Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12 Science Maths
12 Science Maths
Uploaded by
GALAXY GROUP SCIENCEOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12 Science Maths
12 Science Maths
Uploaded by
GALAXY GROUP SCIENCECopyright:
Available Formats
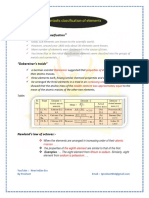
Dobereiner’s law of Triads: (1829): According to Dobereiner in certain triads (groups of three
elements which possessed similar chemical properties) the atomic mass of the central
element was merely the arithmetic mean of the atomic masses of the other two elements
and the properties of the middle element were in between those of the end members. These
families of three elements became known as Dobereiner’s Triads. But in some triads, all the
three elements possessed nearly the same atomic masses, hence the law was rejected.
Triads Mean of atomic masses of 𝟏𝒔𝒕 and 𝟑𝒓𝒅 elements
𝑳𝒊 𝑵𝒂 𝑲 𝟕+𝟑𝟗
7 23 39
= 𝟐𝟑
𝟐
𝑪𝒍 𝑩𝒓 𝑰 𝟑𝟓.𝟓+𝟑𝟗
35.5 80 127
= 𝟖𝟏. 𝟐𝟓
𝟐
𝑪𝒂 𝑺𝒓 𝑩𝒂 𝟒𝟎+𝟏𝟑𝟕
40 88 137
= 𝟖𝟖. 𝟓
𝟐
𝑺 𝑺𝒆 𝑻𝒆 𝟑𝟐+𝟏𝟐𝟕
32 79 127
= 𝟕𝟗. 𝟓
𝟐
𝑷 𝑨𝒔 𝑺𝒃 𝟑𝟏+𝟏𝟐𝟎
31 75 120
= 𝟕𝟓. 𝟓
𝟐
𝑭𝒆 𝑪𝒐 𝑵𝒊 Nearly same atomic masses
𝑹𝒖 𝑹𝒉 𝑷𝒅 Nearly same atomic masses
𝑶𝒔 𝑰𝒓 𝑷𝒕 Nearly same atomic masses
Newland's Law of Octaves:
According to this law, the elements when arranged in order of their increasing atomic masses,
the eighth succeeding element was the repetition of the first one like 8th note of the musical
scale, i.e., after a difference of seven, elements with similar characteristics were observed.
The following are the five horizontal rows of the Newland's classification:
Musical Sa Re Ga Ma Pa Dha Ni
Scale 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
𝟏𝒔𝒕 𝑯 𝑳𝒊 𝑩𝒆 B 𝑪 𝑵 𝑶
𝒏𝒅 𝑭 𝑵𝒂 𝑴𝐠 𝑨𝒍 𝑺𝒊 𝑷 𝑺
𝟐
𝟑𝒓𝒅 𝑪𝒍 𝑲 𝑪𝒂 𝑪𝒓 𝑻𝒊 𝑴𝒏 𝑭𝒆
𝒕𝒉 𝑪𝒐, 𝑵𝒊 𝑪𝒖 𝒁𝒏 𝒀 𝑰𝒏 𝑨𝒔 𝑺𝒆
𝟒
𝟓𝒕𝒉 𝑩𝒓 𝑹𝒃 𝑺𝒓 𝑪𝒆, 𝑳𝒂 𝒁𝒓 − −
The system worked quite well for the lighter elements only up to calcium. For example H, F
and Cl show similar properties and similarly Li, Na and K exhibit same characteristics. The
system, however, fails in the case of heavier elements as manganese has been placed along
with nitrogen and phosphorus or iron has been placed along with oxygen and sulphur, i.e.,
dissimilar elements have been grouped which is against the aim of classification. This clearly
shows that in the classification, the properties of the elements were not taken into account
and only the elements were arranged in order of ascending atomic masses. No space was left
for the elements which were unknown at that time and many elements were provided wrong
positions on account of wrong values of atomic masses in this classification. Thus, Newland's
classification was not accepted as an appropriate arrangement.
