Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bridges: Bridge Rails Gravel Beam Structure Figure XI.1. Scheme of Railroad
Bridges: Bridge Rails Gravel Beam Structure Figure XI.1. Scheme of Railroad
Uploaded by
Djemil Ramy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 pageBridges are structures built to allow the passage of people, animals, or materials over obstacles both natural and man-made. There are two main types of bridges: stationary and movable. Bridges can also be classified by their supported services, natural accidents crossed, basic geometry, and structural systems. The design of bridges must consider standards, length and width needs, geometric and hydraulic specifications, materials selection, safety, aesthetics, economics, and ease of operation and maintenance. Bridges must be able to support both dead and live loads without failure, including loads from permanent installations, vehicles, animals, people, centrifugal forces, pressure, earthquakes, and water.
Original Description:
Original Title
B R I D G E S
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBridges are structures built to allow the passage of people, animals, or materials over obstacles both natural and man-made. There are two main types of bridges: stationary and movable. Bridges can also be classified by their supported services, natural accidents crossed, basic geometry, and structural systems. The design of bridges must consider standards, length and width needs, geometric and hydraulic specifications, materials selection, safety, aesthetics, economics, and ease of operation and maintenance. Bridges must be able to support both dead and live loads without failure, including loads from permanent installations, vehicles, animals, people, centrifugal forces, pressure, earthquakes, and water.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 pageBridges: Bridge Rails Gravel Beam Structure Figure XI.1. Scheme of Railroad
Bridges: Bridge Rails Gravel Beam Structure Figure XI.1. Scheme of Railroad
Uploaded by
Djemil RamyBridges are structures built to allow the passage of people, animals, or materials over obstacles both natural and man-made. There are two main types of bridges: stationary and movable. Bridges can also be classified by their supported services, natural accidents crossed, basic geometry, and structural systems. The design of bridges must consider standards, length and width needs, geometric and hydraulic specifications, materials selection, safety, aesthetics, economics, and ease of operation and maintenance. Bridges must be able to support both dead and live loads without failure, including loads from permanent installations, vehicles, animals, people, centrifugal forces, pressure, earthquakes, and water.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
BRIDGES
TOPIC 1.- READING
Definition
Bridges are structures to facilitate motion of people, animals or materials over natural or
artificial obstacles. Bridges can be made of wood, masonry, concrete and steel.
Types of Bridges
There are two general types of bridges: Stationary and movable. They also can be
classified according to the following features:
Supported services or installations. For the use on highways, railroads, channels or
aqueducts, as a path for people or cattle, for the transportation of goods or as a tubing support.
Bridges for natural accidents. For highways, railroads, bays, lakes, rivers, valleys and
so on.
Basic geometry. Bridges used at a ground level, can be curved, straight, L-shaped, square
and protractile; at elevated height (which can be of low level like the ones constructed over
swampy terrain), trestle bridges and high-level bridges.
Structural systems. Continuous girder bridges, arched bridges (which can be composed
of one or multiple arches), hanging bridges and steel-armor-plated bridges.
Design Considerations
Their design is always based on specific standards for highway bridges of the American
Association State Highway and Transportation Official (AASHTO), the manual for Railway
Engineering published by the American Railway Engineering Association (AREA), standard
plans for highway bridges, Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) and other rules and
regulations published by several highway administrations and railroad companies.
The length, width, alignment and intersecting angles for bridges should satisfy the
functioning needs of the installations to be built.
The geometric requirements, hydraulic specifications, selection of structural systems and
construction materials, safety standards, esthetics, economical aspects and, ease for operation and
maintenance are other important factors to take into consideration.
Highway bridges should be of a smooth asphalt surfaces with sufficient drainage. Both
the longitude slope and the cross section are subject to similar restrictions as for those used for
open highways. Long bridges must be supplied with an adequate lighting, signs and service, and
emergency stations. The protective railings should keep vehicles within the bridge and if
46
necessary, away from pedestrians. Installations over or under bridges should be able to absorb
both expansions or contractions of the structure.
