Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Potato Conclsusion
Uploaded by
lxyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Potato Conclsusion
Uploaded by
lxyCopyright:
Available Formats
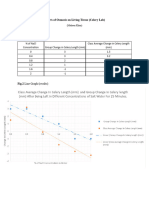
Concentration of Initial mass Final mass Change in mass Percentage change
sucrose solution (g), ±0.05 (g) ±0.05 (g) ±0.05 in mass
(mol/dm3) (%)
0 (distilled water) 0.56 0.64 +0.08 14.29
0.25 0.63 0.75 +0.12 19.05
0.50 0.40 0.44 +0.04 10.0
0.75 0.43 0.42 -0.01 -2.33
1.00 0.53 0.51 -0.02 -3.77
Measuring water potential of a potato cell
The purpose of this investigation was to study the effect of changes in the water potential gradient on the
osmolarity of the potato cell by measuring changes in mass after submerging the potato cells in different
concentrations of sucrose solution. The table above demonstrates that there is a correlation between the change
in mass and the change in water potential. The table shows that regions of high water potential (distilled water)
would cause the potato cell to increase in mass (+0.08g) due to the movement of water molecules into the cell
whereas regions of low water potential (1.00 mol/dm3 of sucrose solution) would cause a decreases in the mass
of the potato cell (-0.02g) due to the movement of water molecules out of the cell. It can be established that
osmolarity and water potential have a negative correlation.
When the water potential increases, the mass of the potato cell also increases. This is because of osmosis.
Osmosis is the passive movement of water molecules from a region of lower solute concentration to a region
of higher solute concentration, across a partially permeable membrane. The water molecules will continue to
move through the partially permeable membrane until osmotic equilibrium is achieved. Osmotic equilibrium
refers to when there is an equal concentration of water molecules in both sides of the membrane. Osmotic
equilibrium is vital to the cell as it ensures optimal concentrations for the cell to carry out its functions and to
prevent the cell from accumulating waste.
As seen in the table, placing the potato cell in a boiling the of distilled water will create a hypotonic
environment for the cell. In a hypotonic solution, there are fewer active solutes. Active solutes are substances
that dissolve by forming intramolecular bonds with water molecules. Hypotonic solutions have more free water
molecules that can move across the partially permeable membrane and therefore, regulating the osmotic
balance in both sides of the membrane. The partially permeable membrane will only allow water molecules to
enter, larger molecules such as glucose would not be able to enter it as they are too large.
During the observation of this investigation, there was no visible change.
In future experiments, it would be suitable to rerun each trial for at least seven times and taking the average in
order to secure more precise results.
In the table above, an anomaly can be identified which is that the potato cell in 0.25mol/dm 3 of sucrose
solution had the highest percentage change in mass (19.05%). Scientifically, the potato cell that should have
the highest percentage change is the cell in distilled water. This anomaly could be investigated further, or it
could be an error in methodology. Overall, a repetition would be required to obtain more accurate results.
You might also like
- AP Biology Lab 1Document10 pagesAP Biology Lab 1Abby Loneker0% (1)
- Osmosis and Diffusion Lab For AP BioDocument11 pagesOsmosis and Diffusion Lab For AP Bioitssabbyx3No ratings yet
- Diffusion and Osmosis LabDocument7 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis Labapi-299480033100% (2)
- Bell Delaware Method English 2Document10 pagesBell Delaware Method English 2aldairNo ratings yet
- Homemade FoundryDocument9 pagesHomemade FoundryHerman HeseNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Diffusion AP Biology Lab ReportDocument11 pagesOsmosis Diffusion AP Biology Lab ReportJameson SchultsNo ratings yet
- CAPE Biology Labs - OsmosisDocument9 pagesCAPE Biology Labs - OsmosisAshleigh SmithNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 8 Q3Document3 pagesDLL Science 8 Q3IAN BERNARDONo ratings yet
- Understanding PH MeasurementDocument10 pagesUnderstanding PH MeasurementAnnisa Novita Putri SiregarNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Movement of substancesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Movement of substancesNo ratings yet
