Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bacterial Cell Structure
Bacterial Cell Structure
Uploaded by
abdullaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bacterial Cell Structure
Bacterial Cell Structure
Uploaded by
abdullaCopyright:
Available Formats
Bacterial Cell Structure
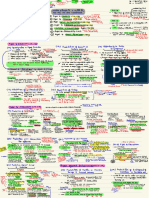
staining be unstained bacteria difficult to detect of light
is
microscope
Gram stain: most bacteria fall into of those categories Cones one
what cell wall can't be identified)
bacteria to sell wall
separates composition
-
ace -ve
gram
+ve
gran
violet saln *ok
3
crystal =>
purple stain + salvent (ak/acetone gram the keep stain removes stain from
preceeded fixation
*
·gram-we lose stain (colorless)
+ iodine for fixation for 5 seas
since it has thinner
little heating gram-ve
by -
+
saframin
(counterstain)
=>
staining pink
colors lighter
or
than
red
violet so
-
peptidoglycan whereas grow the
has thicker peptidoglycan
are
*since
slight color change/ graw color
gram
the -ve
gains
importance: -
differ antibiotic susceptibility
the and -
we in it so can be a
first line
of treatment (family specific but not to the specific bacterial
be diagnostic (nature,
morphology
·
can
variety, relative number)
limitations: needs large volume (TO "organisms(nL)
-
centrifugation to get desired concentration
Acid fast stain: reserved
from pet factstop rathereberestart
for bacterial infection
suspicion of my
identify organisms
w/
waxy
materials (mysolic acids) in
their cell walls
carb fuchsin stains + acidic alcohol >
fast keep stain
acid
-normally lose stain
Prokaryotic cell:
1. cytoplasmic membrane: phospholipid bilayer selectively permeable (polar and nonpolar in
2.
Peptidoglycan: cross linked polymer mesh determines cell shape
lycan linear N-acetylglucosamine backbone
polymer
*
is
9 a
N.acetyl muramic acid
short as
string that crosslinks
adjacent polysacc strands at NAM subunits
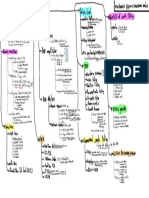
Diff
*
by gram are and
graw-we
cell walls.
2
gram
are: thick, multilayeredpeptidoglycan cell walls (outside plasma membrane) noendotoin our enter
peptidoglycan is
covalently linked to techoic acid (polymer of substituted glyceral
linked
by phosphodiester bonds)
cell surface antigens
ecture major
Sintegrated into peptidogly not plasmedemma I can
lipoteicboic acid
=>
integrated into outer leaflet of cytoplasmic
are
membrane
9.
gram-ve:
outer layer lembedded lipopolysaccharide) cytoplasm membrane
separated by periplasmic space thinner
peptidoglycan wall succeptibility to physical damage ****
degradative enzymes transport proteins
I
2
2. external capsule and
glycocalyx: sticky, viscous material (usually polysaccharidal extracellular coating
pathogenic
*
capsule
Bacillus anthracic
of poly D.glutamic is made ·
acid
· excep
- .
tion
fightly sell, organized
bound to structure capsule ->
loosely bound, amorphous glycocalyx (slime layer)->
Functions: salfor cell to adhere to surfaces ->
aids multiplication and colonization (+* pathogenicity)
9.
protect from antibodies and
phagocytosis (by WBC or
protozoal
(a
3.
diffusion barriers
against some antibiotics pathogenicity)
↑
protect against dessication (can be reserve for nutrients)
Appendagedin
4.
one or
many long, semingid, helicd, hollor, tubular structures from several thousand molecules of Stagetting protein
anchored cell membranes basal body that rotates it like of propeller ship
in
by a scrow
enable movement in directed fashion
highly antigenic
don't but its still COLONY
form compact colonies just it
*
swarm a
agar,
on over
6. Pili/imbrae: shorter and thinner attachment structures (specific cell-cell contact) made from pillin protein
(
function bacteria-entaryofhalfadhere a re
it
*
receptor specific determining where it
is adhere (GF/urinary tract/respiratory tract...)
can
=
Antigenic variation: expression of alternative outgen forms cell surface
various on
LPS, capsules, lipoteichoic acid, pilli, flagella are
subject to antigenic variation
imp for immune evasion
detected by serology
Sporulation: majorly Bacillus clostridium
environment hostility - structural/metabolic changes ->
endospore (inside of
cell)
can be released as
free spares
spores are the most resistant life forms known (survive boiling, dessication, UV...)
