Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cognitive Psychotherapies Mapa
Cognitive Psychotherapies Mapa
Uploaded by
igresOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cognitive Psychotherapies Mapa
Cognitive Psychotherapies Mapa
Uploaded by
igresCopyright:
Available Formats
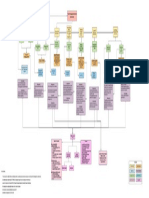
CBT (Cognitive-Behav.
Therapy) CMT (ControlCognitiva
TCS (Terapia Mastery Theory)
Standard) TCS(Cognitive
CAT (Terapia Cognitiva
Analytic Standard)
Therapy) TCS (Terapia
Schema Cognitiva Standard)
Therapy TCS (Terapia(based
Mindfulness Cognitiva Standard)
Therapy) DBT
TCS (Dialectical Behavior
(Terapia Cognitiva Therapy)
Standard)
• is a very pragmatic intervention • compared to CBT, with which it shares the merits, • is naive and rough in its epistemology • interventions are not focused on rationalizing • possible onset of severe dissociative phenomena • has an unsurpassed efficacy in the treatment of • is a complex intervention
• the sequence analysis of test-intervention- • still remains to demonstrate that it is applicable (Same as CBT)
• consist of a variety of techniques • is a stereotyped psychotherapy has a more explanatory and procedural intent • does not refer to any scientific theory dysfunctional emotions during treatment
response is an invaluable tool for monitoring the outside the therapeutic process and therefore • is brief • is a stereotyped psychotherapy severe personality disorders • requires a powerfully organized implementation
• is very goal-orented • is a non-explanatory model • is attentive to the needs of the patient • is fragmented and uncoordinated in his quest for • possible pragmatic switch off and change
therapeutic process usable in the"real life" of the patient • is very suitable for public territorial services • is a non-explanatory model structure
• is based on active and explicit collaboration • minimizes the unconscious processes • has an undoubted clinical utility description completeness strategies invalidation in the subject
• makes possible to effectively monitor the • minimizes the unconscious processes • is socially costly
between therapist and patient • considers the emotions a product of beliefs • represents an attempt to integrate different • assumes a management of the therapeutic • possible attitudes of complacency toward the
therapeutic relationship • considers the emotions a product of beliefs • requires accurately trained therapists
• is centered on the patient's current problem • sees cognitive processes as a mere stimulus approaches (not necessarily cognitives) relationship potentially hazardous for both operator
• the unconscious plan concept provides a valuable • sees cognitive processes as a mere stimulus
• provides the patient with the tools to become expression and not an epistemic need patient and therapist as well as confounding
explanatory element expression and not an epistemic need
therapist of himself • leaves aside the therapeutic relationship
• leaves aside the therapeutic relationship
• its effectiveness is scientifically documented • ignores the sistemic dimension of the patient
• ignores the sistemic dimension of the patient
• is relatively brief
• requires a relatively simple training
+ - + - + - + - + - + -
Cognitive Psychotherapies Developed on the
observation that patients
with psychopathological
Personal constructs as keys to
understand the world and
make it intelligible.
Repertory grid based on the
Very effective Integrated model
of psychotherapy that uses
TOOLS derived from the main It is a meditative practice developed on the concepts of: awareness, acceptance, absence of
(v 1.3.1) problems related to
depression and anxiety
disorders, had thought
assumption that is possible to
estmate the mathematical
relationships between the
cognitive models integrated with
group behavioral ,
psychoeducational and
judgment. There are four different programs based on mindfulness. With the exception of DBT
(Dialectical Behavioral Therapy), which is an authentic, complex and effective intervention model,
It an adaptation of the CBT the ACT (Acceptance and Commitment Therapy), the MBSR (Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction)
streams considered various constructs that can mindfulness interventions ,
for personality disorders and MBCT (Mindfulness Based Cognitive Therapy for Depression) are substantially intervention
dysfunctional and responsible be assessed using non- articulated in a residential
treatment. Focuses its techniques.
for painful emotions. parametric factor analysis. context
intervention as well as on the
Oriented on the TOOLS: "repertory grid"
It ‘s a highly structured and dysfunctional patterns and
dysfunctional thoughts that organized by pairs of
protocolled therapy. It allows interpretative distortions that
usually accompany the antithetical attributes
a number of sessions, limited accompany them, on the
therapeutic relationship and experienced emotions.
