Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M08 Mari2603 07 Se C08
Uploaded by
LENARD GUINSATAOOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
M08 Mari2603 07 Se C08
Uploaded by
LENARD GUINSATAOCopyright:
Available Formats
E X E R C IS E
8 REVIEW SHEET
The Axial Skeleton
Name _______________________________________________________ Lab Time/Date ___________________________________
The Skull
1. The skull is one of the major components of the axial skeleton. Name the other two.
bony thorax
____________________________________________________ vertebral column
and ____________________________________________________
What structures does each of these three components of the axial skeleton protect? _____________________________
1. skull protects the brain
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2. the bony thorax protects the heart and lungs
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3. vertebral column protects the spinal cord
interlocking joints of the skull
2. Define suture: _______________________________________________________________________________________________
3. With one exception, the skull bones are joined by sutures. Name the exception. The mandible or the jaw is attached
_________________________________
by a movable joint.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4. What are the four major sutures of the skull, and what bones do they connect?
1. Sagittal suture joins the left and right parietal bones
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2. Coronal suture joins the parietal and frontal bones
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3. Squamous suture joins the parietal and temporal bones
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4. Lambdoid suture joins the parietal and occipital bones
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
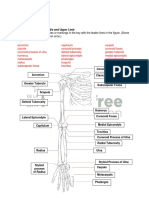
5. Name the eight bones composing the cranium.
frontal right temporal left temporal right parietal
left parietal occipital ethmoid sphenoid
1. reduce the weight of the skull to allow the head to be held upright.
6. Give two possible functions of the sinuses. ____________________________________________________________________
2. add resonance to the voice
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
7. What is the orbit? The bony cavity containing the eye.
___________________________________________________________________________________________
8. Why can the sphenoid bone be called the keystone of the cranial floor? The sphenoid forms a plateau that runs
_________________________________________
across the width of the skull.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
94 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc.
Review Sheet 8 95
9. Match the bone names in column B with the descriptions in column A. (Some choices may be used more than once.)
Column A Column B
frontal
1. bone forming anterior cranium, or forehead ethmoid
zygomatic 2. cheekbone frontal
maxilla 3. upper jaw hyoid
nasal 4. bridge of nose lacrimal
palantine
5. posterior roof of mouth mandible
parietal
6. bone pair united by the sagittal suture maxilla
temporal
7. site of jugular foramen and carotid canal nasal
sphenoid
8. contains a “saddle” that houses the pituitary gland occipital
lacrimal 9. has an opening that allows tears to pass palatine
maxilla 10. forms most of hard palate parietal
ethmoid 11. superior and medial nasal conchae are part of this bone sphenoid
temporal 12. site of external auditory meatus temporal
sphenoid 13. has greater and lesser wings vomer
ethmoid 14. its “holey” plate allows olfactory fibers to pass zygomatic
maxilla 15. facial bone that contains a sinus
frontal spenoid ethmoid
, , and 16. three cranial bones
containing paranasal sinuses
occipital 17. its oval-shaped protrusions articulate with the atlas
occipital 18. spinal cord passes through a large opening in this bone
hyoid 19. not really a skull bone
mandible 20. forms the chin
vomer 21. inferior part of nasal septum
mandible maxilla
, 22. contain alveoli bearing teeth
ethmoid
23. bears an upward protrusion called the rooster’s comb
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc.
