Professional Documents
Culture Documents
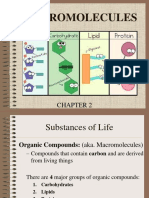
Biomolecules
Uploaded by
pogi si mark lee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesOriginal Title
biomolecules
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesBiomolecules
Uploaded by
pogi si mark leeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
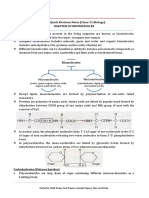
Biomolecules
I. What are Biomolecules?
- Large organic molecules necessary for life
- Found in bodies and cells of living organisms
- Also known as macromolecules
- Organic - mainly contains carbon
- Has relatively large size
- Known as polymers
- Compose of repeating units or monomers
II. Classification of Biomolecules
Biomolecule (Polymer) Example Sub-unit/s (Monomer/s)
Carbohydrates Polysaccharide Monosacchride
Lipids Fat Glycerol and fatty acids
Proteins Polypeptide Amino acids
Nucleic Acids DNA Nucleotide
III. Proteins
- Organic compound composed of C, H, O, N, and sometimes S.
- Amino acids is the fundamental building block of proteins
- Peptide bond is the link between amino acids
- Amino acids are compounds that contain an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group, and a side
chain (R).
1. Dehydration synthesis of Proteins
- It is the removal of water and formation of bond between atoms of two monomer molecules
- Joining two monomers together results to dehydration synthesis
- For every 2 amino acids joined together, 1 water molecule is released
- The number of amino acids - 1
- In dehydration synthesis of proteins, water molecules and polypeptide chains would be formed
2. Types of Proteins
Fibrous Proteins
Insoluble in water
Main structural
Components of the body
Examples: collagen, actin, and keratin
3. Protein Functions
4.
IV.
You might also like
- Topic 2 - Molecular BiologyDocument140 pagesTopic 2 - Molecular BiologyyourstrulyrahulNo ratings yet
- Biological Macromolecules PDFDocument31 pagesBiological Macromolecules PDFAngeline CortezNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules - Worksheet Answers - OdtDocument4 pagesMacromolecules - Worksheet Answers - OdtRachel JimenezNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules - Chapter 4Document9 pagesBiological Molecules - Chapter 4Bimbo, Arabela June G.No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsFrom EverandAnatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Chapter 2 - Macromolecules NotesDocument41 pagesUnit 2 - Chapter 2 - Macromolecules Notesapi-375285021No ratings yet
- Amino Acids are linked by peptide bonds to form formed by linking the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid to the α-amino group of another amino acid with a peptide bond (also called an amide bond)Document2 pagesAmino Acids are linked by peptide bonds to form formed by linking the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid to the α-amino group of another amino acid with a peptide bond (also called an amide bond)Noviemae TuandaNo ratings yet
- Secondary OneDocument103 pagesSecondary Oneroqayaehab.elsNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds 2010Document52 pagesOrganic Compounds 2010Judy MelegritoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument38 pagesUnit 2 NotesElen Mae PadugaNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument7 pagesBio Moleculesmarkkevingonzales1235No ratings yet
- Botnay Notes Class 11Document138 pagesBotnay Notes Class 11Suresh chand100% (1)
- 2.0 Chemiccal ComponentDocument12 pages2.0 Chemiccal ComponentmiftahNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Reviewer Final 1Document5 pagesGen Bio Reviewer Final 1Emmanuelle CalleNo ratings yet
- Senior 1: Chemical Basis of LifeDocument20 pagesSenior 1: Chemical Basis of LifeLujain HammadNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesBiomoleculesgeecyjane YguintoNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Intro To Biomolecules and The Biochem LabDocument2 pagesTopic 1 - Intro To Biomolecules and The Biochem LabKrysta CarinoNo ratings yet
- Chem of LifeDocument1 pageChem of LifeAllen ChristianNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NOTES IN Biochemistry of The CellDocument6 pagesLECTURE NOTES IN Biochemistry of The CellPearica LopezNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument58 pagesBio Moleculescheryl tayasNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Lynnette A. EjemDocument103 pagesBiomolecules: Lynnette A. EjemAirene Mae SupilarNo ratings yet
- Basic Biology and Physiology-Lecture 2-Biomacromolecules-NewDocument32 pagesBasic Biology and Physiology-Lecture 2-Biomacromolecules-NewRajdeep PawarNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Molecules To MetabolismDocument7 pages2.1 Molecules To MetabolismlhabNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecules 1Document19 pagesBio Molecules 1sanjog kshetriNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I Biomolecules: March 2018Document19 pagesUNIT-I Biomolecules: March 2018Tomas PinedaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesDocument5 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesSIDHARTH SBNo ratings yet