It ‘s a form of psychotherapy
that combines the pragmatism
to 16, which become 24 in
the treatment of personality on the early schemas. It TOOLS: reformulation of
cognitive schemas through
MBSR MBCT
of the CBT with a disorders. proposes 18 maladaptive - Kabat-Zinn -
ABC and laddering - Segal & Al. -
metapsychological angle close
to the psychoanalytic model.
TOOLS: 1 session for
assessment and presentation
patterns grouped into five
domains linked with as much ACT
The underlying hypothesis of the intervention, 4 existential needs.
TOOLS: "limited reparenting"
- Hayes -
states that the patient is sessions for problem
guided in the therapeutic formulation , sessions 5 to 16 reformulation of "corrective
relationship from an
"unconscious plan" aimed at
the solution of its problems.
for problem re-formulation
and implementation of
procedures designed to
emotional experience"
concept of Alexander DBT
This proposal is hampered by achieve the objectives. - Linehan - MINDFULNESS
"pathogenic beliefs" similar to Additional sessions address
the cognitive schemas through issues of greater complexity
which the patient “test" in an relating to personality
unconscious way, the reliability disorders
of the therapist.
TOOLS: the "test" of the
patient, is followed by the
'"intervention" of the therapist
and then by the "response" of
the patient, through a constant
monitoring reminiscent of the
Guidano’s "slow motion
tecnique" applied to the
therapeutic relationship
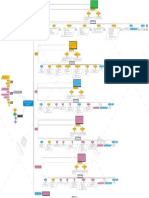
SCHEMA
THERAPY
- Young -
CAT PERSONAL
CONSTRUCT
- Kelly - POST –
- Ryle- RATIONALIST
CBT «COGNITIVE
PROCESSES &
EMOTIONAL
MODEL
- Guidano -
CMT - Beck - DISORDERS»
- Weiss &
Sampson - ‘70 - Guidano & Liotti -
COGNITIVE -
MIT
‘80 REBT EVOLUTIONARY
-Terzo Centro -
‘90
MODEL
- Ellis - - Liotti -
MAHONEY'S
‘00
«STUDI
Italy
CRITIQUE COGNITIVI»
MODEL
- Sassaroli -
FAP
- Kohlenberg &
Tsai -
The hypothesis is that the
psychic activity, both normal
and pathological is
EMDR constituted by a set of
patterns similars to the
schema therapy domains. In
particular, the concepts of
Interpersonal Cycles and
It is built in accordance with Metacognitive Functions
the assumptions of represent the most original
attachment theory of John contribution to the model.
Bowlby, and more generally The MF are defined as the
of ethology. Refers to the subject's ability to regulate,
construction of meanings coordinate, integrate their
Guidano & Liotti welcome the mental representations and
critique of Mahoney that that are structured based on
innate rules of conduct coping with problematic
blame the CBT of substantial states.
empiricism. Development of evolutionarily selected. The
Mahoney focuses on the "Cognitive Organizations." conceptual , emotional and
stereotyped character of CBT, TOOLS: “Slow Motion behavioral constructs,
according to a rationalist It argues that each individual
the absence of an Tecnique”
It is based on the behavioral mode are applied to acquires its logic mode
explanatory model, the (identity), with which
analysis of the therapeutic It shares the same functional structural motivational
It is used to access, neutralize marginal role reserved to the organizes the knowledge of
relationship. It is designed to approach of CBT with a frames evolutionarily
and lead to an adaptive emotions and the lack of self and the world and
be used with the traditional focus more oriented on the selected that from time to
resolution, memories of emphasis on the therapeutic through which interprets and
behavioral approaches or dysfunctional emotional time modify the meaning
traumatic experiences that relationship. builds his own reality. This
when the client's ability to experience aspect itself .
relate to others is central in underlie the current assumption , that can also be
his clinical difficulties. problems of the patient. applied to constructivist
These traumatic experiences It is directly derived from models in the post-rationalist
TOOLS: “shaping “of new and
may include: CBT, it uses some aspects of stream, goes further in
more functional behaviors
small / large trauma during schema therapy (the depicting a ceaseless
provided by the therapist's
childhood, common stressful "criticism" and the tendency autopoietic self within which
contingent responses to
events (grief, chronic illness, to “ruminative ideation") as the self-reflection and
patient problems that occur
financial loss, marital conflict, a key to the treatment of observation of the
during the sessions
changes) ,extraordinary eating disorders. phenomenon, constantly
stressful natural change the field of
(earthquakes, floods) or
manmade (serious accidents,
observation, internal and
external . Development of
TCS (Terapia Cognitiva
Post-Rationalist
Mindfulness Model
(based Standard)
Therapy)
torture, violence) events "Personal Meaning
Organizations “.
