For Treating Edentulous Patients (Protocol)Padmini ReddyNo ratings yet
- M J A S: in Vitro Nitric Oxide Scavenging and Anti InflammatoryDocument12 pagesM J A S: in Vitro Nitric Oxide Scavenging and Anti InflammatoryNicolás GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Speech OutlineDocument3 pagesSpeech Outlinekarlymae33% (3)
- 1 s2.0 S0260691719300668 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0260691719300668 Mainruby susmawatiNo ratings yet
- Skenario DrillDocument2 pagesSkenario DrillArianto WibowoNo ratings yet
- Research Lit MatrixDocument32 pagesResearch Lit MatrixLoreto Alipio IIINo ratings yet
- The Consequences of A Cracked or Missing CrownDocument20 pagesThe Consequences of A Cracked or Missing Crownibrahim bataNo ratings yet
- Patriciabennerfinalppt 140830010517 Phpapp02Document29 pagesPatriciabennerfinalppt 140830010517 Phpapp02rainNo ratings yet
- Ventilation For Enclosed Parking GaragesDocument6 pagesVentilation For Enclosed Parking GaragesAbdelrahman HosniNo ratings yet
- Peter E Pormann and Emily Savage Smith MDocument7 pagesPeter E Pormann and Emily Savage Smith MNICOLÁS AGUILERA FUENTESNo ratings yet
- Sensory Processing Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSensory Processing Lesson Planapi-354218226No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Chapter 9 Fire Protection SystemsDocument13 pagesLesson 5 Chapter 9 Fire Protection Systemsyoli lealNo ratings yet
- Narrative For Final ProjectDocument2 pagesNarrative For Final Projectapi-508903095No ratings yet
- SilgramDocument6 pagesSilgramJacqueline SweetNo ratings yet
- CCE REPORT-21Document6 pagesCCE REPORT-21BHAIRAB BAURINo ratings yet
- FINAL RESEARCH PAPER On JUVENILE DELINQUENCYDocument41 pagesFINAL RESEARCH PAPER On JUVENILE DELINQUENCYMesbaul Ratul100% (1)
- Neonatal Gastroschisis GuidelineDocument2 pagesNeonatal Gastroschisis GuidelineAnonymous 9wHscMNo ratings yet
- Article and Review TTLDocument11 pagesArticle and Review TTLRoxane faye AbrencilloNo ratings yet
- MSDSDocument9 pagesMSDSrofano aswanNo ratings yet
- Aging and The Life Course An Introduction To Social Gerontology 7th Edition Quadagno Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesAging and The Life Course An Introduction To Social Gerontology 7th Edition Quadagno Solutions Manualrodolfohollandugev100% (21)
- Octave Allegro 7-8Document3 pagesOctave Allegro 7-8faisal zafryNo ratings yet
- Qwerph (PP (TH (Document7 pagesQwerph (PP (TH (Muhammad Hisyam AjimulyaNo ratings yet
- Anakazi Empowerement Project ProposalDocument8 pagesAnakazi Empowerement Project ProposalDiana BwalyaNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Your Cyclesense ChartDocument4 pagesWelcome To Your Cyclesense ChartAndreea CiausNo ratings yet
- Develop Soft Skills That Industry DemandsDocument13 pagesDevelop Soft Skills That Industry DemandsDSZGNo ratings yet
- 11.08.23 Annex A BOIS Form Revised 2023 TineDocument2 pages11.08.23 Annex A BOIS Form Revised 2023 TineSamantha marquez50% (2)