Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2011-08-PATHOLAB-Hemodynamic Disorder
Uploaded by
dtimtimanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2011-08-PATHOLAB-Hemodynamic Disorder
Uploaded by
dtimtimanCopyright:
Available Formats
Subject: Pathology Topic: HEMODYNAMIC DISORDER (Pre-Lab) Lecturer: Dr.
Gladysgay Malimban Transcriptionist: Angry Birds Editor: Angry Birds Pages: 4
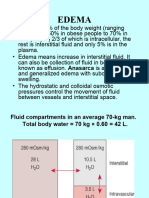
HEMODYNAMIC DISORDER I. EDEMA -accumulation of fluids within the cells, interstitial tissues and body cavities -Transudate: caused by increased hydrostatic pressure or reduced plasma protein -Exudate: caused by increased vascular permeability NASAL POLYP -Non-neoplastic; inflammatory edema due to frequent irritation
Microsopically: Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with loose stroma infiltrated by inflammatory cells (eosinophils); edematous mucosa Gross: Fingerlike, Grayish, Polypoid, With fluid
II. HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION HYPEREMIA- an active process in which arteriolar dilation leads to increased blood flow CONGESTION- a passive process resulting from reduced outflow of blood from a tissue ACUTE SUPPURATIVE APPENDICITIS (hyperemia)
Loose stroma with infiltrated inflammatory cells
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
SY 2011-2012
1
CHRONIC PASSIVE CONGESTION, LIVER
NUTMEG APPEARANCE
Microscopically: neutrophilic infiltration within muscularis DILATED CENTRAL VEINS, CENTRAL HEMORRHAGIC NECROSIS CHRONIC PASSIVE CONGESTION, LUNGS CARDIAC SCLEROSIS
Microscopically: Thickened alveolar walls (due to dilation of capillaries). - dilated blood vessels containing abundant RBCs. presence of protein rich edematous fluid.
PRESENCE OF FIBROSIS BREACHING BETWEEN THE CENTRAL ZONAL REGIONS II. HEMORRHAGE -extravasation of blood into the extravascular space ASPERGILLOSIS (with intra-alveolar hemorrhages)
HEMOSIDERIN-LADEN MACROPHAGES
Gross: sharply delineated, rounded, gray foci with necrotic borders
Microscopically: septate hyphae with acute-angle branching
IV. THROMBOSIS -pathologic coagulation of blood resulting in the formation of solid mass with a chamber of the heart or with the blood vessels -Virchows triad: endothelial injury, alterations in normal blood flow (turbulence, stasis), hypercoagulability MURAL THROMBUS
V. INFARCTION -an area of ischemic necrosis caused by occlusion of either the arterial supply or the venous drainage -Anemic (white) infarct: in arterial occlusion; in solid tissues; end arteries -Hemorrhagic (red) infarct: venous occlusion,in loose tissues, tissues with rich anastomosis RENAL INFARCTION
GROSS: (+)focal necrosis: wedge-shaped Apex hilum base: cortical surface
LEFT VENTRICLE. Red circle: mural thrombi
Histo: Focal necrosis; Necrosis of glomerulus Acidophilic tombstone HEMORRHAGIC INFARCTION, LUNGS
Gross: wedge-shape; red/hemorrhagic
Left: normal lung tissue. Right: infracted area
----------------END OF TRANSCRIPTION----------
You might also like
- Hemodynamic DisoderDocument4 pagesHemodynamic DisodermutimuthiNo ratings yet
- Lec 7Document27 pagesLec 7helenyakhyNo ratings yet
- HemorrhageDocument13 pagesHemorrhageSadam IrshadNo ratings yet
- 7-8 v-наруш Мест КровообрDocument49 pages7-8 v-наруш Мест КровообрMayank RajNo ratings yet
- Ischemia, Infarction, Shock and EdemaDocument44 pagesIschemia, Infarction, Shock and Edemakiran kcNo ratings yet
- Edema Hyperemia & Congestion: Miriam Al Battal, MDDocument20 pagesEdema Hyperemia & Congestion: Miriam Al Battal, MDHassoun hassounNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of EdemaDocument7 pagesPathophysiology of EdemaTaniaNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic DysorderDocument158 pagesHemodynamic DysorderTemesgen EndalewNo ratings yet
- Lecture #5 - Circulatory DisturbanceDocument36 pagesLecture #5 - Circulatory DisturbanceEl Farouk100% (1)
- Hemodynamic Disorders-RevisedDocument118 pagesHemodynamic Disorders-Revisedspringding0% (1)
- 5 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolism and ShockDocument162 pages5 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolism and Shocksinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Hemodinamic Disorder, Thrombosis, and ShockDocument50 pagesHemodinamic Disorder, Thrombosis, and Shockbagir_dm10No ratings yet