96 Review Sheet 8
10. Using choices from column B in question 9 and from the key to the right, identify all bones and bone markings pro-
vided with leader lines in the diagram below. (Some terms from the key may not be used.)
alveolar process
Coronal suture Sagittal suture
Nasal
coronal suture
Frontal
foramen magnum
Parietal greater wing of sphenoid
Greater wing inferior nasal concha
of sphenoid
Temporal middle nasal concha of ethmoid
Ethmoid sagittal suture
Lacrimal
squamous suture
Middle nasal
Zygomatic concha of ethmoid
Inferior nasal concha
Vomer
Maxilla
Alveolar process Mandible
The Fetal Skull
No
11. Are the same skull bones present in the adult also found in the fetal skull? ______________________________________
12. How does the size of the fetal face compare to its cranium? The face is smaller in comparison to the cranium of a
____________________________________________________
fetus.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
The adult skull is 1/8th total body length, and the fetal skull is 1/4th
How does this compare to the adult skull? ____________________________________________________________________
total body length.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
13. What are the outward conical projections in some of the fetal cranial bones? They are ossification centers.
____________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
A fibrous membrane found between bones of the fetal skull.
14. What is a fontanel? __________________________________________________________________________________________
The fontanels ossify or become bone by around age of 22 months.
What is its fate? __________________________________________________________________________________________
Fontanels allow the brain to grow, and allow the skull to be
What is the function of the fontanels in the fetal skull? _________________________________________________________
compressed during child birth.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc.
Review Sheet 8 97
15. Using the terms listed, identify each of the fontanels shown on the fetal skull below.
anterior fontanel mastoid fontanel posterior fontanel sphenoidal fontanel
Anterior fontanel
Sphenodial
Parietal
bone Frontal
bone
Posterior
fontanel
Occipital
bone
Mastoid fontanel
Temporal bone
The Vertebral Column
16. Using the key, correctly identify the vertebral parts/areas described below. (More than one choice may apply in some
cases.) Also use the key letters to correctly identify the vertebral areas in the diagram.
Key: a. body d. pedicle g. transverse process
b. intervertebral foramina e. spinous process h. vertebral arch
c. lamina f. superior articular facet i. vertebral foramen
i 1. cavity enclosing the nerve cord
e
a g
2. weight-bearing portion of the vertebra c h
e g
, 3. provide levers against which muscles pull
a g
, 4. provide an articulation point for the ribs
b 5. opening providing for exit of spinal nerves
f
a h i
, 6. structures that form an enclosure for the
spinal cord
d a
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc.
98 Review Sheet 8
17. The distinguishing characteristics of the vertebrae composing the vertebral column are noted below. Correctly
identify each described structure or region by choosing a response from the key. (Some choices may be used more
than once.)
Key: atlas coccyx sacrum
axis lumbar vertebra thoracic vertebra
cervical vertebra—typical
cervical vertebra—typical
1. vertebral type with a bifid (forked) spinous process
atlas 2. pivots on C2; lacks a body
thoracic vertebra 3. bear facets for articulation with ribs; form part of bony thoracic cage
sacrum 4. forms a joint with the hip bone
lumbar vertebra 5. vertebra with blocklike body and short, stout spinous process
coccyx
6. “tailbone”
atlas 7. articulates with the occipital condyles
lumbar vertebra 8. five components; unfused
thoracic vertebra 9. twelve components; unfused
sacrum 10. five components; fused
18. Identify as specifically as possible each of the vertebrae types shown in the diagrams below. Also identify and label
the following markings on each: transverse processes, spinous process, body, superior articular processes, as well
as the areas provided with leaders.
Body
Transverse Body Transverse
process process
Superior
articular
process
Spinous
process Costal facet for Vertebral Spinous
head of the rib foramen process
thoracic
_____________________________ cervical
______________________________
Fibrocartilage
19. What kind of tissue makes up the intervertebral discs? _________________________________________________________
a slipped disc; or when the fibrocartilage protrudes from the vertebra
20. What is a herniated disc? _____________________________________________________________________________________
pain and numbness
What problems might it cause? _______________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc.
Review Sheet 8 99
21. On this illustration of an articulated vertebral column, identify each structure provided with a leader line by using the
key terms.
Key: atlas Atlas
axis
intervertebral disc Axis
two thoracic vertebrae
two lumbar vertebrae
sacrum
Two thoracic
vertebrae
Intervertebral
disc
Two lumbar
vertebrae
Sacrum
The Bony Thorax
sternum
22. The major components of the bony thorax (excluding the vertebral column) are the
ribs
and the .
cone-shaped
23. What is the general shape of the thoracic cage? _______________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc.