You might also like
- TEXT Higher Power2006 - Murdo MacDonald-BayneDocument268 pagesTEXT Higher Power2006 - Murdo MacDonald-BayneLisa Brack100% (17)
- ISO 19901-5-2016 Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries. Specific Requirements For Offshore Structures. Weight Control During Engineering and Construction PDFDocument88 pagesISO 19901-5-2016 Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries. Specific Requirements For Offshore Structures. Weight Control During Engineering and Construction PDFMohamad Zularif Ayup100% (8)
- GasDocument12 pagesGasJesza Mei GanironNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument64 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsHarshit SwayamNo ratings yet
- KToG NoteDocument10 pagesKToG NoteLai Chooi FongNo ratings yet
- Unit III: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument53 pagesUnit III: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Propertiessauvikraha2285No ratings yet
- Lec 10 - The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic TheoryDocument162 pagesLec 10 - The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic TheoryNikky SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument33 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsHarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Early Classification of Elements NotesDocument5 pagesEarly Classification of Elements NotesosasosasyeyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2045 GassesDocument109 pagesChemistry 2045 GassesJeff FosterNo ratings yet
- Sai Vignesh 22w91a05h7Document21 pagesSai Vignesh 22w91a05h7Masireddy NithinreddyNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument3 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsDemons DevilNo ratings yet
- Pravalika Gangoni 22W91A0422Document19 pagesPravalika Gangoni 22W91A0422Masireddy NithinreddyNo ratings yet
- A Historical BackgroundDocument92 pagesA Historical BackgroundBibek BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- (L1) Periodic Table Class9Document22 pages(L1) Periodic Table Class9sunita mundeNo ratings yet
- MYP Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsDocument24 pagesMYP Atomic and Nuclear Physicszaidsarhan801No ratings yet
- PeroidicityDocument11 pagesPeroidicityNafees AliNo ratings yet
- .Trashed 1702966745 1700327617018Document28 pages.Trashed 1702966745 1700327617018gno667533No ratings yet
- 10th Physics Notes and Home Assignment 4thnovDocument8 pages10th Physics Notes and Home Assignment 4thnovArogya Raju PudhotaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5-Periodic-Classification-Of-Elements/: Dobereiner's TriadsDocument6 pagesChapter-5-Periodic-Classification-Of-Elements/: Dobereiner's TriadsAhmed shakilNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5-Periodic-Classification-Of-Elements/: Dobereiner's TriadsDocument6 pagesChapter-5-Periodic-Classification-Of-Elements/: Dobereiner's TriadsAhmed shakilNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements & Periodic PropertiesDocument7 pagesClassification of Elements & Periodic PropertiesHarsh TyagiNo ratings yet
- BalancingDocument3 pagesBalancingIan Rey Mahipos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements NotesDocument13 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements NotesArchitaNo ratings yet
- 2 - PERIODIC TABLE SYNOPSIS-59-75.pmdDocument17 pages2 - PERIODIC TABLE SYNOPSIS-59-75.pmdSai Shri Harshit DNo ratings yet
- CLASS XI CH 3 NOTES (Typed) 1Document16 pagesCLASS XI CH 3 NOTES (Typed) 1Prabhjot SinghNo ratings yet
- Peroidic ClassifcationDocument18 pagesPeroidic ClassifcationRoushan SinghNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: Particulate Nature of MatterDocument253 pagesCourse Outline: Particulate Nature of MatterzakNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements NotesDocument6 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements Notesluubkhan037No ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument4 pagesPeriodic TableKamal Deep SinghNo ratings yet