A sporulation: bacterial to
form little water
repackaging of DNA slower than germination
*
copy
a new
no metabolic activity
doesn't divide
restructured, highly impermeable, multilayered envelope
process: invagination of cell membrane => double membrane of isolated
copy of bacterial DNA (future core
-new
spore specific enzymes
are
synthesized at the core
high
C spore retains
calcium
machinery for protein synthesis
cell
many enzymes of vegetive are
degraded dipicolinate
topenvironment
**
protection
parent cell
lysis releasing the
ready endospore
P-serviceptionrates rotterasecond
process:
destruction
of
its
cortex by lytic enzymes
the
·
uptake of water
release of calcim dipicalinate
C. medical
significance.
remain viable for many years
autoclaring (T>100° +pressure ( death =>
1st bood/normal conditions induce less viable
germination +Ind boil death than
autoclary
Chromosome & plasmid:
stranded essential non-essential (2x-4K)
chromosome: long piece of circular double DNA w/ and
genes
plasmids small DNA circle (10 size
of chromosome
·replicate independant of chromosome (can exist in 1+
copies)
for growth/replication
stormus
no
encoding
· *
carries
genes genes
to other calls
promoting plasmid transfer
·transposons mobile DNA antibiotic resistance
plasmid plasmid plasmid chromosome repository for many
*
that
sequences
more or
they responsible for
are some
plasmids being able to
integrate into chromosome
genes
You might also like
- IB Biology Topic 7 - Nucleic Acids HL Revision SheetDocument1 pageIB Biology Topic 7 - Nucleic Acids HL Revision SheetLexieNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Genetic Engineering PowerpointDocument49 pagesUnit 9 Genetic Engineering Powerpointapi-235160519No ratings yet
- 5 - Sections PDFDocument1 page5 - Sections PDFforbeskaNo ratings yet
- Reaction: PhaseDocument8 pagesReaction: Phaseعبدالله ممدوحNo ratings yet
- PKEL-s.muyhelp-sfystolicmurmmb - Be: MiserDocument6 pagesPKEL-s.muyhelp-sfystolicmurmmb - Be: Miserkvs gouthamNo ratings yet
- Biology Short Notes 2Document6 pagesBiology Short Notes 2Humayun KhanNo ratings yet
- 5 PDFDocument1 page5 PDFSim Pei YingNo ratings yet
- 50D BCB 246Document10 pages50D BCB 246laura MtNo ratings yet
- 50D-BCSDocument12 pages50D-BCSCorjuc StefanNo ratings yet
- William J Borbely Contact Information WhitepagesDocument1 pageWilliam J Borbely Contact Information WhitepagesJimmy CavagnaroNo ratings yet
- Fund RightsDocument2 pagesFund RightsAkansha GuptaNo ratings yet
- AclsDocument23 pagesAclsAnastazia AdeelaNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Resistance of Coupling MaterialsDocument15 pagesCorrosion Resistance of Coupling Materialswhite9013No ratings yet
- PediatricDocument12 pagesPediatricdirty harryNo ratings yet
- 09 13 17Document28 pages09 13 17WoodsNo ratings yet
- 3 TCP-DTRFDocument1 page3 TCP-DTRFHaevu BNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document1 pageChapter 3Shaurya JainNo ratings yet
- Alteraciones de La HemostasiaDocument3 pagesAlteraciones de La HemostasiaJENNIFER DIANA MORENO PRECIADONo ratings yet
- MLS Listing Facts, Jan 2011Document1 pageMLS Listing Facts, Jan 2011Maggie ChandlerNo ratings yet
- S-23-01 Saraswati Singh TKDocument3 pagesS-23-01 Saraswati Singh TKTanweer KhanNo ratings yet
- Amended IFC - CubeDocument10 pagesAmended IFC - Cubemohsin khanNo ratings yet
- Intensive ReviewDocument3 pagesIntensive ReviewMine CraftNo ratings yet
- (FactRecall) Particle ClassificationDocument1 page(FactRecall) Particle Classificationvesode6821No ratings yet
- Butter BTS ButterDocument2 pagesButter BTS ButterIvy Tan Yin ShuinNo ratings yet
- Secondary Annual Result 2023 PDFDocument1 pageSecondary Annual Result 2023 PDFDharmendra KumarNo ratings yet