100 Review Sheet 8
24. Using the terms at the right, identify the regions and landmarks of the bony thorax.
b a. body
b. costal cartilage
c. false ribs
d. floating ribs
e. manubrium
e
f. sternum
g. true ribs
h. xiphoid process
g a
f
d
L1 vertebra
A true rib will have its own individual costal cartilage attachment to the
25. Differentiate a true rib from a false rib. ________________________________________________________________________
sternum, and a false rib will attach indirectly to the sternum or not attach at all to the sternum
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
A rib that does not attach to the sternum or does not have any sternal attachments.
26. What is a floating rib? _______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc.
You might also like
- MRCPCH Clinical: Short Cases, History Taking & Communication Skills 3eDocument19 pagesMRCPCH Clinical: Short Cases, History Taking & Communication Skills 3ePasTestBooks100% (6)
- Acr 2018 Dxit Exam SetDocument113 pagesAcr 2018 Dxit Exam SetElios NaousNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 8Document7 pagesLaboratory 8Diana Rose SaludoNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Cagayan University: WorksheetDocument7 pagesLiceo de Cagayan University: WorksheetLol lolNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 7Document8 pagesLaboratory 7Diana Rose SaludoNo ratings yet
- Bio001l - Ex009 Axial BonesDocument9 pagesBio001l - Ex009 Axial Boneslow key100% (1)
- Work Sheet 6 Skeletal System A28 Group1Document8 pagesWork Sheet 6 Skeletal System A28 Group1Japet Floyd AlipioNo ratings yet
- Skull WorksheettDocument2 pagesSkull WorksheettJingle Capistrano TarucNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Marieb Solutions ManualDocument20 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Marieb Solutions Manualstephenthanh1huo100% (28)
- Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Marieb Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument41 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Marieb Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFserenafinnodx100% (10)
- Cranial Anatomy RevisionDocument20 pagesCranial Anatomy Revisionbannanastew7975No ratings yet
- Digestive SsDocument46 pagesDigestive SsLeon L GayaNo ratings yet
- Bones Notes - Pdf-Copy 1 PDFDocument38 pagesBones Notes - Pdf-Copy 1 PDFSuraj YadavNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Axial - Skeleton - AtlasDocument59 pagesLab Manual - Axial - Skeleton - Atlaspertemuan blok3.3No ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Appendicular - Skeleton - AtlasDocument58 pagesLab Manual - Appendicular - Skeleton - AtlasShao KahnNo ratings yet
- SFSFSFDocument6 pagesSFSFSFFatima MartinezNo ratings yet
- Part-I The SkullDocument29 pagesPart-I The SkullRuth MenelikNo ratings yet
- Bones of The HeadDocument17 pagesBones of The HeadDindin Lou MendozaNo ratings yet
- Biol 109 Study Sheet - Skeletal System - F14Document2 pagesBiol 109 Study Sheet - Skeletal System - F14jakpykeNo ratings yet
- Canine Radiographs by Louisa White: Click Skeleton To EnterDocument455 pagesCanine Radiographs by Louisa White: Click Skeleton To EnteranacampsNo ratings yet
- ANAT 1 Lab Homework 3-2 - JMDocument11 pagesANAT 1 Lab Homework 3-2 - JMJadeanna MartinezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The SkullDocument29 pagesAnatomy of The Skullaya abdullahNo ratings yet
- The Skull - Anatomy BonesDocument100 pagesThe Skull - Anatomy BonesFatima Kh SalahNo ratings yet
- Act 8Document6 pagesAct 8Rose CostaNo ratings yet
- Open AnatomyDocument50 pagesOpen AnatomyalukiasuNo ratings yet
