Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cloud Computing
Uploaded by
dcwjknCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cloud Computing
Uploaded by
dcwjknCopyright:
Available Formats
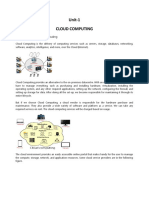
Cloud computing:
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of different services through the Internet to
offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. These resources
include tools and applications like data storage, servers, databases, networking, and
software.
Examples of Cloud Services:
1. Email
2. Storage, backup, and data retrieval
3. Creating and testing apps
4. Analyzing data
5. Audio and video streaming
6. Delivering software on demand
Benefits of Cloud Computing:
Cost
It eliminates the capital expense of buying hardware and software and setting up and running
on-site datacenters—the racks of servers, the round-the-clock electricity for power and
cooling, and the IT experts for managing the infrastructure. It adds up fast.
Speed
Most cloud computing services are provided self service and on demand, so even vast
amounts of computing resources can be provisioned in minutes, typically with just a few
mouse clicks, giving businesses a lot of flexibility and taking the pressure off capacity
planning.
Global scale
The benefits of cloud computing services include the ability to scale elastically. In cloud
speak, that means delivering the right amount of IT resources—for example, more or less
computing power, storage, bandwidth—right when they’re needed, and from the right
geographic location.
Prepared by: Bibaswan Prasai (KAN075BCT020)
Productivity
On-site datacenters typically require a lot of “racking and stacking”—hardware setup,
software patching, and other time-consuming IT management chores. Cloud computing
removes the need for many of these tasks, so IT teams can spend time on achieving more
important business goals.
Performance
The biggest cloud computing services run on a worldwide network of secure datacenters,
which are regularly upgraded to the latest generation of fast and efficient computing
hardware. This offers several benefits over a single corporate datacenter, including reduced
network latency for applications and greater economies of scale.
Reliability
Cloud computing makes data backup, disaster recovery, and business continuity easier and
less expensive because data can be mirrored at multiple redundant sites on the cloud
provider’s network.
Security
Many cloud providers offer a broad set of policies, technologies, and controls that strengthen
your security posture overall, helping protect your data, apps, and infrastructure from
potential threats.
Types of cloud computing
Not all clouds are the same and not one type of cloud computing is right for everyone.
Several different models, types, and services have evolved to help offer the right solution
for your needs.
First, you need to determine the type of cloud deployment, or cloud computing
architecture, that your cloud services will be implemented on. There are three different
ways to deploy cloud services: on a public cloud, private cloud, or hybrid cloud.
Prepared by: Bibaswan Prasai (KAN075BCT020)
Public cloud
Public clouds are owned and operated by a third-party cloud service providers, which deliver
their computing resources, like servers and storage, over the Internet. Microsoft Azure is an
example of a public cloud. With a public cloud, all hardware, software, and other supporting
infrastructure is owned and managed by the cloud provider. You access these services and
manage your account using a web browser. Some of the largest public cloud providers
include Alibaba Cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, and
Microsoft Azure.
Private cloud
A private cloud refers to cloud computing resources used exclusively by a single business or
organization. A private cloud can be physically located on the company’s on-site datacenter.
Some companies also pay third-party service providers to host their private cloud. A private
cloud is one in which the services and infrastructure are maintained on a private network.
Hybrid cloud
Hybrid clouds combine public and private clouds, bound together by technology that allows
data and applications to be shared between them. By allowing data and applications to move
between private and public clouds, a hybrid cloud gives your business greater flexibility,
more deployment options, and helps optimize your existing infrastructure, security, and
compliance.
Prepared by: Bibaswan Prasai (KAN075BCT020)
Cloud services
Cloud services are infrastructure, platforms, or software that are hosted by third-party
providers and made available to users through the internet. There are 3 main types of as-a-
Service solutions: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. Each facilitates the flow of user data from front-end
clients through the internet, to the cloud service provider’s systems, and back—but vary by
what’s provided.