- Measuring Water Potential On The Potato StripsDocument5 pagesMeasuring Water Potential On The Potato StripsSueEe100% (1)
- Osmosis Lab ReportDocument11 pagesOsmosis Lab Reportoscarwu1100% (1)
- Band1 Fundamentals NeuDocument102 pagesBand1 Fundamentals Neus_m_taheri100% (1)
- Biology Lab Report - OsmosisDocument6 pagesBiology Lab Report - OsmosisXannyNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document7 pagesLab 6Zachary MedwinterNo ratings yet
- Solute LabDocument5 pagesSolute LabshylburnabyNo ratings yet
- Lab Report (Lab 2)Document12 pagesLab Report (Lab 2)RONALD DECK YAMINo ratings yet
- Potato Osmosis - Torsten HoldarDocument7 pagesPotato Osmosis - Torsten HoldarTorsten HoldarNo ratings yet
- Biology Water Potential Lab ReportDocument5 pagesBiology Water Potential Lab ReportnyshamordaniNo ratings yet
- Jaka Patafta Lab Report OsmolarityDocument11 pagesJaka Patafta Lab Report OsmolarityJaka PataftaNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Lab ReportDocument5 pagesOsmosis Lab ReportChessman ChessmanNo ratings yet
- Water PotentialDocument5 pagesWater PotentialTyrese BaxterNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Investigatio1Document3 pagesOsmosis Investigatio1Hamza QasimNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab1Document9 pagesBio Lab1David SolingerNo ratings yet
- Research SampleDocument11 pagesResearch SampleosamaNo ratings yet
- Scientific ReportDocument3 pagesScientific ReportJoel ChanNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Lab Report 2.0Document8 pagesOsmosis Lab Report 2.0iren dogruNo ratings yet
- Rh10203 Practical 1 (Mohammad Irfan Bin Laji Br20110065Document8 pagesRh10203 Practical 1 (Mohammad Irfan Bin Laji Br20110065MOHAMMAD IRFAN LAJINo ratings yet
- MD - Saiful Islam 17... 101Document25 pagesMD - Saiful Islam 17... 101izarul islamNo ratings yet
- Osmosis DCP and Ce LabDocument5 pagesOsmosis DCP and Ce LabAbbey HeNo ratings yet
- Osmosis & Diffusio N Lab: Taylor Downs AP Biology Period ThreeDocument9 pagesOsmosis & Diffusio N Lab: Taylor Downs AP Biology Period ThreeinfinitememoryNo ratings yet
- LAB#4Document2 pagesLAB#4nataliya reidNo ratings yet
- Investigating Osmolarity in Plant TissuesDocument2 pagesInvestigating Osmolarity in Plant TissuessofiaNo ratings yet
- Osmosis & Diffusio N Lab: Taylor Downs AP Biology Period ThreeDocument8 pagesOsmosis & Diffusio N Lab: Taylor Downs AP Biology Period ThreeinfinitememoryNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Lab 1Document5 pagesAP Bio Lab 1Kiran ShilaNo ratings yet
- Practical Portfolio Report: Spectrophotometry Report Buffer Solution ReportDocument8 pagesPractical Portfolio Report: Spectrophotometry Report Buffer Solution ReportSeyi ColeNo ratings yet
- DPAR Partial Molar VolumeDocument22 pagesDPAR Partial Molar VolumeFritz FestejoNo ratings yet
- BIO Lab 7Document4 pagesBIO Lab 7Antonio WilloughbyNo ratings yet
- UTAR Chem Lab 1 Full Report Exp10Document3 pagesUTAR Chem Lab 1 Full Report Exp10Izykiel EdwardNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Diffusion AP Biology Lab Report PDFDocument11 pagesOsmosis Diffusion AP Biology Lab Report PDFLaura Nivar100% (1)
- Bio Ku 1Document5 pagesBio Ku 1Echa NoviandiniNo ratings yet
- Informe Laboratorio Biologia OsmolaridadDocument7 pagesInforme Laboratorio Biologia OsmolaridadDiego LancherosNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument6 pagesSolutionLexiaYapNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PracticalDocument4 pagesChemistry Practicalsuleiman kassimNo ratings yet
- Luke Stainer Osmosis Practical Write UpDocument5 pagesLuke Stainer Osmosis Practical Write UpMaan PatelNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry, Osmosis, Cellular Respiration & Photosynthesis Lab StationsDocument9 pagesBiochemistry, Osmosis, Cellular Respiration & Photosynthesis Lab StationsRaina KimNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Lab ReportDocument4 pagesOsmosis Lab ReportaliceNo ratings yet
- Estimating Osmolarity of Plant CellsDocument5 pagesEstimating Osmolarity of Plant CellssilverpjNo ratings yet
- Student Camryn Lewis Investigation Osmosis and Water Potential StudentDocument6 pagesStudent Camryn Lewis Investigation Osmosis and Water Potential StudentKhushi PatelNo ratings yet
- Potato Lab ReportDocument10 pagesPotato Lab ReportsimplylailaNo ratings yet
- BIO703 Practical 2 2020Document11 pagesBIO703 Practical 2 2020Litia LeegetNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab ReportDocument3 pagesBiology Lab ReportMaya PlewniaNo ratings yet