- Chap4 Hemodynamics F2Document12 pagesChap4 Hemodynamics F2Twinkle Salonga100% (3)
- Hemodynamics ModifiedDocument175 pagesHemodynamics ModifiedAyele AsefaNo ratings yet
- Haemodyanamics Flash PointsDocument3 pagesHaemodyanamics Flash PointsHassan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolic Disease and ShockDocument13 pagesHemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolic Disease and Shockpjcanero100% (5)
- Hemodynamic Disorders: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.DDocument59 pagesHemodynamic Disorders: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.Dchocoholic potchiNo ratings yet
- Path 3Document26 pagesPath 3رؤى مصطفىNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Disorders ThrombosisDocument106 pagesHemodynamic Disorders ThrombosisRamez AnaniNo ratings yet
- 5) Circulatory Disturbance BPT - 093303Document106 pages5) Circulatory Disturbance BPT - 093303Crystal GamingNo ratings yet
- Unit Four Ateration in Body FluidDocument26 pagesUnit Four Ateration in Body Fluid555556666667777777No ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock GWAIDocument102 pagesHemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock GWAIkavindukarunarathnaNo ratings yet
- Pathology For Dentistry Lect 10Document9 pagesPathology For Dentistry Lect 10Mohamad AladdinNo ratings yet
- (٦) المحاضرة السادسةDocument43 pages(٦) المحاضرة السادسةAbdulMalik AlHarbiNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Disturbance: Dr. Usha.MDocument77 pagesHemodynamic Disturbance: Dr. Usha.MOlumide Omotola AjayiNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Circulatory DisturbanceDocument162 pages1.4 Circulatory DisturbanceКатя ШаповалNo ratings yet
- 4 Circulation Disorders PDFDocument69 pages4 Circulation Disorders PDFSetiawan SukmadjaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Disorders: Djoko Legowo Drh. MkesDocument67 pagesCirculatory Disorders: Djoko Legowo Drh. MkesPilar Mitra QurbanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document5 pagesLecture 5Isak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Hemodynamic Disorders PDFDocument66 pages6 - Hemodynamic Disorders PDFNogra CarlNo ratings yet
- CHP 4 HemodynamicsDocument29 pagesCHP 4 HemodynamicsmaryannejkiemNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic DisordersDocument34 pagesHemodynamic DisordersLiesel Illyry100% (1)
- Inflammatory RespondeDocument28 pagesInflammatory RespondeAbhijith S. PNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis and ShockDocument127 pagesHemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis and ShockMowlidAbdirahman Ali madaaleNo ratings yet
- Haemodynamic DisordersDocument28 pagesHaemodynamic DisordersOROKE JOHN EJENo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Disorder PC1Document227 pagesHemodynamic Disorder PC1Bereket weybaNo ratings yet
- Is and ThrombosisDocument5 pagesIs and ThrombosisQurat KhanNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic PathologyDocument9 pagesHemodynamic PathologyjoeNo ratings yet
- ), Leading To Increased Capillary HydrostaticDocument1 page), Leading To Increased Capillary HydrostaticastaganagaNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Disorders Edema, Hyperemia/Congestion, HemorrhageDocument5 pagesHemodynamic Disorders Edema, Hyperemia/Congestion, HemorrhageZwit Maria PaasNo ratings yet
- Pengelolaan Kasus: Cutaneous Changes in Venous and Lymphatic InsufficiencyDocument4 pagesPengelolaan Kasus: Cutaneous Changes in Venous and Lymphatic InsufficiencyAlmas PrawotoNo ratings yet
- Pengelolaan Kasus: Cutaneous Changes in Venous and Lymphatic InsufficiencyDocument4 pagesPengelolaan Kasus: Cutaneous Changes in Venous and Lymphatic InsufficiencyZakiyah ArrohmahNo ratings yet
- Hemostatic Disorders Quantitative and Qualitative DisordersDocument25 pagesHemostatic Disorders Quantitative and Qualitative DisordersKlein’s Gaming ChannelNo ratings yet
- Emailing Patologi Anatomi GANGGUAN HEMODINAMIK Trombosis DAN SHOCK - Output PDFDocument38 pagesEmailing Patologi Anatomi GANGGUAN HEMODINAMIK Trombosis DAN SHOCK - Output PDFHaykal FathirrahmanNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Etiology of DiseasesDocument68 pagesWeek 5 Etiology of DiseasesShaira InditaNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic DisorderDocument7 pagesHemodynamic DisorderYana MilyushinaNo ratings yet