• is very elegant in epistemological sense • is not interested in nosography
• is an explanatory model • is not suitable for treatment of childhood
• is centered on an inalienable individual need : the • does not take adequate account of the narrative
narrative continuity discontinuity, characteristic not only of some
psychopathological situations, but also of
normality
• does not address the issue of metacognition
• can leave aside the experiential reality of the
Copyright 2012 – www.psicoterapie.pro patient concentrating more on the therapeutic
process
+ -
TCS (Functional
FAP (Terapia Cognitiva
AnalyticStandard)
Psycht.) EMDR «Studi
TCS Cognitivi»
CAT (Terapia ModelStandard)
Cognitiva
(Cognitive Analytic Therapy) MIT
TCS (Metacognitive
(Terapia
Schema Int.Standard)
Cognitiva
Therapy Therapy) TCS
C.P. (Terapia
&
Mindfulness Cognitiva
E.D (Guidano
(based & Standard)
Liotti
Therapy) ’83) Cognitive-Evolutionary Model
• is effective • has an unclear scientific basis (The same as CBT and Schema Therapy) • is not an explanatory model • is an integrated model • sometimes lack of theoretical roundedness • is an explanatory model • does not explain the concept of disorganization • is a real explanatory model • explicitly neglects the narrative dimension
• has a great attention to the therapeutic • the focus on the therapeutic relationship can • try to take the best of many cognitive models • leaves aside the subjective dimension of the
• is simple to implement • not always provide stable results • is simple • leaves aside the therapeutic relationship • offers suggestions for clinical intervention and discontinuity of narrative and consciousness • is perfectly adapted to the treatment of childhood • leaves aside other motivational aspects related to
relationship scotomize the problematic reality of the patient • allows outcome studies therapist
• does not require metacognitive skills in the • could be effective in terms of "nonspecific • appears to be effective in the treatment of eating • leaves aside some clinical evidence • allows the patient to be recognized in his identity • focus on the therapeutic process rather than on • focus on patients needs the theory of evolution
out of the setting • is applicable in any clinical setting • can produce empathic failures in the therapeutic
patients factors" (not controlled and in this sense disorders and in his narratives the real life of the patient • is suitable in multiple contexts • set the therapist in a position close to that
• does not require complex training by the therapist potentially iatrogenic) • Is suitable for quantitative outcome studies relationship • is suitable for treatment of personality disorders as • leaves aside the subjective dimension of the • is perfectly compatible with CBT, which appears as expressed by the "limited reparenting" of the
for Axis I disorders therapist a development schema therapy (with the related difficulties )
+ - + - + - + - + - + -
You might also like
- Post-Traumatic Stress DisorderDocument1 pagePost-Traumatic Stress DisorderJoan MonzonesNo ratings yet
- Anterior Cruciate LigamentDocument26 pagesAnterior Cruciate LigamentAmandeep Singh100% (2)
- A380 Family Maintenance ConceptDocument1 pageA380 Family Maintenance Conceptyazan999100% (1)
- Wellness Massage: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Planning The Wellness Program of ClientDocument36 pagesWellness Massage: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Planning The Wellness Program of Clientrhaine91% (11)
- TrakCare Overview 09012015Document5 pagesTrakCare Overview 09012015keziajessNo ratings yet
