Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Joseph Bejogan - September 2021: 1. Introduction To Anatomy
Uploaded by
Carren SabioOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Joseph Bejogan - September 2021: 1. Introduction To Anatomy
Uploaded by
Carren SabioCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Introduction to Anatomy Anatomy and
Joseph Bejogan || September 2021 Physiology Lab
Transcriber: Rebueno, Jerry Mari S.
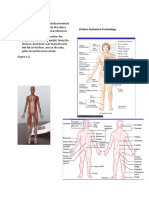
Anatomy
Language of Anatomy
• Exact terms are used for:
▪ Position
▪ Direction
▪ Regions
▪ Structure
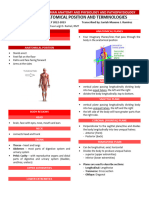
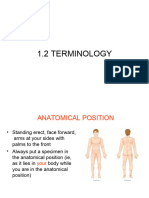
Anatomical Position
• Person stands erect with feet together and eyes forward
• Palms face anteriorly with thumbs pointed away
• Right and left always refers to the specimen being
viewed
• Their ventral side is on the inferior side and the dorsal is
in the superior side
• In humans, ventral and anterior are the same and so is Planes and Sections
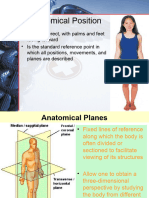
dorsal and posterior • Sagittal Plane
o runs vertically from top to bottom, divides left
area to right area
• Midsagittal Plane
o sagittal plane that runs through the center
• Parasagittal Plane
o sagittal plane that does not run through the
center
• Oblique Plane
o plane that is in any type of angle other than
vertical or horizontal
• Transverse Plane
o also known as “horizontal plane”
o divides the superior and inferior portions of the
body
• Frontal Plane
o also known as “coronal plane”
o plane that runs vertically from top to bottom that
divides the body to the anterior and posterior
side
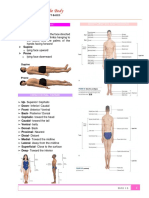
Directional Terms
• Superior – towards the head
• Inferior – towards the feet / downwards
• Ventral/Anterior – front of the body
• Dorsal/Posterior – back of the body
• Medial – point closer to the middle
• Lateral – point farther from the middle
• Intermediate – point between two structures
• Proximal – point closer to the area of insertion
• Distal – point farther to the area of insertion
*Note: Proximal and Distal are only used on extremities
• Superficial
• Deep
JMR – 1BSMT4 – UST-L
1
[AnaPhy with Pathophysiology] 1. Intro to Anatomy – Joseph Bejogan
Body Cavities
Cranial Cavity
• Formed by the cranial bone and encompasses the brain
Vertebral Canal
• Formed by the vertebral column and contains the spinal
cord and the beginnings of the spinal nerves
Thoracic Cavity
• Also known as the “chest cavity”
• Contains the pleural and pericardial cavities and the
mediastinum
➢ Pleural Cavity
o A potential space between the layers of the
pleura that surrounds the lungs
➢ Pericardial Cavity
o A potential space between the layers of the
pericardium that surrounds the heart
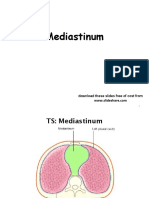
➢ Mediastinum
o Central portion of the thoracic cavity between
the lungs
o Extends from the sternum to the vertebral
column and from the first rib to the diaphragm
o Contains the heart, thymus, esophagus,
trachea, and several large blood vessels
Abdominopelvic Cavity
• Subdivided into abdominal and pelvic cavities
➢ Abdominal Cavity
o Contains the stomach, spleen, gallbladder,
small intestine, and most of the large intestine
o The serous membrane is called the
peritoneum
➢ Pelvic Cavity
o Contains the urinary bladder, portions of the
large intestines, and internal organs of
reproduction
Abdominopelvic Regions
Right hypochondriac Liver and Gallbladder
Epigastric Stomach
Left hypochondriac Diaphragm, Spleen and Stomach
Right lumbar Ascending Colon and areas of
the Small Intestine
Umbilical Small Intestines and the
Transverse Colon