- Edema Hyperemia CongestionDocument23 pagesEdema Hyperemia Congestionraanja2No ratings yet
- Shock: Dr. P. Manoj Kumar Asst. Professor, Dep. of Gen. Surgery, CaimsDocument61 pagesShock: Dr. P. Manoj Kumar Asst. Professor, Dep. of Gen. Surgery, CaimsManoj Kumar PasunooriNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhage, Hyperemia, CongestionDocument16 pagesHemorrhage, Hyperemia, Congestionhussain4017No ratings yet
- 33 Penyakit Vaskuler Sentral Dan Perifer DR - WinangunDocument69 pages33 Penyakit Vaskuler Sentral Dan Perifer DR - WinangunSurya ArhNo ratings yet
- Bleeding (Haemorrhagia)Document63 pagesBleeding (Haemorrhagia)hatirebNo ratings yet
- Arterial InsufficiencyDocument48 pagesArterial InsufficiencySyAmil MeNzaNo ratings yet
- Answers: Hemodynamic ChangesDocument8 pagesAnswers: Hemodynamic ChangesUday KolheNo ratings yet
- Goljan - CardiovascularDocument22 pagesGoljan - Cardiovascularcollege3No ratings yet
- Hemodynamic DisordersDocument16 pagesHemodynamic DisordersHussein Al SaediNo ratings yet
- OEDEMADocument4 pagesOEDEMAambiliNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamics - PDF 20 21Document172 pagesHemodynamics - PDF 20 21ayahnaser20No ratings yet
- Approach To Patients With Motor and Sensory Disorder 3-2012Document7 pagesApproach To Patients With Motor and Sensory Disorder 3-2012dtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Factors That Affect LaborDocument9 pagesFactors That Affect LabordtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Eating, Elimination and Impulse Control DisordersDocument4 pagesEating, Elimination and Impulse Control DisordersdtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Basic Approaches in Clinical Practice Guideline DevelopmentDocument11 pagesBasic Approaches in Clinical Practice Guideline DevelopmentdtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Behavior by Dra PacificoDocument6 pagesBehavior by Dra PacificodtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Affective Disorders and SuicideDocument5 pagesAffective Disorders and SuicidedtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Addendum To Epidemic Investigation 2 NotesDocument2 pagesAddendum To Epidemic Investigation 2 NotesAna Cristina MontillanoNo ratings yet
- Epidemic Investigation 2Document3 pagesEpidemic Investigation 2Ana Cristina MontillanoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine HistologyDocument21 pagesEndocrine HistologydtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Pedia 1st Evals 2011-2012Document1 pageAnswer Key Pedia 1st Evals 2011-2012dtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Evals 1, SY 11-12Document4 pagesPediatrics Evals 1, SY 11-12dtimtimanNo ratings yet
- 2012-01-MEDICINE-Cardinal Manifestation of Renal DiseaseDocument15 pages2012-01-MEDICINE-Cardinal Manifestation of Renal Diseasedtimtiman100% (1)
- Food Poisoning TableDocument1 pageFood Poisoning TabledtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Associated With GIT 3 FOOD POISONINGDocument5 pagesBacteria Associated With GIT 3 FOOD POISONINGdtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Dyspnea and HypoxiaDocument9 pagesDyspnea and Hypoxiadtimtiman100% (3)
- Skills in CV1Document7 pagesSkills in CV1dtimtimanNo ratings yet
- 2011 11 PHARMA GIT Anti Diarrhea and Pro KineticDocument5 pages2011 11 PHARMA GIT Anti Diarrhea and Pro KineticdtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Parasitism: ProtozoansDocument10 pagesIntestinal Parasitism: ProtozoansdtimtimanNo ratings yet
- 2011-11-PHARMA-GIT-antidiarrhea and Prokinetic-TableDocument3 pages2011-11-PHARMA-GIT-antidiarrhea and Prokinetic-TabledtimtimanNo ratings yet
- 2011-11-PATHO-Dses of Small and Large IntestineDocument9 pages2011-11-PATHO-Dses of Small and Large IntestinedtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Commed Research Design1Document6 pagesCommed Research Design1Hedley ChuaNo ratings yet
- Macrolides Ketolides Chloram Oxazolinodines StreptogamisDocument6 pagesMacrolides Ketolides Chloram Oxazolinodines StreptogamisdtimtimanNo ratings yet
- 2011-08-PATHO-WBC Disorder 01 and 02Document30 pages2011-08-PATHO-WBC Disorder 01 and 02dtimtimanNo ratings yet