IaaS
IaaS means a cloud service provider manages the infrastructure for you—the actual servers,
network, virtualization, and data storage—through an internet connection. The user has
access through an API or dashboard, and essentially rents the infrastructure. The user
manages things like the operating system, apps, and middleware while the provider takes
care of any hardware, networking, hard drives, data storage, and servers; and has the
responsibility of taking care of outages, repairs, and hardware issues. This is the typical
deployment model of cloud storage providers.
Prepared by: Bibaswan Prasai (KAN075BCT020)
PaaS
PaaS means the hardware and an application-software platform are provided and managed by
an outside cloud service provider, but the user handles the apps running on top of the
platform and the data the app relies on. Primarily for developers and programmers, PaaS
gives users a shared cloud platform for application development and management (an
important DevOps component) without having to build and maintain the infrastructure
usually associated with the process.
SaaS
Prepared by: Bibaswan Prasai (KAN075BCT020)
SaaS is a service that delivers a software application—which the cloud service provider
manages—to its users. Typically, SaaS apps are web applications or mobile apps that users
can access via a web browser. Software updates, bug fixes, and other general software
maintenance are taken care of for the user, and they connect to the cloud applications via a
dashboard or API. SaaS also eliminates the need to have an app installed locally on each
individual user’s computer, allowing greater methods of group or team access to the
software.
Prepared by: Bibaswan Prasai (KAN075BCT020)
You might also like
- Cloud ComputingDocument4 pagesCloud ComputingZinzy MNo ratings yet
- CC Lab FileDocument42 pagesCC Lab FileRitika SinghNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument4 pagesCloud ComputingChuru iddyNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument4 pagesCloud ComputingjeffNo ratings yet
- Cloud Module 1Document8 pagesCloud Module 1Sasidhar GanugapentaNo ratings yet
- Op Benefits of Cloud Computing: Learn More About Public, Private and Hybrid CloudsDocument3 pagesOp Benefits of Cloud Computing: Learn More About Public, Private and Hybrid CloudsshettyNo ratings yet
- BA160 Concepts of Information Systems, Project On Microsoft Azure by Henok Seifu & Natnael NegussieDocument8 pagesBA160 Concepts of Information Systems, Project On Microsoft Azure by Henok Seifu & Natnael NegussieHenok SeifuNo ratings yet
- Unit I Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument36 pagesUnit I Introduction To Cloud Computingkomalpopatshinde2345No ratings yet
- ACFrOgAmRkmvZIyh8RjvaErPGd4NFOqw0T21AQxjqCt Wtz7-Yt io1Gdv5jrsGNqXCCWgQclmeF NQjx8NvyYBelD762ZYqlbfYhx4VqDcIeKO99dJ2WrzqgO6MprXwc-iIbaVpexhxGzXTLLn1Document30 pagesACFrOgAmRkmvZIyh8RjvaErPGd4NFOqw0T21AQxjqCt Wtz7-Yt io1Gdv5jrsGNqXCCWgQclmeF NQjx8NvyYBelD762ZYqlbfYhx4VqDcIeKO99dJ2WrzqgO6MprXwc-iIbaVpexhxGzXTLLn1tanishNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument16 pagesCloud ComputingMurtaza MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument20 pagesCloud ComputingانجنیرخرمNo ratings yet
- ETI Micro Project Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesETI Micro Project Cloud ComputingSheshrao LandgeNo ratings yet
- What exactly is cloud computingDocument8 pagesWhat exactly is cloud computingrahulNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Information Communication TechnologyDocument8 pagesInformation Communication TechnologyMalik KhawarNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesWhat Is Cloud Computingstorm8811No ratings yet
- Unit1 1Document30 pagesUnit1 1HimajanaiduNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing PresentationDocument17 pagesCloud Computing PresentationCielo MarzanNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics: Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesBusiness Analytics: Cloud ComputingShadab MirzaNo ratings yet