- Exp 5 Physical ChemistryDocument8 pagesExp 5 Physical ChemistryHuiling GohNo ratings yet
- Diffusion, Osmosis, and Water Potential: Samantha A. Price A.P. Biology 10-8-09 Lab #2Document12 pagesDiffusion, Osmosis, and Water Potential: Samantha A. Price A.P. Biology 10-8-09 Lab #2fallenangel325920% (2)
- BIO411 Lab 3Document8 pagesBIO411 Lab 3Alis SyamimiNo ratings yet
- JJJJNJJDocument4 pagesJJJJNJJReizel Joice GragantaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Osmosis On Living Tissue (Celery Lab)Document5 pagesEffects of Osmosis On Living Tissue (Celery Lab)animeanimism12No ratings yet
- Osmosis ReportDocument14 pagesOsmosis ReportMysha KhanNo ratings yet
- AP Lab #1 - Diffusion and OsmosisDocument4 pagesAP Lab #1 - Diffusion and OsmosisAmanda YoungNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Water Potential FinalDocument6 pagesLab Report Water Potential Finalade2001fr3113No ratings yet
- Measuring Water Potential in Potato Tubers LABDocument10 pagesMeasuring Water Potential in Potato Tubers LABMonica Paris SisourathNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry: Submitted ToDocument11 pagesPhysical Chemistry: Submitted ToMubashir MazharNo ratings yet
- Potato Cytoplasm LabDocument4 pagesPotato Cytoplasm LabNickNo ratings yet
- Virtual Transport LabDocument3 pagesVirtual Transport Labapi-522847737No ratings yet
- Biology Lab Report: Lhamo RichoeDocument12 pagesBiology Lab Report: Lhamo RichoeLhamo RichoeNo ratings yet
- A A 52524aDocument4 pagesA A 52524amuhammed emin akgülNo ratings yet
- 62f PDFDocument20 pages62f PDFMohsenNo ratings yet
- Master Thesis SuerbaevaDocument75 pagesMaster Thesis Suerbaevajason manajNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics 2006Document22 pagesLocal Anesthetics 2006Shashikant DrShashikant BagadeNo ratings yet
- Kohl Surma Galena CollyriumDocument5 pagesKohl Surma Galena CollyriumjivasumanaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Lithium Ore With Avio 550 Max Icp Oes 359050Document6 pagesAnalysis of Lithium Ore With Avio 550 Max Icp Oes 359050seninhentayNo ratings yet
- Materi Aplikasi Reaksi RedoksDocument28 pagesMateri Aplikasi Reaksi Redokszaharo putriNo ratings yet
- Industrial Types of Gold Deposits of The East KazakhstanDocument9 pagesIndustrial Types of Gold Deposits of The East KazakhstanGEOLINKS International Conference 2019No ratings yet
- IscienceDocument22 pagesIscienceValentin MusetNo ratings yet
- Pit Iagi37 Sdg043 Lambok Full Paper Gas Geochemistry Final PDFDocument12 pagesPit Iagi37 Sdg043 Lambok Full Paper Gas Geochemistry Final PDFakun cadanganNo ratings yet
- Ramax Hh-Eng P 1604 E6Document8 pagesRamax Hh-Eng P 1604 E6venkithankamNo ratings yet
- Assignment Chemical Kinetics JH Sir-4309Document44 pagesAssignment Chemical Kinetics JH Sir-4309T sidharth100% (2)
- Identification of The Best Model and Parameters For T-Y-X Equilibrium Data of Ethanol-Water MixtureDocument7 pagesIdentification of The Best Model and Parameters For T-Y-X Equilibrium Data of Ethanol-Water MixtureMeghana SNo ratings yet
- Chemical PulpingDocument18 pagesChemical PulpingAnis KewwNo ratings yet
- Getting Started in Steady StateDocument24 pagesGetting Started in Steady StateamitNo ratings yet
- 77 EvacuatedU TubeSolarWaterHeating PDFDocument9 pages77 EvacuatedU TubeSolarWaterHeating PDFSubash VeluNo ratings yet
- High Efficiency Transformation of Escherichia Coli With PlasmidsDocument6 pagesHigh Efficiency Transformation of Escherichia Coli With PlasmidsAnthony TeeNo ratings yet
- Full Download Human Biology 15th Edition Mader Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Human Biology 15th Edition Mader Test Bankpardonstopping.q54x100% (29)
- Exp11 Electrical - Conductivity.sum17Document1 pageExp11 Electrical - Conductivity.sum17joshua_98548No ratings yet
- Topic10 SeismicDesignofSteelStructuresHandoutsDocument20 pagesTopic10 SeismicDesignofSteelStructuresHandoutsrk6482No ratings yet
- Polyethylene TerephthalateDocument4 pagesPolyethylene TerephthalateClarisse Joyce GenerNo ratings yet
- Sulphuric AcidDocument4 pagesSulphuric Acidaliyah_ilmiNo ratings yet
- Nitocote AC: Weather Resistant Flexible Acrylic CoatingDocument2 pagesNitocote AC: Weather Resistant Flexible Acrylic CoatingWahlee SatuNo ratings yet
- Protect Rubber Goods To Prevent Failure: Tears ProtuberanceDocument2 pagesProtect Rubber Goods To Prevent Failure: Tears ProtuberancePedro SarmientoNo ratings yet
- 02 Fers Resins For Abrasives Fsac05 To CD VersionDocument32 pages02 Fers Resins For Abrasives Fsac05 To CD VersionpmalexNo ratings yet