- Adriaan Louw - Pain Neuroscience Education - Teaching People About Pain - Libgen - LiDocument538 pagesAdriaan Louw - Pain Neuroscience Education - Teaching People About Pain - Libgen - LielfisiooficialNo ratings yet
- Bpce Natixis Sa France Entity: Countries Can Develop DD Checklist To Address Local Requirements As Country AnnexDocument1 pageBpce Natixis Sa France Entity: Countries Can Develop DD Checklist To Address Local Requirements As Country AnnexTimNo ratings yet
- 16 Upper Extremity (FINAL)Document30 pages16 Upper Extremity (FINAL)kath-kath100% (1)
- 1 - BABOK 3 - Cheat Sheet - Tasks Vs Techniques V2Document1 page1 - BABOK 3 - Cheat Sheet - Tasks Vs Techniques V2Kevin BarthelotNo ratings yet
- HIRADC Asphalt RoadDocument1 pageHIRADC Asphalt RoadAshadi Amir100% (1)
- 1 - BABOK 3 - Cheat Sheet - Tasks Vs Techniques V2Document1 page1 - BABOK 3 - Cheat Sheet - Tasks Vs Techniques V2luavanloc100% (1)
- ACL Tear InjuryDocument5 pagesACL Tear InjuryNicole VazNo ratings yet
- Risk Intelligence Map Health Care Providers (Old)Document1 pageRisk Intelligence Map Health Care Providers (Old)mattsaavedradNo ratings yet
- HIRADC - Pekerjaan 20 KV - PLTGU - Update 5 March 2018Document5 pagesHIRADC - Pekerjaan 20 KV - PLTGU - Update 5 March 2018ghieee100% (1)
- Daftar Nilai Siswa Madrasah Ibtidaiyah Negeri 2 JeparaDocument21 pagesDaftar Nilai Siswa Madrasah Ibtidaiyah Negeri 2 Jeparasiti saudahNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Healthcare CommunicationsDocument1 pageThe Periodic Table of Healthcare Communicationscoolarun86No ratings yet
- Dashboard Graphics Catalogue v2 - 0Document49 pagesDashboard Graphics Catalogue v2 - 0feeNo ratings yet
- Jsu T5 Bi K1Document1 pageJsu T5 Bi K1MOHD FAHMI BIN ABD ALIAN MoeNo ratings yet
- ContentDocument1 pageContentserena7205No ratings yet
- AG 1st Two ClassesDocument4 pagesAG 1st Two ClassesAtashi MandalNo ratings yet
- Cutoff TamilDocument1 pageCutoff TamilBlooming BudsNo ratings yet
- NCoE Cutoff Marks 2018Document7 pagesNCoE Cutoff Marks 2018ifazafathi56% (27)
- Strategic Roadmap TemplateDocument1 pageStrategic Roadmap TemplateTheerapan CNo ratings yet
- Qatar: Persian GulfDocument1 pageQatar: Persian Gulfhassanzafar9090No ratings yet
- University of Delhi Undergraduate Admission Arts & Commerce 2nd Cut-Off ListDocument11 pagesUniversity of Delhi Undergraduate Admission Arts & Commerce 2nd Cut-Off ListriyaNo ratings yet
- Straumann Dental System Map BoneLevelProstheticsDocument1 pageStraumann Dental System Map BoneLevelProstheticscarla1315No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Optimal Control Applied To Disease ModelsDocument37 pagesAn Introduction To Optimal Control Applied To Disease ModelsMohammad Umar RehmanNo ratings yet
- Stroke 2014 Flowchart A3-FormatDocument2 pagesStroke 2014 Flowchart A3-FormateliansubiratsNo ratings yet
- Bi Kls 5e - SM Genap 2022Document21 pagesBi Kls 5e - SM Genap 2022siti saudahNo ratings yet
- Branch Wise 2016-17Document3 pagesBranch Wise 2016-17Vaibhav ShuklaNo ratings yet
- MoistDocument3 pagesMoistKenWin NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy Interventions in The BTS Guidelines On The Management of Asthma (2011) : A Need For Change?Document2 pagesPhysiotherapy Interventions in The BTS Guidelines On The Management of Asthma (2011) : A Need For Change?Christi Adriana GeaNo ratings yet
- Neo Vent Comp - Kacmerek 2019 AARCDocument1 pageNeo Vent Comp - Kacmerek 2019 AARCAbraham HaneineNo ratings yet
- Set 3 - Jsu t5 Bi k3Document1 pageSet 3 - Jsu t5 Bi k3MOHD FAHMI BIN ABD ALIAN MoeNo ratings yet