- What is cloud computingDocument7 pagesWhat is cloud computingDivya GNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesChapter 19 - Cloud ComputingAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Semester 5Document7 pagesCloud Computing: Semester 5Pratham KangraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Cloud ComputingNithish GowdaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Service ModelsDocument10 pagesCloud Service ModelsmanasyogiNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Introduction To Cloud)Document15 pagesUnit-1 (Introduction To Cloud)Binay YadavNo ratings yet
- AWS ClassDocument15 pagesAWS ClassAshishNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument72 pagesIntroduction To Cloud ComputingLipsa Rani JenaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Types and ModelsDocument6 pagesCloud Computing Types and ModelsDivyasriNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesCloud ComputingRyan FabianNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument36 pagesCloud Computingsubhayanmanna1234No ratings yet
- What Is Cloud Computing ?Document4 pagesWhat Is Cloud Computing ?ADITYA KUMAR MITTALNo ratings yet
- Unit 1stDocument11 pagesUnit 1stAmanNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument12 pagesCloud ComputingELSADNo ratings yet
- Seminaroncloudcomputingbyprashantgupta 130712214346 Phpapp01Document26 pagesSeminaroncloudcomputingbyprashantgupta 130712214346 Phpapp01PLHNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocument17 pagesWhat Is Cloud ComputingVictor ImarhiagbeNo ratings yet
- Zarmina DDB Ass#1Document13 pagesZarmina DDB Ass#1Meena JadoonNo ratings yet
- Anurag CC LAB File CompleteDocument27 pagesAnurag CC LAB File CompleteBaby SauravNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing IntroductionDocument95 pagesCloud Computing IntroductionjanuaryNo ratings yet
- Cloud ServiceDocument4 pagesCloud Servicethe.elysian.shop2022No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Risks and ServicesDocument9 pagesCloud Computing Risks and ServicesSelormNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Azure FundamentalsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Azure FundamentalsReeghesh JuleemunNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument64 pagesUntitledlekhaNo ratings yet
- Cloud and Network Securityt10Document19 pagesCloud and Network Securityt10Md. EmdadNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1Document10 pagesUnit - 1HimajanaiduNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument24 pagesCloud Computingeffective thinkerNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument5 pagesCloud ComputingRo TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- CC 1Document58 pagesCC 1VISHNU VASHISHTHNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument9 pagesCloud ComputingAvik BachharNo ratings yet
- PG Cloud Computing Unit-IDocument33 pagesPG Cloud Computing Unit-Ideepthi sanjeevNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document13 pagesUnit 1Bnod MsraNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Notes For BSC and BCADocument48 pagesCloud Computing Notes For BSC and BCAPvlsowjanya100% (3)
- Cloud Computing OverviewDocument23 pagesCloud Computing OverviewpallaviNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing1Document32 pagesCloud Computing1NiharikaNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesWhat Is Cloud ComputingDillip Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument10 pagesCloud ComputingtejuNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: - BY Banu Pooja Kannikanti 17H71A05C4Document19 pagesCloud Computing: - BY Banu Pooja Kannikanti 17H71A05C4Bhavana GummaNo ratings yet
- Cloud - Computing UNIT-3 Material .Document17 pagesCloud - Computing UNIT-3 Material .kavists20No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Security Issues and ChallengesDocument6 pagesCloud Computing: Security Issues and ChallengesIJAET JournalNo ratings yet