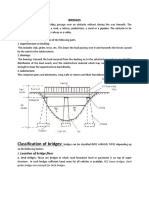
Most of railroad bridges require a gravel beam between structure and rails as is shown in
figure XI.1 to absorb vertical movements.
bridge
rails
gravel
beam
structure
Figure XI.1. Scheme of railroad
Design Loads
Bridges should support the following loads without failures:
Dead loads. They include permanent installations.
Live loads. These are caused by the vehicles, animals or people crossing over bridges and
making a variable weight.
These loads can be of different types such as centrifugal, pressure, longitudinal, seismic,
hydraulic, and so on
You might also like
- UCSB Ladder Inspection Form2 02042014 REVDocument2 pagesUCSB Ladder Inspection Form2 02042014 REVabu7omar-1No ratings yet
- SSP 298 Touareg ElectricsDocument31 pagesSSP 298 Touareg Electricsภูเก็ต เป็นเกาะ100% (3)
- Structural Analysis of BridgesDocument35 pagesStructural Analysis of BridgesRafa OchoaNo ratings yet
- Suspension BridgeDocument38 pagesSuspension BridgeRohith Grandhi100% (4)
- What Is Bridge EngineeringDocument13 pagesWhat Is Bridge EngineeringNOCHU COME THRUNo ratings yet
- Ceng 7509. Bridge Engineering: Dr. John, Me, Mba, PHD, Ce, Mie, FivDocument80 pagesCeng 7509. Bridge Engineering: Dr. John, Me, Mba, PHD, Ce, Mie, FivTesfamichael Abathun100% (1)
- Bridge EngineeringDocument16 pagesBridge EngineeringJoson Anquillano Villegas100% (1)
- Bridge Engineering - Introduction and TerminologiesDocument40 pagesBridge Engineering - Introduction and TerminologiesRoda CadizNo ratings yet
- Bridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsFrom EverandBridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- Building Landmarks - Bridges, Tunnels and Buildings - Architecture and Design | Children's Engineering BooksFrom EverandBuilding Landmarks - Bridges, Tunnels and Buildings - Architecture and Design | Children's Engineering BooksNo ratings yet
- Truss Bridge Analysis: Meng101-ProjectDocument12 pagesTruss Bridge Analysis: Meng101-ProjectMohamed Nour eldenNo ratings yet
- Bridges PDF 1Document83 pagesBridges PDF 1Karmath budthapaNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Road BridgesDocument1,178 pagesReinforced Concrete Road BridgesStructural SpreadsheetsNo ratings yet
- CONTROL-M Concepts GuideDocument50 pagesCONTROL-M Concepts Guideatreis_NB12523No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Eim 10Document17 pagesLesson 1 Eim 10stfup zeliaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Lecture MaterialDocument161 pagesWeek 1 Lecture MaterialAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Plate Girder BridgesDocument116 pagesPlate Girder Bridgesbasanth_712982100% (4)
- Design Considerations For Bridges - WEEK 3 LECTURE NOTESDocument32 pagesDesign Considerations For Bridges - WEEK 3 LECTURE NOTESDammy Taiwo-AbdulNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis and Design of Steel and Steel–Concrete Composite BridgesFrom EverandFinite Element Analysis and Design of Steel and Steel–Concrete Composite BridgesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (16)
- H-Series Gyrasphere Parts Catalog: Model 44Document51 pagesH-Series Gyrasphere Parts Catalog: Model 44emilio garavito100% (1)
- BRIDGE ENGINEERING DefinitionDocument3 pagesBRIDGE ENGINEERING DefinitionFor TwitterNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To BridgesDocument94 pages1-Introduction To BridgesMANUPRIYA MANUPRIYANo ratings yet
- Course Outline: Amit Kumar Varma Geotechnical Engineer Department of RoadDocument5 pagesCourse Outline: Amit Kumar Varma Geotechnical Engineer Department of RoadVarma AmitNo ratings yet