- It's So Easy Going Green: An Interactive, Scientific Look at Protecting Our EnvironmentFrom EverandIt's So Easy Going Green: An Interactive, Scientific Look at Protecting Our EnvironmentNo ratings yet
- 70D BCS 63BR0Document12 pages70D BCS 63BR0Ramnath KNo ratings yet
- 40D-BC-51Q (SN - 201253) PachecoDocument10 pages40D-BC-51Q (SN - 201253) PachecoRicardo RomeroNo ratings yet
- 1061 A1 Sols FinalDocument7 pages1061 A1 Sols Final9ygtd7w2wqNo ratings yet
- Typical Install Detail: (Socket Bottom)Document1 pageTypical Install Detail: (Socket Bottom)D MNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectrometry - FactRecallDocument2 pagesMass Spectrometry - FactRecallFarhan TanveerNo ratings yet
- L1 - Gene ExpressionDocument5 pagesL1 - Gene Expressiontowalovesports920No ratings yet
- Valuation of Goodwill PDFDocument17 pagesValuation of Goodwill PDFSanskriti SenNo ratings yet
- 4361 Prestige Dew Drops Lifestyle Brochure LR 16.03.2023Document26 pages4361 Prestige Dew Drops Lifestyle Brochure LR 16.03.2023amitktiwariNo ratings yet
- Poor Living Standard For Humanity: Limited Food ResourcesDocument1 pagePoor Living Standard For Humanity: Limited Food ResourcesharnoorNo ratings yet
- entitie: NeverDocument1 pageentitie: NeverMr. ACDCNo ratings yet
- 25D BCB 53ar0Document10 pages25D BCB 53ar0brianleeariasNo ratings yet
- Status of Conventions: Io N, e TC NDocument24 pagesStatus of Conventions: Io N, e TC NCapt-Umesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Greektheateritsd 00 FlicuoftDocument444 pagesGreektheateritsd 00 FlicuoftValentin BiscocheaNo ratings yet
- Parts Manual: CascadeDocument10 pagesParts Manual: CascadeantonioNo ratings yet
- Proliferation Lymphatic: Leading ?Document6 pagesProliferation Lymphatic: Leading ?flzhathrhNo ratings yet
- Parts Manual: CascadeDocument10 pagesParts Manual: CascadeantonioNo ratings yet
- 35D MCS 67ar0Document10 pages35D MCS 67ar0Ricardo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Date Revised by Approved by Change Description REV ECN: DG 5Tn-ODocument2 pagesDate Revised by Approved by Change Description REV ECN: DG 5Tn-Okostas formulagrNo ratings yet
- MLS® Listings Facts, April 2011Document1 pageMLS® Listings Facts, April 2011Maggie ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Brezza Accessories BrochureDocument8 pagesBrezza Accessories BrochureVarshant KumarNo ratings yet
- Ground Floor Lighting Layout Second Floor Lighting Layout: General NotesDocument1 pageGround Floor Lighting Layout Second Floor Lighting Layout: General NotesDanica Mae AmicayNo ratings yet
- Architecture..wc SectionsDocument1 pageArchitecture..wc SectionsReham HashimNo ratings yet
- Real Estate Board of Vancouver BC MLS Sales Facts Jan 2011Document1 pageReal Estate Board of Vancouver BC MLS Sales Facts Jan 2011Maggie ChandlerNo ratings yet
- GT Bearings Six SigmaDocument12 pagesGT Bearings Six SigmaJJ100% (1)
- Module 3Document7 pagesModule 3bobby brownNo ratings yet
- MacroDocument2 pagesMacroCarolyneNo ratings yet
- Sportex GraphenonDocument1 pageSportex Graphenonpikemanserbia100% (1)
- Flower Arrangement: Vase 02 : © Canon Inc. © MinyaDocument4 pagesFlower Arrangement: Vase 02 : © Canon Inc. © MinyaViet HoangNo ratings yet
- Crain India 11-Apr-2024Document3 pagesCrain India 11-Apr-2024amitk397115No ratings yet
- CraniumDocument19 pagesCraniumstelian.bgNo ratings yet
- 全身動脈圖表整理Document1 page全身動脈圖表整理irenesong922840053No ratings yet
- Letter To Karen Kidd-Witch Hunt Aimed at Polish Immigrant and U.S Supreme Court Justice Hon. Brett KavanaughDocument149 pagesLetter To Karen Kidd-Witch Hunt Aimed at Polish Immigrant and U.S Supreme Court Justice Hon. Brett KavanaughJerry VashchookNo ratings yet
- Calc Lec 1Document1 pageCalc Lec 1Nirved JainNo ratings yet