- CP Blood CoagulationDocument14 pagesCP Blood CoagulationdtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal AttachmentDocument2 pagesProject Proposal AttachmentdtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Commed Research Design 2Document6 pagesCommed Research Design 2ninjaningNo ratings yet
- Site MapDocument2 pagesSite MapdtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Flow of Events and BudgetDocument4 pagesFlow of Events and BudgetdtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Orphanage Project ProposalDocument3 pagesOrphanage Project ProposaldtimtimanNo ratings yet
- Chest and Lungs 1Document6 pagesChest and Lungs 1dtimtimanNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Evidence - Desccribing A Famous Person - LUIS EDUARDO CASTILLO TISERC-3Document5 pages1.2 Evidence - Desccribing A Famous Person - LUIS EDUARDO CASTILLO TISERC-3LUIS EDUARDO CASTILLO GARCIANo ratings yet
- DLL On Respiratory System Irah Jane L. Valentino San Teodoro Nhs Grade 9Document3 pagesDLL On Respiratory System Irah Jane L. Valentino San Teodoro Nhs Grade 9Sher-ann May Labaguis Abo100% (2)
- Funda Lab Mod 5-7Document13 pagesFunda Lab Mod 5-7Liane BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Print SGD Ein Fix Gastritis BHDocument21 pagesPrint SGD Ein Fix Gastritis BHSagita Wulan SariNo ratings yet
- Study Guide: Section 1: Animal CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesStudy Guide: Section 1: Animal CharacteristicsosamaNo ratings yet
- Struktur Dan Fungsi Sistem PenghadamanDocument133 pagesStruktur Dan Fungsi Sistem PenghadamanStephanie Ming FunNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Drugs 2020 Part 1 IntroDocument29 pagesAutonomic Drugs 2020 Part 1 Introعون عليNo ratings yet
- ScalpDocument17 pagesScalpKaruna PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of FishDocument11 pagesAnatomy of FishrafumiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 7 The Muscular SystemDocument13 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 7 The Muscular System俺気健人No ratings yet
- Adipogenesis and Metabolic Health PDFDocument17 pagesAdipogenesis and Metabolic Health PDFalbertoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan LiverDocument9 pagesLesson Plan LiverSAYMABANUNo ratings yet
- Science Year 6Document13 pagesScience Year 6BARAATHY SRI A/P UTHRAPATHY Moe100% (1)
- CSF & SemenDocument9 pagesCSF & SemenIrish De VeraNo ratings yet
- Science Test-10TH-SCIENCEDocument5 pagesScience Test-10TH-SCIENCEtensazangestuiit24No ratings yet
- Joseph Bejogan - September 2021: 1. Introduction To AnatomyDocument2 pagesJoseph Bejogan - September 2021: 1. Introduction To AnatomyCarren SabioNo ratings yet
- Total Abdominal HysterectomyDocument19 pagesTotal Abdominal HysterectomyMeidina Rachma Amanda100% (1)
- VestibularDocument4 pagesVestibularFero RigelaNo ratings yet
- General Certificate of Education June 2007 Advanced Subsidiary ExaminationDocument20 pagesGeneral Certificate of Education June 2007 Advanced Subsidiary ExaminationWk SoohgNo ratings yet
- Celiakie Nif AnDocument4 pagesCeliakie Nif AnAhmed EliasNo ratings yet
- Who-Is-It Teacher SwitcherDocument21 pagesWho-Is-It Teacher SwitcherАлина СолонскаяNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ImagingDocument118 pagesCardiac ImagingSay DieukayNo ratings yet
- A. Strelnikova Breathing Exercises - Unique Method of Treating Chronic DiseasesDocument121 pagesA. Strelnikova Breathing Exercises - Unique Method of Treating Chronic Diseaseslance wong100% (1)
- C7 SC L2 AssignmentDocument6 pagesC7 SC L2 Assignmentshashi_kandariNo ratings yet
- CerebellumDocument22 pagesCerebellumJasvinder Singh NayyarNo ratings yet
- Imci Case StudyDocument60 pagesImci Case StudyVida RoseNo ratings yet
- Phlebotomy Handbook: Blood Collection EssentialsDocument55 pagesPhlebotomy Handbook: Blood Collection EssentialsayooniaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Sporophytes and Gametophytes in BryophytesDocument7 pagesEvolution of Sporophytes and Gametophytes in BryophytesKhan KhanNo ratings yet
- VMERGAL-HUman Physiology Online Course SyllabusDocument13 pagesVMERGAL-HUman Physiology Online Course Syllabusreynar nikijuluwNo ratings yet
- Drug Delivery - Exam 2 NotesDocument30 pagesDrug Delivery - Exam 2 NotesfelixNo ratings yet