- ContentsDocument1 pageContentsserena7205No ratings yet
- Puso2019 FinalresultsDocument3 pagesPuso2019 Finalresultsapi-454740047No ratings yet
- Intervention Name: Word - Problem MnemonicsDocument3 pagesIntervention Name: Word - Problem MnemonicsJamuna Pandiyan MuthatiyarNo ratings yet
- FGHS2655PF Ref FrigidaireDocument2 pagesFGHS2655PF Ref FrigidaireVasti Diaz AguilarNo ratings yet
- Contoh Research GapDocument1 pageContoh Research GapDhika AdhityaNo ratings yet
- Ahnikamrutam Main TextDocument226 pagesAhnikamrutam Main TextGowardhan TamirisaNo ratings yet
- Rank Jumlah Nama No Rata-RataDocument2 pagesRank Jumlah Nama No Rata-Ratanurul adriyaniNo ratings yet
- Surgical Planning by Case TypeDocument1 pageSurgical Planning by Case TypeNikYes RegmiNo ratings yet
- Short Title Description: Author Date Created Rough Size (S/M/L)Document1 pageShort Title Description: Author Date Created Rough Size (S/M/L)Joan RocaNo ratings yet
- Grama SachivalayamDocument172 pagesGrama Sachivalayamanon_726486703No ratings yet
- SenseCAP Pruduct Brief EnglishDocument2 pagesSenseCAP Pruduct Brief Englishali aghajaniNo ratings yet
- Venditti - ASH 2023 - Ven in Elderly Patients Poster With COIs - 13nov2023Document1 pageVenditti - ASH 2023 - Ven in Elderly Patients Poster With COIs - 13nov2023molly.kottemannNo ratings yet
- Now Short Term Medium Term Long Term: Step 1: Step 2: Step 4aDocument1 pageNow Short Term Medium Term Long Term: Step 1: Step 2: Step 4amzansigirlNo ratings yet
- Handbook MeasuringDocument60 pagesHandbook MeasuringReneAcebeyGomezNo ratings yet
- Integration MatrixDocument1 pageIntegration MatrixMurat SezginNo ratings yet
- 2Dbc /taat (PCX ) BWX - B 2Dbc /Tabtv/T) CB Ep (Dt?A - BXCX ) B:Th0Rcxexcxtb:Th?Pac) TabDocument1 page2Dbc /taat (PCX ) BWX - B 2Dbc /Tabtv/T) CB Ep (Dt?A - BXCX ) B:Th0Rcxexcxtb:Th?Pac) TabAnderson Jose AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- BIOL 221 - PharmacologyDocument5 pagesBIOL 221 - PharmacologyFinleyMurdainNo ratings yet
- SM Slides 2upDocument63 pagesSM Slides 2upSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Message No. 2 - Format Infrastructure Data Collection 30.01.2019Document1 pageMessage No. 2 - Format Infrastructure Data Collection 30.01.2019Bhaskar Victor DasNo ratings yet
- Kamber SELFDocument1 pageKamber SELFAbdurrazzaqNo ratings yet
- 12 - Dec2020 - YCP Quality Dashboard (Latest)Document6 pages12 - Dec2020 - YCP Quality Dashboard (Latest)guillaumenzi195No ratings yet
- Effect of Patient Size On Radiation Dose of Abdominal MDCT With Automatic Tube Current ModulationDocument6 pagesEffect of Patient Size On Radiation Dose of Abdominal MDCT With Automatic Tube Current Modulationdestian ryanNo ratings yet
- Soler - MindfulnessDocument35 pagesSoler - MindfulnessHikari TakahashiNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Vasospasme After Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument10 pagesCerebral Vasospasme After Traumatic Brain Injurydavid wyantoNo ratings yet
- DR.M Rafat Ka Tassure IlmDocument5 pagesDR.M Rafat Ka Tassure IlmMuhammad GhitreefNo ratings yet
- Preference For Long Acting Injectable (Lai) Antiretrovirals For Hiv Treatment or Prep in ArgentinaDocument1 pagePreference For Long Acting Injectable (Lai) Antiretrovirals For Hiv Treatment or Prep in ArgentinaAli CamelliNo ratings yet
- Business Model Canvas PosterDocument1 pageBusiness Model Canvas PosterfabioNo ratings yet
- Business Model Canvas Poster PDFDocument1 pageBusiness Model Canvas Poster PDFfabioNo ratings yet
- JEC Health Chart 11-7-09Document1 pageJEC Health Chart 11-7-09Stix1972No ratings yet