Left lumbar Descending Colon and areas of
the Small Intestine
Right iliac (inguinal) Cecum and the Appendix
Hypogastric Areas of the Small intestine and
the Urinary bladder
Left iliac (inqguinal) Initial part of the Sigmoid Colon
[Date] 2
You might also like
- The Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormFrom EverandThe Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Introduction To Anatomy TransDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy Transchynne ongNo ratings yet
- Language of AnatomyDocument31 pagesLanguage of AnatomyTerlita B. LlanderNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PositionDocument36 pagesAnatomical PositionMoza AlaliliNo ratings yet
- Oral Recitation Notes.Document13 pagesOral Recitation Notes.Angela LagartoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Anatomical Position and TerminologiesDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Anatomical Position and TerminologiesniaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document11 pagesLecture 1Jose Emmanuel DolorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 PDFDocument11 pagesLecture 1 PDFJose Emmanuel DolorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 PDFDocument11 pagesLecture 1 PDFJose Emmanuel DolorNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Structural Kinesiology: Lesson 1 PHED 349Document28 pagesFoundations of Structural Kinesiology: Lesson 1 PHED 349Rachel ChristensenNo ratings yet
- 1.0 AnatomyDocument16 pages1.0 AnatomychaaarrNo ratings yet
- Terminology - SlidesDocument30 pagesTerminology - SlidesMokakatlela RatauNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AnatomyDocument232 pagesIntroduction To AnatomyShreya PatilNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Planes, Sections, Terminologies, & Movements: Dr. Syed Wajahat Hasib LecturerDocument25 pagesAnatomical Planes, Sections, Terminologies, & Movements: Dr. Syed Wajahat Hasib LecturerRameen ZahraNo ratings yet
- General Orientation To Human Anatomy: Atlas ADocument33 pagesGeneral Orientation To Human Anatomy: Atlas AEmilie ArvidsonNo ratings yet
- Transes Anaphy Lab (Activity 6)Document3 pagesTranses Anaphy Lab (Activity 6)Reign SaplacoNo ratings yet
- The Human Body - An OrientationDocument13 pagesThe Human Body - An OrientationAkanksha ChoutiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: DR - Arun Kumar Gupta Mbbs. MD (2 Year) Department of Respiratorymedicine, MczuDocument22 pagesAnatomy: DR - Arun Kumar Gupta Mbbs. MD (2 Year) Department of Respiratorymedicine, Mczuapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Anatomical Terminologies 108Document108 pagesAnatomical Terminologies 108ferbflynn07No ratings yet
- Anatomical Positions, Planes and Terms Presentation 3Document20 pagesAnatomical Positions, Planes and Terms Presentation 3Zoafshan AshfaqueNo ratings yet
- Human Body and Directional TermsDocument29 pagesHuman Body and Directional TermsShaira UsmanNo ratings yet
- 1P - Medical Terminology of Anatomical PositionsDocument29 pages1P - Medical Terminology of Anatomical PositionsMission AidNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Positioning & Radiologic Procedure: RT 204 Richard A. Pabunag, RRTDocument33 pagesRadiographic Positioning & Radiologic Procedure: RT 204 Richard A. Pabunag, RRTbianca buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: - The Study of The Structure of Body Parts and Their Relationships To One AnotherDocument71 pagesAnatomy: - The Study of The Structure of Body Parts and Their Relationships To One AnotherAisha YolaNo ratings yet
- LEC1Document49 pagesLEC1youssef.yma999No ratings yet