- MLS® Sales Facts MLS® Sales April 2011Document1 pageMLS® Sales Facts MLS® Sales April 2011Maggie ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Zirconia Graphite RefractoryDocument6 pagesZirconia Graphite RefractoryBagas Prasetyawan Adi NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology IntroDocument3 pagesMolecular Biology IntroabdullaNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesProtein SynthesisabdullaNo ratings yet
- Transcription & RNA ProcessingDocument3 pagesTranscription & RNA ProcessingabdullaNo ratings yet
- DNA SynthesisDocument3 pagesDNA SynthesisabdullaNo ratings yet
- Systems Biology ProblemSet1Document5 pagesSystems Biology ProblemSet1Elegant UniverseNo ratings yet
- Buenasher Learning Academy IncDocument8 pagesBuenasher Learning Academy IncEl CruzNo ratings yet
- INtroduction To InformaticsDocument61 pagesINtroduction To InformaticsDita Merry Diah VanonyNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To EcologyDocument6 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To EcologyNelzen GarayNo ratings yet
- BIOL2162 Course Outline March 2012Document19 pagesBIOL2162 Course Outline March 2012slackerzzNo ratings yet
- NSEB Question Paper 2017Document28 pagesNSEB Question Paper 2017Ashutosh100% (1)
- Ustet ReviewerDocument16 pagesUstet ReviewerVinzynt Isler Carmona100% (19)
- Bio - Chemistry T& D PaperDocument12 pagesBio - Chemistry T& D PaperPNo ratings yet
- MSC Biotechnology SyllabusDocument24 pagesMSC Biotechnology SyllabusNarendra KelkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document56 pagesChapter 13Hậu VũNo ratings yet
- Odisha Public Service Commission: SL No Subject No of Vacancies No of Posts Reserved For S.T. S.C. Sebc U.RDocument82 pagesOdisha Public Service Commission: SL No Subject No of Vacancies No of Posts Reserved For S.T. S.C. Sebc U.RPradyumna Keshari NahakNo ratings yet
- Lethal Genes - Learn Science at ScitableDocument2 pagesLethal Genes - Learn Science at ScitablePaulina CisnerosNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument25 pagesIlovepdf Mergedyufm2008No ratings yet
- GENBIO2 3rd QTest Sy23 24reviewerDocument9 pagesGENBIO2 3rd QTest Sy23 24reviewerJohn Lopez CruzNo ratings yet
- 5 Hard Truths PDFDocument3 pages5 Hard Truths PDFBhavya BNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology: Ordinary Level (Syllabus NP04)Document13 pagesBiotechnology: Ordinary Level (Syllabus NP04)JuanNo ratings yet
- Ready Reckoner BiologyDocument19 pagesReady Reckoner BiologyMrigank MitraNo ratings yet
- Genetic Nomenclature BacteriaDocument2 pagesGenetic Nomenclature BacteriaGybran VargasNo ratings yet
- Presentasi MutasiDocument33 pagesPresentasi MutasimilatiNo ratings yet
- Test Planner-2022-2023 (CF OYM) Phase-01 - FT, & TE Version 1.0Document5 pagesTest Planner-2022-2023 (CF OYM) Phase-01 - FT, & TE Version 1.0NannuNo ratings yet
- Arabidopsis Thaliana GENOME PROJECTDocument28 pagesArabidopsis Thaliana GENOME PROJECTmaluNo ratings yet
- BT102 - Microbiology (Solved Questions FINAL TERM (PAST PAPERS)Document33 pagesBT102 - Microbiology (Solved Questions FINAL TERM (PAST PAPERS)Awais BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Jab and Spike Detox For Optimal Health 2021Document23 pagesJab and Spike Detox For Optimal Health 2021Alan N100% (2)
- Gene Therapy.Document3 pagesGene Therapy.Louisse Angeli AbucejoNo ratings yet
- Swyer Syndrome: Genetics Home ReferenceDocument7 pagesSwyer Syndrome: Genetics Home ReferenceCarl Lawrence R. CarpioNo ratings yet
- Control Over GenesDocument125 pagesControl Over GenesSwati GautamNo ratings yet
- Genetics Unit PlanDocument5 pagesGenetics Unit Planapi-264255406No ratings yet
- BIO 101-Introductory Biology-Amir Faisal-Muhammad Tariq-Aziz MithaniDocument4 pagesBIO 101-Introductory Biology-Amir Faisal-Muhammad Tariq-Aziz MithaniTeyyaba KhanNo ratings yet