- Gutjnl 2018 March 67 3 574 Inline Supplementary Material 1Document1 pageGutjnl 2018 March 67 3 574 Inline Supplementary Material 1igresNo ratings yet
- 772012v1 FullDocument36 pages772012v1 FulligresNo ratings yet
- Disfraces RabiaDocument3 pagesDisfraces RabiaigresNo ratings yet
- Historiografia Dels Jaciments Plistocens Al MassisDocument35 pagesHistoriografia Dels Jaciments Plistocens Al MassisigresNo ratings yet
- Punjab Police Constable Past PapersDocument37 pagesPunjab Police Constable Past Papersali135raza421No ratings yet
- Design The Upper Limb Exoskeleton Arm For Reinforcement The Weakness in The Human MusclesDocument8 pagesDesign The Upper Limb Exoskeleton Arm For Reinforcement The Weakness in The Human MusclesYASH SANJAY.INGLENo ratings yet
- Annie Elizabeth ResumeeDocument1 pageAnnie Elizabeth ResumeeLizNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Hip and PelvisDocument62 pagesSession 1 Hip and PelvisNixon BiasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Basic Biomechanical Concepts: Mahlet TDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Basic Biomechanical Concepts: Mahlet Tsamrawit zerihunNo ratings yet
- Sports MedicineDocument25 pagesSports MedicinedhanushrcksNo ratings yet
- Effect of A Physiotherapy Program in Women With Primary DysmenorrheaDocument6 pagesEffect of A Physiotherapy Program in Women With Primary DysmenorrheaPaula RangelNo ratings yet
- Cancer - 1 August 1987 - Broadwell - Rehabilitation Needs of The Patient With Cancer PDFDocument6 pagesCancer - 1 August 1987 - Broadwell - Rehabilitation Needs of The Patient With Cancer PDFdrfahad1045No ratings yet
- EMG Activation of The Vastus Medialis Oblique and Vastus LateraliDocument9 pagesEMG Activation of The Vastus Medialis Oblique and Vastus LateraliWilliam ChienNo ratings yet
- Proximal - Mid Hamstring Strains Rehab GuidelineDocument4 pagesProximal - Mid Hamstring Strains Rehab GuidelinejavierNo ratings yet
- Secretome YaDocument75 pagesSecretome YaogynugrahNo ratings yet
- 6779 Physiotherapy Specialist - 13!06!2022 - Website - 0Document2 pages6779 Physiotherapy Specialist - 13!06!2022 - Website - 0Rubab ashiqNo ratings yet
- Personal EssayDocument2 pagesPersonal Essayshruti sriNo ratings yet
- Standards Physiotherapy Service Final 2023625844Document27 pagesStandards Physiotherapy Service Final 2023625844mohdshaik9993No ratings yet
- Gait Analysis in Cerebral PalsyDocument3 pagesGait Analysis in Cerebral PalsyAmr Mohamed GalalNo ratings yet
- BFO-Ankle Foot Orthotics - Introduction and Biomechanical PrinciplesDocument9 pagesBFO-Ankle Foot Orthotics - Introduction and Biomechanical PrinciplesnovitaNo ratings yet
- Statement of PurposeDocument2 pagesStatement of Purposesakina sadriwalaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of HandDocument15 pagesMuscles of HandAhmed TarekNo ratings yet
- Physicswallah Mediclaim BenefitDocument17 pagesPhysicswallah Mediclaim BenefitᎷᏒ ᏗᏕᏂᎥᏕᏂ ᎶᏬᎮᏖᏗNo ratings yet
- Quantum Reflex IntegrationDocument2 pagesQuantum Reflex IntegrationAarif SharifNo ratings yet
- Bridging Ortho NotesDocument4 pagesBridging Ortho NotesJonathan TayNo ratings yet
- Types of Healthcare ProvidersDocument4 pagesTypes of Healthcare ProvidersHannah Sharen JabidoNo ratings yet
- Muscular System NotesDocument6 pagesMuscular System NotesZussette Corbita VingcoNo ratings yet
- Technical: Obtain Position Environment Wherei Can Appiy MyDocument2 pagesTechnical: Obtain Position Environment Wherei Can Appiy MyArvindNo ratings yet
- Affiliated To CTEVT: Chabahil, KTMDocument22 pagesAffiliated To CTEVT: Chabahil, KTMBinita ShresthaNo ratings yet