- Public-Private-Hybrid CCDocument28 pagesPublic-Private-Hybrid CCharry HarithaNo ratings yet
- RAJVARDHAN OAK CLOUD COMPUTINGDocument17 pagesRAJVARDHAN OAK CLOUD COMPUTINGRaj OakNo ratings yet
- LolDocument4 pagesLoldcwjknNo ratings yet
- ManifestDocument3 pagesManifestdcwjknNo ratings yet
- Repeated billionaire statusDocument3 pagesRepeated billionaire statusdcwjknNo ratings yet
- EES DraftDocument13 pagesEES DraftdcwjknNo ratings yet
- Database and OS SecurityDocument27 pagesDatabase and OS SecurityShaza KhotNo ratings yet
- 8.7.1.3 Lab - (Optional) Configuring A Remote Access VPN Server and Client - InstructorDocument30 pages8.7.1.3 Lab - (Optional) Configuring A Remote Access VPN Server and Client - InstructorSalem TrabelsiNo ratings yet
- CS Cours StructureDocument23 pagesCS Cours StructureSushilPangarkarNo ratings yet
- Core BSS IVR SolutionDocument4 pagesCore BSS IVR SolutionRafiq MagdyNo ratings yet
- Investigate TCP Behavior with Wireshark LabDocument12 pagesInvestigate TCP Behavior with Wireshark LabMaria Eduarda RosaNo ratings yet
- PL12-1001EN Progamming ManualDocument80 pagesPL12-1001EN Progamming ManualAbraham Josue Segundo SoriaNo ratings yet
- ENISA Report - Post-Quantum Cryptography Current State and Quantum Mitigation-V2Document46 pagesENISA Report - Post-Quantum Cryptography Current State and Quantum Mitigation-V2anlemacoNo ratings yet
- Blockchain ProgrammingDocument30 pagesBlockchain ProgrammingUri FontesNo ratings yet
- Partitioning The Titan Hard DriveDocument3 pagesPartitioning The Titan Hard DriveRogerio CastroNo ratings yet
- Lab2 - Data Manipulation Language (DML) CommandsDocument5 pagesLab2 - Data Manipulation Language (DML) CommandsAnie Fred BayagNo ratings yet
- Current LogDocument54 pagesCurrent LogErmiyas AschalewNo ratings yet
- List MOOC Courses Jan-2024 CSEDocument3 pagesList MOOC Courses Jan-2024 CSESatyaki Ujan DasNo ratings yet
- MAJOR PROJECT REPORT (Financial Management System)Document46 pagesMAJOR PROJECT REPORT (Financial Management System)Krishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Se Unit3Document138 pagesSe Unit3kishoreNo ratings yet
- CTE - Introduction To Programming With Python HandoutDocument3 pagesCTE - Introduction To Programming With Python HandoutChinmay GokhaleNo ratings yet
- Aloo GobhiDocument18 pagesAloo GobhiDrishti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tomcat Servlet InteractionDocument3 pagesTomcat Servlet InteractionEddy BoutrosNo ratings yet
- Reading Guide - Internet and Computing Core Certification (IC3)Document340 pagesReading Guide - Internet and Computing Core Certification (IC3)Nguyên Phan CaoNo ratings yet
- ML NotesDocument15 pagesML NotesPooja GangapureNo ratings yet
- FactoryTalk Historian SE - PI Web Services vs. PI Web APIDocument5 pagesFactoryTalk Historian SE - PI Web Services vs. PI Web APIDiegoFonsecaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Getting StartedDocument25 pagesChapter 1. Getting StartedevgenNo ratings yet
- Top 50 SQL Question AnswersDocument11 pagesTop 50 SQL Question AnswersChitresh lodhiNo ratings yet
- Notes & Password Manager: ObjectiveDocument9 pagesNotes & Password Manager: ObjectiveJai RamtekeNo ratings yet
- Computer RiddlesDocument3 pagesComputer RiddlesJC Samar EsbietoNo ratings yet
- SemIWCMonitor log file with QAI updatesDocument1,157 pagesSemIWCMonitor log file with QAI updatesRulver Quiroz CabanillasNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument1 pageSodapdfMarcos WilkerNo ratings yet
- 2023 Cloud Product CatalogueDocument44 pages2023 Cloud Product CatalogueCloudInfotechNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Engineering - Software DescriptionsDocument4 pagesHydraulics Engineering - Software DescriptionsBenjamín UreñaNo ratings yet
- 310SV+TurboSafe Rev.3Document2 pages310SV+TurboSafe Rev.3Demetri M. ScytheNo ratings yet
- X-Nucleo-Iks01a3 Motion MEMS and Environmental Sensor Expansion Board For STM32 NucleoDocument4 pagesX-Nucleo-Iks01a3 Motion MEMS and Environmental Sensor Expansion Board For STM32 NucleoepawxcwktvmhqnhobrNo ratings yet