- 1.11 ANATOMY - The Nose and Paransal SinusesDocument4 pages1.11 ANATOMY - The Nose and Paransal SinusesPaolo NaguitNo ratings yet
- Amano, Miles M. - Human AnaPhyW5-6Document4 pagesAmano, Miles M. - Human AnaPhyW5-6Khalil, Mikaela VictoriaNo ratings yet
- GRDA Intro Head&NeckDocument18 pagesGRDA Intro Head&NeckKingNo ratings yet
- 1 - The SkullDocument68 pages1 - The Skullaboody omerNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck1Document61 pagesHead and Neck1Rherhe ChecheNo ratings yet
- FORAMINA OF SKULL AND STRUCTURES PASSING THROUGH THEM - True Value Dental InstituteDocument1 pageFORAMINA OF SKULL AND STRUCTURES PASSING THROUGH THEM - True Value Dental InstituteRusseiNo ratings yet
- Anatomia para Estética Parte 1Document45 pagesAnatomia para Estética Parte 1Rodolpho VilelaNo ratings yet
- Yyyyycrash Course Anatomy - Head & NeckDocument52 pagesYyyyycrash Course Anatomy - Head & Neck黃芳昌No ratings yet
- Lab II 09studentDocument7 pagesLab II 09student03152788No ratings yet
- ZOOL30040 Practical HandoutDocument10 pagesZOOL30040 Practical Handoutannabelledarcy247No ratings yet
- OutlineDocument43 pagesOutlineJulia MundoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2/3 Pronunciation Focus Bones of The OrbitDocument11 pagesUnit 2/3 Pronunciation Focus Bones of The OrbitIon NagomirNo ratings yet
- Overview of Anatomy of The Skeletal System - Midterm LessonsDocument133 pagesOverview of Anatomy of The Skeletal System - Midterm LessonsArvic Pascua MaltizoNo ratings yet
- Neuroimaging: Head & Neck Neuroimaging: Head & Neck Neuroimaging: Head & NeckDocument107 pagesNeuroimaging: Head & Neck Neuroimaging: Head & Neck Neuroimaging: Head & NeckWenhui ZhouNo ratings yet
- Chap2 MageeDocument66 pagesChap2 MageeSerenelaNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet 7 The Muscular System A28 Group1Document5 pagesWork Sheet 7 The Muscular System A28 Group1Japet Floyd AlipioNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy IiDocument5 pagesGeneral Anatomy IijamjamjamNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck Radiology: Skull X-RayDocument20 pagesHead and Neck Radiology: Skull X-RayadiningtitisNo ratings yet
- RADIOLOGYDocument45 pagesRADIOLOGYLucifer GNo ratings yet
- ENT - Anatomy of The Nose and Paranasal SinusesDocument6 pagesENT - Anatomy of The Nose and Paranasal SinusesChristian LantanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Extraoral and Occlusal Anatomic LandmarksDocument22 pagesChapter 04 Extraoral and Occlusal Anatomic LandmarksFaith AnneessaNo ratings yet
- Axial SkeletonDocument34 pagesAxial SkeletonFachriza EffendiNo ratings yet
- Norma FrontalisDocument79 pagesNorma Frontalisrenzvalorant28No ratings yet
- Skeletal System: I. General CharacteristicsDocument34 pagesSkeletal System: I. General CharacteristicsMason BruceNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Head NeckDocument84 pagesAnatomy Head NeckLISTRIKPENDINGIN SMKN1TALIWANGNo ratings yet
- SkullDocument23 pagesSkullurjaNo ratings yet
- Special-Senses FormatDocument5 pagesSpecial-Senses FormatSeaNo ratings yet
- Head and NeckDocument208 pagesHead and NeckStephanie ThompsonNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: A Fixed Learning ModuleDocument38 pagesThe Respiratory System: A Fixed Learning ModulerezaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of External Nose & Nasal SeptumDocument20 pagesDiseases of External Nose & Nasal Septumggg225201No ratings yet
- Posterior Cranial Fossa-Decamber2009Document47 pagesPosterior Cranial Fossa-Decamber2009mmaam_11No ratings yet