- Xii-Chem-Chptr-1-Periodic ClassificationDocument8 pagesXii-Chem-Chptr-1-Periodic ClassificationTanveer AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2 Periodic Classification of Elements New Indian Era by PrashantDocument7 pages2 Periodic Classification of Elements New Indian Era by PrashantJuned MulaniNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument24 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsRanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Ionic and Covalent BondDocument46 pagesTopic 3 Ionic and Covalent BondChrystelle Grace TonoganNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and PeriodicityDocument40 pagesClassification of Elements and PeriodicityMayank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Slide 7Document13 pagesSlide 7toby121802No ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Periodic Exam in Math ReviewerDocument4 pages2nd Quarter Periodic Exam in Math ReviewerAsh RchaNo ratings yet
- Class X Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument3 pagesClass X Periodic Classification of ElementsElite PaladinNo ratings yet
- F57 Ptutfuwz HB 3 S7 XQJMDocument19 pagesF57 Ptutfuwz HB 3 S7 XQJMVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Quarter 3 ReviewerDocument6 pagesGrade 8 Science Quarter 3 Reviewerasuit9135No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument9 pagesAtomic Structurejackie.chanNo ratings yet
- PPDocument4 pagesPPrameshNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table & PeriodicityDocument22 pagesPeriodic Table & PeriodicityMike hunkNo ratings yet
- Notes - Periodic Classification of Elements - C-XDocument4 pagesNotes - Periodic Classification of Elements - C-Xpratishtha MishraNo ratings yet
- Periodicity - of - Elements - Prince Sir PDFDocument37 pagesPeriodicity - of - Elements - Prince Sir PDFpallab mukherjee100% (1)
- Classification of Elements & Periodic Table Part-A (Periodic Table)Document51 pagesClassification of Elements & Periodic Table Part-A (Periodic Table)Abhishek NNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Qualifying Exam ReviewDocument115 pagesChemistry Qualifying Exam ReviewKent John Labaclado DugaNo ratings yet
- Order Parameters, Broken Symmetry, and Topology: PACS Numbers: KeywordsDocument10 pagesOrder Parameters, Broken Symmetry, and Topology: PACS Numbers: KeywordsDanielleMcGillicuttyNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 Unit 3 Crystal Structure Final NotesDocument63 pagesSem 1 Unit 3 Crystal Structure Final Notespwasu12350No ratings yet
- CheemmmmmmmmmmmmDocument4 pagesCheemmmmmmmmmmmmarabela albairaNo ratings yet
- CH2 Lecture NotesDocument42 pagesCH2 Lecture Noteskoka992009No ratings yet
- Early Models of Periodic TableDocument2 pagesEarly Models of Periodic TableOm TipsetwarNo ratings yet
- Balance Method 1Document12 pagesBalance Method 1Ricard Revuelto Orengo100% (2)
- Termodinamika Teknik Kimia 2 - Week3Document76 pagesTermodinamika Teknik Kimia 2 - Week3SandyPratamaAdhiNo ratings yet
- Relative Atomic Masses Mass SpectrometryDocument43 pagesRelative Atomic Masses Mass SpectrometryClaytonMitchellJr.No ratings yet
- Chap 13 Gas Laws & Kinetic Theory SummaryDocument2 pagesChap 13 Gas Laws & Kinetic Theory SummarySyakirah MunirNo ratings yet
- Science Notes - Lession-5 - Periodic Clasification of Elements - ChemistryDocument14 pagesScience Notes - Lession-5 - Periodic Clasification of Elements - ChemistryHimanshi guptaNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Their Styructure Chapt4Document57 pagesAtoms and Their Styructure Chapt4Manoy KolokoyNo ratings yet
- Classification of ElementsDocument17 pagesClassification of Elementsaaranyaka shobinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Periodic TableDocument23 pagesChapter 1 Periodic TablevsyoiNo ratings yet
- Computer Job Bio Data ResumeDocument5 pagesComputer Job Bio Data ResumeGALAXY GROUP SCIENCENo ratings yet
- 2chemicalkinetics D15 Sep 2018Document10 pages2chemicalkinetics D15 Sep 2018GALAXY GROUP SCIENCENo ratings yet
- CH5MCQ - D18 Jul 2023Document45 pagesCH5MCQ - D18 Jul 2023GALAXY GROUP SCIENCENo ratings yet
- 2sem3electrochemistry - D18 Nov 2018Document8 pages2sem3electrochemistry - D18 Nov 2018GALAXY GROUP SCIENCENo ratings yet