- Bridges: English For Civil EngineeringDocument13 pagesBridges: English For Civil EngineeringBANG MANNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8-BridgesDocument2 pagesLesson 8-BridgesMohamed MraouiNo ratings yet
- Bridge Design ConceptDocument7 pagesBridge Design ConceptEarch DesignersNo ratings yet
- Structure Built River Road Railroad Allow People Vehicles SideDocument7 pagesStructure Built River Road Railroad Allow People Vehicles SideAnonymous UyFZUD1DfNo ratings yet
- 1.1 General Introduction: Chapter - 1 Bridge InvestigationDocument25 pages1.1 General Introduction: Chapter - 1 Bridge InvestigationTeshu NigusieNo ratings yet
- Brigde NoteDocument8 pagesBrigde Noteayodejiayinde765No ratings yet
- Ceng 5322Document32 pagesCeng 5322dawitdeginet096No ratings yet
- CE 417: Design of Bridges (2 Units) : Presenter: Assessment: 2 Tests + 2 Assignments 40%Document31 pagesCE 417: Design of Bridges (2 Units) : Presenter: Assessment: 2 Tests + 2 Assignments 40%Edsony NyamwelaNo ratings yet
- CNM NotesDocument14 pagesCNM NotesMicaiah HendricksNo ratings yet
- Auxillo Ulo Week1-3Document8 pagesAuxillo Ulo Week1-3JOYLYN CRIS AUXILLONo ratings yet
- BridgeDocument58 pagesBridgeIyœ Møsisæ100% (1)
- Lecture 1Document31 pagesLecture 1JohaNo ratings yet
- Culvert and BridgeDocument16 pagesCulvert and BridgeAljondear RamosNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document39 pagesPresentation 1Bertrand TuyishimeNo ratings yet
- Classification of Bridges: Bridge Engineering Unit-2Document4 pagesClassification of Bridges: Bridge Engineering Unit-2vinitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bridge EngineeringDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Bridge Engineering21-06580No ratings yet
- Intro To BridgesDocument5 pagesIntro To Bridges2BA19CV059 Rakshita SarangmathNo ratings yet
- Bridge EngineeringDocument10 pagesBridge EngineeringLaeek PatelNo ratings yet
- Aashto:: Truss BridgeDocument5 pagesAashto:: Truss BridgeSajjad Amin AminNo ratings yet
- Civil EngineeringDocument6 pagesCivil EngineeringNour el houda MerabetNo ratings yet
- Transportation Is One of The Important Things in Any Country Wants To Keep Everything Alive and Develop The SocietyDocument3 pagesTransportation Is One of The Important Things in Any Country Wants To Keep Everything Alive and Develop The SocietyMohamed Nour eldenNo ratings yet
- 1.1 General: The Main Parts of A Bridge Structure Are As BelowDocument6 pages1.1 General: The Main Parts of A Bridge Structure Are As BelowPranay ReddyNo ratings yet
- VivasDocument11 pagesVivasGautam RaiNo ratings yet
- Studies On Major Elements of An Elevated Metro Bridge by Using by Using Staad ProDocument9 pagesStudies On Major Elements of An Elevated Metro Bridge by Using by Using Staad Promanish tomarNo ratings yet
- Module # 1 - IntroductionDocument12 pagesModule # 1 - IntroductionANNA BETH ESMUNDONo ratings yet
- I. History: Steel Truss - Made of Individual Members With Equal Counteracting Tensile and Compressive Forces, ItsDocument14 pagesI. History: Steel Truss - Made of Individual Members With Equal Counteracting Tensile and Compressive Forces, ItsShai AranasNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Bridge Design Lecture NotesDocument40 pagesFundamentals of Bridge Design Lecture NotesSami IGNo ratings yet
- Bridge 1st UnitDocument18 pagesBridge 1st UnitFE3056 NAGARAJ.SNo ratings yet
- C-1 IntrodutionDocument17 pagesC-1 IntrodutionDaniel SolomonNo ratings yet
- Road ComponentsDocument5 pagesRoad ComponentsLmtc DhulikhelNo ratings yet
- 1 - Intro & History Bridge Design AbdulDocument91 pages1 - Intro & History Bridge Design Abduldawitdeginet096No ratings yet