- Generalities PDFDocument5 pagesGeneralities PDFNibshian Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- AP Human Body OrientationDocument27 pagesAP Human Body OrientationWaqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Terminology f2f-s1b2-23Document19 pages1.2 Terminology f2f-s1b2-23shlokNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature and Descriptive TerminologiesDocument28 pagesNomenclature and Descriptive TerminologiesEzri ChilengweNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Pelvis and Fetal SkullDocument41 pagesAnatomy of Pelvis and Fetal SkullHakimah K. Suhaimi100% (1)
- Ana Physio PPT - 1Document56 pagesAna Physio PPT - 1spalte48No ratings yet
- Intro To Abdominal Cavity (Merrick)Document35 pagesIntro To Abdominal Cavity (Merrick)Sidiq AboobakerNo ratings yet
- Ana - Intro (Snell + Lecture)Document17 pagesAna - Intro (Snell + Lecture)Ma Rhodalyn Mae AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology 01Document26 pagesMedical Terminology 01muhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Wala LangDocument7 pagesWala Langmorla holaNo ratings yet
- 1 An&phssssDocument57 pages1 An&phssssabelashe2No ratings yet
- Anatomical TermsDocument32 pagesAnatomical Termsidokofavour2015100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology: Camposano, Frusa, Laurente, Ranoa, YaoDocument36 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Camposano, Frusa, Laurente, Ranoa, YaoAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 1. Anatomical Position and TerminologiesDocument2 pagesLaboratory 1. Anatomical Position and TerminologiesAANo ratings yet
- Introduction in Human AnatomyDocument60 pagesIntroduction in Human AnatomyAngela Bautista85% (13)
- Basic CXR Interpretation Learning Material 2018Document74 pagesBasic CXR Interpretation Learning Material 2018Slindy Noty MtetwaNo ratings yet
- Anatomical TermsDocument82 pagesAnatomical TermsRichelle Ann Gatchola EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: General Consideration On Animal Form: Other Anatomical TermsDocument3 pagesActivity 1: General Consideration On Animal Form: Other Anatomical TermsKamille PobleteNo ratings yet
- 9 Lungs - Gemp 1 - 2018 - BBDocument68 pages9 Lungs - Gemp 1 - 2018 - BBsandyNo ratings yet
- General Orientation of The Body Part 1Document11 pagesGeneral Orientation of The Body Part 1Maria Faith Jeneen Bisnar100% (1)
- LABORATORY MANUAL in GENERAL ANATOMY 1 PART 1Document29 pagesLABORATORY MANUAL in GENERAL ANATOMY 1 PART 1Ian Mar ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE Anatomical TerminologyDocument32 pagesCOMPREHENSIVE Anatomical TerminologyKavita MahaseNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 OutlineDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 OutlineCJ DaodaoenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 PDFDocument9 pagesLecture 04 PDFNuta Marius AlexandruNo ratings yet
- The Language of AnatomyDocument4 pagesThe Language of Anatomyjava_biscocho122950% (2)
- Radiographic Procedures Riverside1 1Document461 pagesRadiographic Procedures Riverside1 1jesel algoyNo ratings yet
- Presentation 10Document8 pagesPresentation 10Sristi ChNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PositionsDocument20 pagesAnatomical PositionskimberlynNo ratings yet
- Terms of Position and MovementDocument41 pagesTerms of Position and Movementobehi4rNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomical Terms PPTDocument30 pagesBasic Anatomical Terms PPTInsatiable Clee100% (1)
- Anatomy Booster HODocument59 pagesAnatomy Booster HOJo Hn VengzNo ratings yet
- Lab 2.0Document5 pagesLab 2.0Faizan AhmadNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument30 pagesAnatomyKavita MalhotraNo ratings yet
