Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Edj 2
Edj 2
Uploaded by
Reichelle Arellano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
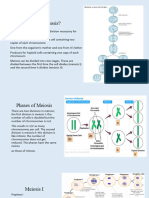
13 views1 pageMeiosis I involves a diploid cell dividing into haploid cells through chromosomal crossing over of genes, resulting in genetic diversity between parent and daughter cells. During Metaphase II of meiosis, the meiotic spindles pull chromosomes back to the metaphase plate in the two daughter cells created in the initial meiotic division, allowing division without DNA replication. As a result, each allele will have two copies in every cell.
Original Description:
Original Title
edj2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMeiosis I involves a diploid cell dividing into haploid cells through chromosomal crossing over of genes, resulting in genetic diversity between parent and daughter cells. During Metaphase II of meiosis, the meiotic spindles pull chromosomes back to the metaphase plate in the two daughter cells created in the initial meiotic division, allowing division without DNA replication. As a result, each allele will have two copies in every cell.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageEdj 2
Edj 2
Uploaded by
Reichelle ArellanoMeiosis I involves a diploid cell dividing into haploid cells through chromosomal crossing over of genes, resulting in genetic diversity between parent and daughter cells. During Metaphase II of meiosis, the meiotic spindles pull chromosomes back to the metaphase plate in the two daughter cells created in the initial meiotic division, allowing division without DNA replication. As a result, each allele will have two copies in every cell.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
The cells engaged in meiosis I are similar in that a diploid cell
divides into a haploid cell, and it works by involving
chromosomal crossing across genes, which results in genetic
diversity in the daughter cells of the next generation from the
parent cells. Metaphase II is the stage of meiosis when the
meiotic spindles of the two daughter cells created during the
initial meiotic division begin to pull the chromosomes back to
the metaphase plate, allowing the cells to divide without any
DNA replication. As a consequence, every allele will have two
copies in each cell.
You might also like
- Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell DivisionLavanya Thevi100% (1)
- 4 MeiosisDocument5 pages4 MeiosisVarun GoseinNo ratings yet
- The Main Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis .: Name: Yousef Raed Monather, Group: C4Document1 pageThe Main Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis .: Name: Yousef Raed Monather, Group: C4yousefreed73No ratings yet
- Mitosis: Labeled Diagram: Interphase: Gap 1 Phase (Growth), Synthesis Phase (Copy of DNA), Gap 2 Phase (OrganelleDocument7 pagesMitosis: Labeled Diagram: Interphase: Gap 1 Phase (Growth), Synthesis Phase (Copy of DNA), Gap 2 Phase (Organelleazzahra adeliaNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q4 M2Document6 pagesScience8 Q4 M2Arabella BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesCell DivisionNusrat ShoshiNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 6 Exercise (ANSWERS)Document4 pagesBiology Chapter 6 Exercise (ANSWERS)NURUL AMIRA BINTI R AZMI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- What Happens During Prophase IIDocument9 pagesWhat Happens During Prophase IILotusNo ratings yet
- CN 6 BioDocument2 pagesCN 6 BioJanna PaduaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument1 pageCell DivisionManas AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Mitosis & Meiosis and Their DiferrencesDocument11 pagesCytogenetics Mitosis & Meiosis and Their DiferrencesGeemilReyNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument3 pagesMeiosisJaja Jr. Evasco EmbarqueNo ratings yet
- Meiosis I and Meiosis IIDocument2 pagesMeiosis I and Meiosis IIyori rafiadliNo ratings yet
- Meiosis I & 2Document17 pagesMeiosis I & 2Mar Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 1Document6 pagesMeiosis 1E32 ESTERLINENo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument6 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionJeyanthiNo ratings yet
- Meiosis IIDocument3 pagesMeiosis IIArdhiansyah BaskaraNo ratings yet
- Meiosis.-Meiosis (del griego μείωσις meíōsis 'disminución')Document6 pagesMeiosis.-Meiosis (del griego μείωσις meíōsis 'disminución')julioNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Chromatids (The Two Halves of A Duplicated Chromosome), As inDocument29 pagesMeiosis: Chromatids (The Two Halves of A Duplicated Chromosome), As inyamamaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument7 pages4.2 Cell As A Unit of Lifehola adiosNo ratings yet