- 11 A English (S.L) p-2Document4 pages11 A English (S.L) p-2GALAXY GROUP SCIENCENo ratings yet
- (12 Eng) PhysicsDocument4 pages(12 Eng) PhysicsGALAXY GROUP SCIENCENo ratings yet
- Bord Form Instruction PageDocument1 pageBord Form Instruction PageGALAXY GROUP SCIENCENo ratings yet
- Yogyata Pramanpatra 2019-20Document14 pagesYogyata Pramanpatra 2019-20GALAXY GROUP SCIENCENo ratings yet
- UnitTest - D30 Jun 2022Document3 pagesUnitTest - D30 Jun 2022GALAXY GROUP SCIENCENo ratings yet
- Verifying L.C. Certy.Document1 pageVerifying L.C. Certy.GALAXY GROUP SCIENCENo ratings yet
- UnitTest - D30 Jun 2022 1Document9 pagesUnitTest - D30 Jun 2022 1GALAXY GROUP SCIENCENo ratings yet
- Strategi Bisnis Umkm Selama Pandemi Covid-19Document9 pagesStrategi Bisnis Umkm Selama Pandemi Covid-19nabila zhafirah100% (1)
- AK53 Service ManualDocument62 pagesAK53 Service Manualb6481136No ratings yet
- Jurnal Pengabdian EjoinDocument7 pagesJurnal Pengabdian EjoinAde SulistyawatiNo ratings yet
- RuletaDocument9 pagesRuletahermes731No ratings yet
- Project On Solar Treadmill BicycleDocument18 pagesProject On Solar Treadmill BicycleIshwarjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Pyrometallurgy Towards Clean Metallurgical Processing 2012Document438 pagesPyrometallurgy Towards Clean Metallurgical Processing 2012Abie BadhurahmanNo ratings yet
- Tuberia Espaciador RACI 1Document16 pagesTuberia Espaciador RACI 1RicNo ratings yet
- Physical Development of Primary Schoolers (Middle Childhood)Document5 pagesPhysical Development of Primary Schoolers (Middle Childhood)Ginaly PicoNo ratings yet
- That Humans Can Understand. - Martin Fowler ": 4 Simple Ways To Make Your Code Cleaner!Document2 pagesThat Humans Can Understand. - Martin Fowler ": 4 Simple Ways To Make Your Code Cleaner!Md. Habibur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Esp ReviewerDocument6 pagesEsp ReviewerAltea Kyle CortezNo ratings yet
- Mendeley Teaching PresentationDocument36 pagesMendeley Teaching PresentationpatrickNX9420No ratings yet
- Porting U Boot: Michael OpdenackerDocument6 pagesPorting U Boot: Michael OpdenackerBhaskar DevanNo ratings yet
- ClutchDocument9 pagesClutchAndryanNo ratings yet
- Powder Coatings Product Guide - 20-219767Document7 pagesPowder Coatings Product Guide - 20-219767zagNo ratings yet
- Math 100Document3 pagesMath 100Leorafe C. SosasNo ratings yet
- West Pakistan Hazardous Occupations (Lead) Rules, 1963Document7 pagesWest Pakistan Hazardous Occupations (Lead) Rules, 1963WaqarAhmedButtNo ratings yet
- Report On Command Agriculture Fact Finding Public HearingDocument12 pagesReport On Command Agriculture Fact Finding Public Hearingkennie kennias shonhiwa chikwanhaNo ratings yet
- Project Standard Specification: Air Terminals 15845 - Page 1/7Document7 pagesProject Standard Specification: Air Terminals 15845 - Page 1/7adel rihanaNo ratings yet
- Ajay Hasia and Ors Vs Khalid Mujib Sehravardi and s800498COM116754Document18 pagesAjay Hasia and Ors Vs Khalid Mujib Sehravardi and s800498COM116754BHAVYANSHI DARIYANo ratings yet
- Tax Calculation On Freight Different ScenariosDocument15 pagesTax Calculation On Freight Different Scenarioslostrider_991No ratings yet
- Session 2 - Wireline Techniques For Advanced Modulation SchemesDocument1 pageSession 2 - Wireline Techniques For Advanced Modulation Schemesranickng1No ratings yet
- Ec-Type Examination Certificate: DEMKO 09 ATEX 0909372XDocument3 pagesEc-Type Examination Certificate: DEMKO 09 ATEX 0909372XmsuiaNo ratings yet
- ELMACH Packages India Pvt. LTD - EDocument3 pagesELMACH Packages India Pvt. LTD - EYosses Sang NahkodaNo ratings yet
- Brennan Thread ChartDocument1 pageBrennan Thread ChartKOMATSU SHOVELNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic - 319+990 PDFDocument8 pagesHydraulic - 319+990 PDFArun ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document28 pagesChapter 1Suzaini SupingatNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 MTH 3401Document4 pagesTutorial 6 MTH 3401Mohd Azman SuwandiNo ratings yet
- Oral Defense RubricsDocument3 pagesOral Defense RubricsHanah Crista CaparasNo ratings yet