- Otot WajahDocument5 pagesOtot WajahSalsabila Nada PNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Student Learning ObjectivesDocument15 pagesSkeletal System: Student Learning ObjectivesJM Arevalo100% (1)
- Anatomy Lect of Skull 2Document36 pagesAnatomy Lect of Skull 2sanullah123khan.13No ratings yet
- HFBFB Chariza Therese A. Mira BSN 1-C: Page 1 of 8Document8 pagesHFBFB Chariza Therese A. Mira BSN 1-C: Page 1 of 8Mira Chariza Therese A. - BSN 1- CNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System SheetDocument11 pagesCardiovascular System SheetBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Diaphragmatic Hernia RepairDocument4 pagesDiaphragmatic Hernia RepairGizem ÖztürkNo ratings yet
- TAPVCDocument67 pagesTAPVCIhsan AmalNo ratings yet
- Case Study Elective1Document32 pagesCase Study Elective1Jhem SiribanNo ratings yet
- Lungs & Pleura PDFDocument24 pagesLungs & Pleura PDFEl SpinnerNo ratings yet
- E363 FullDocument4 pagesE363 FullRamadhyanNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy of The Coronary SinusDocument7 pagesThe Anatomy of The Coronary Sinusmihalcea alinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Biomechanics of SpineDocument69 pagesAnatomy and Biomechanics of SpinehisslNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3 - Blood Vessels I - Histology of Artery and Vein ArteriesDocument28 pagesLaboratory 3 - Blood Vessels I - Histology of Artery and Vein ArteriesSofia NNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Function TestsDocument10 pagesCardiac Function TestsHari Prasath100% (1)
- Basic ECG InterpretationDocument16 pagesBasic ECG InterpretationKim BadillesNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular PDFDocument148 pagesCardio Vascular PDFStefana RoxanaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory QuizDocument3 pagesCirculatory QuizBello Nelson100% (1)
- Thorax PDFDocument33 pagesThorax PDFPanda MimiNo ratings yet
- 2020 Heart and Neck Vessels 2Document66 pages2020 Heart and Neck Vessels 2Faith madayag100% (2)
- Science9 q1 Mod1 SDOv2Document32 pagesScience9 q1 Mod1 SDOv2Qwerty Anime100% (1)
- Circulation and Transportation in Gen - Bio 2 For Grade 11 STEMDocument60 pagesCirculation and Transportation in Gen - Bio 2 For Grade 11 STEMDead Eye100% (1)
- ECG Study GuideDocument70 pagesECG Study GuideFatima Chrystelle NuñalNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Mechanical Circulatory SupportDocument8 pagesPediatric Mechanical Circulatory SupportselvakumarNo ratings yet
- RTS1-K13-Anatomy of LungsDocument22 pagesRTS1-K13-Anatomy of LungsYohanna SinuhajiNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesCardiac Anatomy and PhysiologyKarina YurchenkoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Electrophysiology Basics (RL-204-Tn)Document5 pagesCardiac Electrophysiology Basics (RL-204-Tn)Navojit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube Manual Atrium Green HandbookDocument40 pagesChest Tube Manual Atrium Green HandbookprogramgrabberNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination of The Thorax, Abdomen and PelvisDocument42 pagesClinical Examination of The Thorax, Abdomen and PelvisTunnelssNo ratings yet
- Transthoracic Echocardiography Report: Reason For ExamDocument4 pagesTransthoracic Echocardiography Report: Reason For ExamJeff BakerNo ratings yet
- Clinical Significance of Azygos VeinDocument6 pagesClinical Significance of Azygos VeinChavdarNo ratings yet
- The Human HeartDocument1 pageThe Human HeartMae TanNo ratings yet
- Ganglioni MediastinaliDocument1 pageGanglioni Mediastinaliburaga madalinaNo ratings yet