- General Consideration On Animal Form: Activity 1Document15 pagesGeneral Consideration On Animal Form: Activity 1Dimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Thoracic Wall & Pleura-DikonversiDocument69 pagesAnatomy of Thoracic Wall & Pleura-DikonversiFira TasyaNo ratings yet
- Neurological Physiotherapy Evaluation Form 2 0Document82 pagesNeurological Physiotherapy Evaluation Form 2 0Eman SabryNo ratings yet
- Posterior and Anterior MediastinumDocument6 pagesPosterior and Anterior MediastinumYheng GaosaiiNo ratings yet
- Uropoetica Organ: Shafira Zahra Ovaditya ANATOMI 2014Document46 pagesUropoetica Organ: Shafira Zahra Ovaditya ANATOMI 2014zahrazhfNo ratings yet
- Cara Membaca CT ThoraxDocument43 pagesCara Membaca CT Thoraxeliana100% (3)
- PEMBIMBING: Dr. Yudi Ambeng, Sp.UDocument72 pagesPEMBIMBING: Dr. Yudi Ambeng, Sp.UClarissa SuheryNo ratings yet
- Modul Bedah 2 - DR RianDocument18 pagesModul Bedah 2 - DR RianDendy AgusNo ratings yet
- 10 Jan 08 Abdominals PDFDocument9 pages10 Jan 08 Abdominals PDFprofines2051No ratings yet
- Seven Cardinal MovementDocument14 pagesSeven Cardinal MovementLeonita DwiNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Human Heart - A+p - StudentDocument24 pagesLab Manual - Human Heart - A+p - Studentsyl0% (1)
- Mediastinum: Download These Slides Free of Cost FromDocument23 pagesMediastinum: Download These Slides Free of Cost FromYashfa Yasin - PharmDNo ratings yet
- 1.the SuperiorDocument10 pages1.the SuperiorIdrissa ContehNo ratings yet
- AJCC 8thed TNMDocument34 pagesAJCC 8thed TNMPrarthna PatelNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Anatomy of Liver23Document8 pagesLesson Plan - Anatomy of Liver23Delphy Varghese100% (1)
- Bams 1st Rachna Sharir Surface Marking of Lungs Pleura 12-05-2020Document13 pagesBams 1st Rachna Sharir Surface Marking of Lungs Pleura 12-05-2020Pooja JangirNo ratings yet
- Lecture 22 - The Digestive TractDocument32 pagesLecture 22 - The Digestive TractCarl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- MCQ Anatomy-thorax-Abdo-PelvisDocument100 pagesMCQ Anatomy-thorax-Abdo-PelvisMatt McCannNo ratings yet
- Block Vii Module 1 Cheat Sheet PDFDocument32 pagesBlock Vii Module 1 Cheat Sheet PDFMark FuerteNo ratings yet
- Basic Coronary Anatomy - Paul Fefer, MD.Document57 pagesBasic Coronary Anatomy - Paul Fefer, MD.enzomontresolNo ratings yet
- Introductio To:: SplanchnologyDocument36 pagesIntroductio To:: Splanchnologyrambabs369No ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument15 pagesFetal CirculationPujani SenevirathnaNo ratings yet
- PilatesDocument6 pagesPilateskhushboopakhrani98No ratings yet
- NEW Normal Tissue Tolerance Master 11-2014Document11 pagesNEW Normal Tissue Tolerance Master 11-2014damodara kumaranNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Exam IIIDocument8 pagesAnatomy Exam IIIJonathanNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide To Abdominal TrainingDocument223 pagesComplete Guide To Abdominal TrainingLynseyNo ratings yet
- Anatomi GenitourinariaDocument30 pagesAnatomi Genitourinariamelya susantiNo ratings yet
- Possible Spotter Questions Taken During LabDocument1 pagePossible Spotter Questions Taken During LabHugh JacobsNo ratings yet
- SOAL UTS GERONTIK TINGKAT IV REGULER DOSEN ROSMINA & MUS TA 22 - 23 (Jawaban)Document39 pagesSOAL UTS GERONTIK TINGKAT IV REGULER DOSEN ROSMINA & MUS TA 22 - 23 (Jawaban)rosmina situngkirNo ratings yet
- Hernia Inguinal 1, Anatomia, SCNA 2018Document15 pagesHernia Inguinal 1, Anatomia, SCNA 2018Angie Cristina Hoyos EcheverriNo ratings yet
- Testicular BreathingDocument8 pagesTesticular BreathingYCY57% (30)