- Prelim Task 4Document1 pagePrelim Task 4Kagami TaigaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Worksheet 4.2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument6 pagesBIOLOGY Worksheet 4.2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisEvcha WangagNo ratings yet
- Group H Pathology PresentationDocument15 pagesGroup H Pathology PresentationdorsukendraNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle-TRFDocument8 pagesThe Cell Cycle-TRFmaniiiiiiiiNo ratings yet
- 4 MeiosisDocument14 pages4 MeiosisMary Joy ReyesNo ratings yet
- GenbioDocument3 pagesGenbioMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 6 ExerciseDocument4 pagesBiology Chapter 6 ExerciseNURUL AMIRA BINTI R AZMI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Science ResearchDocument3 pagesScience ResearchShaira Jea ConsultaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle LectureDocument3 pagesCell Cycle LectureR Jay LagdaminNo ratings yet
- Biology CH # 5 To 9 NoteDocument83 pagesBiology CH # 5 To 9 Notefurqanshaikh2334No ratings yet
- Meiosis - Clay ModellingDocument4 pagesMeiosis - Clay ModellingAlexandra M.No ratings yet
- Script (2 Copies)Document3 pagesScript (2 Copies)Zendrix PauloNo ratings yet
- Function of MeiosisDocument7 pagesFunction of MeiosisPhilip AtmaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division-AnswerDocument5 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division-AnswerSWASTIKA MALONo ratings yet
- 6b SamiDocument21 pages6b Samidanyaalahmad7No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell DivisionDocument70 pagesCell Structure and Cell DivisionAMALIA INDAH ALLIZA ALLIZANo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document26 pagesChapter 10Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument2 pagesMeiosisK8Y KattNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Vs MitosisDocument1 pageMeiosis Vs MitosisRivera Franco EmilianoNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio (October 10, 2023)Document9 pagesGen Bio (October 10, 2023)Rhian Kassi Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologyJikah JiKiNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionLief LifeNo ratings yet
- The Cell CycleDocument9 pagesThe Cell Cyclesalahuddin_md5935No ratings yet
- Kunal Pandurang ThipeDocument14 pagesKunal Pandurang ThipeKUNALPANDURANGTHIPENo ratings yet
- Science Grade-VIIDocument20 pagesScience Grade-VIIGie Ann GongobNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument2 pagesMitosis and MeiosisFrances Isko FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Meiosis ReviewerDocument2 pagesMeiosis ReviewerGlenn GalvezNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Growth: General Biology IDocument17 pagesCell Division and Growth: General Biology IJhana DanoNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Growth: General Biology IDocument17 pagesCell Division and Growth: General Biology IJhana DanoNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Growth: General Biology IDocument17 pagesCell Division and Growth: General Biology IJhana DanoNo ratings yet
- (FRANCISCO) Activity 4.2Document1 page(FRANCISCO) Activity 4.2Kyle Isabelle FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Overview of Cell Cycle by Javali.GDocument15 pagesOverview of Cell Cycle by Javali.GJavali.GNo ratings yet
- Meiosis-Advanced 20240304 125003 0000Document25 pagesMeiosis-Advanced 20240304 125003 0000Jaja Jr. Evasco EmbarqueNo ratings yet
- Activity 4.2Document2 pagesActivity 4.2Jam TabucalNo ratings yet
- LSPU BSBIO - ZOO1 - SLM4 ExerciseDocument11 pagesLSPU BSBIO - ZOO1 - SLM4 ExerciseJohn ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division, Differentiation and DiversityDocument7 pagesCell Division, Differentiation and DiversityT MNo ratings yet
- MitosismeiosisDocument44 pagesMitosismeiosisalanamaharaj20No ratings yet
- What Is Mitosis & MeiosisDocument7 pagesWhat Is Mitosis & MeiosisMuhammad VaizNo ratings yet
- Cell Division, Mitosis, Meiosis, AmitosisDocument27 pagesCell Division, Mitosis, Meiosis, AmitosisAngryBird_jinx100% (1)
- (Biology Form 4) Stage in MeiosisDocument6 pages(Biology Form 4) Stage in MeiosisFuzieanna BakhtiarNo ratings yet
- I. Procedure:: Human InheritanceDocument1 pageI. Procedure:: Human InheritanceReichelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- SpongesDocument2 pagesSpongesReichelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Oo 1Document1 pageOo 1Reichelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Eeh 3Document1 pageEeh 3Reichelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- DishesDocument1 pageDishesReichelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Garbage CanDocument1 pageGarbage CanReichelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Printer: 7 Ways To Care Your KeyboardDocument1 pagePrinter: 7 Ways To Care Your KeyboardReichelle ArellanoNo ratings yet