- Inbound 1618874845485050315Document10 pagesInbound 1618874845485050315benntin10No ratings yet
- Organic MoleculesDocument7 pagesOrganic MoleculesJames CadizNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Reviewer 2324Document7 pagesBiomolecules Reviewer 2324heraloesaNo ratings yet
- 2.3 BiomoleculesDocument25 pages2.3 Biomoleculesvivitri.dewiNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules - Are Large Molecules Composed of Thousands of Covalently Connected AtomsDocument6 pagesMacromolecules - Are Large Molecules Composed of Thousands of Covalently Connected AtomsBon Joey BernestoNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculeDocument6 pagesBio MoleculeAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Carbohydrates Preiy Julian M de GuiaDocument3 pagesActivity 2 Carbohydrates Preiy Julian M de GuiaPreiy Julian De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Section 4Document7 pagesSection 4Debarshi SahooNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument11 pagesBio Moleculesdemonzslayer809No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lecture: Prepared By: Rozalina R. Adonis, RMT, MsmlsDocument30 pagesBiochemistry Lecture: Prepared By: Rozalina R. Adonis, RMT, MsmlsKhryzell CabangonNo ratings yet
- Bab 11 Kidas 2019Document16 pagesBab 11 Kidas 2019marianaNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 Lesson 4Document28 pagesBio 1 Lesson 4sattNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Organic Compounds - 1) Carbohydrates: - A) Monosaccharaides: (C H O)Document13 pagesBiochemistry: Organic Compounds - 1) Carbohydrates: - A) Monosaccharaides: (C H O)Ziad KandilNo ratings yet
- UNITI BiomoleculesDocument19 pagesUNITI BiomoleculesPriyanka YadavNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes On MolecularDocument13 pagesBiology Notes On Molecularanon_490197571No ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES NOTE 11aaDocument9 pagesBIOMOLECULES NOTE 11aaGyaniNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Activity 2 BiomoleculesDocument2 pagesScience 10 Activity 2 BiomoleculesAeron AndayaNo ratings yet
- PRELIM Biochemistry Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesPRELIM Biochemistry Lecture Noteskwgchyrn1No ratings yet
- 2-1 Molecules To MetabolismDocument21 pages2-1 Molecules To MetabolismEdward YaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document47 pagesChapter 1homamunfatNo ratings yet
- Most Organic Molecules Are Made Up of 3 Types of AtomsDocument28 pagesMost Organic Molecules Are Made Up of 3 Types of Atomssai kishoreNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules: Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic AcidsDocument23 pagesBiological Molecules: Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic AcidsAMEER HANAFI JIKIRI. JUL-ASRINo ratings yet
- BioChem LESSON 1 and 2Document8 pagesBioChem LESSON 1 and 2Elvira MirajulNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistryapi-233187566No ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundsDocument11 pagesCarbon CompoundsDannia RoblesNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellanmbeltran31No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 VocabDocument2 pagesChapter 5 VocababNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composotion of The CellDocument38 pagesChemical Composotion of The CelliQalyanaNo ratings yet
- MoleculesDocument60 pagesMoleculesCharlize Jeneah MedinaNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules - For K 12 TrainingDocument185 pagesBiological Molecules - For K 12 TrainingVj RanchesNo ratings yet
- Nucleotide - Monomer of Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesNucleotide - Monomer of Nucleic AcidsMika Sophia GonzagaNo ratings yet
- The "Stuff" of LifeDocument46 pagesThe "Stuff" of LifeMarcela UrbnNo ratings yet
- 87314094-83be-428d-9d4d-a459e43691a9Document21 pages87314094-83be-428d-9d4d-a459e43691a9SAMPATH SPNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 - Integrated Principles of Zoology 18th Edition (Summary of Chapter 2)Document10 pagesBio 101 - Integrated Principles of Zoology 18th Edition (Summary of Chapter 2)Kaeya's asscheeksNo ratings yet
- Chemone 2Document4 pagesChemone 2pogi si mark leeNo ratings yet
- Process by Which Distantly Related Ogranisms Develop Similar Same Function Different StructureDocument1 pageProcess by Which Distantly Related Ogranisms Develop Similar Same Function Different Structurepogi si mark leeNo ratings yet
- Science - Plate TectonicsDocument4 pagesScience - Plate Tectonicspogi si mark leeNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech and Basic GrammarDocument3 pagesParts of Speech and Basic Grammarpogi si mark leeNo ratings yet
- General ScienceDocument12 pagesGeneral Sciencepogi si mark leeNo ratings yet