- Imp Design of Rail Over BridgeDocument5 pagesImp Design of Rail Over BridgeShivangi MishraNo ratings yet
- Bridges PDFDocument5 pagesBridges PDFBasavaraj HsNo ratings yet
- Bridge Lecture - BDocument229 pagesBridge Lecture - BHiezen UndayNo ratings yet
- Bailey BridgeDocument10 pagesBailey BridgeAdnan AnsariNo ratings yet
- Bridge Engineering:: Introduction To BridgesDocument38 pagesBridge Engineering:: Introduction To BridgesDoreen Claire Lagado SuperableNo ratings yet
- Bridge Engineering NotesDocument26 pagesBridge Engineering NotesPacha Khan KhogyaniNo ratings yet
- Intro Railway DesignDocument5 pagesIntro Railway DesignNarte, Angelo C.No ratings yet
- Design of High Level Bridge Across River: Rathod Chiranjeevi Sabbineni RamyakalaDocument11 pagesDesign of High Level Bridge Across River: Rathod Chiranjeevi Sabbineni RamyakalaimamtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document40 pagesChapter 1Fuad AhmedinNo ratings yet
- Andre Rangga Nugraha - 120130039 - 1A - EnglishDocument1 pageAndre Rangga Nugraha - 120130039 - 1A - EnglishAndre RanggaNo ratings yet
- Bridge Is A Structure Which Provides Passage Over The Obstacles Like Valley, River, Road or RailwayDocument59 pagesBridge Is A Structure Which Provides Passage Over The Obstacles Like Valley, River, Road or RailwayVinay BagodiNo ratings yet
- CW & CCW CW CCW (Normal) Mod. 1 Mod. 2Document2 pagesCW & CCW CW CCW (Normal) Mod. 1 Mod. 2mukeshkumarjNo ratings yet
- CVLE451-Online Lecture 3 PDFDocument28 pagesCVLE451-Online Lecture 3 PDFbasharNo ratings yet
- Why MastercamDocument30 pagesWhy MastercamMarius CucuietNo ratings yet
- Shafts Sheq Meeting Minutes - December 2022Document3 pagesShafts Sheq Meeting Minutes - December 2022Victor NdlovuNo ratings yet
- Teorema Thevenin Dan NortonDocument24 pagesTeorema Thevenin Dan NortonIkki Purnama100% (1)
- Radio WaveDocument35 pagesRadio WaveMuruganNo ratings yet
- JVC LCD Lt-32d200 Lt-32dv20Document38 pagesJVC LCD Lt-32d200 Lt-32dv20ngoclinhdtddNo ratings yet
- Use of Recycled Aggregate Concrete in Prestressed Structural ElementsDocument4 pagesUse of Recycled Aggregate Concrete in Prestressed Structural Elementsmarcob74No ratings yet
- TPM Conference With Peter WillmottDocument1 pageTPM Conference With Peter WillmottAniko AntalNo ratings yet
- FOrdDocument29 pagesFOrdSoporte TGUNo ratings yet
- MechanicalDocument13 pagesMechanicaldenisNo ratings yet
- Hot Melt TechnologiesDocument12 pagesHot Melt TechnologiesaaaammmeeNo ratings yet
- Yhdc SCTDocument3 pagesYhdc SCTDavid S. CastNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Parallel Resonance Circuits: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Parallel Resonance Circuits: Objectiveayesha amjadNo ratings yet
- Activate AluminaDocument3 pagesActivate AluminaNazar AhmedNo ratings yet
- K004en PDFDocument49 pagesK004en PDFuziNo ratings yet
- Critical Point Consulting: Gary PalmerDocument148 pagesCritical Point Consulting: Gary Palmerenavsantos100% (1)
- Acid Base Eqm. Worksheets UPDATED 2022Document24 pagesAcid Base Eqm. Worksheets UPDATED 2022Sara MolinaroNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1Document4 pagesInformation Sheet 1KèlǐsītǎnKǎPáng0% (1)
- CH 6Document3 pagesCH 6atmroo9No ratings yet
- HoneypotsDocument17 pagesHoneypotsNipun VermaNo ratings yet
- Aislador Epoxi Catalogo 2011 ENGDocument56 pagesAislador Epoxi Catalogo 2011 ENGmk116dNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of RocksDocument13 pagesMechanical Properties of RocksRizette Palogan100% (1)
- 03MA BiopharmsumDocument8 pages03MA BiopharmsumApoloTrevinoNo ratings yet
- Sop Piping Tubes Standard Repair ProcedureDocument3 pagesSop Piping Tubes Standard Repair ProceduresbmmlaNo ratings yet